Alberta
The Canadian Northern Railway’s legacy at Big Valley, Alberta.

By Shawn I. Smith, Canadian Northern Society

“The newly constructed train station circa 1913, Big Valley. Photo- Canadian Northern Society Archives

“Visitors explore the Big Valley Roundhouse Ruins” Photo- Canadian Northern Society Archives
While not obvious to the guests who have enjoyed the 21-mile excursion train ride from Stettler aboard the Alberta Prairie Railway, the scene that unfolds on summer days in Big Valley is part of a legacy left by two dynamic railroaders who over a century earlier had an ambitious and grand vision for Western Canada. Today, both active and abandoned rail lines in central Alberta, related historic structures and sites, and indeed the communities that owe their existence to the Canadian Northern Railway (CNoR) share this common heritage.
Energy, Enterprise, and Ability

“The Canadian Northern Railway lines map, 1916” Map- Atlas of Alberta Railways

“Bustling Big Valley railroad yard, roundhouse, 1920’s” Photo- Canadian Northern Society Archives

“Train time at Big Valley. A Southbound train at Big Valley, 1920’s.” Photo- Canadian Northern Society Archives
The National

“The end of daily passenger train service between Edmonton – Drumheller. VIA Rail’s Dayliner at Big Valley, 1981” Photo-Charles Bohi

Alberta
World’s first direct air capture test centre to open doors in Innisfail

From the Canadian Energy Centre
Deep Sky Alpha facility will trial technologies that suck CO2 from the sky
Innisfail, Alta. is set to host the world’s first test centre for technology that removes carbon dioxide directly from the air to fight climate change.
This June, Montreal-based Deep Sky completed construction of a $110-million carbon removal innovation and commercialization centre in the town about 120 kilometres north of Calgary.
It is a key piece of the company’s vision to build 100 large-scale facilities across Canada and become a pioneer in the emerging market for direct air capture (DAC) technology.
“As of this summer, we will begin not only carbon removal, which is actually sucking it out of the air through these very powerful fans, but also liquefying it and then putting it underground for storage,” Deep Sky CEO Alex Petre told CTV News.
Work began in August 2024 on the project known as Deep Sky Alpha, which aims to begin testing up to 10 different DAC technologies in real-world conditions. It is expected to be up and running this August.
The Government of Alberta is investing $5 million in the facility through Emissions Reduction Alberta.
Deep Sky’s facility will capture up to 3,000 tons of CO2 per year over the next 10 years, with room for future expansion.
Captured CO2 will be transported by tanker trucks about 200 kilometres north to Sturgeon County where it will be injected more than two kilometres below the surface into the Meadowbrook Carbon Storage Hub.
Operated by Bison Low Carbon Ventures, the project is the first approved under Alberta’s open-access carbon sequestration hub initiative and is expected to begin operations before year-end.
“We’re going to line up these eight units side by side and run them to see how they operate in the summer and in the cold of winter,” said Damien Steel, former Deep Sky CEO who continues to serve as a company advisor.
“We’ll be tracking everything to see how all these best-in-class technologies compare – what are their strengths and weaknesses – so that ultimately we can choose the best solutions to scale up for the major commercialization of carbon removal projects that are needed.”
Unlike typical carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects that scrub CO2 from the exhaust of heavy industrial facilities such as power plants, refineries, cement plants or steel mills, DAC utilizes different technology to remove much lower concentrations of CO2 directly from the atmosphere.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), there are 27 DAC plants operating worldwide, capturing almost 10,000 tonnes of CO2 per year. In order to reach net zero emissions by 2050, the IEA estimates DAC capacity must expand to more than 60 million tonnes per year by 2030.
Deep Sky selected Alberta for its test facility because of the province’s experience with CCS, including its advanced regulatory system for CO2 sequestration.
“To be successful at carbon removal you need three things: you need access to geologic storage, you need talent, and you need a reliable supply of renewable power to operate DAC facilities. Canada is blessed with these things, and Alberta especially has all of these attributes in spades,” Steel said.
Deep Sky Alpha is one of several clean tech projects underway in a five-acre industrial park in Innisfail as part of an economic diversification plan that was launched in 2022 to make the town a centre for energy innovation.
A municipal solar farm and a power plant that burns garbage and will be equipped with CCS to eliminate emissions are also under development.
Deep Sky says that more than 110 jobs were created during the construction phase of its Innisfail project and it will employ 15 people for annual operations.
Subsequent commercial plants it hopes to build across Canada will employ approximately 1,000 workers for construction and 150 for annual operations.
Steel said he expects the DAC test facility will become a destination for those looking to advance CCS projects around the world, showcasing Canadian expertise in the process.
“My hope is that not only will we learn and improve carbon removal technology, but we will also put Canada on the map in terms of being a place where innovation can thrive and this industry can work,” he said.
“It will be a place where corporate leaders, government officials and customers from around the world can come and see what direct air capture really is, how it works, and how Canada is the place to do it.”
Alberta
Alberta’s savings trust fund jumps by $2.8 billion, hitting a record high of $30 billion.

