Alberta
Alberta cracking down on mask exemptions – Note required

Masking exceptions for health conditions
- Starting May 13, the rules around exemptions from wearing a mask due to a medical condition are changing. Individuals will now be required to obtain a medical exception letter verifying their health condition from an authorized health-care provider.
- The medical exception letter must come from a nurse practitioner, physician or psychologist. It may be presented when in a public setting, if requested by enforcement officials or retrospectively in court if a ticket is issued.
- This is modelled after the approaches currently used in Saskatchewan and other provinces.
Update 221: COVID-19 pandemic in Alberta (May 13, 4:15 p.m.)
Cases remain high in all parts of Alberta. Continue following the restrictions in place to stop the spread of COVID-19 and protect the health-care system.
Latest updates
- Over the last 24 hours, 1,558 new cases were identified.
- There are 722 people in hospital due to COVID-19, including 177 in intensive care.
- There are 24,586 active cases in the province.
- To date, 188,475 Albertans have recovered from COVID-19.
- In the last 24 hours, there were nine additional COVID-related deaths reported: one on April 28, one on May 8, two on May 10, one on May 11, three on May 12, and one on May 13.
- The testing positivity rate was 10.6 per cent.
- There were 15,266 tests (4,375,995 total) completed in the last 24 hours and a total of 2,103,334 people tested overall.
- All zones across the province have cases:
- Calgary Zone: 11,584 active cases and 75,055 recovered
- South Zone: 1,255 active cases and 10,227 recovered
- Edmonton Zone: 5,470 active cases and 67,097 recovered
- North Zone: 3,618 active cases and 20,117 recovered
- Central Zone: 2,647 active cases and 15,961 recovered
- 12 active cases and 18 recovered cases in zones to be confirmed
- Additional information, including case totals, is online.
- Alberta has identified 276 additional cases of variants of concern, bringing the provincial total to 39,989.
- Currently, 907 schools, about 38 per cent, are on alert or have outbreaks, with 6,736 cases in total.
- 439 schools are on alert, with 1,067 total cases.
- Outbreaks are declared in 468 schools, with a total of 5,669 cases.
- In-school transmission has likely occurred in 818 schools. Of these, 273 have had only one new case occur as a result.
- There are currently 115 active and 9,487 recovered cases at long-term care facilities and supportive/home living sites.
- To date, 1,251 of the 2,121 reported deaths (59 per cent) have been in long-term care facilities or supportive/home living sites.
COVID-19 vaccination program
- As of May 12, 2,019,714 doses of COVID-19 vaccine have been administered in Alberta, with 38 per cent of the population having received at least one dose. There are now 322,247 Albertans fully vaccinated with two doses.
- All Albertans age 12 and older are eligible to book appointments through AHS or a participating pharmacy provincewide.
- Legislation now allows Albertans up to three hours of paid, job-protected leave to get a COVID-19 vaccine.
New vaccination campaign launches
- Back to Normal is a new phase of Alberta’s vaccination campaign, intended to emphasize the crucial importance of Albertans getting vaccinated so life can return to normal.
- This advertisement is the first element of the campaign. Additional advertising showing other aspects of daily life will be released soon.
Masking exceptions for health conditions
- Starting May 13, the rules around exemptions from wearing a mask due to a medical condition are changing. Individuals will now be required to obtain a medical exception letter verifying their health condition from an authorized health-care provider.
- The medical exception letter must come from a nurse practitioner, physician or psychologist. It may be presented when in a public setting, if requested by enforcement officials or retrospectively in court if a ticket is issued.
- This is modelled after the approaches currently used in Saskatchewan and other provinces.
Restrictions in place for high case regions
- Restrictions are in place. Outdoor gatherings are limited to five people, most schools have moved to online learning, retail capacity is reduced and in-person dining and services are not allowed at restaurants, bars and cafés.
