Alberta
In his own words: Alberta’s Justice Minister repulses federal firearm confiscation

OP/ED submitted to Todayville by Alberta Justice Minister Shandro
Challenging the federal firearms ban
Last month, the federal minister responsible for the RCMP wrote to me to request that Alberta provide resources starting this fall to begin confiscating an estimated 30,000 legally acquired firearms from Albertans. We have rejected their request and will not offer any resources.
The firearms that they are seeking to confiscate were part of a list of over 1500 models that were banned by the federal Liberals in 2020. An amnesty is currently in effect until October 2023, after which time they will be prohibited to possess.
The list of banned models were all previously non-restricted and restricted firearms, including hunting rifles and shotguns as well as historical artifacts almost a hundred years old. Why ban these firearms? A committee of federal bureaucrats decided that these firearms look scary – which is why they describe them as “assault-style.” In reality, we know these firearms, no matter how they may be styled, are in no way materially different from more familiar looking rifles and shotguns.
To challenge this ban, Alberta will apply to intervene in six ongoing lawsuits challenging the constitutionality of the prohibition.
I have also been advised that the Commanding Officer of K Division does not support using provincial police resources to administer the federal government’s confiscation program. Despite this, we have been told that the Federal Liberals intend to conscript provincial RCMP officers into acting as confiscation agents.
Alberta taxpayers pay over $750 million per-year for the RCMP and we will not tolerate taking officers off the streets in order to confiscate the property of law-abiding firearms owners.
To take action, I have used the authorities that we have as a province to identify the confiscation program as an activity that is not appropriate for the RCMP to be used for. Should the federal government proceed with their plan, I will launch a formal dispute under the Provincial Police Service Agreement.
However, because the RCMP is a federal entity, we believe that the Federal Liberals will again interfere in police operations – just as they did when they politicized the mass shooting in Nova Scotia in order to bolster their case for the same pending firearms ban – and order that the RCMP act as confiscation agents.
If this happens, we will consider all options at our disposal to protect Albertans and the property rights that they are entitled to.
Tyler Shandro
Minister of Justice and Solicitor General
Alberta
Temporary Alberta grid limit unlikely to dampen data centre investment, analyst says
From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Cody Ciona
‘Alberta has never seen this level and volume of load connection requests’
Billions of investment in new data centres is still expected in Alberta despite the province’s electric system operator placing a temporary limit on new large-load grid connections, said Carson Kearl, lead data centre analyst for Enverus Intelligence Research.
Kearl cited NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang’s estimate from earlier this year that building a one-gigawatt data centre costs between US$60 billion and US$80 billion.
That implies the Alberta Electric System Operator (AESO)’s 1.2 gigawatt temporary limit would still allow for up to C$130 billion of investment.
“It’s got the potential to be extremely impactful to the Alberta power sector and economy,” Kearl said.
Importantly, data centre operators can potentially get around the temporary limit by ‘bringing their own power’ rather than drawing electricity from the existing grid.
In Alberta’s deregulated electricity market – the only one in Canada – large energy consumers like data centres can build the power supply they need by entering project agreements directly with electricity producers.
According to the AESO, there are 30 proposed data centre projects across the province.
The total requested power load for these projects is more than 16 gigawatts, roughly four gigawatts more than Alberta’s demand record in January 2024 during a severe cold snap.
For comparison, Edmonton’s load is around 1.4 gigawatts, the AESO said.
“Alberta has never seen this level and volume of load connection requests,” CEO Aaron Engen said in a statement.
“Because connecting all large loads seeking access would impair grid reliability, we established a limit that preserves system integrity while enabling timely data centre development in Alberta.”
As data centre projects come to the province, so do jobs and other economic benefits.
“You have all of the construction staff associated; electricians, engineers, plumbers, and HVAC people for all the cooling tech that are continuously working on a multi-year time horizon. In the construction phase there’s a lot of spend, and that is just generally good for the ecosystem,” said Kearl.
Investment in local power infrastructure also has long-term job implications for maintenance and upgrades, he said.
“Alberta is a really exciting place when it comes to building data centers,” said Beacon AI CEO Josh Schertzer on a recent ARC Energy Ideas podcast.
“It has really great access to natural gas, it does have some excess grid capacity that can be used in the short term, it’s got a great workforce, and it’s very business-friendly.”
The unaltered reproduction of this content is free of charge with attribution to the Canadian Energy Centre.
Alberta
Alberta Next: Taxation
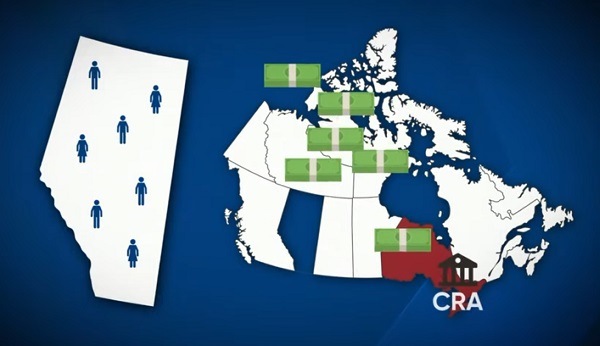
A new video from the Alberta Next panel looks at whether Alberta should stop relying on Ottawa to collect our provincial income taxes. Quebec already does it, and Alberta already collects corporate taxes directly. Doing the same for personal income taxes could mean better tax policy, thousands of new jobs, and less federal interference. But it would take time, cost money, and require building new systems from the ground up.
-

 Fraser Institute1 day ago
Fraser Institute1 day agoBefore Trudeau average annual immigration was 617,800. Under Trudeau number skyrocketted to 1.4 million annually
-

 MAiD1 day ago
MAiD1 day agoCanada’s euthanasia regime is already killing the disabled. It’s about to get worse
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day agoNew Book Warns The Decline In Marriage Comes At A High Cost
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoPrime minister can make good on campaign promise by reforming Canada Health Act
-

 Addictions1 day ago
Addictions1 day ago‘Over and over until they die’: Drug crisis pushes first responders to the brink
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoChicago suburb purchases childhood home of Pope Leo XIV
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoUSAID Quietly Sent Thousands Of Viruses To Chinese Military-Linked Biolab
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoLNG Export Marks Beginning Of Canadian Energy Independence



