Alberta
Investigation reveals terrifying life and death situation faced by police officer forced to shoot attacking suspect
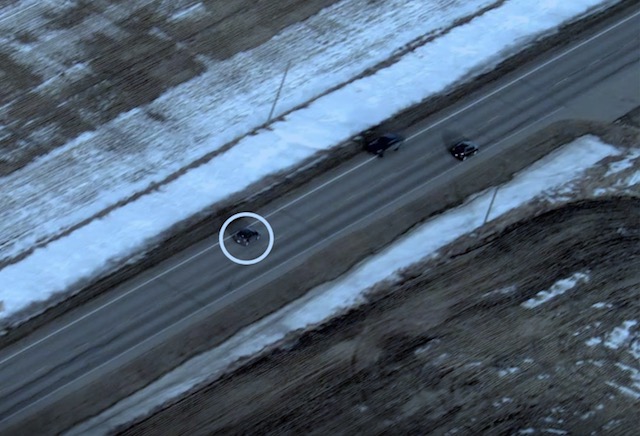

Figure 1 – HAWCS video showing the AP (circled in white) driving on the wrong side of the highway and forcing a vehicle off the road.
News release from the Alberta Serious Incident Response Team (ASIRT)
ASIRT’s Investigation
ASIRT’s investigation was comprehensive and thorough, conducted using current investigative protocols, and in accordance with the principles of major case management. Investigators interviewed all relevant police and civilian witnesses, and secured and analyzed all relevant radio communications.
This incident was captured on video by a Calgary Police Service (CPS) helicopter air watch community safety (HAWCS) helicopter. Some of the incident was also captured on cameras in the RCMP vehicles. These videos provide objective evidence and are therefore extremely valuable to ASIRT investigations.
Circumstances Surrounding the Incident
At approximately 1:50 p.m. on February 12, 2023, CPS received a 9-1-1 call about the affected person (AP). The caller was concerned that she was suicidal. RCMP officers responded to an area east of Calgary, and a CPS helicopter went to assist.
At 3:35 p.m., the witness officer (WO) located the AP in her vehicle on the side of Highway 564. The AP sped off and the WO followed. The CPS helicopter located the AP and the WO shortly after and began to record the incident.
The AP was driving extremely fast, including at speeds of over 175 km/h, and often on the wrong side of the highway. There were other vehicles on the road at that time. The AP drove through a stop sign at the intersection of Highways 564 and 9 and was briefly launched into the air due to her speed and the elevated intersection. The AP continued to drive on the wrong side of the highway (Figure 1).
At Highway 21, the AP turned around and travelled back west. She then briefly went off the road and into the ditch. At 3:51 p.m., the SO used a tire deflation device that punctured some of the AP’s tires. The AP then came to a stop and, at 3:52 p.m., the SO stopped his marked police vehicle behind the AP.
As the SO stopped, the AP exited her vehicle. She had a knife in her left hand and a beer in her right (Figure 2).
Figure 2 – The SO’s vehicle video showing the AP with a knife in her left hand.
The SO can be heard to yell, “drop the knife!” on the police vehicle video. The AP took a few steps toward the SO and then began to run toward him (Figure 3).
As she was running, the AP said, “I’m going to fucking kill you!” The SO said “drop the knife” repeatedly. The SO moved backwards and drew a handgun and then a conductive energy weapon (CEW).
Figure 3 – HAWCS video showing the AP running at the SO.
The AP continued to run at the SO until she reached the rear of his police vehicle, when she turned and attempted to go into the police vehicle (Figure 4).
Figure 4 – HAWCS video showing the AP entering the SO’s police vehicle.
The SO ran back to his vehicle and used his CEW on the AP. The AP then turned and ran at the SO again (Figure 5).
Figure 5 – HAWCS video showing the AP running at the SO again.
The AP again said, “I’m going to fucking kill you!” The SO then fired seven shots at 3:53 p.m., hitting the AP and causing her to fall to the road and drop her knife (Figure 6).
The SO approached the AP and kicked away the knife. The SO began to assess the AP, and other officers arrived within one minute to provide first aid to the AP. At 4:06 p.m., emergency medical services arrived and assumed care of the AP. An air ambulance was then used to transport the AP to hospital.
The AP had seven gunshot wounds to her chest, midsection, arms, and legs. She required surgeries and stayed in the hospital for some time.
Figure 6 – HAWCS video showing the AP falling to the road after being shot by the SO.
A knife was found in the ditch near the AP (Figure 7).
Figure 7 – Knife found in ditch near the AP.
Civilian Witnesses
ASIRT investigators interviewed or reviewed interviews with eight individuals who saw the incident or the AP driving that day. Their evidence was generally consistent with the above.
Affected Person’s (AP) Statement
ASIRT investigators interviewed the AP on February 28, 2023. She told them that she was suicidal on February 12. Initially she planned to find a semi-truck to run her over.
After the WO had stopped chasing her, she turned around to reengage with the police. She drove over the tire deflation device and then pulled over. Before she left her vehicle, she grabbed a knife because she thought that the police would not shoot her unless she had something. She left her vehicle and walked fast toward the SO, saying something like “just hit me” or “shoot me.”
The SO used his CEW on her but she pushed through the pain and continued to move toward the SO. She said something like “fucking hit me you little bitch” and the SO shot her. She continued to approach the SO and he then jumped on her, taking her to the ground and injuring her leg.
The police officers provided her with medical attention immediately. She asked them to let her die.
The AP said it was her goal to die and she did not want to hurt any police officers.
Subject Officer’s (SO) Statement
On May 1, 2023, ASIRT investigators interviewed the SO. He provided a written statement and then answered questions after reading it. Subject officers, like anyone being investigated for a criminal offence, can rely on their right to silence, and do not have to speak to ASIRT.
