COVID-19
Peckford, Bernier take travel restrictions to Supreme Court of Canada

News release from the Justice Centre for Constitutional Freedoms
The Justice Centre announces that the Honourable Brian Peckford, the Honourable Maxime Bernier, and other applicants seek to appeal their vaccine mandate challenge to the Supreme Court of Canada. These Applicants argue that vaccine mandates are an issue of national importance and that Canadians deserve to receive court rulings regarding any emergency orders that violate the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms.
In November 2021, the Government of Canada required all travelers of federally regulated transportation services (e.g., air, rail, and marine) to provide proof of Covid vaccination. These restrictions on the Charter freedom of mobility prevented approximately 5.2 million unvaccinated Canadians from traveling by air and rail.
In response to these restrictions, the Honourable Brian Peckford (last living signatory of the Charter and former Premier of Newfoundland), the Honourable Maxime Bernier (leader of the People’s Party of Canada), and other Canadians took the federal government to court in February 2022, arguing that the Charter freedoms of religion and conscience, assembly, democratic rights, mobility, security, privacy, and equality of Canadians were infringed by these restrictions. In addition, affidavits filed in this court action (e.g., the affidavit of Robert Belobaba at paragraph 19) attest that, in a country as large as Canada, prohibitions on domestic and international air travel have significant, negative impacts on Canadians.
In an affidavit (at paragraph 29), Jennifer Little, Director General of Covid Recovery at Transport Canada, provided her Covid Recovery Team’s October 2, 2021 presentation, entitled Implementing a Vaccine Mandate for the Transportation Sector. The presentation outlined options and considerations for the purposes of seeking the Minister of Transport’s approval of the travel vaccination mandate. Her presentation outlined (at pages 12 and 13) that the Canadian travel restrictions in question were “unique in the world in terms of strict vaccine mandate for domestic travel” and were coupled with “one of the strongest vaccination mandates for travelers in the world.” She admitted during cross examination (at paragraphs 162-163, PDF page 61) that she had never seen a recommendation from Health Canada or the Public Health Agency of Canada to the Ministry of Transport to implement a mandatory vaccination policy for travel.
At the same time, Dr. Lisa Waddell, a senior epidemiologist and the knowledge synthesis team lead at the Public Health Agency of Canada, admitted during a cross examination (at paragraphs 300-305, PDF pages 91-93) that there was no recommendation from the Public Health Agency of Canada to impose vaccination requirements on travelers.
In June 2022, the Government of Canada announced that it would suspend the travel vaccine restrictions, but that it would not hesitate to reinstate the mandates if the government considered it necessary.
As a result, the federal government (the Crown) moved to have Premier Peckford’s constitutional challenge struck for mootness (irrelevance). The Crown argued that the travel restrictions were no longer a live issue because they had been lifted and should not, therefore, take up further court resources. The Crown brought this motion after each side had produced expert evidence, called on experts to testify under oath, cross-examined the other side’s experts and witnesses daily for six weeks, conducted significant legal research, and prepared substantive written arguments. Lawyers for both sides spent hundreds of hours placing all the evidence and legal arguments before the Federal Court for its consideration. The only remaining step in the trial process was the presentation of oral argument, scheduled for October 31, 2022. The Federal Court was fully and properly equipped to render a thoughtful decision as to whether the travel restrictions had been a justified violation of Charterfreedoms.
Even though the federal government can impose these same travel restrictions on Canadians again, without notice, the Federal Court granted the Crown’s motion on November 9, 2023, and dismissed this Charter challenge as moot. The Federal Court of Appeal affirmed this lower court ruling on November 9, 2023. Effectively, the courts determined that a constitutional challenge to the use of unprecedented emergency powers was neither sufficiently interesting to the Canadian public nor an appropriate use of court resources.
Premier Peckford, Maxime Bernier, and other Canadians now seek to have the Supreme Court of Canada hear their case. This involves a two-step process, whereby the applicants first ask whether the Court is willing to hear the appeal. If so, the appeal will then be scheduled for a hearing several months later. The applicants in this case argue that the issues raised in their case are of national importance and that Canadians deserve access to court rulings about policies that violate the Charter freedoms of millions of Canadians.
(See the January 8, 2024 Leave Application of Premier Peckford here. See the January 8, 2024 Leave Application of Maxime Bernier here.)
Further, Premier Peckford and the other applicants warn that all challenges to emergency orders risk being deemed irrelevant due to the simple fact that emergency orders are normally implemented only for short periods of time. In most cases, emergency orders will be rescinded by the time a constitutional challenge makes its way through the court process and all the relevant evidence, along with legal arguments, has been put before the judge. For this reason, the Applicants argue that the courts should provide guidance on how emergency orders should be handled in the context of the mootness doctrine.
