Calgary
Calgary Crime Group Linked to Fentanyl Lab, Drug Importation, Homicide

A year-long investigation by ALERT has dismantled an alleged organized crime group operating out of Calgary. ALERT worked alongside the Calgary Police Service and the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration to link the group to numerous alleged criminal offences.
Project Arbour was an investigation by ALERT Calgary’s organized crime and gang team that uncovered a Calgary organized crime group’s alleged operation of a fentanyl and steroids lab; cross-border drug trade and Utah’s largest meth seizure; and the alleged role in the murder of Colin Reitberger and Anees Amr. Project Arbour concluded on February 15, 2018, when several Calgary homes were searched and arrests were made.
“I want to applaud all investigators and officers involved in Project Arbour for helping to keep Alberta communities safe. Thanks to the hard work of ALERT, CPS and their partner agencies, this year-long investigation has taken deadly drugs off our streets,” said Kathleen Ganley, Alberta Minister of Justice and Solicitor General. “Project Arbour is proof that ALERT’s cooperative approach to policing works.”
Project Arbour began shortly after 100 kilograms of meth was found in a vehicle occupied by three Calgary-area men in October 2016. The vehicle was stopped just south of Provo, Utah, and was part of an investigation by Utah Highway Patrol, DEA Los Angeles and DEA Salt Lake City. The seizure was described as the state’s largest meth bust and it is believed the drugs were destined for Canada.
Since the record seizure and arrest, ALERT has worked alongside the DEA to share intelligence and enforcement strategies. It is the investigators’ belief that the Canadians arrested were couriers and working for a Calgary-based organized crime group under the direction of Allistair Chapman. ALERT further alleges that the group was involved in the importation and exportation of drugs from Alberta, British Columbia, and the United States.
Meanwhile, north of the border, a suspected clandestine drub laboratory was located in Calgary as part of the investigation. A garage in the Rosscarrock area was allegedly being used to produce fentanyl and steroid pills. The RCMP’s Clandestine Lab Enforcement and Response (CLEAR) Team dismantled the suspected lab and, in the process, seized a functioning pill press, pill press punch dies, a 50-litre powder mixer, and more than 17 kilograms of various chemical powders.
The pill press seized was capable of producing an estimated 18,000 pills an hour and the dies bore the stamps familiar to fentanyl of “80” and “CDN”. The pill press was contaminated with fentanyl and submitted for destruction.
The RCMP CLEAR team was later utilized to dismantle a suspected cannabis resin manufacturing lab in the Cougar Ridge neighbourhood, where an additional 500 grams of suspected fentanyl powder was seized along with varying amounts of cannabis products.
A total of four search warrants were conducted during Project Arbour. In addition to the large quantities of drugs seized, investigators also seized five firearms – including two shotguns and three rifles – and body armour.
CPS has worked closely with ALERT on Project Arbour, as it is believed Colin Reitberger was killed because of his link to the drug trade and Anees Amr was an unintended target. Christian Ouellette was arrested weeks after the shooting in June 2017, and the 20-year-old is allegedly part of Chapman’s criminal organization. Project Arbour yielded evidence to suggest that Blais Delaire, another member of Chapman’s group, assisted Ouellette in obtaining the weapon used in the homicides.
Three other members of Chapman’s group were arrested as part of Project Arbour: Matthew Speirs, 24; Drew Mann, 25; and Bryan Livingston, 32. A total of 46 charges have been laid related to drug offences, conspiracy to import/export, firearms trafficking, and participating/instructing a criminal organization.
Project Arbour resulted in the following items being seized:
- 5 firearms;
- 18 kilograms of suspected fentanyl powder;
- Pill press and dies;
- 50-litre powder mixer;
- 7 kilograms of methamphetamine;
- 2 kilograms of cocaine;
- 700 grams of heroin;
- 8.5 kilograms of cannabis products; and
- Two vehicles seized.




The powder substances have been submitted for complete chemical analysis and ALERT is awaiting the full results.
A number of partner agencies were involved in Project Arbour, including various teams within the Calgary Police Service and RCMP; RCMP Ridge Meadows; Alberta Sheriffs; Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA); Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre of Canada (FINTRAC); and DEA offices in Salt Lake City, Los Angeles, Imperial County, and Vancouver.
Members of the public who suspect drug or gang activity in their community can call local police, or contact Crime Stoppers at 1-800-222-TIPS (8477). Crime Stoppers is always anonymous.
ALERT was established and is funded by the Alberta Government and is a compilation of the province’s most sophisticated law enforcement resources committed to tackling serious and organized crime. Members of the Calgary Police Service, Edmonton Police Service, Lethbridge Police Service, Medicine Hat Police Service and RCMP work in ALERT.
Alberta
Gondek’s exit as mayor marks a turning point for Calgary

