Alberta
Fighting Food Waste in 2021 – The Leftovers Foundation
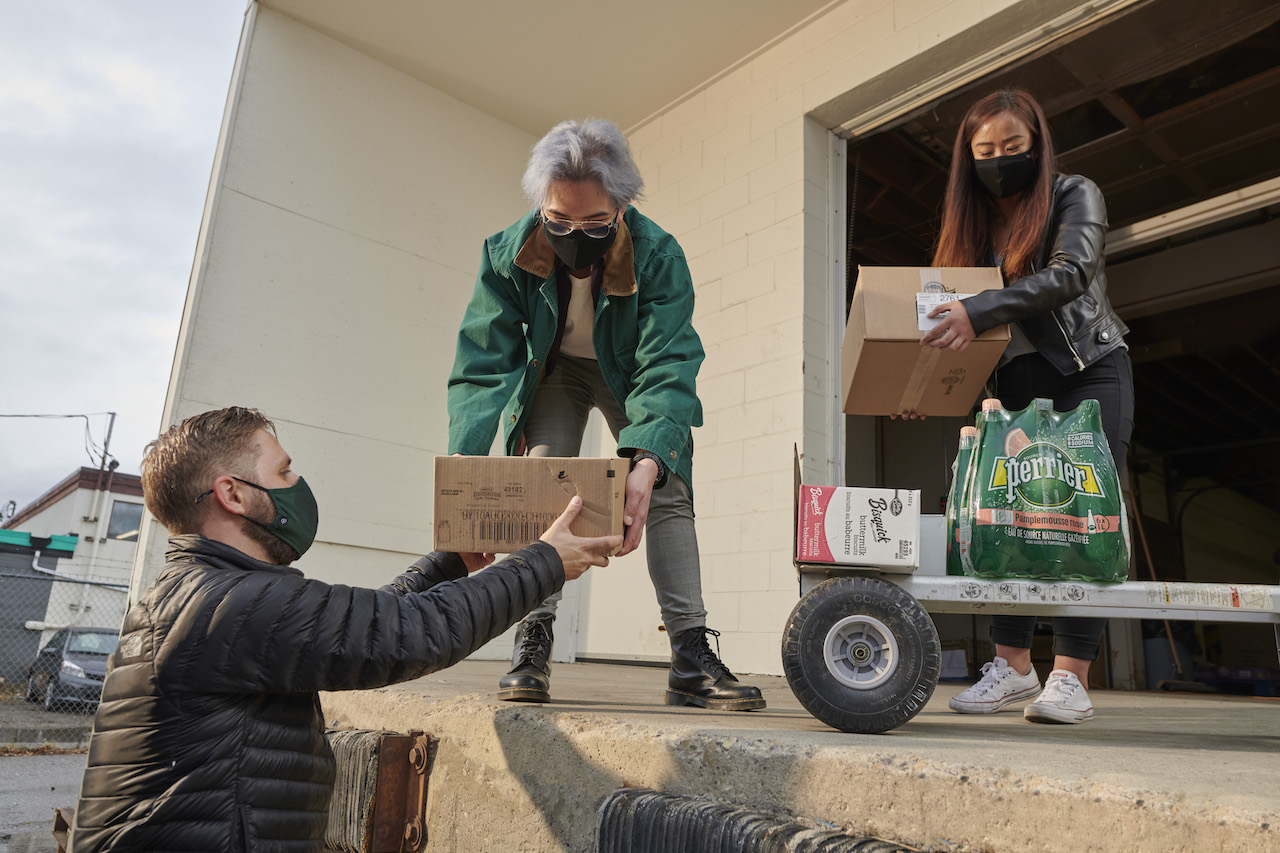

It’s 2021, and world hunger persists.
Statistics show the global agricultural industry produces enough food to successfully feed the population of the entire planet. Yet, hundreds of millions of people in both developing and developed nations experience food insecurity and poverty every single day. Food waste represents a massive modern crisis.

Live Green Toronto, 2018
Food waste, not to be confused with food loss, refers specifically to edible items that are discarded, despite being completely fit for human consumption, following initial production stages such as harvest and transportation.
Between restaurant, retailer and household waste, massive amounts of edible food are wasted every single day, all around the globe. Despite much of this waste being avoidable, the fact remains that thousands of pounds of viable food travel from farms to landfills each year. From both a human interest and environmental perspective, food waste represents a crisis with significant consequences.