“If courts are going to affirm and uphold emergency orders that violate our Charter rights and freedoms whenever the emergency order is no longer in force, how can the Charter protect Canadians from government abuses?” asks John Carpay, President of the Justice Centre.
Emergency orders are not debated in, or approved by, federal Parliament or provincial legislatures. Rather, they are discussed confidentially in Cabinet such that ordinary Canadians are prevented from understanding the reasons for, or the legality of, emergency orders, such as mandatory vaccination policies that discriminated against Canadians who chose not to get injected. Therefore, it is only through court rulings that Canadians can learn whether a mandate or emergency order is constitutional.
“The Supreme Court of Canada has an opportunity to create an important precedent for how Canadian courts deal with all so-called ‘moot’ cases involving questions about the constitutionality of emergency orders,” stated lawyer Allison Pejovic, who represents Premier Peckford and Maxime Bernier.
“The public interest in this case is staggering. Canadians need to know whether it is lawful for the federal government to prevent them from travelling across Canada, or from leaving and re-entering their own country, based upon whether they have taken a novel medication,” continued Ms. Pejovic.
“The Court’s dismissal of constitutional challenges to Covid orders for ‘mootness’ has deprived thousands of Canadians from knowing whether their governments’ emergency orders were lawful or not. It is time for the Supreme Court of Canada to expand the legal test for mootness to account for governments’ use of emergency orders, which are devoid of transparency and accountability. Canadians have a right to know whether unprecedented mandatory vaccination policies, which turned millions of Canadians into second-class citizens, were valid under our Constitution,” concluded Ms. Pejovic.
COVID-19
The Trials of Liberty: What the Truckers Taught Canada About Power and Protest

Half the country still believes the convoy was a menace; the other half thinks it was a mirror that showed how fragile our freedoms had become.
This Thanksgiving I am grateful for many things. The truckers who stood up to injustice are among them.
When the first rigs rolled toward Ottawa in January 2022, the air was sharp, but not as sharp as the mood of the men and women behind the wheels. They were not radicals. Seeing a CBC a campaign of disinformation about them begin as soon as their trek started, even when Ottawa political operatives hadn’t yet heard, I started following several of them on their social media.
They were truckers, small business owners, independent contractors, and working Canadians who had spent two years hauling the essentials that kept a paralyzed nation alive. They were the same people politicians, including Prime Minister Trudeau, had called “heroes” in 2020. By 2022, they had become “threats.”
The Freedom Convoy was born from exhaustion with naked hypocrisy. The federal government that praised them for risking exposure on the road now barred the unvaccinated from crossing borders or even earning a living. Many in provincial governments cheered Ottawa on. The same officials who flew to foreign conferences maskless or sat in private terraces to dine, let’s recall, still forced toddlers to wear masks in daycare. Public servants worked from home while police fined citizens for walking in parks.
These contradictions were not trivial; they were models of tyrannical rule. They told ordinary people that rules were for the ruled, not for rulers.
By late 2021, Canada’s pandemic response had hardened into a hysterical moral regime. Compliance became a measure of virtue, not prudence. Citizens who questioned the mandates were mocked as conspiracy theorists. Those who questioned vaccine efficacy were treated as fools; those who refused vaccination were treated as contagious heretics. Even science was no longer scientific. When data showed that vaccines did not prevent transmission, officials changed definitions instead of policies. The regime confused authority with truth. One former provincial premier just this week was still hailing the miracle of “life-saving” COVID vaccines.
For truckers, the breaking point came with the federal vaccine mandate for cross-border transport. Many had already complied with provincial rules and workplace testing. Others had recovered from COVID and had natural immunity that the government refused to recognize. To them, the new rule was not about safety; it was about humiliation. It said, “Obey, or you are unfit to work.”
So they drove.
Donna Laframboise, one of the rare journalists who works for citizens instead of sponsors, described the convoy in her book Thank You, Truckers! with gratitude and awe. She saw not a mob but a moral statement. She showcased for us Canadians who refused to live by lies. Their horns announced what polite society whispered: the emergency had become a creepy habit, and the habit had become a tool of control.
When the convoy reached Ottawa, it was messy, loud, and human. There was singing, prayer, laughter, dancing and some foolishness, but also remarkable discipline. For three weeks, amid frigid temperatures and rising tension, there were no riots, no arsons, no looting. In a country that once prized civility, that should have earned respect.
Instead, it attracted the media’s and government’s contempt.
