Alberta
Danielle Smith: Is there Going to Be a Central Bank Digital Currency? Almost Certainly
This newsletter was distributed by Danielle Smith.
I started my Western Standard show last week in the same week I was moderating a two-day conference for the Canadian Blockchain Consortium. So my shows last week were centred around trying to educate people as to what is cryptocurrency and Bitcoin, in particular, and how it is being used by regular people: such as when governments hyperinflate their currencies – like this story in Venezuela where people use it to buy food – or when countries fall apart like in Ukraine – where this man used the Bitcoin in the wallet on his phone to escape from the country before conscription came in.
As a side note, I can tell you I haven’t missed the cesspit of social media commentary. Part of the agreement with Western Standard is they broadcast on the social media channels so I get social media trolls shit posting me through the entire show. Delightful.
But I do take seriously those in our community who write me emails and approach me at events to express concerns.
Amanda is an example. She thanked me for the primers and said, “I was just chatting with a friend who said Poilievre needs to tone it down on that (cryptocurrency) because he is losing people like her because it is not well understood.” Others told me they wanted me to stop talking about Bitcoin also because they don’t understand it and they said I should just talk about freedom instead.
My dears…
I wish I could stop the world so we could all get off.
I’d probably get off in the year 2005 – just when we had all the advantages of technology but none of creepiness. I could easily live in a world before iPhone. I loved my blackberry. My husband would probably choose the 1950s when we still had passenger rail service and men wore hats. He can do without technology completely.