Alberta’s Heritage Fund reaches new heights
Alberta is growing the Heritage Fund for what matters most – saving for the future to ensure a strong health care system, quality education and the lowest tax environment in Canada. By investing in the Heritage Fund, by 2050 Alberta will be on the path to energize its economy, create new opportunities and fund projects that make life better for all Albertans.
This $2.8-billion contribution marks a new record for the fund and keeps the province on track to reach its goal of $250 billion by 2050. The goal is to grow the fund to the point where, after 2050, Alberta would be able to withdraw some of the income the fund earns each year while still allowing it to grow over time. Those withdrawals could help cover fluctuations in resource revenue, invest in important infrastructure and keep taxes low.
“Alberta is turning resource strength into lasting financial security. By growing the Heritage Fund, we’re strengthening core services like health care and education, while preserving the low-tax Alberta advantage. This $2.8-billion boost to the Heritage Fund is a bold step that sets the province on the path to success and puts Albertans first.”
“This investment is a key step in securing a prosperous future with stable revenues and competitive taxes for Albertans today and tomorrow.”
Alberta’s government recently launched their plan, Renewing the Alberta Heritage Savings Trust Fund: A Roadmap to Securing Alberta’s Future. This plan outlines how Alberta will grow the Heritage Fund to $250 billion by 2050 through strategic investments, global partnerships and strong governance, securing long-term economic growth and stability. These strategic investments will eventually fund the public services and infrastructure vital to supporting the growing province.
Central to the plan is the leadership of the Heritage Fund Opportunities Corporation. The updated corporation will modernize the fund’s management and help Alberta access global investment opportunities to create meaningful wealth and future prosperity. Led by board chair Joe Lougheed, the corporation will strengthen the governance of Heritage Fund assets and support investment decisions independent from government.
“Our role is to ensure the Heritage Fund is managed with the highest standards of governance and independence. By embracing global opportunities and modernizing oversight, we’re safeguarding Alberta’s wealth to deliver steady, long-term prosperity for Alberta’s future generations.”
This historic boost to Alberta’s Heritage Fund isn’t just about the numbers – it’s about building a future where families thrive, communities grow and Alberta stays strong no matter what comes next.
Quick facts:
- Alberta’s government invested $2.8 billion from the 2024-25 surplus cash in the Heritage Fund, growing the fund to $30 billion from $27.2 billion in 2024-25.
- This is up from $22.9 billion in 2023-24, the previous fiscal year.
- Alberta’s goal is to grow the fund to $250 billion by 2050.
- Once $250 billion is reached, interest from the fund will help stabilize resource revenue, invest in infrastructure and keep taxes low.
- Since 2019-20, the Heritage Fund has grown more than 84 per cent:
- from $16.3 billion to $30 billion.
- Since 2022-23, the Heritage Fund has grown more than 41.5 per cent:
- from $21.2 billion to $30 billion.
- The board of the Heritage Fund Opportunities Corporation brings together the skills and expertise of Alberta and international leaders in investment management to set Alberta up for long-term success. The current members are:
- Joe Lougheed, board chair, Alberta
- Kate White, director, Alberta
- Jacqueline Curzon, director, Switzerland
- Jouko Karvinen, director, Finland
- Chana Martineau, director, Alberta
- Mary Ritchie, director, Alberta
Related information
-

