Fraser Institute
Bill Maher is right about Canadian health care
From the Fraser Institute
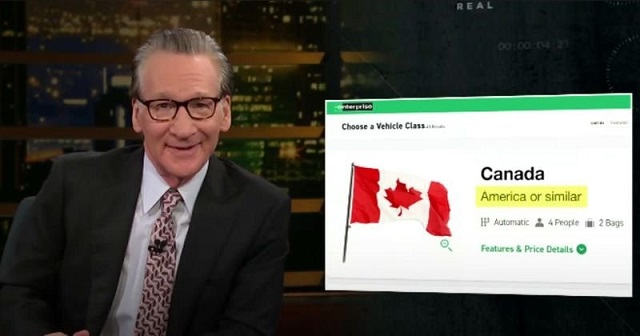
Recently, popular American comedian and talk show host, Bill Maher, took aim at some of Canada’s public policy failings in one of his monologues. In entertaining fashion, Maher highlighted our high housing costs, unemployment rates and “vaunted” health-care system.
Indeed, citing work published by the Fraser Institute, he explained that after adjusting for age, Canada spends 13.3 per cent of our economy on health care (2020), the highest level of spending by a developed country with universal coverage that year. And that Canada has some of the poorest access to timely appointments with family doctors when compared to our peers.
Unfortunately, while that’s where his segment on health care ended, the bad news for the Canadian system doesn’t stop there.
On top of Canada continuing to be one of the most expensive universal health-care systems in the world, we get little in return when it comes to both available medical resources and wait times. For example, among high-income countries with universal health care, Canada has some of the lowest numbers of physicians, hospital beds, MRI machines and CT scanners.
And in Canada, only 38 per cent of patients report seeing a specialist within four weeks (compared to 69 per cent in the Netherlands) and only 62 per cent report receiving non-emergency surgery within four months (compared to 99 per cent in Germany).
Unfortunately, wait times in Canada aren’t simply long compared to other countries, they’re the longest they’ve ever been. Last year the median wait for a Canadian patient seeking non-emergency care reached 27.7 weeks—nearly three times longer than the 9.3 week-wait Canadians experienced three decades ago.
This raises the obvious question. How do other countries outperform Canada’s health-care system while also often spending less as a share of their economies? In short, their approach to universal health care, and in particular their relationship with the private sector, departs drastically from the approach here at home.
Australia, for example, partners with private hospitals to deliver the majority (58.6 per cent) of all non-emergency surgeries within its universal health-care system. Australia also spends less of its total economy (i.e. GDP) on health care but outperforms Canada on every measure of timely care.
Even with restrictions on the private sector, Canada has some limited experience that should encourage policymakers to embrace greater private-sector involvement. Saskatchewan, for example, contracted with private surgical clinics starting in 2010 to deliver publicly-funded services as part of a four-year initiative to reduce wait times, which were among the longest in the country. Between 2010 and 2014, wait times in the province fell from 26.5 weeks to 14.2 weeks. After the initiative ended, the province’s wait times began to grow.

More recently, Quebec, which has some of the shortest wait times for medical services in the country, contracts out one out of every six day-surgeries to private clinics within the publicly-funded health-care system.
Maher’s monologue, which was viewed by millions online, highlighted the key failings of Canada’s health-care system. If policymakers in Ottawa and the provinces want to fix Canadian health care, they must learn from other countries that deliver universal health-care at the same or even lower cost, often with better access and results for patients.
Author:
Alberta
Albertans need clarity on prime minister’s incoherent energy policy

From the Fraser Institute
By Tegan Hill
The new government under Prime Minister Mark Carney recently delivered its throne speech, which set out the government’s priorities for the coming term. Unfortunately, on energy policy, Albertans are still waiting for clarity.
Prime Minister Carney’s position on energy policy has been confusing, to say the least. On the campaign trail, he promised to keep Trudeau’s arbitrary emissions cap for the oil and gas sector, and Bill C-69 (which opponents call the “no more pipelines act”). Then, two weeks ago, he said his government will “change things at the federal level that need to be changed in order for projects to move forward,” adding he may eventually scrap both the emissions cap and Bill C-69.
His recent cabinet appointments further muddied his government’s position. On one hand, he appointed Tim Hodgson as the new minister of Energy and Natural Resources. Hodgson has called energy “Canada’s superpower” and promised to support oil and pipelines, and fix the mistrust that’s been built up over the past decade between Alberta and Ottawa. His appointment gave hope to some that Carney may have a new approach to revitalize Canada’s oil and gas sector.
On the other hand, he appointed Julie Dabrusin as the new minister of Environment and Climate Change. Dabrusin was the parliamentary secretary to the two previous environment ministers (Jonathan Wilkinson and Steven Guilbeault) who opposed several pipeline developments and were instrumental in introducing the oil and gas emissions cap, among other measures designed to restrict traditional energy development.
To confuse matters further, Guilbeault, who remains in Carney’s cabinet albeit in a diminished role, dismissed the need for additional pipeline infrastructure less than 48 hours after Carney expressed conditional support for new pipelines.
The throne speech was an opportunity to finally provide clarity to Canadians—and specifically Albertans—about the future of Canada’s energy industry. During her first meeting with Prime Minister Carney, Premier Danielle Smith outlined Alberta’s demands, which include scrapping the emissions cap, Bill C-69 and Bill C-48, which bans most oil tankers loading or unloading anywhere on British Columbia’s north coast (Smith also wants Ottawa to support an oil pipeline to B.C.’s coast). But again, the throne speech provided no clarity on any of these items. Instead, it contained vague platitudes including promises to “identify and catalyse projects of national significance” and “enable Canada to become the world’s leading energy superpower in both clean and conventional energy.”
Until the Carney government provides a clear plan to address the roadblocks facing Canada’s energy industry, private investment will remain on the sidelines, or worse, flow to other countries. Put simply, time is up. Albertans—and Canadians—need clarity. No more flip flopping and no more platitudes.
Fraser Institute
Long waits for health care hit Canadians in their pocketbooks

