Business
How the EU could combine carbon passports, digital ID, and social credit for every product

From LifeSiteNews
The European Union is going deep with its plans to introduce digital IDs across industries. Tying a form of digital ID to all products would make the introduction of carbon social credit scores easier to implement.
The concept of “carbon passports,” proposed as a measure to combat climate change, has, for a while now, raised significant concerns regarding civil liberties. These passports are designed to track an individual’s carbon footprint, including travel, energy consumption, and lifestyle choices. While their intention is to encourage environmentally friendly behaviors, they present a substantial threat to personal privacy by enabling continuous monitoring of personal activities.
This intrusion into privacy is not the only issue; carbon passports could potentially lead to discriminatory practices. Those in lower-income brackets, who often have limited access to green alternatives, might find themselves unfairly penalized. This system risks exacerbating social inequalities by disproportionately affecting those less financially equipped to make eco-friendly choices.
Furthermore, carbon passports could restrict movement and personal autonomy. Limiting travel or certain activities based on carbon usage might create a situation where only the wealthy, who can afford carbon offsets or sustainable options, maintain their freedom. This scenario paints a disturbing picture of environmental responsibility being accessible only to those with financial means.

Another concern is the centralization of power in the hands of entities controlling the carbon data. This centralization could lead to a slippery slope where tools designed for climate control evolve into instruments of more oppressive surveillance and control. The balance between addressing environmental concerns and maintaining civil liberties is delicate and crucial.
As part of the push towards carbon passports, a new idea – tying a form of digital ID to all products is also being pushed. It makes the introduction of carbon social credit scores easier to implement.
The European Union is going deep with its plans to introduce digital IDs (in this case, “digital product passports, DDPs”) across industries. DDPs specifically refer to apparel, accessories and electronics.
Brands are now starting to work on integrating the tech – that the European Commission says is necessary for the greater good of citizens, such as meeting “sustainability goals” – the so-called green deal, carbon emissions, all the things – and then there’s access to services and contactless payment.

Critics, on the other hand, say it’s simply yet another way to abuse consumers by harvesting even more of their data. The opponents’ fears appear to rely on solid facts since some of the data collected thanks to the EU’s proposed scheme will profile people based on their behavior, preferences, and even the value of their “resale profile.”
The deadline mentioned is as early as 2026 – that’s how soon brands would have to incorporate digital passports into their products.
And, don’t expect any resistance from brands. Reports are saying that they are working hard to meet the deadline of meeting what is referred to as the European Commission’s “real-world uses for digital identities.”
READ: EU claims digital ID wallet will be voluntary. India said the same before it became mandatory
On the side of the fashion industry, there will be the need to let the EU know – no longer voluntarily – about how they manufacture items, organize their supply chains, and the materials used.
Well, don’t expect brands to only implement the tech to make the EU feel good about itself. “Brands currently testing the technology are figuring out ways for it to collect customer data and add perks beyond the point of purchase,” writes Vogue Business.
Already trying to go a step above linking physical items with digital identity – as is the case with QR and NFC – and meet EU goals are the likes of Balenciaga, RealReal, and Boss, the article mentions.

And unlike that “old tech” that was there mostly to facilitate and protect transactions, manufacturers and customers, Mojito CEO Raakhee Miller had this interesting take on what’s referred to as the upcoming, “physical first” method: it “not only enhances the product’s value,” said Miller, “but also deepens consumer engagement.”
So, how deeply does the EU – and brands following its diktat – want to “engage” customers, other than people handing over money for a product they buy? This is where what’s basically data harvesting and mining comes into play, even if it is explained in fancy (and unsurprisingly, equally meaningless) terms like “phygital goods” and “metaverse approach.”
But, so to speak, the proof is in the word salad: the point is to have services and use cases “more anchored in client needs.” And clearly, to know what those needs are, one must first better know the client. Meaning, beyond what the client is currently comfortable sharing with multinational conglomerates.
Can’t we all just buy what we want, and move along? Please?
Not so fast, the EU says, and people like Vestiaire Collective VP of Partnerships Laura Escure explain it by no less than what might seem to many as basically questioning the customers’ cognitive abilities.
“The barriers around Web3 were not helping consumers to think thoroughly about luxury,” Escure is quoted.
READ: World Bank president advocates global digital ID scheme at tech summit
And did you know that if you dish out a lot of money on a luxury product, there’s a whole “story” behind it – beside the one in your bank statement? That’s how Aura Blockchain Consortium CEO Romain Carrere wants you to think about the situation.
“We believe in a future where every customer feels connected to the story behind their products, and the DPP is the key to unlocking that narrative. It’s not just a digital passport, it’s a journey of trust and empowerment for every consumer,” said Carrere.
But mostly, it would seem, it’s a narrative. There to empower itself, and those in positions of power, rather than the customer.
Back in EU’s bureaucracy, the digital product passport proposals first saw the light of day in the spring of 2022, naturally, as “sustainability” enhancing mechanisms related to products, and about a year later, this was officially presented on the European Commission website as a way to share key information about a product.
The information would be shared “across all the relevant economic actors,” a press release said in May 2023. Things are happening in this space under the Proposal for Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR).
The EU claims its goals are to boost what it calls circular economy, material and energy efficiency, and extend product lifetimes, as well as the way waste from those products is eventually handled.
The bloc also declares some grand ambitions here – like creating new business opportunities – “based on improved data access,” though.
And the EU is not above putting down consumers either, while at once working to elevate the level of data scrounged off of them. The DDP scheme, the Commission says, will “help consumers in making sustainable choices.”
And, for now – “allow authorities to verify compliance with legal obligations.”
Reprinted with permission from Reclaim The Net.
Alberta
Pierre Poilievre – Per Capita, Hardisty, Alberta Is the Most Important Little Town In Canada

