Business
Law prohibiting replacement workers will worsen Canadian services, says MEI

From the Montreal Economic Institute
Without replacement workers, CPKC and CN strike could impact commuter rail in large Canadian cities.
Ottawa’s proposed ban on the use of temporary replacement workers during work stoppages will significantly disrupt vital services, asserts the Montreal Economic Institute in a study released this morning.
“Banning the use of replacement workers for federally regulated industries will enable small groups of unionized employees to stop key transportation infrastructure from working,” explains Gabriel Giguère, public policy analyst at the MEI and author of the study. “Our trains, airports, and seaports could effectively be at risk of shutting down whenever a union needs to settle a wage dispute.”
On May 27, the House of Commons adopted Bill C-58, which will prohibit the use of temporary replacement workers during labour disputes between employees and employers in federally regulated sectors once it takes effect, 12 months after receiving royal assent.
Unionized workers will continue to be able to seek temporary employment elsewhere, whereas federally regulated employers will be unable to continue operations, which would impact the entire Canadian economy.
This announcement comes just as unionized employees of Canadian Pacific Kansas City Limited (CPKC) and Canadian National (CN) prepare to strike simultaneously.
The adoption of Bill C-58 ensures that work stoppages in sectors including banking, telecommunications, and rail and air travel will be even more detrimental to the Canadian economy than under the current regulatory framework.
Quebec and British Columbia have similar laws in place provincially, and these tend to make work stoppages longer and more frequent there than in provinces without such legislation.
In the context of upcoming rail strikes, the banning of replacement workers means that thousands of Canadians who use commuter rail to get to work would be stranded or would add to road congestion.
The researcher gives the example of CPKC’s 80 Calgary-based rail traffic controllers which, if they go on strike after the law goes into effect, would prevent commuter rail traffic on a number of important transit lines.
“Trains can’t move on a railroad unless you have rail traffic controllers, and a number of key transit lines use CPKC’s infrastructure,” explains Giguère. “In the absence of replacement workers, any strike action on their part could shut down TransLink’s West Coast Express, GO Transit’s Milton Line, and Exo’s Candiac, Saint-Jérôme, and Vaudreuil/Hudson lines.
“That’s a whole lot of power to put in the hands of 80 or so unionized staff.”
The MEI study is available here.
* * *
The MEI is an independent public policy think tank with offices in Montreal and Calgary. Through its publications, media appearances, and advisory services to policy-makers, the MEI stimulates public policy debate and reforms based on sound economics and entrepreneurship.
Alberta
Pierre Poilievre – Per Capita, Hardisty, Alberta Is the Most Important Little Town In Canada

From Pierre Poilievre
Business
Why it’s time to repeal the oil tanker ban on B.C.’s north coast