- Municipalities that have fewer than 50 cases per 100,000 people and/or fewer than 30 active cases are able to return to Step 0 level restrictions.
Enforcement of public health measures
- Fines for non-compliance with public health measures have doubled to $2,000.
- Unpaid fines are backstopped with stronger fine collection actions and restrictions on registry services. For example, a person may have to pay their outstanding fine before they can renew their driver’s licence.
- Repeat offenders will be targeted with a new multi-agency enforcement framework.
- Tickets can be given at the time of an incident or post-infraction – someone who isn’t charged immediately may receive a ticket after authorities do further investigation.
Rapid testing
- The province has launched a new rapid testing partnership with Alberta Chambers of Commerce.
- Businesses and service providers are no longer required to have a health-care provider oversee their rapid testing program.
- Rapid tests are available for employers.
Continuing care
- Restrictions for visitors to continuing care facilities have been eased.
- These changes will vary by site based on the design of the building, wishes of residents and other factors.
- Each site must develop their own visiting approach that falls within the guidelines set out and reflects the risk tolerance of the residents who live at that site.
COVID Care Teams outreach
- If you or others in your home have been directed to self-isolate/quarantine by Alberta Health Services and are unable to do so safely at home, please contact 211 to discuss options, including accessing an assigned hotel to safely isolate (free of charge). Financial assistance may also be available in the amount of $625, upon completion of the self-isolation period.
Albertans downloading tracer app
- All Albertans are encouraged to download the secure ABTraceTogether app, which is integrated with provincial contact tracing. The federal app is not a contact tracing app.
- Secure contact tracing is an effective tool to stop the spread by notifying people who were exposed to a confirmed case so they can isolate and be tested.
- As of May 13, 314,511 Albertans were using the ABTraceTogether app, 69 per cent on iOS and 31 per cent on Android.
- Secure contact tracing is a cornerstone of Alberta’s Relaunch Strategy.
MyHealth Records quick access
- Parents and guardians can access the COVID-19 test results for children under the age of 18 through MyHealth Records (MHR) as soon as they are ready.
- More than 600,000 Albertans have MHR accounts.
Addiction and mental health supports
- Confidential supports are available. The Mental Health Help Line at 1-877-303-2642 and the Addiction Help Line at 1-866-332-2322 operate 24 hours a day, seven days a week. Resources are also available online.
- The Kids Help Phone is available 24-7 and offers professional counselling, information and referrals and volunteer-led, text-based support to young people by texting CONNECT to 686868.
- Online resources provide advice on handling stressful situations and ways to talk with children.
Family violence prevention
- A 24-hour Family Violence Information Line at 310-1818 provides anonymous help in more than 170 languages.
- Alberta’s One Line for Sexual Violence is available at 1-866-403-8000, from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m.
- People fleeing family violence can call local police or the nearest RCMP detachment to apply for an Emergency Protection Order, or follow the steps in the Emergency Protection Orders Telephone Applications (COVID-19).
- Information sheets and other resources on family violence prevention are at alberta.ca/COVID19.
Alberta’s government is responding to the COVID-19 pandemic by protecting lives and livelihoods with precise measures to bend the curve, sustain small businesses and protect Alberta’s health-care system.
Quick facts
- Legally, all Albertans must physically distance and isolate when sick or with symptoms.
- Good hygiene is your best protection: wash your hands regularly for at least 20 seconds, avoid touching your face, cough or sneeze into an elbow or sleeve, and dispose of tissues appropriately.