From Pierre Poilievre
Business
Why it’s time to repeal the oil tanker ban on B.C.’s north coast

The Port of Prince Rupert on the north coast of British Columbia. Photo courtesy Prince Rupert Port Authority
From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
Moratorium does little to improve marine safety while sending the wrong message to energy investors
In 2019, Martha Hall Findlay, then-CEO of the Canada West Foundation, penned a strongly worded op-ed in the Globe and Mail calling the federal ban of oil tankers on B.C.’s northern coast “un-Canadian.”
Six years later, her opinion hasn’t changed.
“It was bad legislation and the government should get rid of it,” said Hall Findlay, now director of the University of Calgary’s School of Public Policy.
The moratorium, known as Bill C-48, banned vessels carrying more than 12,500 tonnes of oil from accessing northern B.C. ports.
Targeting products from one sector in one area does little to achieve the goal of overall improved marine transport safety, she said.
“There are risks associated with any kind of transportation with any goods, and not all of them are with oil tankers. All that singling out one part of one coast did was prevent more oil and gas from being produced that could be shipped off that coast,” she said.
Hall Findlay is a former Liberal MP who served as Suncor Energy’s chief sustainability officer before taking on her role at the University of Calgary.
She sees an opportunity to remove the tanker moratorium in light of changing attitudes about resource development across Canada and a new federal government that has publicly committed to delivering nation-building energy projects.
“There’s a greater recognition in large portions of the public across the country, not just Alberta and Saskatchewan, that Canada is too dependent on the United States as the only customer for our energy products,” she said.
“There are better alternatives to C-48, such as setting aside what are called Particularly Sensitive Sea Areas, which have been established in areas such as the Great Barrier Reef and the Galapagos Islands.”
The Business Council of British Columbia, which represents more than 200 companies, post-secondary institutions and industry associations, echoes Hall Findlay’s call for the tanker ban to be repealed.
“Comparable shipments face no such restrictions on the East Coast,” said Denise Mullen, the council’s director of environment, sustainability and Indigenous relations.
“This unfair treatment reinforces Canada’s over-reliance on the U.S. market, where Canadian oil is sold at a discount, by restricting access to Asia-Pacific markets.
“This results in billions in lost government revenues and reduced private investment at a time when our economy can least afford it.”
The ban on tanker traffic specifically in northern B.C. doesn’t make sense given Canada already has strong marine safety regulations in place, Mullen said.
Notably, completion of the Trans Mountain Pipeline expansion in 2024 also doubled marine spill response capacity on Canada’s West Coast. A $170 million investment added new equipment, personnel and response bases in the Salish Sea.
“The [C-48] moratorium adds little real protection while sending a damaging message to global investors,” she said.
“This undermines the confidence needed for long-term investment in critical trade-enabling infrastructure.”
Indigenous Resource Network executive director John Desjarlais senses there’s an openness to revisiting the issue for Indigenous communities.
“Sentiment has changed and evolved in the past six years,” he said.
“There are still concerns and trust that needs to be built. But there’s also a recognition that in addition to environmental impacts, [there are] consequences of not doing it in terms of an economic impact as well as the cascading socio-economic impacts.”
The ban effectively killed the proposed $16-billion Eagle Spirit project, an Indigenous-led pipeline that would have shipped oil from northern Alberta to a tidewater export terminal at Prince Rupert, B.C.
“When you have Indigenous participants who want to advance these projects, the moratorium needs to be revisited,” Desjarlais said.
He notes that in the six years since the tanker ban went into effect, there are growing partnerships between B.C. First Nations and the energy industry, including the Haisla Nation’s Cedar LNG project and the Nisga’a Nation’s Ksi Lisims LNG project.
This has deepened the trust that projects can mitigate risks while providing economic reconciliation and benefits to communities, Dejarlais said.
“Industry has come leaps and bounds in terms of working with First Nations,” he said.
“They are treating the rights of the communities they work with appropriately in terms of project risk and returns.”
Hall Findlay is cautiously optimistic that the tanker ban will be replaced by more appropriate legislation.
“I’m hoping that we see the revival of a federal government that brings pragmatism to governing the country,” she said.
“Repealing C-48 would be a sign of that happening.”
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoOttawa Funded the China Ferry Deal—Then Pretended to Oppose It
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoNew Peer-Reviewed Study Affirms COVID Vaccines Reduce Fertility
-

 MAiD2 days ago
MAiD2 days agoCanada’s euthanasia regime is not health care, but a death machine for the unwanted
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoThe permanent CO2 storage site at the end of the Alberta Carbon Trunk Line is just getting started
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoWorld Economic Forum Aims to Repair Relations with Schwab
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta’s government is investing $5 million to help launch the world’s first direct air capture centre at Innisfail
-
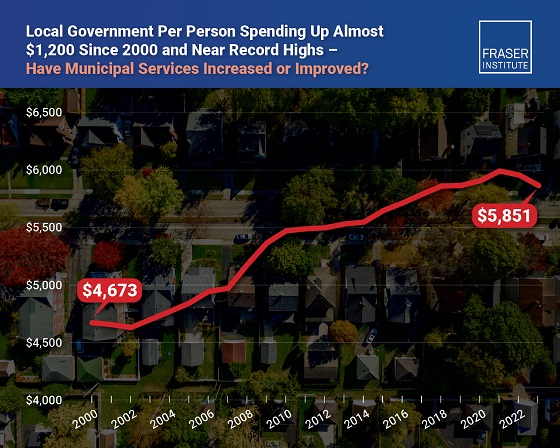
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoMunicipal government per-person spending in Canada hit near record levels
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoA new federal bureaucracy will not deliver the affordable housing Canadians need