But we are in the world of the Technocreepy (to borrow the phrase coined by professor Thomas Keenan) and, ironically, it is one where you will soon be able to fully immerse yourself in whatever world you choose. I’m just learning about the Metaverse, but the concept of it is to use virtual reality goggles to enter into a world of digital avatars and artificial intelligence to meet up with others in a constructed environment. “Meet you for a wine on the train from Calgary to Toronto in 1950” may one day be a weekend date for my husband and me.
Central Bank Digital Currency vs Cryptocurrency…
But the biggest uneasiness I’m hearing is around the concept of a central bank digital currency. Pierre Poilievre has said he is absolutely opposed to a central bank digital currency at the same time as he says he wants to make Canada the blockchain capital of the world and make it easier to receive payments in cryptocurrency. That should tell you right there that a digital currency (issued by a central bank) and a cryptocurrency (not issued by a central bank) aren’t the same thing. More on that in a minute.
I’m hearing from many of you who are feeling unease that you don’t want either one. You say you want to move to bartering or stay in cash.
Two things…
You will always be free to barter goods but I would put it to you that it will be pretty limiting. There a remains a problem that most employers will still want to pay you in cash and most businesses will want to receive cash for your purchases. Anyone who has success in trading their baked bread and jars of chutney at the automechanic should let me know so I can be corrected. But I suspect you won’t find many takers.
I also don’t want our old dears thinking that the safest way to hold money is to withdraw cash from the bank and put it under their mattress. Holding cash in an environment where we have 10 to 15 per cent annual inflation is positively the worst advice anyone could give. Your money just loses its value year after year. That’s no way to preserve wealth either.
People say they want politicians to level with them. But now that I’m levelling with you about what is coming and how you can counter it, you are telling me you are too afraid to listen so I should just shut up about it.
I acknowledge your fears.
But I would ask you to soldier on and try to understand how the world is going to change. Because the World Economic Forum compendium document on digital currencies released in November 2021 shows a central bank digital currency is where the central bankers of the world are moving and it is has already started in China and Russia.
Here’s some background on where we already sit…
Bahamas was the first, but China rolled out its central bank digital currency called the renminbi last year and Time Magazine wrote about it last August in advance of the Beijing Olympics. The Chinese already have 96 per cent of their transactions taking place digitally with private options through Alipay and WeChat. Citizens like it. They simply flash a QR code on their smartphone screen to pay for everything they need: commuter tickets, lunch, convenience store items.
Chinese citizens are now voluntarily switching to the digital central bank renminbi – there are already more than 260 million individual users of the central bank digital coin. Also, 86 per cent of world’s central bankers (according to a survey by the Bank for International Settlements) are actively researching adopting their own.
Why do governments like the idea so much? Oh, so many reasons.
The biggest change of money since the gold standard…
According to Time, “It’s the biggest change in money since the end of the gold standard.”
The reason political leaders like digital coins is because there are “tremendous new functionalities.” For example:
Transfer “tokens” could be created to instantly transfer homes and property. You could own a “token” for a fractional share of any asset including vacation property, precious gems, art or other collectibles. It will reduce cross border transaction fees and costs to the financial services industry, which currently amount to $350 a year for each person in the world. It will make the SWIFT banking system – the one the Americans have used to cut off Iran and Russia – obsolete. And governments will be able to see all financial transactions rather than having to ask banks to provide it. It will also allow 1.7 billion people who have no bank accounts to get access to money.
But there is a dark side too…
There is also a reason authoritarian regimes like China like it too. From the Time article:
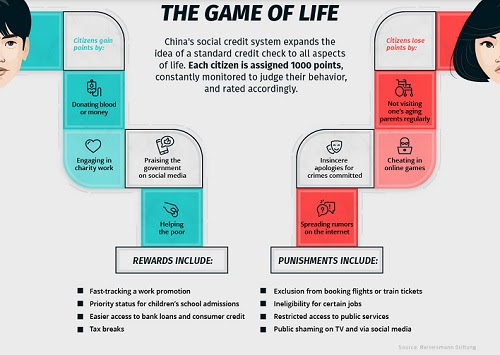
“In the Chinese pilot program, money has an expiration date of a few weeks because authorities are hoping to drive consumption in an economy trying to recover from the pandemic. Cash can be customized for other purposes. If the government is trying to stimulate the hospitality industry in a certain area, for example, it can program money to be used for meals and drinks but not for, say, petrol or power tools… Linked to China’s social credit system, it could see citizens fined in a split second for behaviors deemed undesirable. Dissidents and activists could see their wallets emptied or taken offline.”
So why does Poilievre oppose central bank digital currency and yet support cryptocurrency, the most important of which is Bitcoin? This article in the National Telegraph describes the differences well.
“Bitcoin as a currency functions as an anti-CBDC in a lot of ways. Where CBDCs are completely controlled by a central authority, Bitcoin is 100 percent decentralized, no one can mess with the system. CBDCs can have built-in controls so they can discriminate based on age, sex, wealth, race, or whatever other categories the government wanted, Bitcoin, on the other hand, has no control built-in so discrimination is impossible. While every CBDC transaction can be tracked and recorded Bitcoin transactions can be done peer to peer and are untraceable to a specific person. CBDCs are a windfall for bankers who love to print money and run up inflation, Bitcoin is a deflationary asset that less and less of can be mined every four years.”
Bitcoin is essentially an antidote to central bank coins.
A new geopolitical realignment…
There is a law of the universe: for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. The Americans throwing their weight around by excluding countries from the SWIFT system has accelerated the move from using the US dollar as an intermediary for global transactions and contracts. This will change the US dollar from being the de facto international currency and all the geopolitical shifts that implies.
Will it be good for us, tied as we are to the Americans?
I’m not sure yet, which is why I am following this closely. This article in the Algora blog site believes the change signals the end of Western domination and that we are going to find ourselves isolated from the rest of the world. According to them we are witnessing the end of globalization and the world is being split in two with the US, Europe and its allies (10 per cent of the world population) in one corner and the Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa – BRICS partners – representing 90 per cent of the world population on the other side.

