conflict
Putin Threatens Nuclear War As West Wades Even Deeper Into Russia-Ukraine Conflict

From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By Jake Smith
Russian President Vladimir Putin on Wednesday lowered the threshold for the use of nuclear weapons against the West, marking yet another escalation in an already drawn-out war that has cost hundreds of thousands of lives and shown no signs of ending.
Putin announced during a meeting with the Russian Security Council on Wednesday that the country’s nuclear doctrine was being expanded to include the possible use of such weapons against other nations with nuclear capabilities, should they support a non-nuclear state — such as Ukraine — in a heavy missile attack against Russia. The warning comes amid President Joe Biden’s announcement on Thursday of an additional $8 billion in military aid to Ukraine and reports that Western nations are considering allowing Kyiv to use their long-range weapons to strike deep inside Russian territory.
Ben Friedman, policy director at Defense Priorities, told the Daily Caller News Foundation that Putin is likely “bluffing,” but it is not worth the risk for the U.S. to allow Ukraine to make such a move.
“I think the odds of Russia using a nuclear weapon in response to one of these hypothetical strikes are pretty low. But how much do you want to gamble on that? How much do you want to bet that Putin is bluffing? I’d say not very much,” Friedman told the DCNF. “You want to be very cautious. The U.S. has no security interest in taking those sorts of risks in a conflict that could escalate to a larger war, even a nuclear exchange in a worst-case scenario.”
Putin said during the security meeting that the nuclear doctrine was being updated because of an “emergence of new sources of military threats and risks for Russia and our allies,” according to multiple reports.
“The updated version of the document proposes that aggression against Russia by any non-nuclear-weapon state, but with the participation or support of a nuclear-weapon state, should be considered as a joint attack on the Russian Federation,” Putin told the council on Wednesday, noting that the conditions to launch nuclear weapons would be based on “reliable information about a massive launch of aerospace attack means and their crossing of our state border,” according to the Post.
“We reserve the right to use nuclear weapons in the event of aggression against Russia and Belarus,” Putin said.
Officials from the White House and State Department told the DCNF they were “not surprised” By Putin’s warning.
“Russia has been signaling its intent to update its nuclear doctrine for several weeks,” a State Department spokesperson told the DCNF. “However, Putin’s public comments highlight Russia’s attempts to use irresponsible nuclear rhetoric and employ coercive nuclear signaling as it has done against Ukraine for more than two years.”
Moscow’s threat of using nuclear weapons has been frequently raised as the U.S. and Europe continue to throw their support behind Ukraine’s defense against Russia’s invasion, which began in 2022 and has shown no signs of stopping. Putin has issued such warnings specifically over the West’s indirect involvement in the war, which has largely come in the form of military aid to Ukraine.
The U.S. alone has allocated over $55 billion worth of military assistance to Ukraine since 2022, while European partners have committed roughly $46 billion in the same time frame.
But certain rules and regulations have been imposed on the military aid to Ukraine, particularly around how weapons can be used to strike Russia. For much of the war, Western nations restricted Ukraine from using the weapons to strike inside Russia, although that ban was recently lifted to allow Ukrainian forces to launch attacks against Russia’s border region.
Ukraine wants the West to make further allowances on weapons use, however. Kyiv argues that it should be allowed to use U.S. and European-provided long-range missiles to hit targets deep inside of Russian territory, a move which the U.S. has been wary of due to escalatory risks with Moscow.
But now a number of nations are signaling that they will allow Ukraine to use long-range systems to strike Russia, including Britain and France, though they want the U.S. to give the green light first — and some European partners have become frustrated with the delay for approval.
“It would be really good to stop the delays. And I think that the restrictions on the use of weapons should be lifted,” Denmark Prime Minister Mette Frederiksen told Bloomberg on Monday.
Though the U.S. and West have bolstered Ukraine’s military efforts over the last two years through extensive funding measures, it has done little to change the course of the conflict. Ukraine is suffering from a worsening manpower shortage as its troops are killed in combat along the Eastern line of the war, and has been forced to retreat from regions along that front as Russian forces advance.
Russia has made small territorial gains along the Eastern front, but it has come at the cost of hundreds of thousands of soldiers’ lives and hundreds of billions of dollars in spending. Some Russian forces are currently staging a counterattack against Ukrainian forces that broke through Russia’s border in August and staged an incursion in Kursk, according to Reuters.
Over one million Russians and Ukrainians have thus far been killed or injured since the war began in 2022, according to a confidential Ukrainian estimate reviewed by The Wall Street Journal.
