Business
Federal government’s redistribution economics doesn’t work

From the Fraser Institute
By Jason Clemens, Jake Fuss, and Milagros Palacios
Prime Minister Trudeau’s vision for a more prosperous Canada relies on a much larger role for the federal government, with more spending, regulation, borrowing and higher taxes. By moving existing money around—both from higher-income workers to average Canadians and from the future to the present through borrowing—he believes the Canadian economy will be stronger and living standards will rise. But after nine years of governing, the evidence is clear—the prime minister’s redistribution economics doesn’t work and has actually reduced living standards in Canada.
Let’s first understand the magnitude of the changes made by the Trudeau government. Federal spending (excluding interest costs on debt) has risen from $256.2 billion in the last year of the Harper government to an estimated $483.6 billion this year, an increase of 88.7 per cent.
Even excluding COVID-related spending, the Trudeau government has recorded the five highest years of federal spending (on a per-person basis, after adjusting for inflation) in the history of the country, far surpassing spending during both world wars and the Great Recession.
Under Trudeau, the federal government has introduced several new programs (including dental care, daycare and pharmacare), and expanded several existing programs such as the cash transfer to families with children under 18 and corporate welfare.
Redistributing existing income has been a clear policy goal of the Trudeau government. From 2015 to 2022, average government transfers to families with children have increased from $12,685 to $15,750 (inflation-adjusted), an increase of 24.2 per cent. Yet among these same families, employment income only increased 8.0 per cent during the same period, meaning government transfers grew more than three times faster than their employment income. And as a share of household income, government transfers have increased from an average of 8.0 per cent between 1995 and 2007, when employment income was growing much faster, to 10.3 per cent in 2022.
The Trudeau government has financed this explosion in federal spending by borrowing, which is simply taxation deferred to the future, and tax increases.
Specifically, the government increased personal income taxes on professionals, entrepreneurs and successful business owners. It also increased taxes on businesses, which is an indirect and less transparent way of increasing taxes on average people since businesses don’t actually pay taxes, only people pay taxes. Higher business taxes mean less investment and thus lower wage growth for workers, lower payments to the business owners, and/or higher prices for consumers buying goods and services.
The Trudeau government also opaquely increased taxes on average Canadians. While it lowered the second personal income tax rate, it simultaneously eliminated several tax credits. As a result, 86 per cent of middle-income families experienced an increase in their personal income taxes as did 75 per cent of families with children in the bottom 20 per cent of income-earners.
But again, the government financed much of its new spending by borrowing, which means future tax increases. Consider that total federal debt stood at a little over $1.0 trillion when the Trudeau government took office in late-2015. By the government’s own estimates, total federal debt will reach almost $2.1 trillion next year.
Higher debt means higher interest costs, which divert money away from programs such as health care or badly needed tax relief. From 2015-16 (when Trudeau was first elected) to this year, federal debt interest costs have increased from $21.8 billion to an expected $54.1 billion. For context, this year the federal government expects to raise $54.1 billion from the GST, which means that every cent raised from the national sales tax will go to pay interest costs on the federal debt.
By focusing on moving around existing income (i.e. redistribution) rather than promoting income growth through investment and entrepreneurship, the Trudeau government has helped produce an outright economic growth crisis. Canada’s current decline in per-person GDP, a broad measure of living standards, is one of the longest and deepest declines of the last 40 years. Moreover, as of the end of 2023, the latest year of available data, the decline in living standards had not stopped so there’s a chance this could be the worst fall in living standards since at least the early-1980s.
According to a 2023 study, growth in per-person GDP from 2013 to 2022 was at its lowest rate since the Great Depression. Indeed, Canada’s post-COVID recovery was the 5th-weakest in the industrialized world. And prospects for the future are no better. A recent study by the OECD estimated that Canada would have the slowest growth in living standards among 32 high-income countries for the foreseeable future.
Simply put, the Trudeau government’s policies, which focused on government-led prosperity and moving income around instead of growing incomes, have led to a decline in living standards and economic malaise. Canadians are struggling when we should be leading the world in growth and prosperity. The only way to reverse our economic decline is to embrace a markedly different approach to policy focused on economic growth through entrepreneurship, investment and innovation.
Authors:
Business
Trump’s bizarre 51st state comments and implied support for Carney were simply a ploy to blow up trilateral trade pact

