MacDonald Laurier Institute
Rushing to death in Canada’s MAiD regime

 By Ramona Coelho for Inside Policy
By Ramona Coelho for Inside Policy
Canada legalized Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD) in 2016, encompassing both euthanasia and assisted suicide. Initially limited to those nearing their natural death, eligibility expanded in 2021 to individuals with physical disabilities, with eligibility for individuals with mental illness in 2027. Parliamentary recommendations include MAiD for children. A recent federal consultation explored extending MAiD to those who lack capacity via advance directives, an approach Quebec has already adopted, despite its criminal status under federal law.
Despite its compassionate framing, investigative journalists and government reports reveal troubling patterns where inadequate exploration of reversible suffering – such as lack of access to medical treatments, poverty, loneliness, and feelings of being a burden – have driven Canadians to choose death. As described by our former Disability Inclusion Minister, Canada’s system at times makes it easier to access MAiD than to receive basic care like a wheelchair. With over 60,000 MAiD cases by the end of 2023, the evidence raises grave concerns about Canada’s MAiD regime.
I am a member of Ontario’s MAiD Death Review Committee (MDRC). Last year, the Chief Coroner released MDRC reports, and a new set of reports has just been published. The first report released by the Office of the Chief Coroner, Waivers of Final Consent, examines how individuals in Track 1 (reasonably foreseeable natural death) can sign waivers to have their lives ended even if they lose the capacity to consent by the scheduled date of MAiD. The second, Navigating Complex Issues within Same Day and Next Day MAiD Provisions, includes cases where MAiD was provided on the same day or the day after it was requested. These reports raise questions about whether proper assessments, thorough exploration of suffering, and informed consent were consistently practised by MAiD clinicians. While MDRC members hold diverse views, here is my take.
Rushing to death, Ignoring Reversible Causes of Suffering
In the same-day or next-day MAiD report, Mrs. B, in her 80s, after complications from surgery, opted for palliative care, leading to discharge home. She later requested a MAiD assessment, but her assessor noted she preferred palliative care based on personal and religious values. The next day, her spouse, struggling with caregiver burnout, took her to the emergency department, but she was discharged home. When a request for hospice palliative care was denied, her spouse contacted the provincial MAiD coordination service for an urgent assessment. A new assessor deemed her eligible for MAiD, despite concerns from the first practitioner, who questioned the new assessor on the urgency, the sudden shift in patient perspective, and the influence of caregiver burnout. The initial assessor requested an opportunity for re-evaluation, but this was denied, with the second assessor deeming it urgent. That evening, a third MAiD practitioner was brought in, and Mrs. B underwent MAiD that night.
The focus should have been on ensuring adequate palliative care and support for Mrs. B and her spouse. Hospice and palliative care teams should have been urgently re-engaged, given the severity of the situation. Additionally, the MAiD provider expedited the process despite the first assessor’s and Mrs. B’s concerns without fully considering the impact of her spouse’s burnout.
The report also has worrying trends suggesting that local medical cultures—rather than patient choice—could be influencing rushed MAiD. Geographic clustering, particularly in Western Ontario, where same-day and next-day MAiD deaths occur most frequently, raises concerns that some MAiD providers may be predisposed to rapidly approve patients for quick death rather than ensuring patients have access to adequate care or exploring if suffering is remediable. This highlights a worrying trend where the speed of the MAiD provision is prioritized over patient-centered care and ethical safeguards.
MAiD without Free and Informed Choice
Consent has been central to Canadians’ acceptance of the legalization of euthanasia and assisted suicide. However, some cases in these reports point to concerns already raised by clinicians: the lack of thorough capacity assessments and concerns that individuals may not have freely chosen MAiD.
In the waiver of final consent report, Mr. B, a man with Alzheimer’s, had been approved for MAiD with such a waiver. However, by the scheduled provision date, his spouse reported increased confusion. Upon arrival, the MAiD provider noted that Mr. B no longer recognized them and so chose not to engage him in discussion at all. Without any verbal interaction to determine his current wishes or understanding, Mr. B’s life was ended.
In the same-day or next-day MAiD report, Mr. C, diagnosed with metastatic cancer, initially expressed interest in MAiD but then experienced cognitive decline and became delirious. He was sedated for pain management. Despite the treating team confirming that capacity was no longer present, a MAiD practitioner arrived and withheld sedation, attempting to rouse him. It was documented that the patient mouthed “yes” and nodded and blinked in response to questions. Based on this interaction, the MAiD provider deemed the patient to have capacity. The MAiD practitioner then facilitated a virtual second assessment, and MAiD was administered.
These individuals were not given genuine opportunities to confirm whether they wished to die. Instead, their past wishes or inquiries were prioritized, raising concerns about ensuring free and informed consent for MAiD. As early as 2020, the Chief Coroner of Ontario identified cases where patients received MAiD without well-documented capacity assessments, even though their medical records suggested they lacked capacity. Further, when Dr. Leonie Herx, past president of the Canadian Society of Palliative Medicine, testified before Parliament about MAiD frequently occurring without capacity, an MP dismissed her, advising Parliament to be cautious about considering seriously evidence under parliamentary immunities that amounted to malpractice allegations, which should be handled by the appropriate regulatory bodies or police. These dismissive comments stand in stark contrast with the gravity of assessing financial capacity, and yet the magnitude is greater when ending life. By way of comparison, for my father, an Ontario-approved capacity expert conducted a rigorous evaluation before declaring him incapable of managing his finances. This included a lengthy interview, collateral history, and review of financial documents—yet no such rigorous capacity assessment is mandated for MAiD.
What is Compassion?
While the federal government has finished its consultation on advance directives for MAiD, experts warn against overlooking the complexities of choosing death based on hypothetical suffering and no lived experience to inform those choices. A substitute decision-maker has to interpret prior wishes, leading to guesswork and ethical dilemmas. These cases highlight how vulnerable individuals, having lost the capacity to consent, may be coerced or unduly influenced to die—whether through financial abuse, caregiver burnout, or other pressures—reminding us that the stakes are high – life and death, no less.
The fundamental expectation of health care should be to rush to care for the patient, providing support through a system that embraces them—not rush them toward death without efforts to mitigate suffering or ensure free and informed consent. If we truly value dignity, we must invest in comprehensive care to prevent patients from being administered speedy death in their most vulnerable moment, turning their worst day into potentially their last.
Dr. Ramona Coelho is a family physician whose practice largely serves marginalised persons in London, Ontario. She is a senior fellow at the Macdonald-Laurier Institute and co-editor of the new book “Unravelling MAiD in Canada” from McGill University Press.
armed forces
Underfunded and undermanned, Canada’s Reserves are facing a crisis