This article supplied by Troy Media.
The mayor’s controversial term is over, but a divided conservative base may struggle to take the city in a new direction
Calgary’s mayoral election went to a recount. Independent candidate Jeromy Farkas won with 91,112 votes (26.1 per cent). Communities First candidate Sonya Sharp was a very close second with 90,496 votes (26 per cent) and controversial incumbent mayor Jyoti Gondek finished third with 71,502 votes (20.5 per cent).
Gondek’s embarrassing tenure as mayor is finally over.
Gondek’s list of political and economic failures in just a single four-year term could easily fill a few book chapters—and most likely will at some point. She declared a climate emergency on her first day as Calgary’s mayor that virtually no one in the city asked for. She supported a four per cent tax increase during the COVID-19 pandemic, when many individuals and families were struggling to make ends meet. She snubbed the Dec. 2023 menorah lighting during Hanukkah because speakers were going to voice support for Israel a mere two months after the country was attacked by the bloodthirsty terrorist organization Hamas. The
Calgary Party even accused her last month of spending over $112,000 in taxpayers’ money for an “image makeover and brand redevelopment” that could have benefited her re-election campaign.
How did Gondek get elected mayor of Calgary with 176,344 votes in 2021, which is over 45 per cent of the electorate?
“Calgary may be a historically right-of-centre city,” I wrote in a recent National Post column, “but it’s experienced some unusual voting behaviour when it comes to mayoral elections. Its last three mayors, Dave Bronconnier, Naheed Nenshi and Gondek, have all been Liberal or left-leaning. There have also been an assortment of other Liberal mayors in recent decades like Al Duerr and, before he had a political epiphany, Ralph Klein.”
In fairness, many Canadians used to support the concept of balancing their votes in federal, provincial and municipal politics. I knew of some colleagues, friends and family members, including my father, who used to vote for the federal Liberals and Ontario PCs. There were a couple who supported the federal PCs and Ontario Liberals in several instances. In the case of one of my late
grandfathers, he gave a stray vote for Brian Mulroney’s federal PCs, the NDP and even its predecessor, the Co-operative Commonwealth Federation.
That’s not the case any longer. The more typical voting pattern in modern Canada is one of ideological consistency. Conservatives vote for Conservative candidates, Liberals vote for Liberal candidates, and so forth. There are some rare exceptions in municipal politics, such as the late Toronto mayor Rob Ford’s populistconservative agenda winning over a very Liberal city in 2010. It doesn’t happen very often these days, however.
I’ve always been a proponent of ideological consistency. It’s a more logical way of voting instead of throwing away one vote (so to speak) for some perceived model of political balance. There will always be people who straddle the political fence and vote for different parties and candidates during an election. That’s their right in a democratic society, but it often creates a type of ideological inconsistency that doesn’t benefit voters, parties or the political process in general.
Calgary goes against the grain in municipal politics. The city’s political dynamics are very different today due to migration, immigration and the like. Support for fiscal and social conservatism may still exist in Alberta, but the urban-rural split has become more profound and meaningful than the historic left-right divide. This makes the task of winning Calgary in elections more difficult for today’s provincial and federal Conservatives, as well as right-leaning mayoral candidates.
That’s what we witnessed during the Oct. 20 municipal election. Some Calgary Conservatives believed that Farkas was a more progressive-oriented conservative or centrist with a less fiscally conservative plan and outlook for the city. They viewed Sharp, the leader of a right-leaning municipal party founded last December, as a small “c” conservative and much closer to their ideology. Conversely, some Calgary Conservatives felt that Farkas, and not Sharp, would be a better Conservative option for mayor because he seemed less ideological in his outlook.
When you put it all together, Conservatives in what used to be one of the most right-leaning cities in a historically right-leaning province couldn’t decide who was the best political option available to replace the left-wing incumbent mayor. Time will tell if they chose wisely.
Fortunately, the razor-thin vote split didn’t save Gondek’s political hide. Maybe ideological consistency will finally win the day in Calgary municipal politics once the recount has ended and the city’s next mayor has been certified.
Michael Taube is a political commentator, Troy Media syndicated columnist and former speechwriter for Prime Minister Stephen Harper. He holds a master’s degree in comparative politics from the London School of Economics, lending academic rigour to his political insights.
Troy Media empowers Canadian community news outlets by providing independent, insightful analysis and commentary. Our mission is to support local media in helping Canadians stay informed and engaged by delivering reliable content that strengthens community connections and deepens understanding across the country
Alberta
Calgary’s High Property Taxes Run Counter to the ‘Alberta Advantage’

