Economy
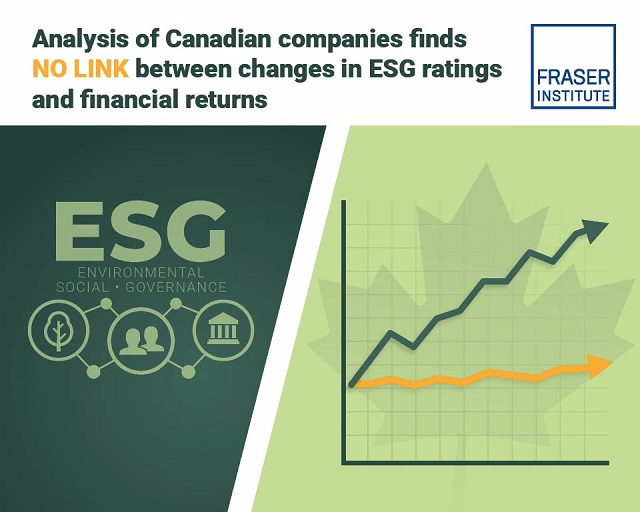
ESG rankings have no significant effect on investment performance of Canadian public companies
From the Fraser Institute
Despite claims to the contrary, the ESG rankings of publicly-traded Canadian companies have no significant effect on investment returns, finds a new study published today by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian
public policy think-tank.
“While government regulators and some industry executives promote the benefits of ESG investing, there’s no evidence of significant advantages for investors,” said Steven Globerman, senior fellow at the Fraser Institute and author of ESG Investing and Financial Returns in Canada.
Environmental, social and governance (ESG) is a movement designed to pressure businesses and investors to pursue larger social goals. In Canada, due to government securities regulation, publicly-traded companies must disclose ESG-related
information on a range of issues including environmental impact, human rights, and equity and inclusion.
ESG advocates claim that government-mandated ESG disclosures improve the financial performance of companies.
However, the study—the first empirical analysis of the relationship between changes in the ESG rankings of Canadian publicly-traded companies and equity returns— tracked 310 companies on the Toronto Stock Exchange from 2013 to 2022 and found no significant relationship between changes in ESG ranking (upgrades or downgrades) and financial returns, as measured by the price of shares and dividend income.
In other words, advocates for greater ESG disclosures cannot accurately claim—based on Canadian evidence—that requiring companies to provide more information for ESG rankings will significantly affect the financial performance of Canadian
investors.
“Better performance on ESG rankings simply does not translate into better financial performance for Canadian firms,” Globerman said.
- ESG investing incorporates environmental (E), social (S), and governance (G) considerations into investment decisions. Until recently, ESG-themed investing comprised an increasing share of investments made by professional money managers and retail investors.
- Financial industry executives and regulators who have promoted ESG-themed investing argue that it will enhance investment performance either by increasing asset returns and/or by reducing investment risk.
- However, empirical studies, on balance, find no consistent and statistically significant evidence of a positive relationship between the ESG rankings of individual companies or portfolios of companies and the financial performances of those companies or investment portfolios.
- Most empirical studies have focused on US-based publicly traded companies. To our knowledge, this study is the first to focus on returns to ESG-themed investing for Canadian-based public companies.
- Using data from MSCI, a leading ESG ratings provider, we estimate the statistical relationship between changes in ESG rankings of companies and changes in equity returns for those companies using a sample of 310 companies listed on the Toronto Stock Exchange between 2013 and 2022.
- Our study finds that neither upgrades nor downgrades in ESG ratings significantly affect stock market returns.
 Read the Full Report
Read the Full Report
Author:
Banks
From Energy Superpower to Financial Blacklist: The Bill Designed to Kill Canada’s Fossil Fuel Sector

From Energy Now
By Tammy Nemeth and Ron Wallace
REALITY: Senator Galvez’s BILL S-238 would force every federally regulated bank, insurer, pension fund and Crown financial corporation to treat the financing of oil, gas, and coal as an unacceptable systemic risk and phase it out through “decommissioning.”
Prime Minister Mark Carney has spent the past weeks proclaiming that Canada will become an “energy superpower” not just in renewables but in responsible conventional energy as well. The newly created Major Projects Office has been proposed to fast-track billions in LNG terminals, transmission lines, carbon-capture hubs, critical-mineral mines, and perhaps oil export pipelines. A rumored federal–Alberta Memorandum of Understanding is said to be imminent from signature, possibly clearing the way for a new million-barrel-per-day oil pipeline from Alberta to British Columbia’s north coast. The message from Ottawa is clear: Canada is open for energy business. Yet quietly moving through the Senate is legislation that would deliver the exact opposite outcome.