The Trudeau government, rattled by its own public failures, sprung to portray the protest as a national security threat. Ministers invoked language fit for wartime. The Prime Minister, who had initially fled the city claiming to have tested positive, returned to declare that Canadians were under siege by “racists” and “misogynists.” The accusations were as reckless as they were false. The government’s real grievance was not chaos but defiance.
Then came the Emergencies Act. Designed for war, invasion, or insurrection, it was now deployed against citizens with flags and thermoses. Bank accounts were frozen without charge or trial. Insurance policies were suspended. Police weilding clubs were unleashed against unarmed citizens. The federal government did not enforce the law; it improvised it.
A faltering government declared itself the victim of its citizens. The Emergency declaration was not a reaction to danger; it was a confession of political insecurity. It exposed a leadership that could not tolerate dissent and recast obedience for peace.
Haultain Research is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts, express your gratitude and support our work, consider becoming a a paid subscriber.
The convoy’s organizers, who kept the protest largely peaceful, were arrested and prosecuted as though they had plotted sedition. They were charged for holding the line, not for breaking it. The state’s behaviour was vindictive, not judicial. Prosecutors went along with it, and so did courts.
In a healthy democracy, such political trials would have shaken Parliament to its core. Legislators would have demanded justification for the use of emergency powers. The press would have asked precisely which law had been broken. Citizens would have debated the limits of government in times of fear, times which seem to continue just under the radar.
Not much of that happened.
Canada’s institutions have grown timid. The press is subsidized and more subservient. The courts happily defer to the administrative state. Law enforcement has learned to follow politics before principle. Academics have been lost for about generation. Under such conditions, how can citizens object to unscientific and coercive policies? What options remain when every channel of dissent—media, science, judiciary, and law enforcement—is captured or cowed?
The convoy’s protest, let’s remember, was not the first major disruption in the Trudeau years. A year earlier, Indigenous activists blocked rail lines and highways in solidarity with Wet’suwet’en hereditary chiefs opposed to a pipeline. The blockades cost the economy millions. They were called “a national conversation.” Few arrests, no frozen accounts, no moral panic.
In 2020, Black Lives Matter marches were cheered by politicians and news anchors. Some protests were peaceful, others destructive. Yet they were treated as expressions of justice, not extremism.
Even today, pro-Hamas Palestinian demonstrations that include violence and intimidation of Jewish citizens are tolerated with a shrug. The police stand back, bring them coffee, citing “the right to protest.”
Why, then, was the Freedom Convoy treated as a crisis of state?
In a liberal democracy, protest is not rebellion. It is a civic instrument, a reminder that authority is contingent. When a government punishes peaceful protest because it disapproves of the message, it turns democracy into décor.
The trials of the convoy organizers are therefore not about law but about legitimacy. Each conviction signals that protest is permitted only when it pleases the powerful. This is the logic of every soft tyranny: it criminalizes opposition while decorating itself with the vocabulary of rights. I see this daily in Nicaragua, my native land.
The truckers’ protest revealed what the pandemic concealed. The COVID regime was unscientific and incoherent. It punished truckers who worked alone in their cabs while allowing politicians to mingle maskless at conferences. It barred unvaccinated Canadians from air travel but allowed infected citizens to cross borders with the proper paperwork. It closed playgrounds and churches while keeping liquor stores open.
These contradictions were not mistakes; they were instruments of obedience. Each absurd rule tested how much submission people would endure.
The truckers said, “Enough.” I am grateful that they did.
For that, Chris Barber (Big Red) and Tamara Lich  are still being punished. Their trials have now concluded, save for possible appeals, yet their quiet defiance remains one of the few honest moments in recent Canadian history. It showed that courage is still possible, even the state seems to forbid reason.
are still being punished. Their trials have now concluded, save for possible appeals, yet their quiet defiance remains one of the few honest moments in recent Canadian history. It showed that courage is still possible, even the state seems to forbid reason.
The government’s response revealed the opposite: that fear, once politicized, is never surrendered willingly. The state that learned to rule through emergency will not soon unlearn it. They cling to its uses still.
Canada lives with the legacy of that winter today. The trials are finished, but the divisions persist. Half the country still believes the convoy was a menace; the other half thinks it was a mirror that showed how fragile our freedoms had become.
Trudeau’s government is no more, yet the spirit of his politics lingers. He did not create the divisions by accident. He cultivated them as a strategy of control. The country that left him behind is also less free, less trusting, and less united than it was before the horns sounded in Ottawa. Carney’s government is Trudeau’s heir.
The trials and sentencing measure the distance between the Canada we imagined and the one we inhabit.