According to a 2018 report on Global Food Waste and its Environmental Impact, “An estimated 1.3 billion tonnes of food is wasted globally each year, one third of all food produced for human consumption.”
A 2019 Technical Report on The Avoidable Crisis of Food Waste by Second Harvest highlights that in Canada alone, the annual avoidable food loss and waste totals 11.2 million metric tonnes, reaching a total value of $49.5 billion. According to the report, this amount “equates to 3% of Canada’s 2016 GDP and would feed every person living in Canada for almost 5 months” (6).
In addition to harming the community, food waste negatively impacts the environment by creating a massive drain on existing resources without reason. “When edible items are discarded, it’s not just food that is wasted. Consider all the resources required to bring food from the farm to your table: water for irrigation, land for planting, fuel for powering harvest and transport vehicles … when restaurant owners fill their rubbish bins with uneaten meals, all those resources are essentially wasted” (1).
 Reallocating surplus goods, as opposed to throwing them away, is a critical step in reducing food waste, minimizing the carbon footprint of the agricultural sector, and aiding individuals in gaining access to basic needs. According to Second Harvest, “Four million Canadians have insufficient access to food. Nevertheless, of the avoidable and edible food loss and waste (FLW) that occurs along the value chain, an estimated 86 percent is currently not rescued and redistributed” (6).
Reallocating surplus goods, as opposed to throwing them away, is a critical step in reducing food waste, minimizing the carbon footprint of the agricultural sector, and aiding individuals in gaining access to basic needs. According to Second Harvest, “Four million Canadians have insufficient access to food. Nevertheless, of the avoidable and edible food loss and waste (FLW) that occurs along the value chain, an estimated 86 percent is currently not rescued and redistributed” (6).
 In Calgary, a number of citywide and business specific “food rescue” programs are in place with the goal of addressing and reducing those staggering statistics. Organizations such as the Leftovers Foundation reduce food waste by collecting and redirecting leftover products to places in need, such as shelters or charities, as opposed to letting them be thrown away at the end of each day.
In Calgary, a number of citywide and business specific “food rescue” programs are in place with the goal of addressing and reducing those staggering statistics. Organizations such as the Leftovers Foundation reduce food waste by collecting and redirecting leftover products to places in need, such as shelters or charities, as opposed to letting them be thrown away at the end of each day.
 With three locations across Calgary, Edmonton and Winnipeg, the Leftovers Foundation works with local restaurants, bakeries, grocers and distributors to redirect excess edible food where it is needed most. In Calgary, city coordinators work closely with food donors and service agencies to establish weekly and bi-weekly routes for pick up and drop off by volunteers. The Leftovers Foundation fulfills service agency food needs on both a scheduled and as-needed basis. “We are the connection point between people who have good, edible, nutritious food to donate,” says Audra Stevenson, Interim CEO for the Leftovers Foundation, “and those who are unable to put food on their plates.”
With three locations across Calgary, Edmonton and Winnipeg, the Leftovers Foundation works with local restaurants, bakeries, grocers and distributors to redirect excess edible food where it is needed most. In Calgary, city coordinators work closely with food donors and service agencies to establish weekly and bi-weekly routes for pick up and drop off by volunteers. The Leftovers Foundation fulfills service agency food needs on both a scheduled and as-needed basis. “We are the connection point between people who have good, edible, nutritious food to donate,” says Audra Stevenson, Interim CEO for the Leftovers Foundation, “and those who are unable to put food on their plates.”
 In 2019, the Leftovers Foundation launched their Food Rescue app in partnership with Technovation, to streamline connections between volunteers and food redirection routes. Stevenson describes the app as a “game-changer” for the organization, and as a result, the Leftovers Foundation has been able to standardize and scale their operations much more effectively.
In 2019, the Leftovers Foundation launched their Food Rescue app in partnership with Technovation, to streamline connections between volunteers and food redirection routes. Stevenson describes the app as a “game-changer” for the organization, and as a result, the Leftovers Foundation has been able to standardize and scale their operations much more effectively.
In this line of work, where the ultimate goal is to reduce food waste, food poverty, and the associated environmental impacts, collaboration is key. The Leftovers Foundation works collaboratively with other food rescue services around the city to avoid duplication and ensure all the food that can be saved, gets saved. “We’re supportive of every possible food rescue initiative,” says Stevenson, “It’s about every pound of food that makes it way onto someone’s plate instead of into the landfill.”