“Reacting swiftly, Russia has convinced its BRICS partners to stop trading in dollars and to eventually create a common virtual currency for their exchanges. Until then, they will proceed in gold. This currency should be based on a basket of BRICS currencies, weighted according to the GDP of each member state, and on a basket of commodities listed on the stock exchange. This system should be much more stable than the current one.”
So if I were a guessing person, I would imagine this is going to be the model for how a new common digital currency will emerge for us.
Canada would develop its own central bank digital currency. Then we would opt in to a common virtual currency that includes the US, Europe, Australia and anyone else who wants to join us based on a basket of our currencies weighted according to GDP and (maybe?) a basket of commodities on the stock exchange.
The reason I think this is inevitable and that it will happen before Pierre Poilievre gets elected in 2025 and gets a chance to stop it, is because the momentum to do something to address our damaged currency is already too great.
The Great Money Printing Crusade of the last two years has rendered western currencies increasingly valueless. Printing money only works in the short term. Eventually you outpace the ability of the economy to keep up with producing goods and it causes inflation. Canadian inflation was 6.7 per cent last month – the highest it’s been in 30 years.
The Central Bank has already started raising rates to rein in spending and rate hikes are expected to continue.
I can imagine a few ways that shifting to a central bank digital coin could bail the government out of the mess it has created.
As we’ve seen in China, if it were implemented as a pilot project I suspect a large number of Canadians would simply sign up. We saw through COVID that at least 90 per cent of the public (or more) will do whatever the government tells them to do. So I suspect there will be a high uptake of the digital coin.
So yes, while I think we have reason to be gravely concerned that the federal government will want to use our transactions to micromanage our affairs, nudge us, monitor our ESG profile, and potentially punish us, I think we should also consider that the real reason for the global desire to suddenly go digital is so government can profit from the digital coin.
How Debt Jubilees Work…
Lyn Alden has done a wonderful write up of the historical experience with debt jubilees, which date back 4000 years. It began because farmers would be severely indebted to their lenders after a harvest failed and to avoid debt servitude, slavery or land seizure, the rulers from time to time (every 50 years or so) would just declare a debt jubilee so that all was forgiven. In the absence of this periodic forgiveness, more and more money would concentrate in the hands of the few, more and more would be pushed into poverty and there would be a popular uprising that would result in more than a few beheaded leaders.
No one in power ever wants that to happen.
And so we find ourselves in a familiar debt trap.
As Alden says, now that we have divorced our currency entirely from gold, we have created a banking ouroboros that makes it (nearly) impossible for central banks to forgive debt. In the past you could simply rebase your currency relative to the price of gold. Now we have a circular system: “Commercial banks store their cash at the central bank, which are assets for the commercial banks and liabilities for the central bank. In turn, the central bank holds government debt as its primary collateral assets. Government debt is backed up by the government’s ability to tax its citizens, and in practice, by having the central bank create new bank reserves to buy its government debt when needed. We can’t just remove one piece of it, like government debt from the central bank balance sheet. The monetary base is collateralized by government debt, and government debt is supported by expanding the monetary base when needed. It’s basically an ouroboros.”

