International
Taiwan Criticizes CBC Correction on United Front Buddhist Land Story, Citing PRC Political Pressure
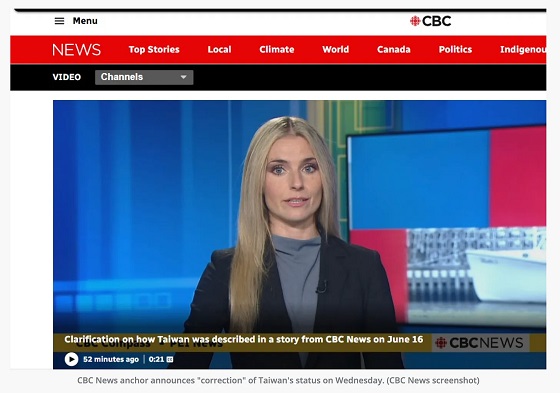
Taiwan’s Foreign Ministry warns that CBC’s editorial change “undermines the essence of press freedom” and reflects growing Chinese pressure on international media.
Canada’s state broadcaster, CBC, is facing diplomatic criticism from Taiwan after issuing a controversial correction to an explosive story regarding Chinese influence via foreign investment in Prince Edward Island—raising new questions about whether Chinese government pressure is compromising Canadian press freedom and influencing media coverage of foreign interference.
On June 14, CBC/Radio-Canada published a report on alleged ties between Bliss and Wisdom, a Buddhist group with growing land holdings on Prince Edward Island, and the Chinese Communist Party’s United Front Work Department. The report—based in part on findings from The Bureau’s contributor Garry Clement—noted deep concerns from PEI residents about the group’s agricultural land acquisitions and its alleged links to Beijing, including its reported advocacy for China’s annexation of Taiwan.
It highlighted a high-ranking monk from Taiwan who traveled “between his home country, Prince Edward Island, and China” in 2023 for ideological outreach, at the invitation of a Buddhist organization affiliated with the United Front Work Department—the Chinese Communist Party’s covert foreign interference arm.
But on June 17, CBC issued a correction: “In that story, the reporter said Taiwan is a country that China is threatening to invade. In fact, Taiwan is a self-governing island, and there is dispute around who controls it.” No explanation was provided for the change.
That revision quickly sparked backlash in Taipei. In a statement to Taiwan News, Taiwan’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MOFA) said it was “regretful and disappointed” to see international media “engage in self-censorship or deliberately avoid using the term ‘country’ to refer to Taiwan due to political pressure from China or concerns about Beijing’s stance.” MOFA reportedly reiterated that Taiwan “is a sovereign and independent country, and is not subordinate to the People’s Republic of China,” and urged foreign media to uphold “objectivity and fairness,” warning that compromise on coverage “undermines the essence of press freedom” and distorts Taiwan’s international status.
CBC did not respond to a request for comment from Taiwan News.
CBC is funded by the federal government and mandated by the Broadcasting Act to serve the public interest with independence, journalistic integrity, and balanced coverage. Taiwan’s concerns, delivered through its Ministry of Foreign Affairs, suggest a de facto state-to-state issue.
The CBC correction was also flagged Thursday by Canadian diaspora advocacy group Friends of Hong Kong, which has documented suspected United Front influence in Canada, including media pressure campaigns. “So disappointing for Canadian media: this is a politically-charged correction, due to either self-censorship or external intervention, and wilfully blind to the reality of #Taiwan the island state,” the group posted to X, calling attention to CBC’s correction notice.
The controversial CBC report was informed by a parallel investigation led by Garry Clement—a former RCMP proceeds-of-crime director—along with former CSIS Asia-Pacific chief Michel Juneau-Katsuya and publisher Dean Baxendale. The three co-authors of the forthcoming book Canada Under Siege spent the past year examining Bliss and Wisdom’s land acquisitions, foreign financial inflows, and political influence on Prince Edward Island. In his column for The Bureau, Clement warned that the RCMP’s refusal to investigate the group reflects “a chilling portrait of political complacency” and asserted that Canadian democracy is being degraded not by coups or force, but by “the quiet neglect of responsibility.”
CBC has not acknowledged external pressure behind the correction, but The Bureau has previously documented similar interference. In November 2024, China’s Consul General Yang Shu directly pressured Vancouver Mayor Ken Sim after he invited Taiwan’s representative to a civic luncheon, stating: “This was inappropriate… The Consulate General of the People’s Republic of China is the only consular mission representing China in Vancouver.” The PRC expressed dissatisfaction with the participation of Taiwan’s envoy in the B.C. Consular Corps luncheon—despite established diplomatic practice allowing their attendance.
Given this backdrop, it is plausible—though not confirmed—that CBC received similar behind-the-scenes pressure following its original PEI report.
That concern finds further grounding in evidence tabled before Canada’s Hogue Commission and leaked intelligence reviewed by The Bureau.
A leaked October 2022 CSIS report analyzed by The Bureau found that China’s election interference and political influence in Canada have been enabled by Beijing’s covert “takeover” of Chinese-language media, along with sophisticated, massively funded schemes targeting mainstream outlets and seeking to control “key media entities,” according to intelligence documents.