- Please share acts of kindness during this difficult time at #AlbertaCares.
- Alberta Connects Contact Centre (310-4455) is open Monday to Friday, 8:15 a.m. to 4:30 p.m.
Alberta
What are the odds of a pipeline through the American Pacific Northwest?
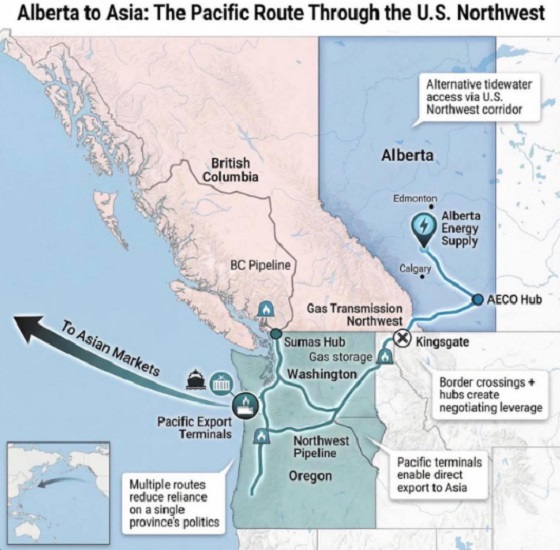
From Resource Works
Can we please just get on with building one through British Columbia instead?
Alberta Premier Danielle Smith is signalling she will look south if Canada cannot move quickly on a new pipeline, saying she is open to shipping oil to the Pacific via the U.S. Pacific Northwest. In a year-end interview, Smith said her “first preference” is still a new West Coast pipeline through northern British Columbia, but she is willing to look across the border if progress stalls.
“Anytime you can get to the West Coast it opens up markets to get to Asia,” she said. Smith also said her focus is building along “existing rights of way,” pointing to the shelved Northern Gateway corridor, and she said she would like a proposal submitted by May 2026.
Deadlines and strings attached
The timing matters because Ottawa and Edmonton have already signed a memorandum of understanding that backs a privately financed bitumen pipeline to a British Columbia port and sends it to the new Major Projects Office. The agreement envisages at least one million barrels a day and sets out a plan for Alberta to file an application by July 1, 2026, while governments aim to finish approvals within two years.
The bargain comes with strings. The MOU links the pipeline to the Pathways carbon capture network, and commits Alberta to strengthen its TIER system so the effective carbon credit price rises to at least 130 dollars a tonne, with details to be settled by April 1, 2026.
Shifting logistics
If Smith is floating an American outlet, it is partly because Pacific Northwest ports are already drawing Canadian exporters. Nutrien’s plan for a $1-billion terminal at Washington State’s Port of Longview highlighted how trade logistics can shift when proponents find receptive permitting lanes.
But the political terrain in Washington and Oregon is unforgiving for fossil fuel projects, even for natural gas. In 2023, federal regulators approved TC Energy’s GTN Xpress expansion over protests from environmental groups and senior officials in West Coast states, with opponents warning about safety and wildfire risk. The project would add about 150 million cubic feet per day of capacity.
A record of resistance
That decision sits inside a longer record of resistance. The anti-development activist website “DeSmog” eagerly estimated that more than 70 percent of proposed coal, oil, and gas projects in the Pacific Northwest since 2012 were defeated, often after sustained local organizing and legal challenges.
Even when a project clears regulators, economics can still kill it. Gas Outlook reported that GTN later said the expansion was “financially not viable” unless it could obtain rolled-in rates to spread costs onto other utilities, a request regulators rejected when they approved construction.
Policy direction is tightening too. Washington’s climate framework targets cutting climate pollution 95 percent by 2050, alongside “clean” transport, buildings, and power measures that push electrification. Recent state actions described by MRSC summaries and NRDC notes reinforce that direction, including moves to help utilities plan a transition away from gas.
Oregon is moving in the same direction. Gov. Tina Kotek issued an executive order directing agencies to move faster on clean energy permitting and grid connections, tied to targets of cutting emissions 50 percent by 2035 and 90 percent by 2050, the Capital Chronicle reported.
For Smith, the U.S. corridor talk may be leverage, but it also underscores a risk, the alternative could be tougher than the Canadian fight she is already waging. The surest way to snuff out speculation is to make it unnecessary by advancing a Canadian project now that the political deal is signed. As Resource Works argued after the MOU, the remaining uncertainty sits with private industry and whether it will finally build, rather than keep testing hypothetical routes.
Resource Works News
Alberta
Alberta’s new diagnostic policy appears to meet standard for Canada Health Act compliance