So with inflation kicking in, interest rates rising, private debt in the stratosphere, government debt in the mesosphere, and no ability to cancel it all, what is a central banker to do?
One, they can do some “debt restructuring” and convert government bonds into 100-year zero coupon bonds, making the debt no longer relevant but allowing the central bank to raise rates for you and me while protecting themselves.
Two, they can hold interest rates below inflation, and let high inflation rates “burn debt away”, even though it will affect you and me in our purchasing power for the goods we need to buy on a daily basis. You can pay off your debt more easily then, but it will cost more to buy food and electricity.
Three, they could just steal it directly by doing a bail in, like they did in Cyprus in 2013, where the government taxed bank deposits up to 9.9 per cent and issued worthless equity certificates in exchange for the theft.
I’m wondering if a central bank digital coin offers a fourth way?
What about a Financial Transactions Tax?…
If it is indeed the case that the financial services industry costs $350 per person per year, it seems to me a digital currency is a way for the government to capture some of this revenue.
If you consider that the dollar from 1971 until today has been a petrodollar based on the flows of oil and natural gas denominated in the US currency, if we are moving to a digital dollar based on the amount of GDP and flow of financial transactions, what new revenue generating possibilities does that open for government?
I remember reading years ago about a proposal from Green Party Leader Elizabeth May for a financial transactions tax. The idea was to levy a tax on all sales of stocks and bonds and other financial holdings, to stick it to the rich but to also discourage speculative trading. In the US, they calculated charging 0.2 per cent ($2 on every $1000 in trade) would generate $777 billion over 10 years. Canada, with half the size, might expect to generate a $77 billion over 10 years.
But what if the concept was expanded to generate a fee for all transactions in Canadian dollars, equivalent to the transaction fees already being paid in the cryptocurrency markets? And what if all governments collaborated to make sure everyone charged the same tax so it couldn’t be avoided?
In Bitcoin, transactions under $10,000 carry a fee of 0.5 per cent. Canada’s Gross Domestic Product is $1.643 Trillion compared to a world GDP of $84.71 Trillion.
So if $1.7 trillion Canadian digital dollars trade hands each year, and the government could generate $5 for every $1000 spent, that would be $8.5 billion a year. But why stop there?
Banks often charge etransfer fees of $1.50 a transaction. At the top end, Visa and Mastercard charge 3.4 per cent on transactions. If the Bank of Canada were to charge rates that high on all Canadian dollar transactions they’d generate $58 billion a year.
Now we are talking some real money…
At the Blockchain conference this week, the keynote fireside chat was with Jeff Booth, author of The Price of Tomorrow: Why Deflation is the Key to an Abundant Future. In the video below he talks with Real Vision Finance about the pattern of inflation we have seen throughout history and how it creates a predictable pattern of behaviour in government to keep getting elected.
First they create internal division to distract people to stay elected, and when that stops working they blame another country. We have a structural change that is happening in the country, he says, and everything we are talking about is two orders of magnitude away from the first principles we should be talking about.
So I know this is uncomfortable. I know you don’t want me to talk about it. But we must. Because money affects everything.
So now you are thinking, if Canada is moving toward a central bank digital currency, and the WEF is championing central bank digital currencies, and if governments can use it to develop social scores (like China) to punish and reward its citizens, how can you escape the system?
How can you get the equivalent of cash that can’t be centrally controlled, monitored, devalued or turned off?
Now you understand why so many of us are interested in Bitcoin and cryptocurrency.
How you can help…
If you want to support me personally there are three ways to do it.
Book me to speak at your event: If you want me to do an event or coffee party in Livingstone Macleod I am happy to line it up. Just email [email protected] and my executive assistant will book it. If you are not in the constituency of Livingstone Macleod and want me to speak about The Future of Alberta and The Alberta First Initiative, my fee is $500 and you can book me by emailing me at [email protected]
The Danielle Smith Show: The Danielle Smith Show launched April 18. I did three 30 minute news monologues on Bitcoin during the week and a weekend long form interview on Saturday with Gord Tulk on health care spending accounts and radical idea to reform confederation. You can tune in live at 9 am or listen on podcast. Send me an email at [email protected] if you want to discuss sponsorship or advertising.
Subscribe to my Free Weekly Newsletter: Subscribe to this newsletter by going online to http://daniellesmith.ca. I will continue to write to you weekly.
See Previous Newsletters Online: Go to https://daniellesmith.ca/
Sign up on Locals: For Subscribers Only I will be doing a one hour livestream call in/text in so you can Ask Me Anything on Friday at 11 am as well as posting my thoughts on the issues of the day. I’ve set the minimum subscription fee very low – $2US a month – because I don’t want to create a barrier but I don’t want to content with anonymous bots and trolls either.
The Livingstone Macleod campaign …
My campaign website is http://daniellesmithucp.ca
You can donate online (sorry no tax receipts unless I am the nominated candidate!) to a maximum individual donation of $4000. This money will be put to use to pay for my campaign manager, scheduler, web designer, social media, signs and literature. I would be grateful for your contribution. I also need the gift of time, so if you can volunteer I will need that too! There is a portal on the website to sign up for campaign specific emails and to buy a UCP membership.
Donate by Mail: Make Cheques out to the Danielle Smith Campaign and send to 5548 Station Main, High River, Alberta, T1V 1H2.
Upcoming Events and Appearances…
April 25 Seminar to the CPAA on The Future of Alberta
April 27 AEG Calgary Event
April 27 Zoom telephone town halls for Livingstone Macleod
April 28 Crownest Pass Responsible Coal Association town hall
April 30 Civitas
May 4 Lethbridge Event with UCP Members
May 7 Airdrie Event with UCP Members
May 12 Canada in Question with Peter McInnon
May 18 High River Event with UCP Members
May 19 Alberta Adolescent Recovery Centre Gala
| Donate |
What’s New?
The Danielle Smith Podcast is now available.
Alberta
Alberta project would be “the biggest carbon capture and storage project in the world”