The Biden administration, with only months left in power, is starting to run out of options to help Ukraine and may turn to allowing Kyiv to use long-range weapons as a possible measure, so long as they are provided by Europe and not the U.S. President Joe Biden and his team have faced criticisms for seemingly failing to work an endgame strategy in the war or outline the road to a peace deal.
“Biden could certainly change direction,” Friedman told the DCNF, by potentially either supporting an even stronger Ukrainian defense operation or putting pressure on Kyiv and Moscow to negotiate a peace deal. “But I don’t think he will, just because of the way this White House seems very set in their approach.”
conflict
US airstrike on Iran’s nuclear facilities. Was it obliteration?

A satellite image of the Isfahan nuclear research center in Iran shows visible damage to structures and nearby tunnel entrances from recent US airstrikes. / Satellite image (c) 2025 Maxar Technologies.
 Seymour Hersh
Seymour Hersh
The US attack on Iran may not have wiped out its nuclear ambitions but it did set them back years
I started my career in journalism during the early 1960s as a reporter for the City News Bureau of Chicago, a now long-gone local news agency that was set up by the Chicago newspapers in the 1890s to cover the police and fire departments, City Hall, the courts, the morgue, and so on. It was a training ground, and the essential message for its aspiring reporters was: “If your mother says she loves you, check it out.”
It was a message I wish our cable networks would take to heart. CNN and MSNBC, basing their reporting on an alleged Defense Intelligence Agency analysis, have consistently reported that the Air Force raids in Iran on June 22 did not accomplish their primary goal: total destruction of Iran’s nuclear-weapons capacity. US newspapers also joined in, but it was the two nominally liberal cable channels, with their dislike—make that contempt—for President Donald Trump, that drove the early coverage.
There was no DIA analysis per se. All US units that engage in combat must file an “after-action report” to the DIA after a military engagement. In this case, the report would have come from the US Central Command, located at MacDill Air Force base in Tampa, Florida. CENTCOM is responsible for all US military operations in the Middle East, Egypt, Central Asia, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. One US official involved in the process told me that “the first thing out of the box is you have to tell your boss what happened.” It was that initial report of the bombing attack that was forwarded to DIA headquarters along the Potomac River in Washington and copied or summarized by someone not authorized to do so and sent to the various media outlets.
The view of many who were involved in the planning and execution of the mission is that the report was summarized and leaked “for political purposes”—to cast immediate doubt on the success of the mission. The early reports went so far as to suggest that Iran’s nuclear program has survived incapacitation by the attack. Seven US B-2 “Spirit” bombers, each carrying two deep-penetration “bunker-busters” weighing 30,000 pounds, had flown without challenge from their base in Missouri to the primary target: Iran’s Fordo nuclear facility, concealed deep inside a mountain twenty miles north of the city of Qom.
The planning for the attack began with the knowledge that the main target—the working area of the nuclear program—was buried at least 260 feet below the rocky surface at Fordo. The gas centrifuges spinning there were repeatedly enriching uranium, in what is known as a cascade, not to weapons-grade level—uranium-235 isotopes enriched to 90 percent—but to 60 percent. Further processing to create weapons grade uranium, if Iran chose to do so, could be done in a matter of weeks, or less. The Air Force planning group had also been informed before the bombing raid, most likely by the Israelis, who have a vast spy network in Iran, that more than 450 pounds of the enriched gas stored at Fordo had been shipped to safety at another vital Iranian nuclear site at Isfahan, 215 miles south of Tehran. Isfahan was the only known facility in Iran capable of converting the Fordo gas into a highly enriched metal—a critical early stage of building the bomb. Isfahan also was a separate target of the US attack on Fordo, and was pulverized by Tomahawk missiles fired by a U.S. submarine operating in the Gulf of Aden, off Yemen.
As a journalist who for decades has covered the nascent nuclear crisis in the Middle East, it seemed clear to me and to informed friends I have in Washington and Israel that if Fordo somehow survived its bunker-buster attack, as was initially suggested, and continued to enrich more uranium, Isfahan would not. No enrichment, no Iranian bomb.
I’ve been frustrated and angry at cable news coverage for years, and that includes Fox News, too, and decided to try and find the real story. If your mother says she loves you, check it out. And I checked out enough of it to share.
I was told that “the first question for the American planners was how big was the actual workspace at Fordo? Was it a structure? We had to find that out before we got rid of it.” Some of the planners estimated that the working space “was the size of two hockey rinks: 200 feet long and 85 feet wide.” It came to 34,000 square feet. The height of the underground working space was assumed to be ten-and-a-half feet—I was not told the genesis of that assumption—and the size of the target was determined to be 357,000 cubic feet.
