International
Hawley: Whistleblowers say Trump’s security detail was unprepared, inexperienced

From The Center Square
Senate committee holding bipartisan investigation, hearing
Multiple whistleblowers have come forward telling U.S. Sen. Josh Hawley, R-Mo., that many working as part of former President Donald Trump’s security detail at a rally in Pennsylvania one week ago weren’t Secret Service and were “unprepared and inexperienced personnel,” Hawley says.
The accusation comes after the U.S. Senate Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs Committee, on which Hawley sits, announced it will conduct a bipartisan investigation into the July 13 assassination attempt of Trump.
Multiple whistleblowers contacted his office “with disturbing new information behind the assassination attempt on the former president,” he said.
They did so after Hawley opened a whistleblower tip line, pledging to protect the anonymity of everyone who contacts his office. Whistleblowers are encouraged to make protected disclosures by calling (202) 224-6154 or emailing [email protected].
In response to the information he has received so far, Hawley contacted Department of Homeland Security Secretary Alejandro Mayorkas, who oversees the U.S. Secret Service, demanding answers.
“Whistleblowers who have direct knowledge of the event have approached my office. According to the allegations, the July 13 rally was considered to be a ‘loose’ security event,” he wrote to Mayorkas.
“Whistleblower allegations suggest the majority of DHS officials were not in fact USSS agents but instead drawn from the department’s Homeland Security Investigations. This is especially concerning given that HSI agents were unfamiliar with standard protocols typically used at these types of events, according to the allegations.”
Other security failures identified, he says, include not using canine units to monitor entry and detect threats among the perimeter or crowd; unauthorized individuals accessing the backstage areas; and DHS personnel not “appropriately polic[ing] the security buffer around the podium and … not stationed at regular intervals around the event’s security perimeter.”
Hawley demanded answers after DHS “has not been appropriately forthcoming with members of Congress,” he said, and after he called on the committee’s chair, U.S. Sen. Gary Peters, D-Mich., to immediately launch an investigation.
“Although we still do not have all the facts, the little that we do know suggests a staggering security failure,” he wrote to Peters. “Evidently, the shooter was able to gain an elevated position on a rooftop with a clear line of sight of the President, well within accurate range, with a firearm. The details of this tragedy must be vigorously investigated by Congress, including the motive of the shooter, and the serious operational failures that occurred on July 13.” Hawley called on Peters to “launch a full, public, and comprehensive committee investigation into this assassination attempt and failures to adequately protect the former president,” including calling Mayorkas and Secret Service Director Kimberly Cheatle to testify.
Peters and U.S. Sen. Rand Paul, R-KY, the ranking member of the committee, announced the committee will conduct a bipartisan investigation and hold a hearing. They first requested an urgent briefing with the Secret Service, DHS and the Federal Bureau of Investigation. A call committee members did have, Hawley says, was ended before they could ask a single question. “This is completely unacceptable and contrary to the public’s interest in transparency,” he added.
Peters said the committee “is focused on getting all of the facts about the security failures that allowed the attacker to carry out this heinous act of violence that threatened the life of former President Trump, killed at least one person in the crowd, and injured several others.”
Peters and Paul also sent letters to Mayorkas and to FBI Director Christopher Wray requesting a range of documents and information on security process, among other information. A briefing was requested before July 25 and a public hearing is scheduled for Aug. 1.
Hawley is also demanding answers from BlackRock CEO Larry Fink requesting all records related to the assassination attempt after it became public that the alleged shooter appeared in one of BlackRock’s commercials.
What appears to be a clip of the commercial “has circulated widely on social media and raised the question about what your company knows about the shooter,” Hawley told Fink.
Fink is requested to provide the information by July 24.
When accepting his party’s nomination for president, Trump said at the Republican National Convention last week that surviving the assassination attempt was “a gift from God.” At a rally on Saturday, one week after the shooting, he said he “took a bullet for democracy.”
Honest reporting on election integrity
Crime
Bryan Kohberger avoids death penalty in brutal killing of four Idaho students

Quick Hit:
Bryan Kohberger will plead guilty to murdering four Idaho college students, avoiding a death sentence but leaving victims’ families without answers. The plea deal means he’ll spend life in prison without ever explaining why he committed the brutal 2022 killings.
Key Details:
- Kohberger will plead guilty at a hearing scheduled for Wednesday at 11 a.m. local time.
- The plea deal removes the possibility of death by firing squad but ensures life in prison without parole.
- Victims’ families say the state “failed” them by agreeing to a deal that denies them an explanation for the murders.
Diving Deeper:
Bryan Kohberger, a former PhD criminology student at Washington State University, is expected to plead guilty to the November 2022 murders of four University of Idaho students, sparing himself the death penalty but also avoiding any explanation for his motive. Idaho defense attorney Edwina Elcox told the New York Post that under the plea, Kohberger will have to admit to the killings but won’t have to provide a reason for his actions. “There is no requirement that he says why for a plea,” Elcox explained.
Prosecutors reached the plea deal just weeks before the scheduled trial, which many believed would have revealed the full details and motives behind the shocking quadruple homicide. Kohberger is accused of murdering Kaylee Goncalves, 21; Madison Mogen, 21; Ethan Chapin, 20; and Xana Kernodle, 20, with a military-style Ka-Bar knife as they slept in their off-campus home in Moscow, Idaho. His DNA was allegedly found on a knife sheath left at the scene.
The Goncalves family blasted the state for the deal, saying, “They have failed us.” They had hoped a trial would uncover why Kohberger targeted their daughter and her friends. Prosecutors, however, argued that the plea ensures a guaranteed conviction and prevents the years of appeals that typically follow a death sentence, providing a sense of finality and keeping Kohberger out of the community forever.
Sentencing will not take place for several weeks following Wednesday’s hearing, which is expected to last about an hour as the judge confirms the plea agreement is executed properly. While the families may find some closure in knowing Kohberger will never be free again, they are left without the one thing a trial could have provided: answers.
(AP Photo/Matt Rourke, Pool)
International
CBS settles with Trump over doctored 60 Minutes Harris interview

