Energy
TMX Pipeline a Success Story – Despite All the Green Battles Against It

From Energy Now
“As we go into winter months, Canada will set new export records”
We remember well the green battles against the “TMX” expansion of the Trans Mountain oil pipeline from Alberta to B.C. The idea was, they said, at best unnecessary and at worst thoroughly dangerous to the world environment.
One group said the expansion “threatens to unleash a massive tar sands spill that would threaten drinking water, salmon, coastal wildlife, and communities.” It would also, others said, impede investment in clean energy and undermine Canada’s efforts to deal with climate change.
Some said the expanded line would be an imposition on First Nations. But a number of First Nations are interested in acquiring an equity stake in the pipeline (and the federal government, which owns the line, is looking to sell a 30-percent stake to them).
Despite the loud opposition, the federal government went ahead and purchased the pipeline and the expansion project in May 2018, completing the pipeline’s expansion this year at a total cost of $31 billion.
Prime Minister Trudeau’s explanation: Ottawa stepped in because owner Kinder Morgan “wanted to throw up their hands and walk away,” and his government wanted to make sure that Canadian oil could reach new markets.
Alberta’s Canadian Energy Centre supported that outlook: “We’re going to be moving into a market where buyers are going to be competing to buy Canadian oil.”
Our Margareta Dovgal wrote: “What matters to us is the benefits to Canada. For one thing, we now will be able to ship more oil by tanker to refineries on the U.S. West Coast at a better price than oil by tanker from Alaska. And . . . we’ll have more oil more readily available for overseas buyers.
“So, all in all, we can expect to see higher returns on our oil, and we can continue to see the immense benefits of high-paying jobs in Canadian energy, and the benefits of revenues to government.”
It has all been happening, in spades.
And the opening of the expanded pipeline on May 1 this year also helped bring down gasoline prices.
In Vancouver, for example, regular gasoline in April ran as high as $2.359 a litre. At the beginning of May, as key refineries returned to normal after seasonal maintenance work, it stood around $2.085. As October opened, the price was as low as $1.579.
Economist G. Kent Fellows said at an event hosted by Resource Works and the Business Council of B.C.: “Our analysis shows that insufficient pipeline capacity was costing B.C. consumers an estimated $1.5 billion per year in higher gasoline prices.
“With TMX now operational, wholesale gasoline prices in Vancouver dropped by about 28 cents per litre compared to earlier this year.”
As for those buyers competing for our oil, some thought the prime export destination would be California. But the summer just past brought exports on tankers from Vancouver to China, Japan, India, Hong Kong, South Korea, and Brunei.
As of now, California is indeed leading as a destination, with Asian buyers having eased off after their initial purchases. Experts say that was expected, with Asian refineries first taking test cargoes to see how their systems handle our oil.
Kevin Birn, chief Canadian oil markets analyst for S&P Global, told Business in Vancouver: “There is always a market for crude oil in the Pacific Basin. We always saw the need for the Trans Mountain pipeline. We saw Canadian production continuing to grow.”
Birn added: “It’s still relatively early. I’d expect volumes to continue to build, cargoes to test different markets all over the place, and over time you’ll start to see patterns.
“As we go into winter months, Canada will set new export records, because as capacity’s been optimized and new product projections and wells are brought online, the winter tends to be the peak period.
“Every year, I think, for the next couple of years, Canada will set new records.”
That would be good news for Canada’s economy — and for Alberta’s.
There are no statistics available yet on the TMX line’s impact on the economy, but in 2019 Trans Mountain estimated that construction and operation would mean $46 billion in revenue to governments over the first 20 years.
Today, as reported by Alberta’s energy minister, Brian Jean, Alberta continues to break records for crude oil production, with global demand continuing to grow.
The latest numbers from the Alberta Energy Regulator show Alberta’s oil production averaged a little over 4 million barrels per day in August — the highest on record for any August.
“The addition of 590,000 barrels per day of heavy oil pipeline capacity from Alberta to the B.C. coast earlier this year with the completion of the Trans Mountain Pipeline expansion project has been instrumental in the recent production increases.”
All this as the International Energy Agency said that while oil demand is decelerating from 2023 levels due to a slowing economy in China, demand is still set to increase by 900,000 barrels per day (bpd) this year. That would push global consumption to a record level of almost 103 million bpd.
And that forecast came as Jonathan Wilkinson, our federal minister of energy and natural resources, declared: “Oil and gas will peak this decade. In fact, oil is probably peaking this year.”
A bevy of market-watchers disagreed with him. Among them, Greg Ebel, CEO of Calgary-based Enbridge, says global oil consumption will be “well north” of 100 million barrels per day by 2050 — and could exceed 110 million barrels.
“You continue to see economic demands, and particularly in the developing world, people continue to say lighter, faster, denser, cheaper energy works for our people. . . And that’s leading to more oil usage.”
Business
Carney should rethink ‘carbon capture’ climate cure