Other food rescue resources:
Calgary Food Bank Food Rescue and Share Program
https://www.calgaryfoodbank.com/foodmovement/
Kerby Centre Food Rescue
https://www.kerbycentre.com/support-services/foodrescue/
Zero Waste YYC
https://www.facebook.com/yyc.zerowaste/
In the war on food waste, every effort counts. “Food insecurity is becoming a bigger and bigger problem with COVID,” says Stevenson, “It’s not going to just go away. Any way you can get involved with our systems, whether it’s volunteering, donating, just paying attention to gaps in the community – now is the time to get involved and help reduce food waste.”
For more information on the Leftovers Foundation and how to get involved in Calgary’s efforts to reduce food waste, visit https://rescuefood.ca
For more stories, visit Todayville Calgary.
Alberta
Alberta Sports Hall of Fame Announces Class of 2026 Inductees

The Alberta Sports Hall of Fame is proud to announce its Class of 2026 inductees, celebrating outstanding athletes, builders, and contributors who have made a lasting impact on Alberta’s sporting community. From motorsport to rugby, rowing, and basketball, this year’s class represents excellence, dedication, and passion for sport across the province.
The Induction Ceremony will take place on Saturday, June 6, 2026, at the Red Deer Resort & Casino. Ticket information will be announced at a later date.
“Each year, the Alberta Sports Hall of Fame has the honour of recognizing remarkable individuals who have shaped sport in our province. The Class of 2026 is no exception,” said Alberta Sports Hall of Fame Board Chair Murray Cunningham. “This group includes Olympians, record breakers, and dedicated sport builders whose impact reaches far beyond competition. We are proud to celebrate their achievements and preserve their stories for future generations.”
Class of 2026 Inductees:
Jen Kish — Rugby Athlete
Jen Kish emerged as a standout talent early, earning her spot on the national team at just 17. Over the next 13 years, she became one of the country’s most influential rugby players, ultimately serving as captain of Canada’s Women’s Rugby Sevens team during its rise onto the world stage. Under her leadership, Canada achieved a series of historic results: silver at the 2013 Rugby World Cup Sevens, gold at the 2015 Pan American Games, and a bronze medal at the 2016 Rio Olympics—the first Olympic tournament for women’s rugby sevens. Her work ethic, competitive intensity, and ability to build trust and resilience became defining elements of the team’s culture. Beyond competition, Kish continued to break ground as an advocate for inclusion, representation, and mental health awareness. She has mentored young athletes at camps, schools, and community events across Alberta, helping broaden the sport’s reach and support future generations. Recognized as an inductee of both the Rugby Canada Hall of Fame and the Edmonton Sports Hall of Fame, Jen remains a powerful voice and mentor within Canadian rugby, solidifying her legacy as a world-class competitor and leader on and off the field.
Shannon Kleibrink — Curling Athlete
Shannon Kleibrink has been a major force in Canadian curling for more than two decades. She began competing at the national level in the early 1990s and went on to become a five-time Alberta Women’s Champion and four-time Alberta Mixed Champion. In 2004, she made history as the only woman to skip a team to a Canadian Mixed Curling Championship title. Kleibrink’s success continued on the world stage. She won an Olympic bronze medal at the 2006 Winter Games and competed in five Scotties, earning multiple national and Grand Slam titles. She also secured three medals at the Canadian Olympic Trials during her competitive career, which spanned from 1993 to 2018 before returning at the senior level in 2023. Beyond competition, Shannon has significantly shaped the sport through coaching and development. As Curling Alberta’s Director of Community Curling Centre Development, she has strengthened rural clubs, expanded post-secondary curling programs, and supported grassroots growth across the province.
James Steacy — Hammer Throw Athlete
James Steacy launched his athletic career at the University of Lethbridge, where he became a five-time CIS weight throw champion and set a national university record that still stands today. His success propelled him onto the international stage, beginning a 17-year career representing Canada. Steacy captured gold at the 2007 Pan American Games and made history at the 2008 Beijing Olympics as the first Canadian in 84 years to reach the hammer throw final. He continued to lead Canadian throwing through the next decade, serving as captain of Canada’s track and field team at the 2012 London Olympics and winning Commonwealth Games gold in 2014. Along the way, Steacy claimed 11 national titles and set a Canadian hammer throw record of 79.13 metres, which remained unbroken for 15 years. After retiring from competition, Steacy remains committed to his community, mentoring young athletes and supporting the Lethbridge sports community.