From the Fraser Institute
Canadians continue to endure long wait times for health care. And while waiting for care can obviously be detrimental to your health and wellbeing, it can also hurt your pocketbook.
In 2024, the latest year of available data, the median wait—from referral by a family doctor to treatment by a specialist—was 30 weeks (including 15 weeks waiting for treatment after seeing a specialist). And last year, an estimated 1.5 million Canadians were waiting for care.
It’s no wonder Canadians are frustrated with the current state of health care.
Again, long waits for care adversely impact patients in many different ways including physical pain, psychological distress and worsened treatment outcomes as lengthy waits can make the treatment of some problems more difficult. There’s also a less-talked about consequence—the impact of health-care waits on the ability of patients to participate in day-to-day life, work and earn a living.
According to a recent study published by the Fraser Institute, wait times for non-emergency surgery cost Canadian patients $5.2 billion in lost wages in 2024. That’s about $3,300 for each of the 1.5 million patients waiting for care. Crucially, this estimate only considers time at work. After also accounting for free time outside of work, the cost increases to $15.9 billion or more than $10,200 per person.
Of course, some advocates of the health-care status quo argue that long waits for care remain a necessary trade-off to ensure all Canadians receive universal health-care coverage. But the experience of many high-income countries with universal health care shows the opposite.
Despite Canada ranking among the highest spenders (4th of 31 countries) on health care (as a percentage of its economy) among other developed countries with universal health care, we consistently rank among the bottom for the number of doctors, hospital beds, MRIs and CT scanners. Canada also has one of the worst records on access to timely health care.
So what do these other countries do differently than Canada? In short, they embrace the private sector as a partner in providing universal care.
Australia, for instance, spends less on health care (again, as a percentage of its economy) than Canada, yet the percentage of patients in Australia (33.1 per cent) who report waiting more than two months for non-emergency surgery was much higher in Canada (58.3 per cent). Unlike in Canada, Australian patients can choose to receive non-emergency surgery in either a private or public hospital. In 2021/22, 58.6 per cent of non-emergency surgeries in Australia were performed in private hospitals.
But we don’t need to look abroad for evidence that the private sector can help reduce wait times by delivering publicly-funded care. From 2010 to 2014, the Saskatchewan government, among other policies, contracted out publicly-funded surgeries to private clinics and lowered the province’s median wait time from one of the longest in the country (26.5 weeks in 2010) to one of the shortest (14.2 weeks in 2014). The initiative also reduced the average cost of procedures by 26 per cent.
Canadians are waiting longer than ever for health care, and the economic costs of these waits have never been higher. Until policymakers have the courage to enact genuine reform, based in part on more successful universal health-care systems, this status quo will continue to cost Canadian patients.
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoLast day and last chance to win this dream home! Support the 2025 Red Deer Hospital Lottery before midnight!
-

 conflict2 days ago
conflict2 days ago“Evacuate”: Netanyahu Warns Tehran as Israel Expands Strikes on Iran’s Military Command
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoKananaskis G7 meeting the right setting for U.S. and Canada to reassert energy ties
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCarney’s Honeymoon Phase Enters a ‘Make-or-Break’ Week
-

 Aristotle Foundation2 days ago
Aristotle Foundation2 days agoThe Canadian Medical Association’s inexplicable stance on pediatric gender medicine
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoCould the G7 Summit in Alberta be a historic moment for Canadian energy?
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlberta announces citizens will have to pay for their COVID shots
-

 conflict1 day ago
conflict1 day agoIsrael bombs Iranian state TV while live on air