The Macdonald Laurier Institute
By J.L. Granatstein for Inside Policy
With the new threats facing Canada and NATO, change must come quickly: Canada needs to fix the Army Reserves.
Canada’s once-proud Reserves force is fading fast – and without urgent action, it risks becoming irrelevant.
The Canadian Armed Forces Primary Reserves have an authorized strength of 30,000, but the present numbers of the Army, Navy and Air Force Reserves as of November 2024 are only 22,024. The RCN Reserves number 3,045, the RCAF 2,162, and the Army 16,817. This is frankly pathetic, all the more so as the regular forces are sadly understrength as well.
The Army Reserves have a long history, with some units dating back before Confederation. Before both world wars the Militia’s strength was roughly 50,000, generated by populations of eight million in 1914 and eleven million in 1939. Amazingly, despite a lack of training and equipment, the Militia provided many of the Army’s officers, up to and including successful division and regimental commanders, and large numbers of the senior non-commissioned officers. A century ago, even after some consolidation following the Great War, almost every town and city had an armoury and a Militia unit with a cadre of officers, good numbers of enlisted men, and some social status in their community. The factory owners, bankers, and well-off were heavily represented, and the Militia had real clout with representation in Parliament and easy access to the defence minister.
Not any longer. The armouries in most of Canada have disappeared, sold off by governments and levelled by developers, and those that still stand are in serious need of maintenance. The local elites – except for honorary colonels who donate funds for extra kit, travel, celebratory volumes, and to try to stop Ottawa from killing their regiment – are noticeably absent.
So too are the working men and women and students. As a result, there are Army Reserve units commanded by a lieutenant-colonel with three majors, half a dozen captains, ten lieutenants, a regimental sergeant major and any number of warrant officers, and under seventy in the ranks. It is a rare Reserve regiment, even those in Canada’s largest cities, which has a strength above 200, and ordinarily when a unit trains on a weeknight or a weekend only half that number turn up. Even in summer, when reservists do their serious training at Petawawa or other large bases, there will be many absentees.
And when a unit is asked to raise soldiers for an overseas posting – say for the Canadian-led brigade in Latvia – it might be able to find ten or so volunteers, but it will be highly unlikely to be able to do so when the next call comes. Reservists have families, jobs or school classes, and few are able and willing to go overseas and even fewer to do so for subsequent deployments.
Without reservists filling the ranks (and even with them providing up to 20 per cent of a battalion’s strength), the undermanned regulars must cobble together a battalion of 600 or so by seconding troops from another Regular unit. After being brought up to Regular force standards before deployment, the reservists have performed well in operations, for example, in Afghanistan.
So why can’t the Army Reserves find the men and women to join their ranks? The reasons are many and much the same as the recruitment difficulties facing the Regular Army. Sexual harassment cases have abounded, affecting the highest ranks and the lowest. Modern equipment has been and is continuing to be lacking.
Procurement is still bogged down with process, paperwork, and long timelines – for instance, approving a new pistol took a decade. And the Reserves get modern equipment only after the Regulars’ needs are met, which unfortunately means never. Instead of a tank or a Light Armoured Vehicle, units get pickup vehicles painted in dark green and see anything more only on their rare days of training in the field.
Leaders of the Reserves have called for a separate budget for years, demanding that they decide how the funds are allocated. National Defence Headquarters has refused, rightly claiming that the underfunded Regulars have higher priority. But the Reserves point to official documents that in 2019-20 demonstrated that of $3.018 million allocated to the Reserves, only $1.3 billion reached them, the rest being unspent or re-allocated to the Regulars.
With some reason this infuriates Reservists who point to this happening every fiscal year.
So too does what they see as the condescension with which they are treated. A Reserve major is equal in rank to a Regular major, but both know that the Regular is almost always far better trained and experienced for his job and that rankles. (Many years ago, when I was a junior officer, I remember another Regular referring to “the ****ing Militia.” I know that Reserve officers reverse the compliment.)