Pathways Alliance CEO Kendall Dilling is interviewed at the World Petroleum Congress in Calgary, Monday, Sept. 18, 2023.THE CANADIAN PRESS/Jeff McIntosh
From Resource Works
Carbon capture gives biggest bang for carbon tax buck CCS much cheaper than fuel switching: report
Canada’s climate change strategy is now joined at the hip to a pipeline. Two pipelines, actually — one for oil, one for carbon dioxide.
The MOU signed between Ottawa and Alberta two weeks ago ties a new oil pipeline to the Pathways Alliance, which includes what has been billed as the largest carbon capture proposal in the world.
One cannot proceed without the other. It’s quite possible neither will proceed.
The timing for multi-billion dollar carbon capture projects in general may be off, given the retreat we are now seeing from industry and government on decarbonization, especially in the U.S., our biggest energy customer and competitor.
But if the public, industry and our governments still think getting Canada’s GHG emissions down is a priority, decarbonizing Alberta oil, gas and heavy industry through CCS promises to be the most cost-effective technology approach.
New modelling by Clean Prosperity, a climate policy organization, finds large-scale carbon capture gets the biggest bang for the carbon tax buck.
Which makes sense. If oil and gas production in Alberta is Canada’s single largest emitter of CO2 and methane, it stands to reason that methane abatement and sequestering CO2 from oil and gas production is where the biggest gains are to be had.
A number of CCS projects are already in operation in Alberta, including Shell’s Quest project, which captures about 1 million tonnes of CO2 annually from the Scotford upgrader.
What is CO2 worth?
Clean Prosperity estimates industrial carbon pricing of $130 to $150 per tonne in Alberta and CCS could result in $90 billion in investment and 70 megatons (MT) annually of GHG abatement or sequestration. The lion’s share of that would come from CCS.
To put that in perspective, 70 MT is 10% of Canada’s total GHG emissions (694 MT).
The report cautions that these estimates are “hypothetical” and gives no timelines.
All of the main policy tools recommended by Clean Prosperity to achieve these GHG reductions are contained in the Ottawa-Alberta MOU.
One important policy in the MOU includes enhanced oil recovery (EOR), in which CO2 is injected into older conventional oil wells to increase output. While this increases oil production, it also sequesters large amounts of CO2.
Under Trudeau era policies, EOR was excluded from federal CCS tax credits. The MOU extends credits and other incentives to EOR, which improves the value proposition for carbon capture.
Under the MOU, Alberta agrees to raise its industrial carbon pricing from the current $95 per tonne to a minimum of $130 per tonne under its TIER system (Technology Innovation and Emission Reduction).
The biggest bang for the buck
Using a price of $130 to $150 per tonne, Clean Prosperity looked at two main pathways to GHG reductions: fuel switching in the power sector and CCS.
Fuel switching would involve replacing natural gas power generation with renewables, nuclear power, renewable natural gas or hydrogen.
“We calculated that fuel switching is more expensive,” Brendan Frank, director of policy and strategy for Clean Prosperity, told me.
Achieving the same GHG reductions through fuel switching would require industrial carbon prices of $300 to $1,000 per tonne, Frank said.
Clean Prosperity looked at five big sectoral emitters: oil and gas extraction, chemical manufacturing, pipeline transportation, petroleum refining, and cement manufacturing.
“We find that CCUS represents the largest opportunity for meaningful, cost-effective emissions reductions across five sectors,” the report states.