By David Hunt and Jeff Park
Of major cities, none compare to Calgary’s nearly 50 percent property tax burden increase between censuses.
Alberta once again leads the country in taking in more new residents than it loses to other provinces and territories. But if Canadians move to Calgary seeking greater affordability, are they in for a nasty surprise?
In light of declining home values and falling household incomes amidst rising property taxes, Calgary’s overall property tax burden has skyrocketed 47 percent between the last two national censuses, according to a new study by the Aristotle Foundation for Public Policy.
Between 2016 and 2021 (the latest year of available data), Calgary’s property tax burden increased about twice as fast as second-place Saskatoon and three-and-a-half times faster than Vancouver.
The average Calgary homeowner paid $3,496 in property taxes at the last census, compared to $2,736 five years prior (using constant 2020 dollars; i.e., adjusting for inflation). By contrast, the average Edmonton homeowner paid $2,600 in 2021 compared to $2,384 in 2016 (in constant dollars). In other words, Calgary’s annual property tax bill rose three-and-a-half times more than Edmonton’s.
This is because Edmonton’s effective property tax rate remained relatively flat, while Calgary’s rose steeply. The effective rate is property tax as a share of the market value of a home. For Edmontonians, it rose from 0.56 percent to 0.62 percent—after rounding, a steady 0.6 percent across the two most recent censuses. For Calgarians? Falling home prices collided with rising taxes so that property taxes as a share of (market) home value rose from below 0.5 percent to nearly 0.7 percent.
Plug into the equation sliding household incomes, and we see that Calgary’s property tax burden ballooned nearly 50 percent between censuses.
This matters for at least three reasons. First, property tax is an essential source of revenue for municipalities across Canada. City councils set their property tax rate and the payments made by homeowners are the backbone of municipal finances.
Property taxes are also an essential source of revenue for schools. The province has historically required municipalities to directly transfer 33 percent of the total education budget via property taxes, but in the period under consideration that proportion fell (ultimately, to 28 percent).
Second, a home purchase is the largest expense most Canadians will ever make. Local taxes play a major role in how affordable life is from one city to another. When municipalities unexpectedly raise property taxes, it can push homeownership out of reach for many families. Thus, homeoowners (or prospective homeowners) naturally consider property tax rates and other local costs when choosing where to live and what home to buy.
And third, municipalities can fall into a vicious spiral if they’re not careful. When incomes decline and residential property values fall, as Calgary experienced during the period we studied, municipalities must either trim their budgets or increase property taxes. For many governments, it’s easier to raise taxes than cut spending.
But rising property tax burdens could lead to the city becoming a less desirable place to live. This could mean weaker residential property values, weaker population growth, and weaker growth in the number of residential properties. The municipality then again faces the choice of trimming budgets or raising taxes. And on and on it goes.
Cities fall into these downward spirals because they fall victim to a central planner’s bias. While $853 million for a new arena for the Calgary Flames or $11 million for Calgary Economic Development—how City Hall prefers to attract new business to Calgary—invite ribbon-cuttings, it’s the decisions about Calgary’s half a million private dwellings that really drive the city’s finances.
Yet, a virtuous spiral remains in reach. Municipalities tend to see the advantage of “affordable housing” when it’s centrally planned and taxpayer-funded but miss the easiest way to generate more affordable housing: simply charge city residents less—in taxes—for their housing.
When you reduce property taxes, you make housing more affordable to more people and make the city a more desirable place to live. This could mean stronger residential property values, stronger population growth, and stronger growth in the number of residential properties. Then, the municipality again faces a choice of making the city even more attractive by increasing services or further cutting taxes. And on and on it goes.
The economy is not a series of levers in the mayor’s office; it’s all of the million individual decisions that all of us, collectively, make. Calgary city council should reduce property taxes and leave more money for people to make the big decisions in life.
Jeff Park is a visiting fellow with the Aristotle Foundation for Public Policy and father of four who left Calgary for better affordability. David Hunt is the research director at the Calgary-based Aristotle Foundation for Public Policy. They are co-authors of the new study, Taxing our way to unaffordable housing: A brief comparison of municipal property taxes.
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoFrom Underdog to Top Broodmare
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoTrans Mountain executive says it’s time to fix the system, expand access, and think like a nation builder
-

 Economy2 days ago
Economy2 days agoIn his own words: Stunning Climate Change pivot from Bill Gates. Poverty and disease should be top concern.
-
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoPaying for Trudeau’s EV Gamble: Ottawa Bought Jobs That Disappeared
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoBiden’s Autopen Orders declared “null and void”
-

 Addictions2 days ago
Addictions2 days agoThe Shaky Science Behind Harm Reduction and Pediatric Gender Medicine
-
 Business2 days ago
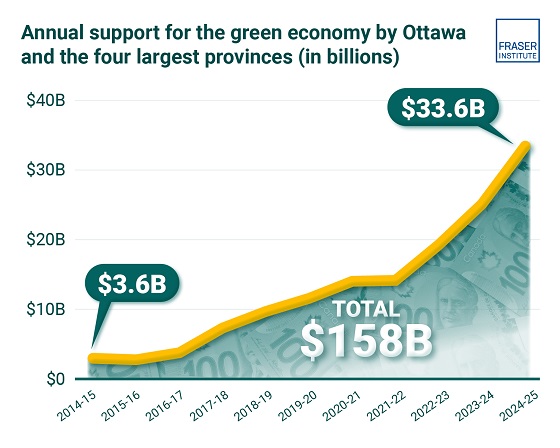
Business2 days agoClean energy transition price tag over $150 billion and climbing, with very little to show for it
-

 Internet1 day ago
Internet1 day agoMusk launches Grokipedia to break Wikipedia’s information monopoly