Senator Rosa Galvez’s reintroduction of her Climate-Aligned Finance Act, now Bill S-238, following the death of its predecessor Bill S-243 on the order paper, is being touted by supporters not only as a vital tool for an “orderly transition” to a low-carbon Canadian economy but also to be “simply inevitable.” This Bill does not simply ask financial institutions to “consider” climate risk it proposes to re-write their core mandate so that alignment with the Paris Agreement’s 1.5 °C target overrides every other duty. In fact, it would force every federally regulated bank, insurer, pension fund and Crown financial corporation to treat the financing of oil, gas, and coal as an unacceptable systemic risk and phase it out through “decommissioning.” For certainty this means to:
“(i) incentivize decommissioning emissions-intensive activities, diversifying energy sources, financing zero-emissions energy and infrastructure and developing and adopting change and innovation,
(ii) escalate climate concerns regarding emissions-intensive activities of financially facilitated entities and exclude entities that are unable or unwilling to align with climate commitments, and
(iii) minimize actions that have a climate change impact that is negative.”
As discussed here in May, the reach of the Climate Aligned Finance Act is vast, targeting emissions-intensive sectors like oil and gas with a regulatory overreach that borders on the draconian. Institutions must shun financing and support of emissions-intensive activities, which are defined as related to fossil fuel activities, and chart a course toward a “fossil-free future.” This would effectively starve Canada’s energy sector of capital, insurance, and investment. Moreover, Directors and Officers are explicitly required to exercise their powers in a manner that keeps their institution “in alignment with climate commitments.” The Bill effectively subordinates traditional financial fiduciary responsibility to climate ideology.
While the new iteration removes the explicit capital-risk weights of the original Bill (1,250% on debt for new fossil fuel projects and 150% or more for existing ones) it replaces those conditions with directives for the Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI) to issue guidelines that “account for exposures and contributions to climate-related risks.” This shift offers little real relief because mandated guidelines would still require “increased capital-risk weights for financing exposed to acute transition risks,” and the “non-perpetuation and elimination of dependence on emissions-intensive activities, including planning for a fossil-fuel-free future.”
These provisions would grant OSFI broad discretion but steer it inexorably toward punitive outcomes. As the Canadian Bankers’ Association and OSFI warned in their 2023 Senate testimony on the original Bill, such mechanisms would likely compel Canadian lenders to curtail or abandon oil and gas financing.
In plain language, Ottawa would be directing the entire financial system to stop lending to, insuring or investing in the very industries that are central to Canada’s economic future. In addition to providing tens of billions in royalties and taxes to governments each year, the oil and gas sector contributes about 3–3.5% of Canada’s GDP, generates over $160 billion in annual revenue and accounts for roughly 25% of Canada’s total exports.
The governance provisions proposed in Bill S-238 are beyond the pale. Board members with any past or present connection to the fossil fuel industry would have to declare it annually, detail any associations or lobbying involving “organizations not in alignment with climate commitments,” recuse themselves from every discussion or vote involving investments in oil, gas or coal, and make these declarations within a Climate Commitments Alignment Report. While oil and gas expertise is not banned outright, it is nonetheless ‘quarantined’ in ways that create a de facto purity test in the boardroom. At the same time, every board must appoint at least one member with “climate expertise”. Contrary to long-established principles for financial management, while seasoned energy experts would not be banned outright from such deliberations, they would effectively be sidelined on the very investment files where their expertise would be most valued.
The contradictions posed by Bill S-238 are simply breathtaking. The Major Projects Office is promising 68,000 jobs and CAD$116 billion in new investment, much of it tied to natural gas and oil-related infrastructure. These new pipeline and LNG export projects will require material private capital investments. Yet under Bill S-238 any bank that provides the capital needed for the projects would face escalating, punitive capital requirements along with public disclosure of its “contribution” to climate risks that are to be declared annually in a “Climate Commitments Alignment Report.” No MoU, Indigenous loan guarantee or federal permit can conjure financing out of thin air once Canada’s banks and insurers have effectively been legally compelled to exit the fossil fuel energy sector.