Today with unemployment above nine per cent and with young Canadians’ unemployment rate even higher, the Reserves pay a new private a daily rate of some $125 (The Carney government recently promised a substantial pay raise). This ought to be a good option to earn some money. The Toronto Scottish, an old and established infantry unit, for example, has a website that lists other benefits: up to $8,000 for educational expenses and up to $16,000 for full-time summer employment. The Toronto Scottish has two armouries in the western suburbs, a female Commanding Officer, but under 200 soldiers. There should be a real opportunity in the current circumstances to increase those numbers by a good advertising campaign pitched directly at young men and women in the Toronto suburbs. The same can be said for every big city.
But the small town and rural units, tiny regiments whatever their storied histories, are unlikely to be able to grow very much. National Defence Headquarters needs to set a number – say 150, 200, or 250 – above which a unit will keep its command structure. Below that standard, however, units will be stripped of their higher ranks and effectively consolidated under the Reserve brigade in their area.
Reservists have fought such suggestions for years, but if the Reserves are to become an efficient and effective force, this is a change that must come. One such experiment has combined the Princess of Wales Own Regiment in Kingston, Ontario, and the Brockville Rifles by putting the Commanding Officer of the first and the Regimental Sergeant Major of the second in charge. Unit badges can remain, but this reduces the inflated command staffs.
In reality, these small regiments are nothing more than company-sized sub-units, and sub-units of less than a hundred simply cannot train effectively or draw enough new members from their small town and rural catchment areas. Combined they can function effectively.
The federal government will soon release an army modernization plan. Change is always difficult but with the new threats facing Canada and NATO, change must come quickly. Canada needs to fix the Army Reserves.
Historian J.L. Granatstein is a member of the Macdonald-Laurier Institute’s Research Advisory Board. A bestselling author, Granatstein was the director and CEO of the Canadian War Museum. In 1995, he served on the Special Commission on the Restructuring of the Reserves.
Housing
Government, not greed, is behind Canada’s housing problem