From the Fraser Institute
In case you missed it amid the din of Trump’s trade war, Prime Minister Carney is a big believer in “carbon capture and storage.” And his energy minister, Tim Hodgson, who said it’s “critical to build carbon capture systems for the oilsands,” wants the Smith government and oilsands companies to get behind a proposed project (which hasn’t been unable to raise sufficient private investment) in Cold Lake, Alberta.
The term “carbon capture and storage” (or CCS) essentially refers to technology that separates carbon dioxide (CO2) from emissions and either stores it or uses it for other products. Proponents claim that CCS could replace other more ham-handed climate regulations such as carbon taxes, emission caps, etc. The problem is, like many (or most) proposed climate panaceas, CCS is oversold. While it’s a real technology currently in use around the world (primarily to produce more oil and gas from depleting reservoirs), jurisdictions will likely be unable to affordably scale up CCS enough to capture and store enough greenhouse gas to meaningfully reduce the risks of predicted climate change.
Why? Because while you get energy out of converting methane (natural gas) to CO2 by burning it in a power plant to generate electricity, you have to put quite a lot of energy into the process if you want to capture, compress, transport and store the attendant CO2 emissions. Again, carbon capture can be profitable (on net) for use in producing more oil and gas from depleting reservoirs, and it has a long and respected role in oil and gas production, but it’s unclear that the technology has utility outside of private for-profit use.
And in fact, according to the International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD), most CCS happening in Canada is less about storing carbon to avert climate change and more about stimulating oil production from existing operations. While there are “seven CCS projects currently operating in Canada, mostly in the oil and gas sector, capturing about 0.5% of national emissions,” CCS in oil and gas production does not address emissions from “downstream uses of those fuels” and will, perversely, lead to more CO2 emissions on net. The IISD also notes that CCS is expensive, costing up to C$200 per tonne for current projects. (For reference, today’s government-set minimum carbon market price to emit a tonne of CO2 emissions is C$95.) IISD concludes CCS is “energy intensive, slow to implement, and unproven at scale, making it a poor strategy for decarbonizing oil and gas production.”
Another article in Scientific American observes that industrial carbon capture projects are “too small to matter” and that “today’s largest carbon capture projects only remove a few seconds’ worth of our yearly greenhouse gas emissions” and that this is “costing thousands of dollars for every ton of CO2 removed.” And as a way to capture massive volumes of CO2 (from industrial emission streams of out the air) and sequestering it to forestall atmospheric warming (climate change), the prospects are not good. Perhaps this is why the article’s author characterizes CCS as a “figleaf” for the fossil fuel industry (and now, apparently, the Carney government) to pretend they are reducing GHG emissions.
Prime Minister Carney should sharpen his thinking on CCS. While real and profitable when used in oil and gas production, it’s unlikely to be useful in combatting climate change. Best to avoid yet another costly climate change “solution” that is overpromised, overpriced and has historically underperformed.
Alberta
World’s first direct air capture test centre to open doors in Innisfail

From the Canadian Energy Centre
Deep Sky Alpha facility will trial technologies that suck CO2 from the sky
Innisfail, Alta. is set to host the world’s first test centre for technology that removes carbon dioxide directly from the air to fight climate change.
This June, Montreal-based Deep Sky completed construction of a $110-million carbon removal innovation and commercialization centre in the town about 120 kilometres north of Calgary.
It is a key piece of the company’s vision to build 100 large-scale facilities across Canada and become a pioneer in the emerging market for direct air capture (DAC) technology.
“As of this summer, we will begin not only carbon removal, which is actually sucking it out of the air through these very powerful fans, but also liquefying it and then putting it underground for storage,” Deep Sky CEO Alex Petre told CTV News.
Work began in August 2024 on the project known as Deep Sky Alpha, which aims to begin testing up to 10 different DAC technologies in real-world conditions. It is expected to be up and running this August.
The Government of Alberta is investing $5 million in the facility through Emissions Reduction Alberta.
Deep Sky’s facility will capture up to 3,000 tons of CO2 per year over the next 10 years, with room for future expansion.
Captured CO2 will be transported by tanker trucks about 200 kilometres north to Sturgeon County where it will be injected more than two kilometres below the surface into the Meadowbrook Carbon Storage Hub.
Operated by Bison Low Carbon Ventures, the project is the first approved under Alberta’s open-access carbon sequestration hub initiative and is expected to begin operations before year-end.
“We’re going to line up these eight units side by side and run them to see how they operate in the summer and in the cold of winter,” said Damien Steel, former Deep Sky CEO who continues to serve as a company advisor.
“We’ll be tracking everything to see how all these best-in-class technologies compare – what are their strengths and weaknesses – so that ultimately we can choose the best solutions to scale up for the major commercialization of carbon removal projects that are needed.”
Unlike typical carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects that scrub CO2 from the exhaust of heavy industrial facilities such as power plants, refineries, cement plants or steel mills, DAC utilizes different technology to remove much lower concentrations of CO2 directly from the atmosphere.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), there are 27 DAC plants operating worldwide, capturing almost 10,000 tonnes of CO2 per year. In order to reach net zero emissions by 2050, the IEA estimates DAC capacity must expand to more than 60 million tonnes per year by 2030.
Deep Sky selected Alberta for its test facility because of the province’s experience with CCS, including its advanced regulatory system for CO2 sequestration.
“To be successful at carbon removal you need three things: you need access to geologic storage, you need talent, and you need a reliable supply of renewable power to operate DAC facilities. Canada is blessed with these things, and Alberta especially has all of these attributes in spades,” Steel said.
Deep Sky Alpha is one of several clean tech projects underway in a five-acre industrial park in Innisfail as part of an economic diversification plan that was launched in 2022 to make the town a centre for energy innovation.
A municipal solar farm and a power plant that burns garbage and will be equipped with CCS to eliminate emissions are also under development.
Deep Sky says that more than 110 jobs were created during the construction phase of its Innisfail project and it will employ 15 people for annual operations.
Subsequent commercial plants it hopes to build across Canada will employ approximately 1,000 workers for construction and 150 for annual operations.
Steel said he expects the DAC test facility will become a destination for those looking to advance CCS projects around the world, showcasing Canadian expertise in the process.
“My hope is that not only will we learn and improve carbon removal technology, but we will also put Canada on the map in terms of being a place where innovation can thrive and this industry can work,” he said.
“It will be a place where corporate leaders, government officials and customers from around the world can come and see what direct air capture really is, how it works, and how Canada is the place to do it.”
-

