By Frank Wright
While globalists screech that Trump has descended into ‘madness,’ his ‘Liberation Day’ tariff plan that has shocked global markets is actually rooted in the combination of two economic theories that argue for ‘balanced’ trade over ‘free’ trade.
We are used to seeing the effects of Trump Derangement Syndrome in the blue-haired, red-faced hysterics who call the President “Orange Hitler.” Yet the introduction of tariffs on “Liberation Day” has seen the constituency of the differently-saned explode in a fit of rage at this “tariff madness.”
As global markets “plunge,” Trump replied to critics that “sometimes you have to take medicine to fix something.”
“We have been treated so badly by other countries – because we had stupid leadership that allowed this to happen. They took our businesses, they took our money, they took our jobs,” he says, saying American wealth has been effectively “moved” abroad. Trump promised that this “will eventually be straightened out – and our country will be solid and strong again”.
Taking Trump’s medicine
Is his remedy worse than the disease? MSNBC said the crash in global stock markets was the “cascading effect of stupid” tariffs imposed by Trump on U.S. imports. Britain’s Sky News came out swinging too, saying they were “the biggest assault on global trade since World War Two.”
Stocks in the USA, London, Europe, China and across Asia have “plummeted,” as the BBC and others have reported. The U.K.’s Financial Times said “political pressure” resulting from the painful “medicine” will mean “Trump’s tariffs won’t last long.” Yet the liberal bastion of The Guardian dared to suggest there may be a “masterplan” in “shaking up the global economy.”
Looking beyond the hysterical headlines, one writer on SubStack – Tree of Woe – has read the book on “scaled tariffs” which explains the method in Trump’s so-called madness.
1. Trump delivers
Tree of Woe, who recommends the medicine of “muscular Christianity” to combat the sickness of our times, introduces his readers to the fact that Trump campaigned on: “…plac[ing] tariffs that would raise revenue, protect American manufacturing, and restore balanced trade to our global economy.”
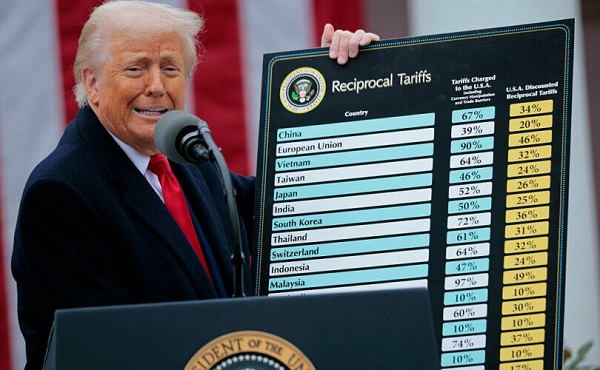
This was followed up on April 2 with the imposition of scaled tariffs – called “Liberation Day for American Trade” by Trump:
As Tree of Woe notes, the reaction from the globalist media was exceptional – even for them:
Soon after the unveiling of Trump’s executive order, the forces of neoliberal globalism orchestrated a counterattack of such rhetorical fierceness and economic malignity that it is virtually unparalleled in the history of fiercely malign economic rhetoric.
Anything seen as a threat to the liberal globalist forced consensus is branded as stupid, extremist or destructive. And so it was with the tariffs, whose aim is to replace imbalance and deepening debt with fair trade – and sustainable prosperity.
2. Theoretical basis for tariffs
Woe then shows how a book on economics provides the “theoretical basis for the Liberation Day tariffs.”
The book is called “Balanced Trade: Ending the Unbearable Cost of America’s Trade Deficits.” It was published in 2014 by three brothers – Jesse, Howard and the late Raymond Richman.
Jesse Richman had first published on “The Scaled Tariff” as a method of “producing balanced trade” in 2011.
As Tree of Woe explains, “…the book challenges the orthodox theory that free trade is always beneficial and argues for an alternate policy they call balanced trade.” He quotes the Richman brothers’ own explanation:
For the last several decades, the United States has generally played a cooperative strategy on trade with China and other[s]… U.S. markets have been open to Chinese goods…American leaders selected free trade on the basis of the (false) hope that China would reciprocate by opening its markets to American firms.
‘Free trade’ = American debt
Did China “liberalize” along with the rest of the global system – as Clinton prophesied in the 1990s?
The answer is no. Is this market balanced? The Richmans say, “In return for Chinese products, Americans go ever deeper into debt.”