Kasia Gruchalla-Wesierski — Rowing Athlete
Kasia Gruchalla-Wesierski began her athletic career as an alpine skier before shifting to rowing in 2014 with the Calgary Rowing Club. Her rapid rise in the sport led to her joining the Canadian senior national team in 2018, marking the start of her impact on the world stage. She became a key member of Canada’s women’s eight, contributing to multiple World Cup podiums and earning a bronze medal at the 2022 World Rowing Championships. One of the defining moments of her career came at the Tokyo 2020 Olympic Games. Just weeks before competition, she suffered a severe cycling accident—breaking her collarbone, bruising her hip, and requiring 56 stitches. Her five-week comeback to reclaim her seat culminated in winning Olympic gold with the W8+, one of the most celebrated stories of the Games. Kasia continued to excel, capturing silver in the women’s eight at Paris 2024 and winning gold at the 2024 World Cup in Lucerne. Beyond competition, she remains deeply involved in the rowing community as a coach in Calgary and will serve as an Athlete Services Officer with the Canadian Olympic Committee at the 2026 Milano Cortina Winter Olympics.
Dennis Allen — Multisport Builder
Dennis Allen has spent a lifetime shaping sport in Alberta as both an athlete and a builder. His time with the 1963-1965 Lethbridge North Star Fastball teams earned him induction into the Softball Alberta Hall of Fame (2003) and the Lethbridge Sports Hall of Fame (2007). Allen’s work as a sport builder began in 1986 when he served as Chair of the Alberta Summer Games in Edson, earning Citizen of the Year for his leadership. That role launched nearly 30 years of service to the Alberta games, where he led marketing, operations, volunteer development, and facility upgrades that supported athlete pathways and contributed to the development of more than 50 future Olympians. He later played a key role in strengthening the Alberta Sports Hall of Fame, helping raise funds for the construction of its current facility and serving as both Director and Chairman of the Board. Known for his mentorship and forward-thinking approach, Allen championed youth engagement programs such as “Live Outside the Box” and secured funding that expanded sport opportunities across the province. His work has left a lasting impact on Alberta’s sport infrastructure, community development, and athlete success at every level.
Bernard “Bernie” Haley — Hockey Builder
Bernard “Bernie” Haley began his hockey career as an elite player, winning an NCAA national championship with the University of North Dakota before moving into senior hockey. He later shifted his focus to officiating, quickly rising through the ranks thanks to his exceptional skating, professionalism, and command of the game. Over his career, Haley officiated across multiple levels of Canadian hockey, including the WHA, national championships, Memorial Cup finals, and the Canada Winter Games, where he was consistently assigned medal rounds and championship games. His skill earned him international recognition as well—he represented Canada as its lone official at several IIHF World Championships and at the 1980 Winter Olympics, where his composure and authoritative presence drew widespread respect. Beyond the ice, Haley shaped the sport through more than 20 years as Hockey Alberta’s Zone 4 assignor, mentoring generations of officials, leading clinics, and instilling the values of preparation, discipline, and respect for the game. His contributions have been honoured through numerous awards, including his Level VI National High Performance Referee designation, the Alberta Achievement Award of Excellence, and the “Bernie Haley Award for Officiating,” named in his honour. Together, these achievements cement his legacy as one of Alberta’s and Canada’s most influential officials and builders in hockey.
Donna Rudakas — Basketball Builder
Donna Rudakas began shaping Alberta basketball in the early years of her coaching career, eventually joining the University of Calgary Dinos and leading the women’s program through a dominant 14-year run. Under her guidance, the Dinos made 13 playoff appearances, captured five Canada West titles, and delivered a historic undefeated 36-0 season in 1988–89—part of a remarkable 69-game winning streak, one of the longest in North American women’s basketball. Donna was known for her forward-thinking approach, pioneering offensive and defensive systems built around the newly introduced three-point line. Her leadership developed numerous national team players, All-Canadians, and athletes who went on to professional and high-profile careers. Off the court, she became a powerful advocate for women in sport. Rudakas delivered clinics, camps, and leadership programs across Alberta, promoting participation, academic success, and lifelong confidence through basketball. Her commitment to developing athletes and empowering young women earned her multiple coaching honours and deep respect across the Canadian basketball community. Widely regarded as a visionary builder, Rudakas’ influence continues to shape the game—and the players—who follow in her footsteps.
