Health
Chronic pain with no real reason?

Do you have chronic pain without a specific cause of injury? Do you have pain that has recurred several times over the course of the year, but never resolves completely? Is your pain persisting without ongoing inflammation or tissue damage? Do you have an injury that is not healing at the expected rate of recovery?
Some chronic pain conditions involving the musculoskeletal system do not seem to improve despite massage and stretching.Tight bands of muscle tissue can develop, which may create pain or cause pain by compressing a nerve that in turn causes pain. This type of dysfunction is called neuropathic pain. When the tight bands of muscle cross over a joint, additional issues can arise due to decreased space for joint movement and stiffness. This can cause issues such as bursitis, tendonitis, and arthritis. Along with muscle shortening, tissues often become supersensitive.
Gunn IMS is a total system for the diagnosis and treatment of myofascial pain syndromes (chronic pain involving the musculoskeletal system when there is no clear sign of recent injury). This approach involves assessment of the whole body to determine where pain is stemming from and what other areas need to be addressed to get long term relief. Not all needling is Gunn IMS, although sometimes the terms can be mistakenly interchanged.
Although comparable, Gunn IMS is different from trigger point needling and acupuncture. A practitioner, knowledgeable in anatomy, completes a thorough physical examination of the whole body to find physical signs of neuropathic pain. If you show signs and symptoms indicative of neuropathic pain and there are no barriers to treatment, Gunn IMS needling can be commenced. Treatment involves a dry needling technique using acupuncture needles to loosen tight bands of muscle tissue. Needling of a normal muscle is painless; however, a shortened supersensitive muscle will grasp the needle or cause a cramping sensation. The effect of the needle causes the muscle bands to relax and lengthen, helps draw blood to the area to support healing, and stimulates the nerve to function normally again. The effects of Gunn IMS are often experienced immediately, with improvements in range of motion, muscle tension and/or pain.
If you think you can benefit from Gunn IMS, contact us and we will get you on the right path to recovery! You can find out more information about Gunn IMS and certified practitioners at www.iSTOP.org
A Little About Us:
Pursuit Physiotherapy in Red Deer, promotes balanced, healthy living through dedicated, individualized physical therapy for those in pain, unable to participate fully in their daily activities, wanting to maximize their function for work or sport, and wanting to prevent potential problems.
If it is affecting your quality of life, then we want to help you to optimize your function and minimize your pain.
We are committed to your health and want to encourage you to be too.
Business
RFK Jr. says Hep B vaccine is linked to 1,135% higher autism rate

From LifeSiteNews
By Matt Lamb
They got rid of all the older children essentially and just had younger children who were too young to be diagnosed and they stratified that, stratified the data
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) found newborn babies who received the Hepatitis B vaccine had 1,135-percent higher autism rates than those who did not or received it later in life, Robert F. Kennedy Jr. told Tucker Carlson recently. However, the CDC practiced “trickery” in its studies on autism so as not to implicate vaccines, Kennedy said.
RFK Jr., who is the current Secretary of Health and Human Services, said the CDC buried the results by manipulating the data. Kennedy has pledged to find the causes of autism, with a particular focus on the role vaccines may play in the rise in rates in the past decades.
The Hepatitis B shot is required by nearly every state in the U.S. for children to attend school, day care, or both. The CDC recommends the jab for all babies at birth, regardless of whether their mother has Hep B, which is easily diagnosable and commonly spread through sexual activity, piercings, and tattoos.
“They kept the study secret and then they manipulated it through five different iterations to try to bury the link and we know how they did it – they got rid of all the older children essentially and just had younger children who were too young to be diagnosed and they stratified that, stratified the data,” Kennedy told Carlson for an episode of the commentator’s podcast. “And they did a lot of other tricks and all of those studies were the subject of those kind of that kind of trickery.”
But now, Kennedy said, the CDC will be conducting real and honest scientific research that follows the highest standards of evidence.
“We’re going to do real science,” Kennedy said. “We’re going to make the databases public for the first time.”
He said the CDC will be compiling records from variety of sources to allow researchers to do better studies on vaccines.
“We’re going to make this data available for independent scientists so everybody can look at it,” the HHS secretary said.
— Matt Lamb (@MattLamb22) July 1, 2025
Health and Human Services also said it has put out grant requests for scientists who want to study the issue further.
Kennedy reiterated that by September there will be some initial insights and further information will come within the next six months.
Carlson asked if the answers would “differ from status quo kind of thinking.”
“I think they will,” Kennedy said. He continued on to say that people “need to stop trusting the experts.”
“We were told at the beginning of COVID ‘don’t look at any data yourself, don’t do any investigation yourself, just trust the experts,”‘ he said.
In a democracy, Kennedy said, we have the “obligation” to “do our own research.”
“That’s the way it should be done,” Kennedy said.
He also reiterated that HHS will return to “gold standard science” and publish the results so everyone can review them.
International
RFK Jr. tells Tucker how Big Pharma uses ‘perverse incentives’ to get vaccines approved