Debt is a major problem here. The U.S. must refinance a quarter of its national debt – 9 trillion dollars – in 2025 and must do the same for a total of 28 trillion dollars in debt over the next four years. How can Americans reverse this decline?
The aptly named Richmans proposed one solution: “The scaled tariff.”
Extraordinary nonsense?
Does this add up to an answer? U.S. author James Surowiecki is billed as “the man who cracked the math” on Trump’s tariffs. He said the tariffs were “absurd,” and “based on imaginary numbers” – leading to a “woefully simplistic” view of world trade whose aim of balancing it was “an impossible, and not even desirable, goal.”
4. Doing the math on tariffs
Yet it seems it is Mr Surowiecki’s sums which do not add up. As Tree of Woe explains:
Now, let’s compare the Richmans’ approach to the Liberation Day tariff formula that Surowiecki called ‘extraordinary nonsense.’
The Liberation Day tariff formula takes the U.S. trade deficit with that country and dividing it by the value of the country’s exports to the United States, then divides that value in half. For instance, if China had a trade deficit with the US of $298 billion, and exports of $427 billion, then 0.5 x $298 billion / $427 billion) ~ 35%.
Do you see? Trump’s Liberation Day tariffs are calculated with the exact same formula as the Richmans’ scaled tariffs.
Tree of Woe explains:
In fact, if you read Trump’s executive order, it reads as if it was written by the Richmans.
Rarely in the history of presidential policy has a scholars policy formulation been so precisely followed.
He then supplies a little more detail:
The only difference is that Trump has also included a national strategic tariff of 10% as a baseline.
Where does this come from? Again, Tree of Woe shows it is inspired by another economist.
Trump trade policy is simply Ian Fletcher’s Free Trade Doesn’t Work combined with the Richmans’ Balanced Trade!
Why are these two models used by Trump?
The difference between the two is fundamentally a difference in priorities.
Fletcher prioritizes protection of key industry, while the Richmans emphasize reciprocity in trade flows.
5. The goal is balanced trade
So what does this mean in practice?
The Trump Administration has hedged its position – it’s adopted the scaled tariff in full, but with a low 10% national strategic tariff (Fletcher recommended 25%).
What is the overall goal? “Balanced trade,” as Tree of Woe puts it, combined with mutual or reciprocal trade agreements.
Both the Richmans’ book and the Trump Administration’s executive order offer the same answer here. Since the goal is not to achieve ‘free trade,’ it is to achieve balanced trade, therefore the method by which this is achieved is not “reciprocity of tariffs” but reciprocity of trade flows.
Conclusion: Balancing power
The wider foreign policy of the Trump administration is heavily influenced by realists like Dr. Sumantra Maitra, whose central point is that “power begs to be balanced.” These are tariffs which correct imbalance in trade and will reduce or even vanish where a balance is reached.
They punish “unfair” trade:
When trade is balanced, tariffs go to zero (or to 10%, in the Trump version). It’s clean, it’s efficient, and it’s effective.
Thus, Trump’s tariffs are reciprocal tariffs – but what they reciprocate against is unfair trade practice in generally, evidenced by an imbalance of trade, and not tariffs specifically.
Rebalancing of strategic power in trade as in diplomacy is the principle here. This is not only a method to a madness but now resembles a recipe for sanity and prosperity.
So there you have it. Far from being ‘extraordinary nonsense,’ Trump’s trade policy is in fact a careful implementation of trade policies that have been developed and detailed at book-length.
One of the cheerleaders of the chorus of disapproval – James Surowiecki writes for the globalist magazine The Atlantic.
He is the author of a 2005 book called “The Wisdom of Crowds.” In it, he spoke of the wisdom of the many versus that of the few. If balanced trade restores the American dream, why does he stand against the cause of the majority of American people?
Is this a wise crowd he leads? It is certainly shouting the loudest. Yet the numbers behind the tariffs are not imaginary, and it seems strange wisdom indeed to call balanced trade and the reduction of national debt an “insane goal.”
Tree of Woe was asked for comment. This is what he said: “America has not pursued a policy of balanced trade in almost a century. The pressure on the White House to revert back to our ordinary course of business is enormous. It remains to be seen whether President Trump will be able to sustain his tariff policy in the face of opposition from the economic elite. One thing is certain: America will never be great again if we don’t re-industrialize.”
You can read The Tree of Woe’s full report here.
Related