By Anthony De Luca-Baratta for Inside Policy
When it comes to housing unaffordability in Canada, Prime Minister Mark Carney has correctly diagnosed the problem – but prescribed the wrong solution. The cost of new homes across the country increasingly exceeds the average family’s budget. But Carney’s proposal to establish a new federal entity, Build Canada Homes, to “get the government back in the business of homebuilding,” will make matters worse.
During the recent election campaign, the Liberal leader promised to make the federal government into an affordable housing developer by, among other proposals, offering low-cost financing to affordable-housing builders. This approach falsely implies that housing is what economists call a public good – something governments provide because the market cannot.
National defence is a perfect example of a public good: private contractors alone would be unable to withhold protection from those who failed to pay for their services, incentivizing many to welcome the security without paying a dime. In economics jargon, this is known as the “free-rider problem.” Defence contractors would quickly go bankrupt, and the nation would be left defenceless. For this reason, the government is the primary provider of national defence in all functioning states.
If housing suffered from the same market failure as national defence, the government’s approach would have some merit. But it does not, indicating that housing is not, in fact, a public good. The laws of supply and demand are thus the most efficient way of determining both the quantity and price of housing.
In a free housing market, when prices begin to rise, builders build more units to earn higher profits. Over time, competition among builders, homeowners, and landlords forces prices back down because individuals who overcharge lose customers to those who do not. Because overcharging is bad for business, the market provides an abundance of housing at prices negotiated among millions of buyers and sellers. The result is a natural supply of affordable housing – no special incentives needed.
Some in Canada might dismiss this logic as hopelessly naïve. According to these individuals, inflated prices come primarily from landlords and developers squeezing Canadians for more profit and greed is running rampant in the Canadian housing market.
The truth is that developers and landlords are responding rationally to bad economic policy, and homebuyers and renters are footing the bill. Municipalities across Canada limit building heights, set aesthetic standards, ban certain types of construction in designated areas, impose parking requirements, and legislate minimum lot sizes, among a host of other land-use regulations.
These rules make housing harder and more costly to build, constraining supply and radically inflating prices. The C.D. Howe Institute estimates that these regulations cost homebuyers an average of $230,000 in Vancouver, Abbotsford, Victoria, Kelowna, Calgary, Toronto, and Ottawa-Gatineau. In Vancouver, that figure is an eye-watering $1 million.
It is this economic reality, not an unwillingness to build affordable housing, that lies at the root of Canada’s housing crisis.
Housing Minister Gregor Robertson inadvertently admitted as much when he cautioned that there would be no quick solution to Canada’s housing crisis because “projects take years to approve and build.” The minister failed to acknowledge that these delays are due to cumbersome municipal regulations.
To solve Canada’s housing crisis, Carney must begin by recognizing that affordable housing in Canada is in short supply because local governments have made it impossible to build. The housing market could provide affordable housing on its own – no taxpayer-funded subsidies required – if only the government would reduce burdensome industry regulations. Just look at jurisdictions with virtually no land-use regulations, like Houston, Texas, where housing is abundant and affordable. Studies have consistently shown that wherever land-use regulations are low, so are home prices.
To be fair, the Liberal Party’s election platform did acknowledge the need to cut federal housing regulations. It also suggested that it wanted local governments to streamline development, though it was short on specifics. But since the election, there is no sign that the government is moving forward with any of these proposals.
The prime minister needs to tell local governments that their federal funds will dry up if they don’t start getting out of the way of housing development. He should also offer bonuses to cities that are especially quick to build new units. Canadians need shovels in the ground now. It is time for the prime minister to use the bully pulpit to put them there.
Anthony De Luca-Baratta is a contributor to the Center for North American Prosperity and Security, a project of the Macdonald-Laurier Institute, and a Young Voices Contributor based in Montreal. He holds a master’s degree in international relations from the Johns Hopkins School of Advanced International Studies in Washington, DC.
-

 Alberta10 hours ago
Alberta10 hours agoFrom Underdog to Top Broodmare
-
 Media1 day ago
Media1 day agoCarney speech highlights how easily newsrooms are played by politicians
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoThe painful return of food inflation exposes Canada’s trade failures
-
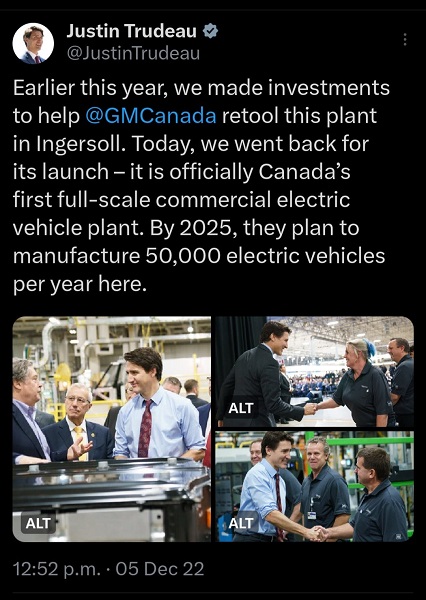
 Business12 hours ago
Business12 hours agoPaying for Trudeau’s EV Gamble: Ottawa Bought Jobs That Disappeared
-

 Business15 hours ago
Business15 hours agoCBC uses tax dollars to hire more bureaucrats, fewer journalists
-

 National13 hours ago
National13 hours agoElection Officials Warn MPs: Canada’s Ballot System Is Being Exploited
-

 Economy7 hours ago
Economy7 hours agoIn his own words: Stunning Climate Change pivot from Bill Gates. Poverty and disease should be top concern.
-

 Addictions9 hours ago
Addictions9 hours agoThe Shaky Science Behind Harm Reduction and Pediatric Gender Medicine