Fuel switching requires higher carbon prices than CCUS.
Measures like energy efficiency and methane abatement are included in Clean Prosperity’s calculations, but again CCS takes the biggest bite out of Alberta’s GHGs.
“Efficiency and (methane) abatement are a portion of it, but it’s a fairly small slice,” Frank said. “The overwhelming majority of it is in carbon capture.”

From left, Alberta Minister of Energy Marg McCuaig-Boyd, Shell Canada President Lorraine Mitchelmore, CEO of Royal Dutch Shell Ben van Beurden, Marathon Oil Executive Brian Maynard, Shell ER Manager, Stephen Velthuizen, and British High Commissioner to Canada Howard Drake open the valve to the Quest carbon capture and storage facility in Fort Saskatchewan Alta, on Friday November 6, 2015. Quest is designed to capture and safely store more than one million tonnes of CO2 each year an equivalent to the emissions from about 250,000 cars. THE CANADIAN PRESS/Jason Franson
Credit where credit is due
Setting an industrial carbon price is one thing. Putting it into effect through a workable carbon credit market is another.
“A high headline price is meaningless without higher credit prices,” the report states.
“TIER credit prices have declined steadily since 2023 and traded below $20 per tonne as of November 2025. With credit prices this low, the $95 per tonne headline price has a negligible effect on investment decisions and carbon markets will not drive CCUS deployment or fuel switching.”
Clean Prosperity recommends a kind of government-backstopped insurance mechanism guaranteeing carbon credit prices, which could otherwise be vulnerable to political and market vagaries.
Specifically, it recommends carbon contracts for difference (CCfD).
“A straight-forward way to think about it is insurance,” Frank explains.
Carbon credit prices are vulnerable to risks, including “stroke-of-pen risks,” in which governments change or cancel price schedules. There are also market risks.
CCfDs are contractual agreements between the private sector and government that guarantees a specific credit value over a specified time period.
“The private actor basically has insurance that the credits they’ll generate, as a result of making whatever low-carbon investment they’re after, will get a certain amount of revenue,” Frank said. “That certainty is enough to, in our view, unlock a lot of these projects.”
From the perspective of Canadian CCS equipment manufacturers like Vancouver’s Svante, there is one policy piece still missing from the MOU: eligibility for the Clean Technology Manufacturing (CTM) Investment tax credit.
“Carbon capture was left out of that,” said Svante co-founder Brett Henkel said.
Svante recently built a major manufacturing plant in Burnaby for its carbon capture filters and machines, with many of its prospective customers expected to be in the U.S.
The $20 billion Pathways project could be a huge boon for Canadian companies like Svante and Calgary’s Entropy. But there is fear Canadian CCS equipment manufacturers could be shut out of the project.
“If the oil sands companies put out for a bid all this equipment that’s needed, it is highly likely that a lot of that equipment is sourced outside of Canada, because the support for Canadian manufacturing is not there,” Henkel said.
Henkel hopes to see CCS manufacturing added to the eligibility for the CTM investment tax credit.
“To really build this eco-system in Canada and to support the Pathways Alliance project, we need that amendment to happen.”
Resource Works News
Alberta
The Canadian Energy Centre’s biggest stories of 2025

From the Canadian Energy Centre
Canada’s energy landscape changed significantly in 2025, with mounting U.S. economic pressures reinforcing the central role oil and gas can play in safeguarding the country’s independence.
Here are the Canadian Energy Centre’s top five most-viewed stories of the year.
5. Alberta’s massive oil and gas reserves keep growing – here’s why