These clandestine operations have involved threats against journalists, the documents state, as well as inducements—such as benefits offered by Vancouver’s Chinese Consulate to cultivate “key editors, producers, and high-ranking managers.”
Among the declassified top-secret records presented to the Hogue Commission by diaspora-group participant Gabriel Yiu is a July 2023 Canadian intelligence report titled “CHINA: Domination of Chinese-Language Media in Canada Poses National Security Threats.” The document details systemic Chinese Communist Party influence over Chinese-language media outlets in Canada.
“Communist Party of China (CPC)-friendly narratives inundate Chinese-language media in Canada,” it says. “Censorship (including self-censorship) is pervasive, and alternative voices are few or marginalized in mainstream Chinese-language media. This includes both traditional media, such as newspapers, and digital platforms like WeChat.”
In a column for The Bureau, Yiu wrote, “I believe the Canadian intelligence agency’s assessment is accurate. From my own experience as a commentator since the 1990s, I have observed these shifts.” He also underscored key excerpts from the CSIS report:
- “The CPC’s strategy to control media operates on two fronts: narrative control and platform control. [redacted] overt and clandestine.”
- “The CPC limits opportunities for dissenting voices [redacted], provides economic incentives [redacted], and fosters self-censorship [redacted].”
- “The CPC’s influence on Chinese-language media, shaping public opinion overseas, also supports other activities, including transnational repression and influencing electoral outcomes.”
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
conflict
Despite shaky start, ceasefire shows signs of holding

Chief of the General Staff LTG Eyal Zamir during a situational assessment following the beginning of the ceasefire with Iran
Quick Hit:
A fragile ceasefire between Israel and Iran appeared to hold Tuesday after early strikes from both sides threatened to unravel it. President Trump, who brokered the deal, criticized the violations and pushed both nations to stand down.
Key Details:
- Trump declared a “complete and total ceasefire” late Monday after Iran fired missiles at a U.S. base in Qatar in response to American strikes on its nuclear sites.
- Hours after the ceasefire was set to begin, Israel accused Iran of violating it by firing missiles into its territory—claims Tehran denied, even as explosions and air raid sirens rocked northern Israel.
- Trump publicly criticized both nations, stating “they don’t know what the f*** they’re doing,” and later confirmed that Israeli warplanes would turn back instead of launching a broader retaliation.
Diving Deeper:
Calm returned to parts of the Middle East Tuesday as a U.S.-brokered ceasefire between Israel and Iran began to settle in—though not without incident. For nearly two weeks, the region was on the brink of a broader war, ignited by Israeli strikes on Iranian nuclear and military targets and exacerbated by retaliatory attacks from Tehran.
President Donald Trump took credit for halting the hostilities. “ISRAEL is not going to attack Iran,” he wrote on Truth Social. “All planes will turn around and head home, while doing a friendly ‘Plane Wave’ to Iran. Nobody will be hurt, the Ceasefire is in effect!”
Despite the ceasefire’s official start early Tuesday morning, it nearly unraveled within hours. Israeli officials said Iran launched at least two missiles after the truce deadline, though they were intercepted before impact. Iran, meanwhile, denied any post-deadline strikes and blamed Israel for earlier attacks.
Speaking before leaving for a NATO summit, Trump said both sides had violated the agreement and did not hold back his frustration. “We basically have two countries that have been fighting so long and so hard that they don’t know what the f*** they’re doing,” he said, adding that he was “not happy with Israel.”
Still, the agreement held. Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s office said the country stood down from further attacks following a direct conversation with Trump. Israel claimed to have achieved its objectives, including weakening Iran’s nuclear and missile capabilities.
The conflict’s origin traces back to Israeli fears that Iran was nearing the threshold of building nuclear weapons, despite Tehran’s insistence that its program is for peaceful energy purposes. Over the weekend, the U.S. deepened its involvement by launching bunker-buster bombs on Iranian nuclear sites. Iran responded with a limited strike on a U.S. base in Qatar—an attack Washington said came with advance warning and caused no casualties.
Meanwhile, fallout from the war continues to spread. Israeli officials said at least 28 of their citizens have been killed and over 1,000 injured. Iranian casualty estimates are far higher, with nearly 1,000 reported dead, including hundreds of civilians and military personnel, according to the Human Rights Activists group.
Even as the ceasefire sets in, the risk of broader conflict remains. Pro-Iran militias in Iraq reportedly launched drone attacks on U.S. bases overnight, though they were intercepted without casualties. The U.S. has begun evacuating American citizens from Israel, and China—one of Iran’s few remaining oil buyers—has condemned the U.S. strikes, warning of a dangerous cycle of escalation.
Trump said he is not seeking regime change in Iran, walking back prior comments. “Regime change takes chaos and, ideally, we don’t want to see much chaos,” he told reporters aboard Air Force One.
Still, the situation remains volatile. The ceasefire, while welcomed, remains fragile—held together largely by Trump’s pressure campaign and the willingness of both sides to pause, if only momentarily, from what could have spiraled into an uncontrollable regional war.