Current actions constitute a clear warning about the potential legal consequences of Bill S-238. Canada’s largest pension fund is currently being sued by four young Canadians who claim the Canada Pension Plan Investment Board (CPPIB) is failing to properly manage climate-related financial risk. Alleged are breaches of fiduciary duty through fossil fuel investments that are claimed to exacerbate climate risks and threaten ‘intergenerational equity’ with the demand that the CPP divest from fossil fuels entirely. The case, filed in Ontario Superior Court, demonstrates how financial institutions may be challenged in their traditional roles as stewards of balanced economic growth and instead used as agents for enforced decarbonization. In short, such legislation enables regulatory laws to re-direct, if not disable, capital investment in the Canadian non-renewable energy sector.
In May 2024, Mark Carney, then Chair of Brookfield Asset Management Inc. and head of Transition Investing, appeared at a Senate Committee hearing. He lauded the original Bill, calling key elements “achievable and actually essential” to champion “climate-related financial disclosures.” He noted that: “Finance cannot drive this transition on its own. Finance is an enabler, a catalyst that will speed what governments and companies initiate.” However, the new revised Bill S-238 goes far beyond disclosure. Like its previous iteration, it remains punitive, discriminatory and economically shortsighted, jeopardizing the very economic resilience that Carney has pledged to fortify. It is engineered debanking dressed up as prudential regulation.
This is at a time in which Richard Ciano described Canada as a land of “investment chaos”:
“While investment risk in the United States is often political, external, and transactional, the risk in Canada is systemic, legal, and structural. For long-term, capital-intensive projects, this deep, internal rot is fundamentally more toxic and unmanageable than the headline-driven volatility of a U.S. administration.
If the “rule of law” in Canada is meant to provide the certainty and predictability that capital demands, it is failing spectacularly. Investors seek clear title and dependable contracts. Canada is increasingly delivering the opposite. Investors don’t witness stability — they witness a fractured federation, a weaponized bureaucracy, and a legal system that injects profound uncertainty into the most basic elements of capitalism, like property rights.”
Bill S-238 is yet another example of how Canada is imposing unrealistic laws and regulations that contribute to investment uncertainty and that directly contradict policies proposed to accelerate projects in the national interest. While the Carney government trumpets Canada as a future energy superpower that produces and exports LNG, responsibly produced “decarbonized” oil and critical minerals, Bill S-238 would effectively limit, if not negate, the crucial financial backing and investments that would be required to accomplish this policy objective.
Rhetoric about nation-building projects is cheap. Access to capital is what turns promises into steel in the ground. This Bill would ensure that one hand of government will be quietly strangling what the other hand is proposing to do in the national interest.
Tammy Nemeth is a U.K.-based energy analyst. Ron Wallace is a Calgary-based energy analyst and former Member of the National Energy Board.
Business
Federal major projects list raises questions

From Resource Works
Once more, we have to shake our collective heads at the (typical) lack of information from the government after the fanfare of announcements, news releases, and video clips.
Prime Minister Mark Carney’s addition of seven new projects to the Major Projects Office (MPO) list of ventures to be accelerated came with a vague promise from the MPO.
Now, said the MPO, it will “work with proponents, provinces, territories and Indigenous Peoples to find the right way forward for these projects.”
The new projects include the Nisga’a Nation’s Ksi Lisims LNG project in BC (and its PRGT pipeline), BC Hydro’s North Coast Transmission Line (NCTL) and the related “Northwest Critical Conservation Corridor,” plus mining projects in Ontario, Quebec and New Brunswick, and an Inuit-owned hydro project near Iqaluit in Nunavut.
In all, a federal news release said, Carney’s announcements “represent more than $56 billion in new investment.” That’s in addition to “$60 billion for investments in nuclear power, LNG, critical minerals, and new trade corridors” that were announced in September.
Carney said: “Unlocking these resources . . . will attract hundreds of billions of dollars in new investment and create thousands of high-paying careers for miners, carpenters, and engineers across the country.”
And it’s all aimed at reducing Canada’s dependence on trade with the U.S. As journalist Thomas Seal of Bloomberg News noted: “The country sells 75% of its goods to the US and projects on the list so far aim to help change that: port developments to ramp up trade with Europe, LNG terminals to sell gas to Asia, and mines to exploit global demand for critical minerals.”
But what does “fast-track” actually mean?
Carney’s Terrace, B.C. announcement raised a so-far unanswered question: What will the addition of these projects to the federal fast-track list mean in practice?
What can, or will, Ottawa actually do to support these projects and help bring them to fruition?
Carney gave no details, but federal officials say the Major Projects Office will coordinate approvals for all components of the projects to accelerate timelines that could otherwise take years.