The next step was to measure the power of the dozen or more bunker-busters that were planned to be “carefully spaced and dropped” by the US B-2 bombers, using the most advanced guidance systems. (During one high-level session in Washington, one of the Air Force planners was asked what would happen if the B-2’s guidance systems were corrupted by an outside signal. “We’d miss the target” was the answer.)
I was assured that even if the rough estimate of the working space at Fordo was far off, the bombers targeting Fordo each carried a 30,000-pound bomb with an explosive payload of as much as five thousand pounds, which was more than enough to pulverize the mythical hockey rinks, or even a much larger working space.
Some of the bombs were also outfitted with what is known as a hard target void sensing fuze, which enabled the bombs to penetrate multiple layers of a site like Fordo before detonating. This would maximize the destructive effect. Each bomb, dropped in sequence, would create a force of rubble that would cause increasing havoc in the working areas deep inside the mountain.
“The bombs made their own hole. We built a 30,000-pound steel bullet,” the official told me, referring with pride to the bunker-busters.
Most important, he said, was that there were no post-strike hints detected of radioactivity—more evidence that the 450 pounds of enriched uranium had been moved from Fordo to the reprocessing site at Isfahan prior to the US attack there, which was code-named “Midnight Hammer.” That operation included a third US strike at yet another nuclear facility at Natanz.
“The Air Force got everything on the hit list,” the official told me. “Even if Iran rebuilds some centrifuges, it will still need Isfahan. There is no conversion capability without it.”
Why not, I asked, tell the public about the success of the raid and the fact that Iran no longer has a potential nuclear weapon?
The answer: “There will be a top-secret report about all of this, but we don’t tell people how hard we work. We tell the public what we think it wants to hear.”
The US official, asked about the future of the Iranian nuclear program, quickly acknowledged that “there is a communication problem” when it comes to the fate of the program.
The intent of the strike planners, he said, “was to prevent the Iranians from building a nuclear weapon in the near term—a year or so—with the hope they would not try again. The clear understanding was that there was no expectation to ‘obliterate’ every aspect of their nuclear program. We don’t even know what that is.
“Obliteration means the glass—[eliminating] Iran’s nuclear program—is full. The planning and the results are the glass is half-full. For Trump critics, the results are the glass is half-empty—the centrifuges may have survived and four hundred pounds of 60 percent enriched uranium are missing. The bombs could not be assured to penetrate the centrifuge chamber . . . too deep, but they could cover them up [with rocks and other bomb debris] and in the process cause unknown damage to them.
“Whether the 60 percent [enriched uranium] was there or not is irrelevant because without centrifuges they cannot refine it to weapons grade. Add to this the research and refinement and conversion from gas to metal—required for a bomb—at Isfahan are also gone.
“Results? Glass is half-full . . . a couple of years of respite and uncertain future. So now Trump’s defense is Full Glass. Critics? Half-empty. Reality? Half-full. There you are.”
The immediate beneficiary of the use of US force in Iran will not be a more placid Middle East, but Israel, and Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. The Israeli Air Force and army are still killing massive numbers of Palestinians in Gaza.
There remains no evidence that Iran was on the cusp of becoming a nuclear power. But as the world has known for decades, Israel maintains a significant nuclear arsenal that it officially claims does not exist.
This is a story not about the bigger picture, which is muddled, but about a successful US mission that was the subject of a lot of sloppy reporting because of a reviled president. It would have been a breakthrough had anyone in the mainstream press spoken or written about the double standard that benefits Israel and its nuclear umbrella, but in America that remains a taboo.
conflict
Obama Dropped Over 26K Bombs Without Congressional Approval
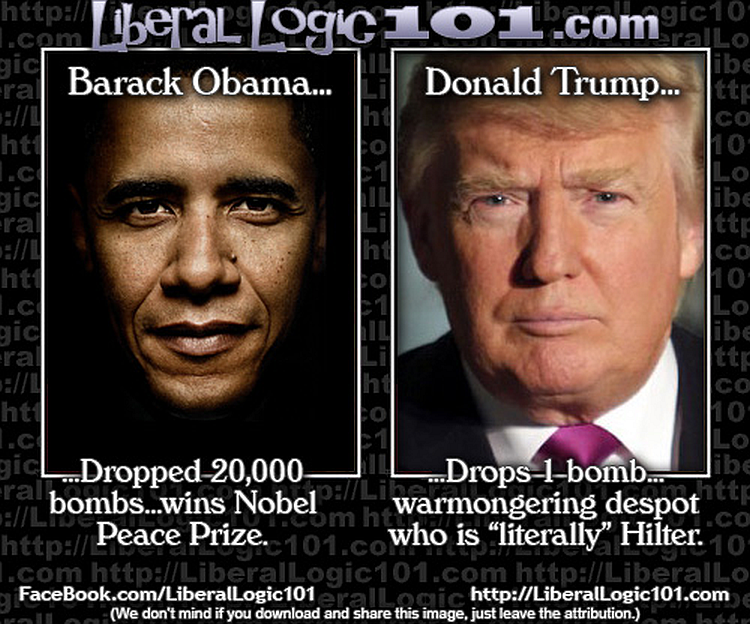
@miss_stacey_ Biden, Clinton, Obama & Harris on Iran #biden #clinton #obama #harris #trump #iran #nuclear
Iran has been the target for decades. Biden, Harris, and Clinton—all the Democrats have said that they would attack Iran if given the opportunity. It appears that Donald Trump is attempting to mitigate a potentially irresolvable situation. As he bluntly told reporters: We basically — we have two countries that have been fighting so long and so hard that they don’t know what the f‑‑‑ they’re doing.”