From LifeSiteNews
Trump’s position on the Canadian election outcome had nothing to do with geopolitical friendships and everything to do with America First economics.
Note from LifeSiteNews co-founder Steve Jalsevac: This article, disturbing as it is, appears to explain Trump’s bizarre threats to Canada and irrational support for Carney. We present it as a possible explanation for why Trump’s interference in the Canadian election seems to have played a large role in the Liberals’ exploitation of the Trump threat and their ultimate, unexpected success.
To understand President Trump’s position on Canada, you have to go back to the 2016 election and President Trump’s position on the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) renegotiation. If you did not follow the subsequent USMCA process, this might be the ah-ha moment you need to understand Trump’s strategy.
During the 2016 election President Trump repeatedly said he wanted to renegotiate NAFTA. Both Canada and Mexico were reluctant to open the trade agreement to revision, but ultimately President Trump had the authority and support from an election victory to do exactly that.
In order to understand the issue, you must remember President Trump, Commerce Secretary Wilbur Ross, and U.S. Trade Representative Robert Lighthizer each agreed that NAFTA was fraught with problems and was best addressed by scrapping it and creating two separate bilateral trade agreements. One between the U.S. and Mexico, and one between the U.S. and Canada.
In the decades that preceded the 2017 push to redo the trade pact, Canada had restructured their economy to: (1) align with progressive climate change; and (2) take advantage of the NAFTA loophole. The Canadian government did not want to reengage in a new trade agreement.
Canada has deindustrialized much of their manufacturing base to support the “environmental” aspirations of their progressive politicians. Instead, Canada became an importer of component goods where companies then assembled those imports into finished products to enter the U.S. market without tariffs. Working with Chinese manufacturing companies, Canada exploited the NAFTA loophole.
Justin Trudeau was strongly against renegotiating NAFTA, and stated he and Chrystia Freeland would not support reopening the trade agreement. President Trump didn’t care about the position of Canada and was going forward. Trudeau said he would not support it. Trump focused on the first bilateral trade agreement with Mexico.
When the U.S. and Mexico had agreed to terms of the new trade deal and 80 percent of the agreement was finished, representatives from the U.S. Chamber of Commerce informed Trudeau that his position was weak and if the U.S. and Mexico inked their deal, Canada would be shut out.
The U.S. Chamber of Commerce was upset because they were kept out of all the details of the agreement between the U.S. and Mexico. In actuality, the U.S. CoC was effectively blocked from any participation.
When they went to talk to the Canadians the CoC was warning them about what was likely to happen. NAFTA would end, the U.S. and Mexico would have a bilateral free trade agreement (FTA), and then Trump was likely to turn to Trudeau and say NAFTA is dead, now we need to negotiate a separate deal for U.S.-Canada.
Trudeau was told a direct bilateral trade agreement between the U.S. and Canada was the worst possible scenario for the Canadian government. Canada would lose access to the NAFTA loophole and Canada’s entire economy was no longer in a position to negotiate against the size of the U.S. Trump would win every demand.
Following the warning, Trudeau went to visit Nancy Pelosi to find out if Congress was likely to ratify a new bilateral trade agreement between the U.S. and Mexico. Pelosi warned Trudeau there was enough political support for the NAFTA elimination from both parties. Yes, the bilateral trade agreement was likely to find support.
Realizing what was about to happen, Prime Minister Trudeau and Chrystia Freeland quickly changed approach and began to request discussions and meetings with USTR Robert Lighthizer. Keep in mind more than 80 to 90 percent of the agreement was already done by the U.S. and Mexico teams. Both President Andres Manuel Lopez Obrador and President Trump were now openly talking about when it would be finalized and signed.
Nancy Pelosi stepped in to help Canada get back into the agreement by leveraging her Democrats. Trump agreed to let Canada engage, and Lighthizer agreed to hold discussions with Chrystia Freeland on a tri-lateral trade agreement that ultimately became the USMCA.
The key points to remember are: (1) Trump, Ross, and Lighthizer would prefer two separate bilateral trade agreements because the U.S. import/export dynamic was entirely different between Mexico and Canada. And because of the loophole issue, (2) a five-year review was put into the finished USMCA trade agreement. The USMCA was signed on November 30, 2018, and came into effect on July 1, 2020.
TIMELINE: The USMCA is now up for review (2025) and renegotiation in 2026!
This timeline is the key to understanding where President Donald Trump stands today. The review and renegotiation is his goal.
President Trump said openly he was going to renegotiate the USMCA, leveraging border security (Mexico) and reciprocity (Canada) within it.
Following the 2024 presidential election, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau traveled to Mar-a-Lago and said if President Trump was to make the Canadian government face reciprocal tariffs, open the USMCA trade agreements to force reciprocity, and/or balance economic relations on non-tariff issues, then Canada would collapse upon itself economically and cease to exist.
In essence, Canada cannot survive as a free and independent north American nation, without receiving all the one-way benefits from the U.S. economy.
To wit, President Trump then said that if Canada cannot survive in a balanced rules environment, including putting together their own military and defenses (which it cannot), then Canada should become the 51st U.S. state. It was following this meeting that President Trump started emphasizing this point and shocking everyone in the process.
However, what everyone missed was the strategy Trump began outlining when contrast against the USMCA review and renegotiation window.
Again, Trump doesn’t like the tri-lateral trade agreement. President Trump would rather have two separate bilateral agreements; one for Mexico and one for Canada. Multilateral trade agreements are difficult to manage and police.
How was President Trump going to get Canada to (a) willingly exit the USMCA; and (b) enter a bilateral trade agreement?
The answer was through trade and tariff provocations, while simultaneously hitting Canada with the shock and awe aspect of the 51st state.
The Canadian government and the Canadian people fell for it hook, line, and sinker.
Trump’s position on the Canadian election outcome had nothing to do with geopolitical friendships and everything to do with America First economics. When asked about the election in Canada, President Trump said, “I don’t care. I think it’s easier to deal, actually, with a liberal and maybe they’re going to win, but I don’t really care.”
By voting emotionally, the Canadian electorate have fallen into President Trump’s USMCA exit trap. Prime Minister Mark Carney will make the exit much easier. Carney now becomes the target of increased punitive coercion until such a time as the USMCA review is begun, and Canada is forced to a position of renegotiation.
Trump never wanted Canada as a 51st state.
Trump always wanted a U.S.-Canada bilateral trade agreement.
Mark Carney said the era of U.S.-Canadian economic ties “are officially declared severed.”
Canada has willingly exited the USMCA trade agreement at the perfect time for President Trump.
Business
China’s economy takes a hit as factories experience sharp decline in orders following Trump tariffs