 Education1 day ago
Education1 day agoWhy more parents are turning to Christian schools
-
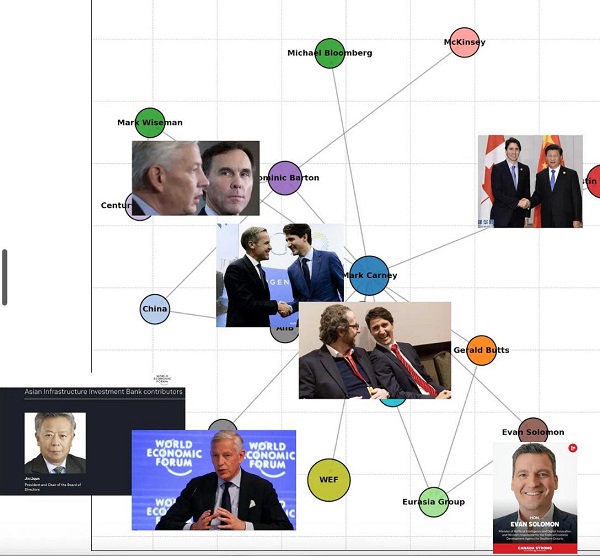
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoDemocracy Watchdog Says PM Carney’s “Ethics Screen” Actually “Hides His Participation” In Conflicted Investments
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoUpgrades at Port of Churchill spark ambitions for nation-building Arctic exports
-
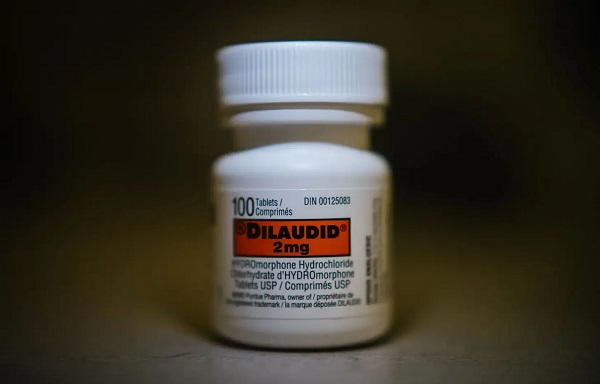
 Addictions2 days ago
Addictions2 days agoAfter eight years, Canada still lacks long-term data on safer supply
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoOPEC+ is playing a dangerous game with oil
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoIs dirty Chinese money undermining Canada’s Arctic?
-

 National2 days ago
National2 days agoLiberals push to lower voting age to 16 in federal elections
-
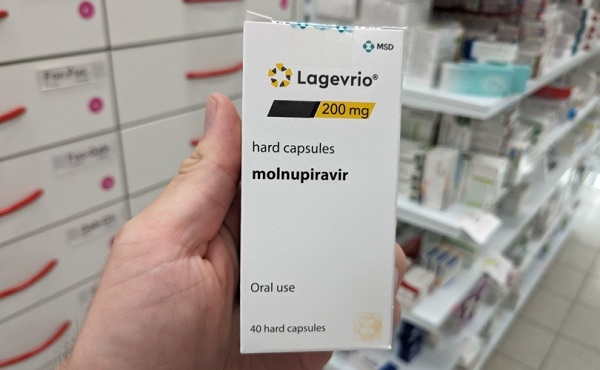
 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoJapan disposes $1.6 billion worth of COVID drugs nobody used