Dale Schulha — Multisport Builder
Dale Schulha began his athletic journey as a multi-sport standout at McNally Composite High School, competing on seven teams in his senior year. He went on to play defensive back for the University of Alberta Golden Bears from 1968 to 1972, serving as team captain during the 1971 and 1972 College Bowl Championship seasons. After completing his education, Schulha entered the Edmonton Public School system as a teacher and quickly moved into coaching. He guided teams at both the high school and junior football levels, coached at Medicine Hat College, and later became Head Coach of the Medicine Hat Rattlers in the Alberta Junior Football League. Schulha transitioned into senior sport administration, holding several leadership roles before serving two terms as the University of Alberta’s Director of Athletics. In that role, he oversaw 25 varsity teams, 80 staff, and more than 475 student-athletes, while helping shape the broader landscape of Canada West and Canadian Interuniversity Sport. He was also a key contributor to the 1983 World University Summer Games in Edmonton. In recognition of his impact, Schulha received the Austin-Matthew Award in 2014 for outstanding contributions to Canadian University sport.
Bud Steen — Football Builder
Bud Steen is regarded as one of Canadian football’s most influential officials and builders. His career began in the late 1970s and grew into more than 30 years on the field, working over 500 CFL games and receiving seven Grey Cup referee assignments—one of the league’s highest honours for an official. Known for his calm presence, professionalism, and command of the rulebook, Steen helped elevate the role of officiating across Canada. In the late 1990s, he founded the Canadian Professional Football Officials Association and served as its first president for 12 years. Under his leadership, the association secured the CFL’s first formal employment agreement for officials, introduced comprehensive insurance coverage, and improved working conditions and professional standards across the league. Steen’s impact extended far beyond game days. He has mentored officials at every level, led decades of film and rules clinics, created Alberta’s Junior Officials Program, and helped implement league-wide evaluation and grading systems that strengthened training and accountability within the CFL. After retiring from on-field officiating in 2010, he continued to serve the league as a game supervisor, evaluator, and rules coach, earning respect from officials, coaches, and players alike. His leadership has been recognized through the CFL Commissioner’s Award and numerous honours for mentorship and professionalism.
1995 Calgary Canucks — Hockey Team
The 1995 Calgary Canucks stand as one of Alberta’s greatest junior hockey teams, built entirely from local Hockey Calgary talent. After finishing second in the regular season, the Canucks powered through the AJHL playoffs to win the league title and then captured the Doyle Cup, earning their spot at the Centennial Cup in Ottawa. Their national championship run became one of the most memorable in tournament history. In the final, the Canucks forced overtime with a goal in the last minute of regulation before Jason Abramoff scored the winner, securing Calgary’s first national title and the final championship contested under the Centennial Cup name before it became the Royal Bank Cup. The team’s success showcased the strength of Calgary’s grassroots development system and reinforced the city’s status as a junior hockey powerhouse. Defined by resilience, leadership, and a deep commitment to team play, the 1995 Calgary Canucks left a legacy that continues to influence junior hockey in Alberta and across Canada.
David Moir —Bell Memorial
David Moir has built a remarkable career in Canadian sports broadcasting after an accomplished athletic youth. Growing up in Calgary, he excelled in football, basketball, hockey, and track and field—earning city championships, All-Star honours, and setting junior football records with the Calgary Colts. He transitioned into sports media in the early 1980s and quickly became a trusted statistician and graphics coordinator for Calgary Flames broadcasts and CFL coverage. Over more than 40 years, Moir has contributed to 37 Grey Cups, 21 Stanley Cup Finals, 8 Olympic Games—including the iconic 2010 Vancouver Olympic hockey gold medal game—and numerous world championship events. He is widely respected for his precision, professionalism, and ability to anticipate broadcaster needs in high-pressure environments. Known for elevating the quality of live sports coverage, Moir has worked alongside many of Canada’s leading media personalities and is regarded as “at the top of his craft.” His decades of service have strengthened sports broadcasting nationwide and reflect a lifelong commitment to Alberta athletics and storytelling.