CBS will pay Donald Trump more than $30 million to settle a lawsuit over a 2024 60 Minutes interview with Kamala Harris. The deal also includes a new rule requiring unedited transcripts of future candidate interviews.
Key Details:
- Trump will receive $16 million immediately to cover legal costs, with remaining funds earmarked for pro-conservative messaging and future causes, including his presidential library.
- CBS agreed to release full, unedited transcripts of all future presidential candidate interviews—a policy insiders are calling the “Trump Rule.”
- Trump’s lawsuit accused CBS of deceptively editing a 60 Minutes interview with Harris in 2024 to protect her ahead of the election; the FCC later obtained the full transcript after a complaint was filed.
Tonight, on a 60 Minutes election special, Vice President Kamala Harris shares her plan to strengthen the economy by investing in small businesses and the middle class. Bill Whitaker asks how she’ll fund it and get it through Congress. https://t.co/3Kyw3hgBzr pic.twitter.com/HdAmz0Zpxa
— 60 Minutes (@60Minutes) October 7, 2024
Diving Deeper:
CBS and Paramount Global have agreed to pay President Donald Trump more than $30 million to settle a lawsuit over a 2024 60 Minutes interview with then–Vice President Kamala Harris, Fox News Digital reported Tuesday. Trump accused the network of election interference, saying CBS selectively edited Harris to shield her from backlash in the final stretch of the campaign.
The settlement includes a $16 million upfront payment to cover legal expenses and other discretionary uses, including funding for Trump’s future presidential library. Additional funds—expected to push the total package well above $30 million—will support conservative-aligned messaging such as advertisements and public service announcements.
As part of the deal, CBS also agreed to a new editorial policy mandating the public release of full, unedited transcripts of any future interviews with presidential candidates. The internal nickname for the new rule is reportedly the “Trump Rule.”
Trump initially sought $20 billion in damages, citing a Face the Nation preview that aired Harris’s rambling response to a question about Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. That portion of the interview was widely mocked. A more polished answer was aired separately during a primetime 60 Minutes special, prompting allegations that CBS intentionally split Harris’s answer to minimize political fallout.
The FCC later ordered CBS to release the full transcript and raw footage after a complaint was filed. The materials confirmed that both versions came from the same response—cut in half across different broadcasts.
CBS denied wrongdoing but the fallout rocked the network. 60 Minutes executive producer Bill Owens resigned in April after losing control over editorial decisions. CBS News President Wendy McMahon also stepped down in May, saying the company’s direction no longer aligned with her own.
Several CBS veterans strongly opposed any settlement. “The unanimous view at 60 Minutes is that there should be no settlement, and no money paid, because the lawsuit is complete bulls***,” one producer told Fox News Digital. Correspondent Scott Pelley had warned that settling would be “very damaging” to the network’s reputation.
The final agreement includes no admission of guilt and no direct personal payment to Trump—but it locks in a substantial cash payout and forces a new standard for transparency in how networks handle presidential interviews.
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoOttawa Funded the China Ferry Deal—Then Pretended to Oppose It
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoNew Peer-Reviewed Study Affirms COVID Vaccines Reduce Fertility
-

 MAiD2 days ago
MAiD2 days agoCanada’s euthanasia regime is not health care, but a death machine for the unwanted
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoThe permanent CO2 storage site at the end of the Alberta Carbon Trunk Line is just getting started
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoWorld Economic Forum Aims to Repair Relations with Schwab
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta’s government is investing $5 million to help launch the world’s first direct air capture centre at Innisfail
-
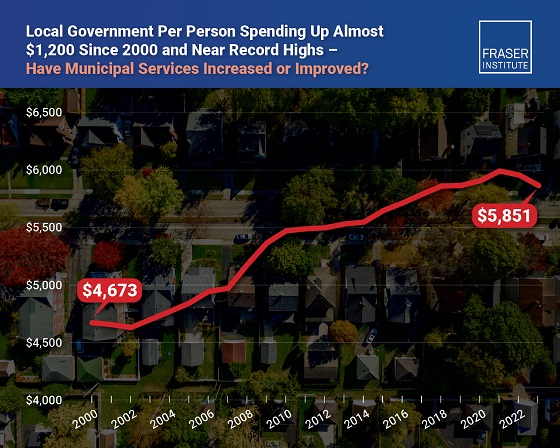
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoMunicipal government per-person spending in Canada hit near record levels
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoA new federal bureaucracy will not deliver the affordable housing Canadians need