The truckers’ convoy was imperfect, yet profoundly democratic. It stood for the right of citizens to say no to a government that had forgotten how to hear them. The echo of that refusal still moves down the Trans-Canada Highway. It is the sound of liberty idling in the cold, waiting for a green light that will not soon come.
This Thanksgiving, I am grateful for the abounding love and understanding in my life. I am grateful for my spirited children and their children. I am grateful for my nonagenarian father and for my siblings. I’m grateful for the legion of aunts, uncles, cousins, nieces and nephews on all sides of the family. I am grateful for loyal friendships and for my colleagues and coworkers who share the quest for a freer country. I’m grateful to my adoptive Alberta, and Albertans, also struggling to be strong and free.
I am grateful for the Truckers, wherever they came from, for their courage.
Haultain Research is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts, express your gratitude and support our work, consider becoming a a paid subscriber.
COVID-19
Devastating COVID-19 Vaccine Side Effect Confirmed by New Data: Study
The Vigilant Fox
In one of the greatest violations of medical ethics in modern history, a new study from South Korea has uncovered devastating consequences from promoting and mandating the COVID-19 injections on the population.
These shots were pushed on babies and pregnant women, directly contradicting the ethical rule against introducing new medical interventions to such vulnerable groups before long-term effects are fully understood.
But they weren’t just aggressively promoted; they were enforced. Refusing the COVID-19 injection could cost you your job, bar you from concerts, businesses, and museums, and, in some cases, even deny you a life-saving surgery unless you complied with the mandate.
Now, as many doctors long warned, the consequences of such reckless health policy are surfacing, and one of the most alarming outcomes is a dramatic rise in cancer risk.
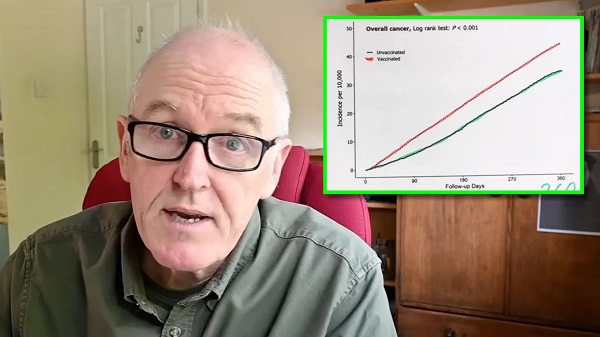
A large-scale population study out of South Korea has now found a 27% overall increase in cancer linked to the COVID-19 injections that were marketed as “safe and effective.”
Dr. John Campbell noted: “There’s a one in a thousand chance that this result arose by chance.” He illustrated the overall cancer rise with a stark graph, as seen in the short video below:
With regard to the details of the study, Children’s Health Defense reports:
The study used data from 2021–2023 for over 8.4 million people in South Korea’s National Health Insurance Service database. The sample was split into two groups based on vaccination status. The vaccinated sample was further split into booster and non-booster groups.
Researchers tracked the patients for one year. The vaccinated group was tracked following vaccination. The results showed a statistically significant higher risk of cancer in the vaccinated group, including:
• Overall cancer: 27% higher risk
• Breast cancer: 20% higher risk
• Colorectal cancer: 28% higher risk
• Gastric cancer: 34% higher risk
• Lung cancer: 53% higher risk
• Prostate cancer: 69% higher risk
• Thyroid cancer: 35% higher risk
These results are nothing short of devastating. Our worst fears have become reality.
And the worst part is that it didn’t have to be this way. Health officials ignored caution, silenced dissent, and turned public health into a reckless experiment.
Now the consequences of such reckless policies have turned the COVID wave into a health tsunami. The longer this issue is ignored, the greater the damage will become. It’s time for health officials to take responsibility for what they’ve done.
-

 Alberta11 hours ago
Alberta11 hours agoFact, fiction, and the pipeline that’s paying Canada’s rent
-

 2025 Federal Election19 hours ago
2025 Federal Election19 hours agoProtestor Behind ‘Longest Ballot’ Chaos targeting Poilievre pontificates to Commons Committee
-

 illegal immigration2 days ago
illegal immigration2 days ago$4.5B awarded in new contracts to build Smart Wall along southwest border
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoMelania Trump quietly reunites children divided by Ukraine war
-

 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoThe Trials of Liberty: What the Truckers Taught Canada About Power and Protest
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoUN, Gates Foundation push for digital ID across 50 nations by 2028
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoHamas releases all living hostages under Trump peace plan
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoTruckers see pay surge as ICE sweeps illegal drivers off U.S. highways