The SO’s evidence was consistent with the video evidence and provided some insight into his view of the incident. The SO did not hear what the AP said when she was running at him. After he shot her, he heard her say things like “let me die” and “you never help me.”
When the AP was running at the SO for the second time, he recognized that he could only run backwards for so long before tripping or falling and being at risk. He feared that the AP would cause him grievous bodily harm or death and fired at the AP until she stopped advancing.
Analysis
Section 25 Generally
Under s. 25 of the Criminal Code, police officers are permitted to use as much force as is necessary for execution of their duties. Where this force is intended or is likely to cause death or grievous bodily harm, the officer must believe on reasonable grounds that the force is necessary for the self-preservation of the officer or preservation of anyone under that officer’s protection. The force used here, discharging a firearm repeatedly at a person, was clearly intended or likely to cause death or grievous bodily harm. The subject officer therefore must have believed on reasonable grounds that the force he used was necessary for his self-preservation or the preservation of another person under his protection. Another person can include other police officers. For the defence provided by s. 25 to apply to the actions of an officer, the officer must be required or authorized by law to perform the action in the administration or enforcement of the law, must have acted on reasonable grounds in performing the action, and must not have used unnecessary force.
All uses of force by police must also be proportionate, necessary, and reasonable.
Proportionality requires balancing a use of force with the action or threat to which it responds. This is codified in the requirement under s. 25(3), which states that where a force is intended or is likely to cause death or grievous bodily harm, the officer must believe on reasonable grounds that the force is necessary for the self-preservation of the officer or preservation of anyone under that officer’s protection. An action that represents a risk to preservation of life is a serious one, and only in such circumstances can uses of force that are likely to cause death or grievous bodily harm be employed.
Necessity requires that there are not reasonable alternatives to the use of force that also accomplish the same goal, which in this situation is the preservation of the life of the officer or of another person under his protection. These alternatives can include no action at all. An analysis of police actions must recognize the dynamic situations in which officers often find themselves, and such analysis should not expect police officers to weigh alternatives in real time in the same way they can later be scrutinized in a stress- free environment.
Reasonableness looks at the use of force and the situation as a whole from an objective viewpoint. Police actions are not to be judged on a standard of perfection, but on a standard of reasonableness.
Section 25 Applied
The SO was assisting on a call that evolved as time went on. It started as a welfare check, became a serious dangerous driving investigation, and ended with dealing with an assaultive person. The SO’s actions throughout were required or authorized by law and he acted on reasonable grounds.
The first stage in assessing whether the force he used was excessive is proportionality. The AP was running at the SO with a knife, which could affect the SO’s self-preservation. He responded with his firearm, which was intended or likely to cause death or grievous bodily harm. These two forces are proportionate.
The necessity element of the assessment recognizes the dynamic nature of incidents such as this. Here, the AP ran at the SO suddenly, which created a serious situation. The SO recognized at this point that he could attempt to deescalate the situation by moving away from the AP. However, the AP then attempted to get into his police vehicle, which would have created a profoundly serious danger to him and other users of the highway. He then used his CEW, which was not effective. The AP began running at him again. With the threat still present and having exhausted reasonable alternatives, it was necessary for the SO to fire at the AP at that time.
The final element, reasonableness, looks at the incident overall. The SO conducted himself carefully and showed restraint at the beginning of the incident. His actions were reasonable.
As a result, the defence under s. 25 is likely to apply to the SO.
Section 34 Generally
A police officer also has the same protections for the defence of person under s. 34 of the Criminal Code as any other person. This section provides that a person does not commit an offence if they believe on reasonable grounds that force is being used or threatened against them or another person, if they act to defend themselves or another person from this force or threat, and if the act is reasonable in the circumstances. In order for the act to be reasonable in the circumstances, the relevant circumstances of the individuals involved and the act must be considered. Section 34(2) provides a non-exhaustive list of factors to be considered to determine if the act was reasonable in the circumstances:
(a) the nature of the force or threat;
(b) the extent to which the use of force was imminent and whether there were other means available to respond to the potential use of force;
(c) the person’s role in the incident;
(d) whether any party to the incident used or threatened to use a weapon;
(e) the size, age, gender and physical capabilities of the parties to the incident;