The MPO is supposed to fast-track resource and infrastructure projects deemed to be “in the national interest.” The new projects have not yet been designated as “in the national interest,” which would qualify them for special treatment in permitting and approvals. Instead, Carney and the MPO used the words “national importance” and “national significance.”
And some of the projects Carney announced are already in progress, and it’s not clear what the MPO could do to move them along.
Does Ottawa plan to give the projects financial support?
The prime minister spoke of Ottawa putting up “huge financing” but, again, gave no further information.
As he listed the additions to the MPO project list, though, the Canada Infrastructure Bank announced a $139.5-million loan to BC Hydro to support “the early works phase” of the NCTL power line.
Does Ottawa see a role for the MPO in negotiating with First Nations and Indigenous peoples that are opposed to one or more of the projects?
PM Carney: “Referring to the MPO, or the Major Projects Office, does not mean the project is approved. It means that all the efforts are being put in place from the federal government in order to create the conditions so it could move forward. But those decisions are taken by many parties, including, very much, First Nations.”
The prime minister’s announcement was the first since the appointment of an Indigenous advisory council that is to help the MPO integrate the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, UNDRIP, into its decision-making.
Carney added that the “huge financing” he promised is aimed at encouraging Indigenous equity ownership of the projects.
Alex Grzybowski, CEO of the Indigenous organization K’uul Power, sees the North Coast Transmission Line as “a pretty solid investment,” but says First Nations would need to raise $275-$300 million to take equity shares in it.
To help First Nations get there, he calls on Ottawa to provide an investment tax credit, to increase the lending cap of the Canada Infrastructure Bank to $300 million from $100 million, and to provide “a federal loan-guarantee with a provincial backstop.”
Ksi Lisims LNG project
Ksi Lisims LNG is coming from a partnership of the Nisga’a Nation, Rockies LNG Ltd. Partnership and Western LNG.
The $10-billion project in northern BC would have two floating production platforms, producing for export 12 million tonnes of LNG per year. Natural gas for Ksi Lisims would come more than 750 km through the PRGT pipeline.
Ksi Lisims LNG says it hopes for construction to begin this year, with operations to start in late 2028 or 2029. It says it aims to be “net-zero ready” by 2030.
Charles Morven, secretary-treasurer for the Nisga’a Nation, said: “A lot of major work has taken place in the past five years, getting everything put together. This announcement gets us so very close to the finish line.”
And Eva Clayton, Nisga’a president, said: “We’re showing BC, Canada, and the world what Indigenous economic independence and shared prosperity can look like.” She spoke of “meaningful opportunities” for the Nisga’a — and for all Nations and communities in northern BC.
The Nisga’a Nation, a partner in Ksi Lisims LNG and its PRGT pipeline, says it is working with Indigenous communities to strike agreements, including equity stakes in the pipeline. A final investment decision on Ksi Lisims is expected early next year.
Environmental groups have also opposed the Ksi Lisims project, and the Union of BC Indian Chiefs cited environmental and climate concerns. But Carney said Ksi Lisims LNG will be one of the world’s cleanest operations, with emissions 94 per cent below the global average.
And the Nisga’a Nation said: “With our co-developers and Treaty Partners we will ensure this project reflects . . . our high standards of environmental protection.”
The prime minister said Ksi Lisims LNG will add $4 billion a year to the nation’s economy. And federal officials say Ksi Lisims could create thousands of skilled jobs, with Indigenous workers among them.
Said Carney: “LNG is an essential fuel for the energy transition. LNG can help Canada build new trading relationships, especially in fast growing markets in Asia. . . .
“Canada will be ready. We’re home to the world’s fourth largest reserves of natural gas, and we have the potential to supply up to 100 million tons annually of new LNG exports to Asia.”
And his announcement led the Canadian Association of Petroleum Producers to say: “Canada is on a path to become one of the top five LNG exporters in the world.”
North Coast Transmission Line
The 450-km North Coast Transmission Line from Prince George to Terrace would feed clean hydro power to LNG projects such as LNG Canada and the Haisla Nation’s coming Cedar LNG project, and it would also power mining projects and regional communities.
Carney said the power line could eventually connect with Alberta and support reliability, clean power development and new industrial investment across the West. Carney also spoke the potential for a northwest trade and energy corridor running from British Columbia through the Yukon with future possibilities for connection into Alberta. But, again, he gave no details of any plans.
Later, BC Premier David Eby called the NCTL “one of the biggest, most transformational opportunities” in a century. BC says the power line “will be co-owned with First Nations and will provide BC’s 98% renewable energy to the northwest.”