From LifeSiteNews
By Matt Lamb
Kennedy defended his decision to fire all 17 members of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which he decried as a tool used to “rubber stamp” vaccines.
The vaccine approval process is a “bundle of perverse incentives” since pharmaceutical companies stand to make billions of dollars in revenue from it, Secretary of Health and Human Services Robert F. Kennedy Jr. told Tucker Carlson recently.
Kennedy appeared on Carlson’s show yesterday to discuss a variety of issues, including the potential link between autism and vaccines and his overhauling of the vaccine advisory committee at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention last month.
Twenty years ago, Bobby Kennedy was exiled from polite society for suggesting a link between autism and vaccines. Now he’s a cabinet secretary, and still saying it.
(0:00) The Organized Opposition to RFK’s Mission
(6:46) Uncovering the Reason for Skyrocketing Rates of Autism… pic.twitter.com/g8T8te3kNC— Tucker Carlson (@TuckerCarlson) June 30, 2025
Kennedy began by explaining that Big Pharma has been targeting academic journals to ensure its products receive favorable reviews.
“The journals won’t publish anything critical of vaccines … there’s so much pressure on them. They’re funded by pharmaceutical companies, and they’ll lose advertising and revenue from reprints,” Kennedy said.
Kennedy then noted that Big Pharma will “pay to get something published in these journals,” before accusing industry leaders of pushing drugs on doctors and of hiring “mercenary scientists” to manipulate data until their product is deemed safe and effective.
The entire complex is broken due to the “perverse incentives,” he lamented.
Later in the interview, Kennedy defended his decision to fire all 17 members of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) in June, which he decried as a mere tool to “rubber stamp” vaccines.
It served as “a sock puppet for the industry that it was supposed to regulate,” Kennedy exclaimed, citing conflicts of interest for the overwhelming majority of its board members.
This sort of “agency capture” explains the lucrative nature of vaccines, he added.
— Matt Lamb (@MattLamb22) July 1, 2025
Kennedy then summarized the “perverse” process as follows:
First of all, the federal government often times actually designs the vaccine, [the National Institutes of Health] would design it, would hand it over to the pharmaceutical company. The pharmaceutical company then runs it … first through [the] FDA, then through [the] ACIP, and gets it recommended.
If you can get that recommendation you now got a billion dollars in — at least — revenues by the end of the year, every year, forever. So, there was a gold rush to add new vaccines to the schedule and ACIP never turned away a single vaccine … that came to them they recommended, and a lot of these vaccines are for diseases that are not even casually contagious.
Kennedy further pointed to the Hepatitis B shot for newborns as an example of how the industry has been corrupted.
In 1999, the CDC “looked at children who had received the hepatitis vaccine within the first 30 days of life and compared those children to children who had received the vaccine later — or not at all. And they found an 1,135% elevated risk of autism among the vaccinated children. It shocked them. They kept the study secret and manipulated it through five different iterations to try to bury the link,” he said.
“We want to protect public health,” Kennedy explained, but “these vaccines … can cause chronic disease, chronic injuries that last a lifetime.”
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoOttawa Funded the China Ferry Deal—Then Pretended to Oppose It
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoNew Peer-Reviewed Study Affirms COVID Vaccines Reduce Fertility
-

 MAiD1 day ago
MAiD1 day agoCanada’s euthanasia regime is not health care, but a death machine for the unwanted
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoThe permanent CO2 storage site at the end of the Alberta Carbon Trunk Line is just getting started
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoWorld Economic Forum Aims to Repair Relations with Schwab
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlberta’s government is investing $5 million to help launch the world’s first direct air capture centre at Innisfail
-
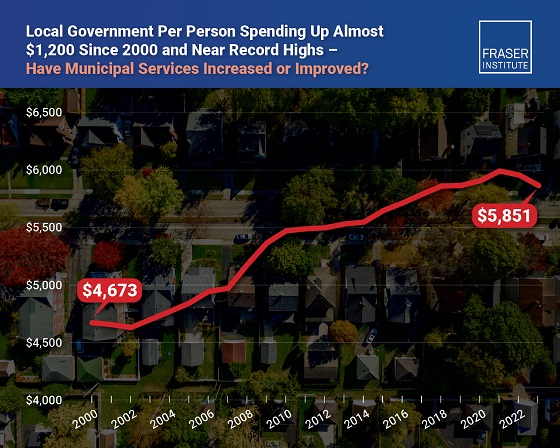
 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoMunicipal government per-person spending in Canada hit near record levels
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoA new federal bureaucracy will not deliver the affordable housing Canadians need