Bjorn Lomborg
The Physics Behind The Spanish Blackout

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
Madrid knew solar and wind power were unreliable but pressed ahead anyway
When a grid failure plunged 55 million people in Spain and Portugal into darkness at the end of April, it should have been a wake-up call on green energy. Climate activists promised that solar and wind power were the future of cheap, dependable electricity. The massive half-day blackout shows otherwise. The nature of solar and wind generation makes grids that rely on them more prone to collapse—an issue that’s particularly expensive to ameliorate.
As I wrote in these pages in January, the data have long shown that environmentalists’ vision of cheap, reliable solar and wind energy was a mirage. The International Energy Agency’s latest cost data continue to underscore this: Consumers and businesses in countries with almost no solar and wind on average paid 11 U.S. cents for a kilowatt hour of electricity in 2023, but costs rise by more than 4 cents for every 10% increase in the portion of a nation’s power generation that’s covered by solar and wind. Green countries such as Germany pay 34 cents, more than 2.5 times the average U.S. rate and nearly four times China’s.
Prices are high in no small part because solar and wind require a duplicate backup energy system, often fossil-fuel driven, for when the sun doesn’t shine or the wind doesn’t blow. The Iberian blackout shows that the reliability issues and costs of solar and wind are worse than even this sort of data indicates.
Grids need to stay on a very stable frequency—generally 50 Hertz in Europe—or else you get blackouts. Fossil-fuel, hydro and nuclear generation all solve this problem naturally because they generate energy by powering massive spinning turbines. The inertia of these heavy rotating masses resists changes in speed and hence frequency, so that when sudden demand swings would otherwise drop or hike grid frequency, the turbines work as immense buffers. But wind and solar don’t power such heavy turbines to generate energy. It’s possible to make up for this with cutting-edge technology such as advanced inverters or synthetic inertia. But many solar and wind farms haven’t undergone these expensive upgrades. If a grid dominated by those two power sources gets off frequency, a blackout is more likely than in a system that relies on other energy sources.
Spain has been forcing its grid to rely more on unstable renewables. The country has pursued an aggressive green policy, including a commitment it adopted in 2021 to achieve “net zero” emissions by 2050. The share of solar and wind as a source of Spain’s electricity production went from less than 23% in 2015 to more than 43% last year. The government wants its total share of renewables to hit 81% in the next five years—even as it’s phasing out nuclear generation.
Just a week prior to the blackout, Spain bragged that for the first time, renewables delivered 100% of its electricity, though only for a period of minutes around 11:15 a.m. When it collapsed, the Iberian grid was powered by 74% renewable energy, with 55% coming from solar. It went down under the bright noon sun. When the Iberian grid frequency started faltering on April 28, the grid’s high proportion of solar and wind generation couldn’t stabilize it. This isn’t speculation; it’s physics. As the electricity supply across Spain collapsed, Portugal was pulled along, because the two countries are tightly interconnected through the Iberian electricity network.
Madrid had been warned. The parent company of Spain’s grid operator admitted in February: “The high penetration of renewable generation without the necessary technical capabilities in place to keep them operating properly in the event of a disturbance . . . can cause power generation outages, which could be severe.”
Yet the Spanish government is still in denial. Even while admitting that he didn’t know the April blackout’s cause, Prime Minister Pedro Sánchez insisted that there was “no empirical evidence” that renewables were to blame and that Spain is “not going to deviate a single millimeter” from its green energy ambitions.
Unless the country—and its neighbors—are comfortable with an increased risk of blackouts, this will require expensive upgrades. A new Reuters report written with an eye to the Iberian blackout finds that for Europe as a whole this would cost trillions of dollars in infrastructure updates. It’s possible that European politicians can talk voters into eating that cost. It’ll be impossible for India or nations in Africa to follow suit.
That may be unwelcome news to Mr. Sánchez, but even a prime minister can’t overcome physics. Spain’s commitment to solar and wind is forcing the country onto an unreliable, costly, more black-out-prone system. A common-sense approach would hold off on a sprint for carbon reductions and instead put money toward research into actually reliable, affordable green energy.
Unfortunately for Spain and those countries unlucky enough to be nearby, the Spanish energy system—as one Spanish politician put it—“is being managed with an enormous ideological bias.”
Bjorn Lomborg is president of the Copenhagen Consensus, a visiting fellow at Stanford University’s Hoover Institution and author of “Best Things First.”
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin2 days ago
Bruce Dowbiggin2 days agoWhat Connor Should Say To Oilers: It’s Not You. It’s Me.
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoFederal fiscal anchor gives appearance of prudence, fails to back it up
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoThe U.S. Strike in Iran-Insecurity About Global Oil Supply Suddenly Makes Canadian Oil Attractive
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlberta poll shows strong resistance to pornographic material in school libraries
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoTrump reins in oil markets with one Truth Social post
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoThe Passage of Bill C-5 Leaves the Conventional Energy Sector With as Many Questions as Answers
-

 Banks2 days ago
Banks2 days agoScrapping net-zero commitments step in right direction for Canadian Pension Plan
-

 conflict1 day ago
conflict1 day agoWar over after 12 days? Ceasefire reached between Israel, Iran