Allen Berg — Motorsport Achievement
Allen Berg is one of Alberta’s most accomplished motorsport athletes and remains the only Albertan to compete in Formula 1. Raised in Calgary, he began karting in the late 1970s and quickly rose through the ranks, winning back-to-back Alberta championships. He advanced into Formula Ford and Formula F, earning multiple Rookie of the Year awards and Canadian Driver of the Year honours before moving onto the international stage. Berg competed in British Formula 3, finishing second overall in 1984. His success earned him a Formula 1 contract with Osella, and in 1986 he competed in nine Grand Prix events against some of the sport’s greatest drivers. He later transitioned into endurance racing, taking part in major events such as the 24 Hours of Le Mans and the IMSA Daytona 24 Hours. After retiring from professional competition, Berg turned his focus to mentorship and driver development. He founded the Allen Berg Racing School, where he has trained more than 10,000 drivers across Canada, the United States, Mexico, and Europe, advancing driver safety and high-performance training worldwide. Inducted into the Canadian Motorsport Hall of Fame in 2019, Berg’s career reflects international success, a dedication to education, and a lasting impact on motorsport in Alberta and beyond.
Dr. Bob Bratton — Volleyball Pioneer
Dr. Bob Bratton is a trailblazer who helped turn volleyball in Alberta from a casual pastime into a powerhouse sport.He discovered the game at 20 while in graduate school in Chicago, earning a silver medal at the U.S. collegiate championship before bringing his passion north. Over the next several decades, Bratton became one of the sport’s strongest architects—serving more than 20 years as President of the Alberta Volleyball Association and later as Vice-President of Volleyball Canada, where he advanced player development, coaching standards, and officiating programs nationwide. As head coach of the University of Calgary men’s team from 1962 to 1976, he led Canada’s first university volleyball tour of Europe, opening doors for international competition. Alberta’s first National Referee, Bratton also created the Masters Officials Program—still a benchmark for training officials at every level. He authored coaching manuals, hosted clinics and camps across the province, and played a key role in bringing the Canadian Men’s National Team to Calgary. Inducted into both the Volleyball Canada Hall of Fame (2003) and Volleyball Alberta Hall of Fame (2005), Bratton’s impact is lasting. His vision and leadership helped establish Alberta as one of the country’s strongest centres for volleyball—nationally and internationally.
“As we embark on the induction journey, our team is genuinely excited to connect with and learn more about each member of the Class of 2026. Every inductee carries an inspiring story shaped by passion, resilience, and achievement. It is a privilege for us to help share these stories with Albertans, and we look forward to celebrating this exceptional group throughout the year,” said Executive Director Tracey Kinsella.
The Alberta Sports Hall of Fame continues to celebrate and preserve the rich sporting heritage of Alberta. Join us in recognizing these incredible contributors at the 2026 Induction Ceremony.
Alberta
Carney’s pipeline deal hits a wall in B.C.

This article supplied by Troy Media.
Carney’s attempt to ease Canada’s dependence on the U.S. stirs a backlash in B.C., raises Indigenous concerns and rattles his own party
The Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) between Prime Minister Mark Carney and Alberta Premier Danielle Smith has opened a political hornet’s nest, exposing deep divisions within the Liberal Party and forcing a national debate that has been avoided for years.
Carney was under mounting pressure to respond to U.S. tariffs that threaten to carve billions out of Canada’s economy. The United States buys more than 95 per cent of Canada’s oil exports, leaving the country highly exposed to U.S. policy decisions. That pressure is now driving his push for a route to the Pacific, a project that could change Canada’s economic future but also destabilize his already fragile minority government.
Carney knows the political risk. His government could fall at any time, which only raises the stakes. Even so, he has pressed ahead. The agreement with Alberta lays early groundwork for a new pipeline to the Pacific. It would expand the oil sands, ease some environmental obligations and revive a proposal industry leaders have pushed for years.
The route is far from settled, but it is expected to run to B.C.’s northern coast and open access to Asian buyers. A Pacific route would finally give Canada a direct path into Asian energy markets, where demand remains strong and prices are often higher than in the United States.
If Carney expected broad support, he did not get it, especially in British Columbia. Because B.C. is the only province with a deep-water port capable of handling large crude carriers, it is the only path a west-coast pipeline can take. The province is now the central battleground, and whether the project succeeds will depend on what happens there.
B.C. Premier David Eby criticized the lack of consultation. “It would have been good for B.C. to be at the table,” he said, warning that the project risks undermining Indigenous support for the province’s liquefied natural gas plans. He also noted that the pipeline has no private backer and no commitments from First Nations, two obstacles that have tripped up projects before.
