Business
UK leader Rishi Sunak signals plan to backtrack on some climate goals
Oxfam’s Rishi Sunak ‘big head’ protests outside the Parliament in London, Tuesday, Sept. 19, 2023. On the eve of the UN Climate Ambition Summit, Oxfam’s Rishi Sunak ‘big head’ staged a protest on top of a giant oil barrel, amongst dozens of real oil drums, supporting the Make Polluters Pay campaign. Calling for oil and gas giants, such as BP and Shell, to pay more tax to raise critical funds to help communities devastated by climate change. (AP Photo/Kin Cheung)
By Jill Lawless in London
LONDON (AP) — Prime Minister Rishi Sunak is preparing to water down some of Britain’s environmental commitments on Wednesday, saying the country must fight climate change without penalizing workers and consumers.
The news drew wide criticism from political opponents, environmental groups and large chunks of U.K. industry, but was welcomed by sections of the governing Conservative Party.
Sunak issued a late-night statement Tuesday in response to a BBC report saying the prime minister is considering extending deadlines for bans on new gasoline and diesel cars — currently set for 2030 — and on new natural-gas home heating, due in 2035.
Sunak said he would set out a “proportionate” approach to the environment. He summoned his Cabinet to an unscheduled conference call to discuss the plans ahead of a speech hastily rescheduled for Wednesday afternoon. It had been due later in the week.
“For too many years, politicians in governments of all stripes have not been honest about costs and trade-offs,” Sunak said. “Instead, they have taken the easy way out, saying we can have it all.”
Sunak did not confirm details of his announcements. He said he would keep a promise to reduce the U.K.’s emissions of climate-warming greenhouse gases to net zero by 2050, but “in a better, more proportionate way.”
The government has previously boasted of Britain being a leader in cutting carbon emissions. U.K. greenhouse gas emissions have fallen by 46% from 1990 levels, mainly because of the almost complete removal of coal from electricity generation. The government had pledged to reduce emissions by 68% of 1990 levels by 2030 and to reach net zero by 2050.
But with just seven years to go until the first goalpost, the government’s climate advisers said in June that the pace of action is “worryingly slow.” Sunak’s decision in July to approve new North Sea oil and gas drilling also spurred critics to question his commitment to climate goals.
Former Prime Minister Boris Johnson, who brought in the 2030 gasoline car target when he was leader, said businesses “must have certainty about our net-zero commitments.”
“We cannot afford to falter now or in any way lose our ambition for this country,” he said.
News of plans to backtrack broke as senior politicians and diplomats from the U.K. and around the world — as well as heir to the British throne Prince William — gathered at the United Nations General Assembly in New York, where climate is high on the agenda. Sunak is not attending, sending his deputy instead.
Greenpeace U.K. policy director Doug Parr said the prime minister was “taking the public for fools.”
“Rowing back on home insulation and commitments to help people move away from gas will ensure we stay at the mercy of volatile fossil fuels and exploitative energy companies,” Parr said.
Environmentalists were not the only ones blindsided by the move. Automakers, who have invested heavily in the switch to electric vehicles, expressed frustration at the government’s apparent change of plan.
“We’re questioning what is the strategy here, because we need to shift the mobility of road transport away from fossil fuels towards sustainable transport,” said Mike Hawes, chief executive of the Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders, an industry body.
Ford U.K. head Lisa Brankin said the company had invested 430 million pounds ($530 million) to build electric cars in Britain.
“Our business needs three things from the U.K. government: ambition, commitment and consistency. A relaxation of 2030 would undermine all three,” she said.
Analyst Tara Clee of investment firm Hargreaves Lansdown said the retreat could undermine Britain’s hard-won reputation for leadership on green technology, threatening the wider economy.
“The market has been directing capital to the net-zero transition and has been working in good faith,” Clee said. “These changes send a message that nothing is set in stone, and committing in earnest to a movable goalpost could be a major business risk.”
Britain’s Conservatives have been openly reassessing their climate change promises after a special election result in July that was widely seen as a thumbs-down from voters to a tax on polluting cars.
The party, which trails behind the Labour opposition nationwide, unexpectedly won the contest for the suburban London Uxbridge district by focusing on a divisive levy on older vehicles imposed by London’s Labour mayor, Sadiq Khan. Some Conservatives believe axing green policies is a vote-winner that can help the party avoid defeat in a national election due by the end of next year.
“We’re not going to save the planet by bankrupting the British people,” Home Secretary Suella Braverman said Wednesday.
But Conservative lawmaker Alok Sharma, who chaired the COP26 international climate conference in Glasgow in 2021, warned that it would be “incredibly damaging … if the political consensus that we have forged in our country on the environment and climate action is fractured.”
“And frankly, I really do not believe that it’s going to help any political party electorally which chooses to go down this path,” he told the BBC.
Alberta
Pierre Poilievre – Per Capita, Hardisty, Alberta Is the Most Important Little Town In Canada

From Pierre Poilievre
Business
Why it’s time to repeal the oil tanker ban on B.C.’s north coast