The Northern Lights, aurora borealis, make an appearance over pumpjacks near Cremona, Alta., Thursday, Oct. 10, 2024. CP Images photo
Analysis commissioned this spring by the Alberta Energy Regulator increased the province’s natural gas reserves by more than 400 per cent, bumping Canada into the global top 10.
Even with record production, Alberta’s oil reserves – already fourth in the world – also increased by seven billion barrels.
According to McDaniel & Associates, which conducted the report, these reserves are likely to become increasingly important as global demand continues to rise and there is limited production growth from other sources, including the United States.
4. Canada’s pipeline builders ready to get to work
Canada could be on the cusp of a “golden age” for building major energy projects, said Kevin O’Donnell, executive director of the Mississauga, Ont.-based Pipe Line Contractors Association of Canada.
That eagerness is shared by the Edmonton-based Progressive Contractors Association of Canada (PCA), which launched a “Let’s Get Building” advocacy campaign urging all Canadian politicians to focus on getting major projects built.
“The sooner these nation-building projects get underway, the sooner Canadians reap the rewards through new trading partnerships, good jobs and a more stable economy,” said PCA chief executive Paul de Jong.
3. New Canadian oil and gas pipelines a $38 billion missed opportunity, says Montreal Economic Institute

Steel pipe in storage for the Trans Mountain Pipeline expansion in 2022. Photo courtesy Trans Mountain Corporation
In March, a report by the Montreal Economic Institute (MEI) underscored the economic opportunity of Canada building new pipeline export capacity.
MEI found that if the proposed Energy East and Gazoduq/GNL Quebec projects had been built, Canada would have been able to export $38 billion worth of oil and gas to non-U.S. destinations in 2024.
“We would be able to have more prosperity for Canada, more revenue for governments because they collect royalties that go to government programs,” said MEI senior policy analyst Gabriel Giguère.
“I believe everybody’s winning with these kinds of infrastructure projects.”
2. Keyera ‘Canadianizes’ natural gas liquids with $5.15 billion acquisition

Keyera Corp.’s natural gas liquids facilities in Fort Saskatchewan, Alta. Photo courtesy Keyera Corp.
In June, Keyera Corp. announced a $5.15 billion deal to acquire the majority of Plains American Pipelines LLP’s Canadian natural gas liquids (NGL) business, creating a cross-Canada NGL corridor that includes a storage hub in Sarnia, Ontario.
The acquisition will connect NGLs from the growing Montney and Duvernay plays in Alberta and B.C. to markets in central Canada and the eastern U.S. seaboard.
“Having a Canadian source for natural gas would be our preference,” said Sarnia mayor Mike Bradley.
“We see Keyera’s acquisition as strengthening our region as an energy hub.”
1. Explained: Why Canadian oil is so important to the United States

Enbridge’s Cheecham Terminal near Fort McMurray, Alberta is a key oil storage hub that moves light and heavy crude along the Enbridge network. Photo courtesy Enbridge
The United States has become the world’s largest oil producer, but its reliance on oil imports from Canada has never been higher.
Many refineries in the United States are specifically designed to process heavy oil, primarily in the U.S. Midwest and U.S. Gulf Coast.
According to the Alberta Petroleum Marketing Commission, the top five U.S. refineries running the most Alberta crude are:
- Marathon Petroleum, Robinson, Illinois (100% Alberta crude)
- Exxon Mobil, Joliet, Illinois (96% Alberta crude)
- CHS Inc., Laurel, Montana (95% Alberta crude)
- Phillips 66, Billings, Montana (92% Alberta crude)
- Citgo, Lemont, Illinois (78% Alberta crude)
-

 Energy6 hours ago
Energy6 hours agoRulings could affect energy prices everywhere: Climate activists v. the energy industry in 2026
-

 Digital ID7 hours ago
Digital ID7 hours agoThe Global Push for Government Mandated Digital IDs And Why You Should Worry
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin5 hours ago
Bruce Dowbiggin5 hours agoThe Rise Of The System Engineer: Has Canada Got A Prayer in 2026?
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoTrump confirms first American land strike against Venezuelan narco networks
-

 International5 hours ago
International5 hours agoMaduro says he’s “ready” to talk
-

 Opinion2 days ago
Opinion2 days agoGlobally, 2025 had one of the lowest annual death rates from extreme weather in history
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoHow convenient: Minnesota day care reports break-in, records gone
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoThe great policy challenge for governments in Canada in 2026