Quick Hit:
President Trump’s tariffs on Chinese imports are delivering a direct blow to China’s economy, with new data showing factory activity dropping sharply in April. The fallout signals growing pressure on Beijing as it struggles to prop up a slowing economy amid a bruising trade standoff.
Key Details:
- China’s manufacturing index plunged to 49.0 in April — the steepest monthly decline in over a year.
- Orders for Chinese exports hit their lowest point since the Covid-19 pandemic, according to official data.
- U.S. tariffs on Chinese goods have reached 145%, with China retaliating at 125%, intensifying the standoff.
Diving Deeper:
Three weeks into a high-stakes trade war, President Trump’s aggressive tariff strategy is showing early signs of success — at least when it comes to putting economic pressure on America’s chief global rival. A new report from China’s National Bureau of Statistics shows the country’s manufacturing sector suffered its sharpest monthly slowdown in over a year. The cause? A dramatic drop in new export orders from the United States, where tariffs on Chinese-made goods have soared to 145%.
The manufacturing purchasing managers’ index fell to 49.0 in April — a contraction level that underlines just how deeply U.S. tariffs are biting. It’s the first clear sign from China’s own official data that the trade measures imposed by President Trump are starting to weaken the export-reliant Chinese economy. A sub-index measuring new export orders reached its lowest point since the Covid-19 pandemic, and factory employment fell to levels not seen since early 2024.
Despite retaliatory tariffs of 125% on U.S. goods, Beijing appears to be scrambling to shore up its economy. China’s government has unveiled a series of internal stimulus measures to boost consumer spending and stabilize employment. These include pension increases, subsidies, and a new law promising more protection for private businesses — a clear sign that confidence among Chinese entrepreneurs is eroding under Xi Jinping’s increasing centralization of economic power.
President Trump, on the other hand, remains defiant. “China was ripping us off like nobody’s ever ripped us off,” he said Tuesday in an interview, dismissing concerns that his policies would harm American consumers. He predicted Beijing would “eat those tariffs,” a statement that appears more prescient as China’s economic woes grow more apparent.
Still, the impact is not one-sided. Major U.S. companies like UPS and General Motors have warned of job cuts and revised earnings projections, respectively. Consumer confidence has also dipped. Yet the broader strategy from the Trump administration appears to be focused on playing the long game — applying sustained pressure on China to level the playing field for American workers and businesses.
Economists are warning of potential global fallout if the trade dispute lingers. However, Beijing may have more to lose. Analysts at Capital Economics now predict China’s growth will fall well short of its 5% target for the year, citing the strain on exports and weak domestic consumption. Meanwhile, Nomura Securities estimates up to 15.8 million Chinese jobs could be at risk if U.S. exports continue to decline.
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoPremier Danielle Smith responds to election of Liberal government
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoIn Defeat, Joe Tay’s Campaign Becomes a Flashpoint for Suspected Voter Intimidation in Canada
-

 Banks2 days ago
Banks2 days agoTD Bank Account Closures Expose Chinese Hybrid Warfare Threat
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoHours after Liberal election win, Alberta Prosperity Project drumming up interest in referendum
-
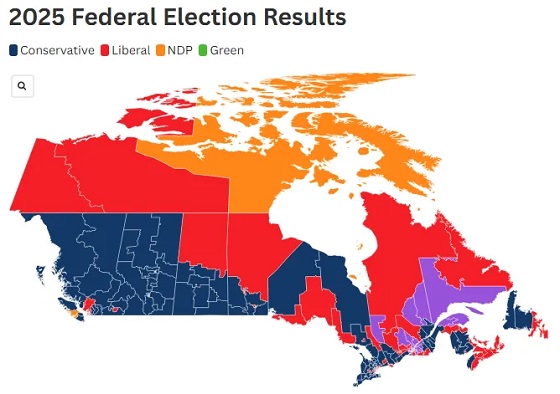
 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoPost election…the chips fell where they fell
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoNew Alberta Election Act bans electronic vote counting machines, lowers threshold for recalls and petitions
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoPoilievre loses seat but plans to stay on as Conservative leader
-

 espionage19 hours ago
espionage19 hours agoLongtime Liberal MP Warns of Existential Threat to Canada, Suggests Trump’s ’51st State’ Jibes Boosted Carney