The Port of Prince Rupert on the north coast of British Columbia. Photo courtesy Prince Rupert Port Authority
From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
Moratorium does little to improve marine safety while sending the wrong message to energy investors
In 2019, Martha Hall Findlay, then-CEO of the Canada West Foundation, penned a strongly worded op-ed in the Globe and Mail calling the federal ban of oil tankers on B.C.’s northern coast “un-Canadian.”
Six years later, her opinion hasn’t changed.
“It was bad legislation and the government should get rid of it,” said Hall Findlay, now director of the University of Calgary’s School of Public Policy.
The moratorium, known as Bill C-48, banned vessels carrying more than 12,500 tonnes of oil from accessing northern B.C. ports.
Targeting products from one sector in one area does little to achieve the goal of overall improved marine transport safety, she said.
“There are risks associated with any kind of transportation with any goods, and not all of them are with oil tankers. All that singling out one part of one coast did was prevent more oil and gas from being produced that could be shipped off that coast,” she said.
Hall Findlay is a former Liberal MP who served as Suncor Energy’s chief sustainability officer before taking on her role at the University of Calgary.
She sees an opportunity to remove the tanker moratorium in light of changing attitudes about resource development across Canada and a new federal government that has publicly committed to delivering nation-building energy projects.
“There’s a greater recognition in large portions of the public across the country, not just Alberta and Saskatchewan, that Canada is too dependent on the United States as the only customer for our energy products,” she said.
“There are better alternatives to C-48, such as setting aside what are called Particularly Sensitive Sea Areas, which have been established in areas such as the Great Barrier Reef and the Galapagos Islands.”
The Business Council of British Columbia, which represents more than 200 companies, post-secondary institutions and industry associations, echoes Hall Findlay’s call for the tanker ban to be repealed.
“Comparable shipments face no such restrictions on the East Coast,” said Denise Mullen, the council’s director of environment, sustainability and Indigenous relations.
“This unfair treatment reinforces Canada’s over-reliance on the U.S. market, where Canadian oil is sold at a discount, by restricting access to Asia-Pacific markets.
“This results in billions in lost government revenues and reduced private investment at a time when our economy can least afford it.”
The ban on tanker traffic specifically in northern B.C. doesn’t make sense given Canada already has strong marine safety regulations in place, Mullen said.
Notably, completion of the Trans Mountain Pipeline expansion in 2024 also doubled marine spill response capacity on Canada’s West Coast. A $170 million investment added new equipment, personnel and response bases in the Salish Sea.
“The [C-48] moratorium adds little real protection while sending a damaging message to global investors,” she said.
“This undermines the confidence needed for long-term investment in critical trade-enabling infrastructure.”
Indigenous Resource Network executive director John Desjarlais senses there’s an openness to revisiting the issue for Indigenous communities.
“Sentiment has changed and evolved in the past six years,” he said.
“There are still concerns and trust that needs to be built. But there’s also a recognition that in addition to environmental impacts, [there are] consequences of not doing it in terms of an economic impact as well as the cascading socio-economic impacts.”
The ban effectively killed the proposed $16-billion Eagle Spirit project, an Indigenous-led pipeline that would have shipped oil from northern Alberta to a tidewater export terminal at Prince Rupert, B.C.
“When you have Indigenous participants who want to advance these projects, the moratorium needs to be revisited,” Desjarlais said.
He notes that in the six years since the tanker ban went into effect, there are growing partnerships between B.C. First Nations and the energy industry, including the Haisla Nation’s Cedar LNG project and the Nisga’a Nation’s Ksi Lisims LNG project.
This has deepened the trust that projects can mitigate risks while providing economic reconciliation and benefits to communities, Dejarlais said.
“Industry has come leaps and bounds in terms of working with First Nations,” he said.
“They are treating the rights of the communities they work with appropriately in terms of project risk and returns.”
Hall Findlay is cautiously optimistic that the tanker ban will be replaced by more appropriate legislation.
“I’m hoping that we see the revival of a federal government that brings pragmatism to governing the country,” she said.
“Repealing C-48 would be a sign of that happening.”
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoOttawa Funded the China Ferry Deal—Then Pretended to Oppose It
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoNew Peer-Reviewed Study Affirms COVID Vaccines Reduce Fertility
-

 MAiD2 days ago
MAiD2 days agoCanada’s euthanasia regime is not health care, but a death machine for the unwanted
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoWorld Economic Forum Aims to Repair Relations with Schwab
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoThe permanent CO2 storage site at the end of the Alberta Carbon Trunk Line is just getting started
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta’s government is investing $5 million to help launch the world’s first direct air capture centre at Innisfail
-
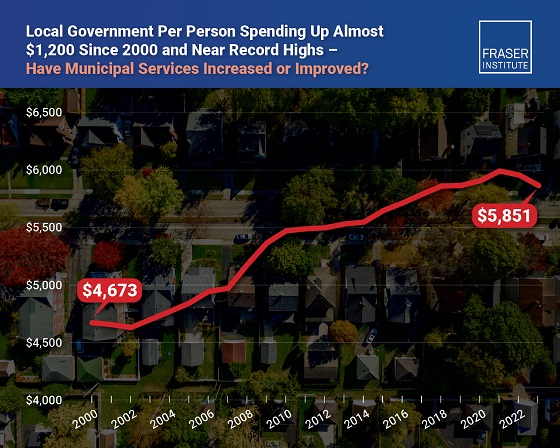
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoMunicipal government per-person spending in Canada hit near record levels
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoA new federal bureaucracy will not deliver the affordable housing Canadians need