The backlash quickly spread to Ottawa. Steven Guilbeault, the former environment minister and the most prominent environmentalist ever to serve in a federal cabinet, resigned from cabinet in direct response to the MOU. He said the proposed pipeline “would have major environmental impacts”. Green Party Leader Elizabeth May said his departure “dashes the last hope that Mark Carney is going to have a good climate record ever.”
Several B.C. Liberal MPs echoed concerns about the political cost. CBC News reported anger inside the caucus, with some MPs “seething” over the agreement and worried about losing climate-focused voters.
The voters those MPs fear may not be as opposed as they think. An October Angus Reid Institute survey found that a solid majority of Canadians support a pipeline from northern Alberta to the northwest B.C. coast. In British Columbia, support outweighs opposition by a wide margin. That challenges Eby’s claim that the project lacks public backing. Carney may have more room to manoeuvre than his critics admit.
The most significant challenge, however, comes from Indigenous leaders. British Columbia is the only province that has formally adopted the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples (UNDRIP) into law, giving First Nations a stronger legal position in major project decisions. Court rulings over the past two decades have affirmed a duty to consult and, in some cases, accommodate Indigenous communities, giving them major influence over large projects.
A group representing Coastal First Nations in B.C. said the pipeline “will never happen”. The Union of B.C. Indian Chiefs said it is “loudly objecting” to the MOU, arguing it was drafted without involvement from coastal First Nations and does not meet consultation standards outlined in UNDRIP. “The answer is still no and always will be,” said UBCIC Grand Chief Stewart Phillip. He also said lifting the crude oil tanker ban would amount to bulldozing First Nation rights. Without Indigenous consent, the project cannot proceed, and Carney knows this is the single largest barrier he faces.
Carney’s reasoning is straightforward. The long-term danger of relying on one market outweighs the short-term turbulence created by the pipeline fight. The MOU suggests Ottawa is prepared to reconsider projects once thought politically impossible in order to protect Canada’s economic future. He is betting that doing nothing is the bigger risk.
Whether this pipeline moves forward is uncertain, and the obstacles are real. One fact, however, remains clear. Canada cannot keep betting its stability on a single market.
Toronto-based Rashid Husain Syed is a highly regarded analyst specializing in energy and politics, particularly in the Middle East. In addition to his contributions to local and international newspapers, Rashid frequently lends his expertise as a speaker at global conferences. Organizations such as the Department of Energy in Washington and the International Energy Agency in Paris have sought his insights on global energy matters.
Troy Media empowers Canadian community news outlets by providing independent, insightful analysis and commentary. Our mission is to support local media in helping Canadians stay informed and engaged by delivering reliable content that strengthens community connections and deepens understanding across the country.
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta Sports Hall of Fame Announces Class of 2026 Inductees
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoCanada’s climate agenda hit business hard but barely cut emissions
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCarney’s Toronto cabinet meetings cost $530,000
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin1 day ago
Bruce Dowbiggin1 day agoIntegration Or Indignation: Whose Strategy Worked Best Against Trump?
-

 Artificial Intelligence2 days ago
Artificial Intelligence2 days agoAI is accelerating the porn crisis as kids create, consume explicit deepfake images of classmates
-
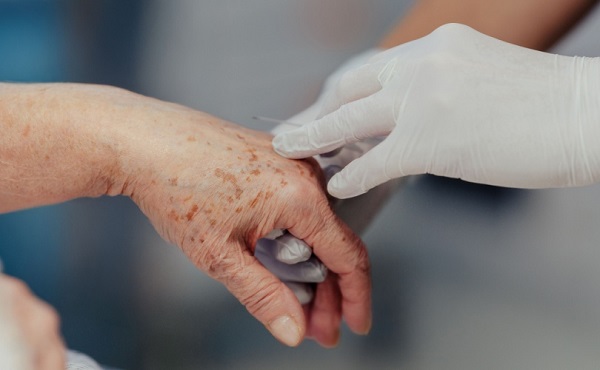
 MAiD1 day ago
MAiD1 day ago101-year-old woman chooses assisted suicide — press treats her death as a social good
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoCanada following Europe’s stumble by ignoring energy reality
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex2 days ago
Censorship Industrial Complex2 days agoConservative MP Leslyn Lewis slams Liberal plan targeting religious exemption in hate speech bil