The Port of Prince Rupert on the north coast of British Columbia. Photo courtesy Prince Rupert Port Authority
From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
Moratorium does little to improve marine safety while sending the wrong message to energy investors
In 2019, Martha Hall Findlay, then-CEO of the Canada West Foundation, penned a strongly worded op-ed in the Globe and Mail calling the federal ban of oil tankers on B.C.’s northern coast “un-Canadian.”
Six years later, her opinion hasn’t changed.
“It was bad legislation and the government should get rid of it,” said Hall Findlay, now director of the University of Calgary’s School of Public Policy.
The moratorium, known as Bill C-48, banned vessels carrying more than 12,500 tonnes of oil from accessing northern B.C. ports.
Targeting products from one sector in one area does little to achieve the goal of overall improved marine transport safety, she said.
“There are risks associated with any kind of transportation with any goods, and not all of them are with oil tankers. All that singling out one part of one coast did was prevent more oil and gas from being produced that could be shipped off that coast,” she said.
Hall Findlay is a former Liberal MP who served as Suncor Energy’s chief sustainability officer before taking on her role at the University of Calgary.
She sees an opportunity to remove the tanker moratorium in light of changing attitudes about resource development across Canada and a new federal government that has publicly committed to delivering nation-building energy projects.
“There’s a greater recognition in large portions of the public across the country, not just Alberta and Saskatchewan, that Canada is too dependent on the United States as the only customer for our energy products,” she said.
“There are better alternatives to C-48, such as setting aside what are called Particularly Sensitive Sea Areas, which have been established in areas such as the Great Barrier Reef and the Galapagos Islands.”
The Business Council of British Columbia, which represents more than 200 companies, post-secondary institutions and industry associations, echoes Hall Findlay’s call for the tanker ban to be repealed.
“Comparable shipments face no such restrictions on the East Coast,” said Denise Mullen, the council’s director of environment, sustainability and Indigenous relations.
“This unfair treatment reinforces Canada’s over-reliance on the U.S. market, where Canadian oil is sold at a discount, by restricting access to Asia-Pacific markets.
“This results in billions in lost government revenues and reduced private investment at a time when our economy can least afford it.”
The ban on tanker traffic specifically in northern B.C. doesn’t make sense given Canada already has strong marine safety regulations in place, Mullen said.
Notably, completion of the Trans Mountain Pipeline expansion in 2024 also doubled marine spill response capacity on Canada’s West Coast. A $170 million investment added new equipment, personnel and response bases in the Salish Sea.
“The [C-48] moratorium adds little real protection while sending a damaging message to global investors,” she said.
“This undermines the confidence needed for long-term investment in critical trade-enabling infrastructure.”
Indigenous Resource Network executive director John Desjarlais senses there’s an openness to revisiting the issue for Indigenous communities.
“Sentiment has changed and evolved in the past six years,” he said.
“There are still concerns and trust that needs to be built. But there’s also a recognition that in addition to environmental impacts, [there are] consequences of not doing it in terms of an economic impact as well as the cascading socio-economic impacts.”
The ban effectively killed the proposed $16-billion Eagle Spirit project, an Indigenous-led pipeline that would have shipped oil from northern Alberta to a tidewater export terminal at Prince Rupert, B.C.
“When you have Indigenous participants who want to advance these projects, the moratorium needs to be revisited,” Desjarlais said.
He notes that in the six years since the tanker ban went into effect, there are growing partnerships between B.C. First Nations and the energy industry, including the Haisla Nation’s Cedar LNG project and the Nisga’a Nation’s Ksi Lisims LNG project.
This has deepened the trust that projects can mitigate risks while providing economic reconciliation and benefits to communities, Dejarlais said.
“Industry has come leaps and bounds in terms of working with First Nations,” he said.
“They are treating the rights of the communities they work with appropriately in terms of project risk and returns.”
Hall Findlay is cautiously optimistic that the tanker ban will be replaced by more appropriate legislation.
“I’m hoping that we see the revival of a federal government that brings pragmatism to governing the country,” she said.
“Repealing C-48 would be a sign of that happening.”
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoOttawa Funded the China Ferry Deal—Then Pretended to Oppose It
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoNew Peer-Reviewed Study Affirms COVID Vaccines Reduce Fertility
-

 MAiD2 days ago
MAiD2 days agoCanada’s euthanasia regime is not health care, but a death machine for the unwanted
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoWorld Economic Forum Aims to Repair Relations with Schwab
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoThe permanent CO2 storage site at the end of the Alberta Carbon Trunk Line is just getting started
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta’s government is investing $5 million to help launch the world’s first direct air capture centre at Innisfail
-
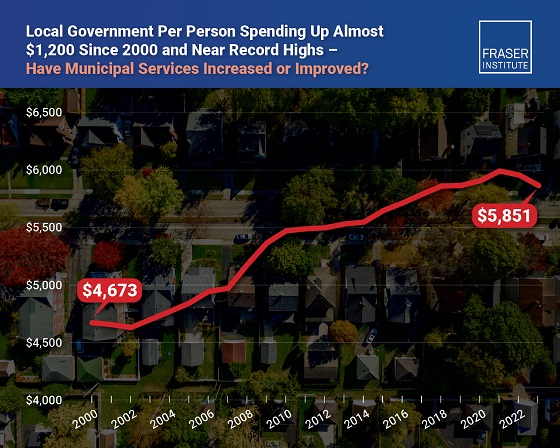
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoMunicipal government per-person spending in Canada hit near record levels
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoA new federal bureaucracy will not deliver the affordable housing Canadians need