 Education1 day ago
Education1 day agoWhy more parents are turning to Christian schools
-
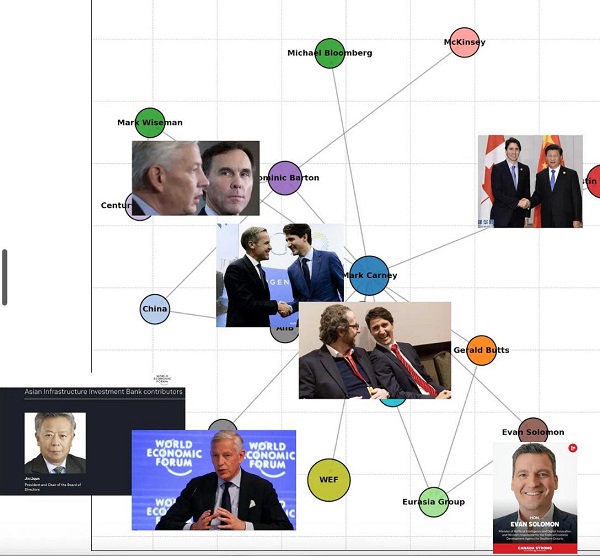
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoDemocracy Watchdog Says PM Carney’s “Ethics Screen” Actually “Hides His Participation” In Conflicted Investments
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoUpgrades at Port of Churchill spark ambitions for nation-building Arctic exports
-
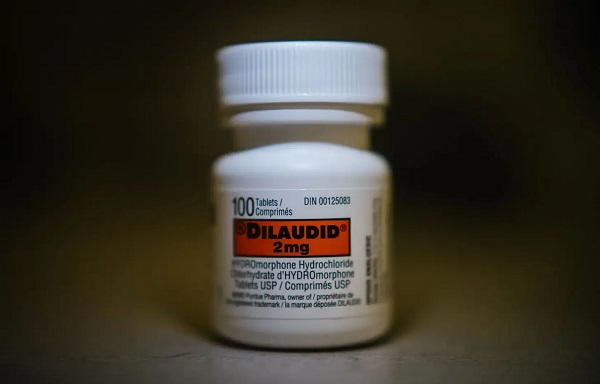
 Addictions2 days ago
Addictions2 days agoAfter eight years, Canada still lacks long-term data on safer supply
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoOPEC+ is playing a dangerous game with oil
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoIs dirty Chinese money undermining Canada’s Arctic?
-

 National2 days ago
National2 days agoLiberals push to lower voting age to 16 in federal elections
-
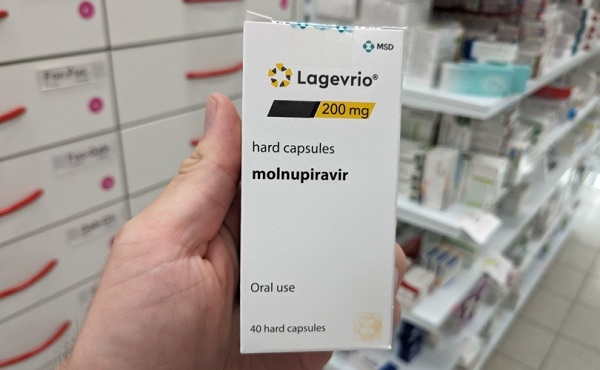
 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoJapan disposes $1.6 billion worth of COVID drugs nobody used