The BC government says the next major steps for the NCTL include finalizing the route. It says construction is expected to start in the summer of 2026, with phased-in completion targeted for 2032-34.
BC legislation would allow First Nations equity in the project and the province also says it plans to direct the B.C. Utilities Commission to allow the project to proceed without needing to go through the usual hearing process, potentially cutting a year to 18 months off the completion date.
To help First Nations acquire equity in the NCTL, Alex Grzybowski, CEO of Indigenous K’uul Power, says three things are needed from government:
“The first and most valuable thing they could do is provide an investment tax credit. And actually that wouldn’t hit their books for six years, so from an immediate financing perspective, that might be the best. . . .
“The next best thing would be to increase the lending cap for the Canada Infrastructure Bank from $100 million to $300 million, and then we would be borrowing money at below Bank of Canada rates, and we would be able to lend that money into construction, which would lower the cost of construction, it would lower the cost for the ratepayers, and it would increase the benefits for the First Nations. . . .
“The third thing they could do is provide a federal loan guarantee with a provincial backstop.”
BC says the NCTL project is expected to create some 9,700 direct full-time jobs, contribute nearly $10 billion per year to GDP and generate approximately $950 million a year in revenues for provincial and municipal governments. BC says it will also help prevent two to three million tonnes of carbon emissions a year.
The NCTL power-line plan also raises key questions, including this: How will BC Hydro come up with the new power to feed into the line? We have seen estimates such as this: “By 2050, BC may need to double or triple its . . . power generation as transportation, buildings and industry are all or partially electrified. Current output is generated with 32 hydro dams. Can the province build another 32 or 64 hydro plants in under 30 years? Of course not, so where will all that power come from?”
And what will NCTL cost? The first estimate from BC Hydro is $6 billion, but Hydro’s costs for the Site C power dam finished up at twice what it initially estimated.
A cautious shift from past policies
Once more, we have to shake our collective heads at the (typical) lack of information from the government after the fanfare of announcements, news releases, and video clips.
We naturally wonder if Ottawa’s promises will be matched by performance, but at least we see some much-needed departure from the anti-project policies of the past Justin Trudeau government.
As CEO François Poirier of TC Energy puts it: “The policy environment is becoming increasingly supportive.”
Heather Exner-Pirot of the Macdonald-Laurier Institute says the new Carney budget shows signs of a better mix of “carrot and stick” than did the Trudeau government. “The last budget was still in the ‘stick’ era. Finally, we’re in a ‘carrot’ era.”
And she adds: “At least under this government, the bad things have stopped happening. And I would say, even with this budget, some of the bad things are actually going away.”
Let us hope so.
Photo credit to the THE CANADIAN PRESS/Sean Kilpatrick.
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoRed Deer’s Jason Stephan calls for citizen-led referendum on late-term abortion ban in Alberta
-

 espionage2 days ago
espionage2 days agoSoros family has been working with State Department for 50 years, WikiLeaks shows
-

 Indigenous2 days ago
Indigenous2 days agoIndigenous activist wins landmark court ruling for financial transparency
-

 Artificial Intelligence22 hours ago
Artificial Intelligence22 hours agoGoogle denies scanning users’ email and attachments with its AI software
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoIs affirming existing, approved projects truly the best we can do in Canada?
-
 Business1 day ago
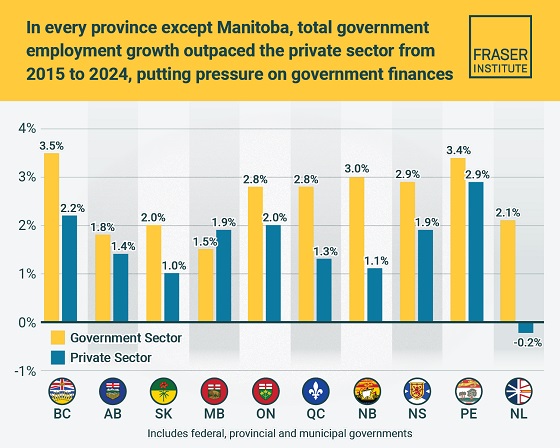
Business1 day agoTaxpayers paying wages and benefits for 30% of all jobs created over the last 10 years
-
 MAiD1 day ago
MAiD1 day agoHealth Canada suggests MAiD expansion by pre-approving ‘advance requests’
-

 Alberta22 hours ago
Alberta22 hours agoPremier Danielle Smith says attacks on Alberta’s pro-family laws ‘show we’ve succeeded in a lot of ways’