(f) the nature, duration and history of any relationship between the parties to the incident, including any prior use or threat of force and the nature of that force or threat;
(f.1) any history of interaction or communication between the parties to the incident;
(g) the nature and proportionality of the person’s response to the use or threat of force; and
(h) whether the act committed was in response to a use or threat of force that the person knew was lawful.
The analysis under s. 34 for the actions of a police officer often overlaps considerably with the analysis of the same actions under s. 25.
Section 34 Applied
For the same reasons as under s. 25, this defence is likely to apply to the SO. The AP was running at him with a knife and, like anyone would be, he was entitled to use force to repel her.
Conclusion
The AP was suicidal on February 12, 2023. She initially intended to drive into a semi- truck, but then decided to force police to shoot her. She did this by running at the SO with a knife in her hand. The SO was justified in responding with his firearm.
The defences available to the SO under s. 25 and s. 34 are likely to apply. As a result, there are no reasonable grounds to believe that an offence was committed.
Alberta
Temporary Alberta grid limit unlikely to dampen data centre investment, analyst says
From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Cody Ciona
‘Alberta has never seen this level and volume of load connection requests’
Billions of investment in new data centres is still expected in Alberta despite the province’s electric system operator placing a temporary limit on new large-load grid connections, said Carson Kearl, lead data centre analyst for Enverus Intelligence Research.
Kearl cited NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang’s estimate from earlier this year that building a one-gigawatt data centre costs between US$60 billion and US$80 billion.
That implies the Alberta Electric System Operator (AESO)’s 1.2 gigawatt temporary limit would still allow for up to C$130 billion of investment.
“It’s got the potential to be extremely impactful to the Alberta power sector and economy,” Kearl said.
Importantly, data centre operators can potentially get around the temporary limit by ‘bringing their own power’ rather than drawing electricity from the existing grid.
In Alberta’s deregulated electricity market – the only one in Canada – large energy consumers like data centres can build the power supply they need by entering project agreements directly with electricity producers.
According to the AESO, there are 30 proposed data centre projects across the province.
The total requested power load for these projects is more than 16 gigawatts, roughly four gigawatts more than Alberta’s demand record in January 2024 during a severe cold snap.
For comparison, Edmonton’s load is around 1.4 gigawatts, the AESO said.
“Alberta has never seen this level and volume of load connection requests,” CEO Aaron Engen said in a statement.
“Because connecting all large loads seeking access would impair grid reliability, we established a limit that preserves system integrity while enabling timely data centre development in Alberta.”
As data centre projects come to the province, so do jobs and other economic benefits.
“You have all of the construction staff associated; electricians, engineers, plumbers, and HVAC people for all the cooling tech that are continuously working on a multi-year time horizon. In the construction phase there’s a lot of spend, and that is just generally good for the ecosystem,” said Kearl.
Investment in local power infrastructure also has long-term job implications for maintenance and upgrades, he said.
“Alberta is a really exciting place when it comes to building data centers,” said Beacon AI CEO Josh Schertzer on a recent ARC Energy Ideas podcast.
“It has really great access to natural gas, it does have some excess grid capacity that can be used in the short term, it’s got a great workforce, and it’s very business-friendly.”
The unaltered reproduction of this content is free of charge with attribution to the Canadian Energy Centre.
Alberta
Alberta Next: Taxation
A new video from the Alberta Next panel looks at whether Alberta should stop relying on Ottawa to collect our provincial income taxes. Quebec already does it, and Alberta already collects corporate taxes directly. Doing the same for personal income taxes could mean better tax policy, thousands of new jobs, and less federal interference. But it would take time, cost money, and require building new systems from the ground up.
-

 Fraser Institute1 day ago
Fraser Institute1 day agoBefore Trudeau average annual immigration was 617,800. Under Trudeau number skyrocketted to 1.4 million annually
-

 MAiD1 day ago
MAiD1 day agoCanada’s euthanasia regime is already killing the disabled. It’s about to get worse
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day agoNew Book Warns The Decline In Marriage Comes At A High Cost
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoPrime minister can make good on campaign promise by reforming Canada Health Act
-

 Addictions1 day ago
Addictions1 day ago‘Over and over until they die’: Drug crisis pushes first responders to the brink
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoChicago suburb purchases childhood home of Pope Leo XIV
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoUSAID Quietly Sent Thousands Of Viruses To Chinese Military-Linked Biolab
-

 illegal immigration2 days ago
illegal immigration2 days agoICE raids California pot farm, uncovers illegal aliens and child labor