From the Fraser Institute
By Nadeem Esmail, Mackenzie Moir and Lauren Asaad
In October, Alberta’s provincial government announced forthcoming legislative changes that will allow patients to pay out-of-pocket for any diagnostic test they want, and without a physician referral. The policy, according to the Smith government, is designed to help improve the availability of preventative care and increase testing capacity by attracting additional private sector investment in diagnostic technology and facilities.
Unsurprisingly, the policy has attracted Ottawa’s attention, with discussions now taking place around the details of the proposed changes and whether this proposal is deemed to be in line with the Canada Health Act (CHA) and the federal government’s interpretations. A determination that it is not, will have both political consequences by being labeled “non-compliant” and financial consequences for the province through reductions to its Canada Health Transfer (CHT) in coming years.
This raises an interesting question: While the ultimate decision rests with Ottawa, does the Smith government’s new policy comply with the literal text of the CHA and the revised rules released in written federal interpretations?
According to the CHA, when a patient pays out of pocket for a medically necessary and insured physician or hospital (including diagnostic procedures) service, the federal health minister shall reduce the CHT on a dollar-for-dollar basis matching the amount charged to patients. In 2018, Ottawa introduced the Diagnostic Services Policy (DSP), which clarified that the insured status of a diagnostic service does not change when it’s offered inside a private clinic as opposed to a hospital. As a result, any levying of patient charges for medically necessary diagnostic tests are considered a violation of the CHA.
Ottawa has been no slouch in wielding this new policy, deducting some $76.5 million from transfers to seven provinces in 2023 and another $72.4 million in 2024. Deductions for Alberta, based on Health Canada’s estimates of patient charges, totaled some $34 million over those two years.
Alberta has been paid back some of those dollars under the new Reimbursement Program introduced in 2018, which created a pathway for provinces to be paid back some or all of the transfers previously withheld on a dollar-for-dollar basis by Ottawa for CHA infractions. The Reimbursement Program requires provinces to resolve the circumstances which led to patient charges for medically necessary services, including filing a Reimbursement Action Plan for doing so developed in concert with Health Canada. In total, Alberta was reimbursed $20.5 million after Health Canada determined the provincial government had “successfully” implemented elements of its approved plan.
Perhaps in response to the risk of further deductions, or taking a lesson from the Reimbursement Action Plan accepted by Health Canada, the province has gone out of its way to make clear that these new privately funded scans will be self-referred, that any patient paying for tests privately will be reimbursed if that test reveals a serious or life-threatening condition, and that physician referred tests will continue to be provided within the public system and be given priority in both public and private facilities.
Indeed, the provincial government has stated they do not expect to lose additional federal health care transfers under this new policy, based on their success in arguing back previous deductions.
This is where language matters: Health Canada in their latest CHA annual report specifically states the “medical necessity” of any diagnostic test is “determined when a patient receives a referral or requisition from a medical practitioner.” According to the logic of Ottawa’s own stated policy, an unreferred test should, in theory, be no longer considered one that is medically necessary or needs to be insured and thus could be paid for privately.
It would appear then that allowing private purchase of services not referred by physicians does pass the written standard for CHA compliance, including compliance with the latest federal interpretation for diagnostic services.
But of course, there is no actual certainty here. The federal government of the day maintains sole and final authority for interpretation of the CHA and is free to revise and adjust interpretations at any time it sees fit in response to provincial health policy innovations. So while the letter of the CHA appears to have been met, there is still a very real possibility that Alberta will be found to have violated the Act and its interpretations regardless.
In the end, no one really knows with any certainty if a policy change will be deemed by Ottawa to run afoul of the CHA. On the one hand, the provincial government seems to have set the rules around private purchase deliberately and narrowly to avoid a clear violation of federal requirements as they are currently written. On the other hand, Health Canada’s attention has been aroused and they are now “engaging” with officials from Alberta to “better understand” the new policy, leaving open the possibility that the rules of the game may change once again. And even then, a decision that the policy is permissible today is not permanent and can be reversed by the federal government tomorrow if its interpretive whims shift again.
The sad reality of the provincial-federal health-care relationship in Canada is that it has no fixed rules. Indeed, it may be pointless to ask whether a policy will be CHA compliant before Ottawa decides whether or not it is. But it can be said, at least for now, that the Smith government’s new privately paid diagnostic testing policy appears to have met the currently written standard for CHA compliance.

Lauren Asaad
Policy Analyst, Fraser Institute
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoOttawa Pretends To Pivot But Keeps Spending Like Trudeau
-

 Agriculture19 hours ago
Agriculture19 hours agoWhy is Canada paying for dairy ‘losses’ during a boom?
-

 Automotive1 day ago
Automotive1 day agoFord’s EV Fiasco Fallout Hits Hard
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex2 days ago
Censorship Industrial Complex2 days agoHow Wikipedia Got Captured: Leftist Editors & Foreign Influence On Internet’s Biggest Source of Info
-

 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days agoThe Uncomfortable Demographics of Islamist Bloodshed—and Why “Islamophobia” Deflection Increases the Threat
-

 Alberta20 hours ago
Alberta20 hours agoAlberta’s new diagnostic policy appears to meet standard for Canada Health Act compliance
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex21 hours ago
Censorship Industrial Complex21 hours agoTop constitutional lawyer warns against Liberal bills that could turn Canada into ‘police state’
-

 espionage2 days ago
espionage2 days agoCarney Floor Crossing Raises Counterintelligence Questions aimed at China, Former Senior Mountie Argues