A portion of the nation believes Trump acted like a dictator by attacking Iran without Congressional approval. I explained how former President Barack Obama decimated the War Powers Resolution Act when he decided Libya was overdue for a regime change. The War Powers Act, or War Powers Resolution of 1973, grants the POTUS the ability to send American troops into battle if Congress receives a 48-hour notice. The stipulation here is that troops cannot remain in battle for over 60 days unless Congress authorizes a declaration of war. Congress could also remove US forces at any time by passing a resolution.
Libya is one of seven nations that Obama bombed without Congressional approval, yet no one remembers him as a wartime president, as the United States was not technically at war. Over 26,000 bombs were deployed across 7 nations under his command in 2016 alone. Libya, Afghanistan, Syria, Yemen, Somalia, Iraq, and Pakistan were attacked without a single vote. Donald Trump’s recent orders saw 36 bombs deployed in Iran.
The majority of those bombings happened in Syria, Libya, and Iraq under the premise of targeting extremist groups like ISIS. Drone strikes were carried out across Somalia, Yemen, and Pakistan as the Obama Administration accused those nations of hosting al-Qaeda affiliated groups. Coincidentally, USAID was also providing funding to those groups.
The 2001 Authorization for Use of Military Force (AUMF) was initially implemented to hunt down the Taliban and al-Qaeda after the 9/11 terrorist attacks. Obama broadened his interpretation of the AUMF and incorporated newly formed militant groups that were allegedly expanding across the entire Middle East. The Bureau of Investigative Journalism believes there were up to 1,100 civilian casualties in Pakistan, Yemen, and Somalia. Thousands of civilians died in Syria and Iraq but the death toll was never calculated. At least 100 innocent people died in the 2016 attacks in Afghanistan alone.
The government will always augment the law for their personal agenda. The War Powers Resolution was ignored and the AUMF was altered. Congress was, however, successful in preventing Obama from putting US troops on the ground and fighting a full-scale war. In 2013, Obama sought congressional approval for military action in Syria but was denied. Obama again attempted to deploy troops in 2015 but was denied. Congress has to redraft the AUMF to specifically prevent Obama from deploying troops in the Middle East. “The authorization… does not authorize the use of the United States Armed Forces on the ground in Syria for the purpose of combat operations.” Obama attempted to redraft the AUMF on his own by insisting he would prohibit “enduring offensive ground combat operations” or long-term deployment of troops. He was met with bipartisan disapproval as both sides believed he was attempting to drag the United States into another unnecessary war.
The United States should not be involved in any of these battles, but here we are. Those living in fear that Donald Trump is a dictator fail to recognize that past leadership had every intention of sending American men and women into battle unilaterally without a single vote cast.
-

 Alberta12 hours ago
Alberta12 hours agoAlberta Independence Seekers Take First Step: Citizen Initiative Application Approved, Notice of Initiative Petition Issued
-

 Crime11 hours ago
Crime11 hours agoNational Health Care Fraud Takedown Results in 324 Defendants Charged in Connection with Over $14.6 Billion in Alleged Fraud
-

 Health10 hours ago
Health10 hours agoRFK Jr. Unloads Disturbing Vaccine Secrets on Tucker—And Surprises Everyone on Trump
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin13 hours ago
Bruce Dowbiggin13 hours agoThe Game That Let Canadians Forgive The Liberals — Again
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoCOVID mandates protester in Canada released on bail after over 2 years in jail
-

 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days agoProject Sleeping Giant: Inside the Chinese Mercantile Machine Linking Beijing’s Underground Banks and the Sinaloa Cartel
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCanada’s loyalty to globalism is bleeding our economy dry
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta uncorks new rules for liquor and cannabis









