Crime
Veteran RCMP Investigator Warns of Coordinated Hybrid Warfare Targeting Canada
 Sam Cooper
Sam Cooper
Central to this strategy is fentanyl—a substance whose reach now extends far beyond Canadian borders.
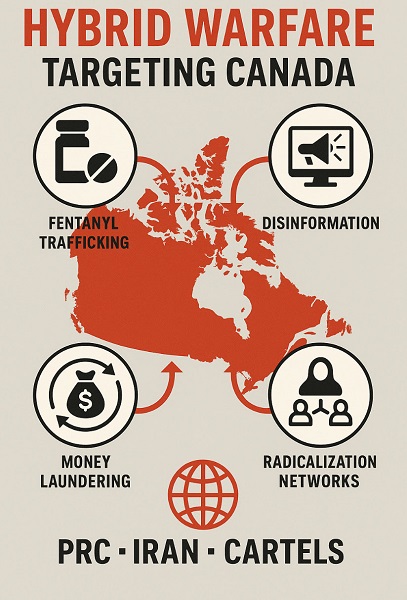
Fentanyl overdoses. Dirty money flooding real estate. Election interference. Foreign-backed antisemitism igniting across Canadian campuses. These are not isolated crises, warns Calvin Chrustie, a veteran RCMP national security and transnational crime investigator. They are interlinked weapons in an accelerating campaign of hybrid warfare targeting Canada—one that is hollowing out state institutions, fracturing social cohesion, and damaging our alliances. In the view of Chrustie, like other North American experts recently interviewed by The Bureau, adversarial regimes are exploiting Canada’s systemic vulnerabilities to destabilize the country from within, with consequences extending into the United States, Australia, the United Kingdom, Taiwan, Japan, and beyond.
In a sweeping interview with the Macdonald-Laurier Institute, Chrustie laid out a sobering account of how foreign states—chiefly China and Iran—are combining their intelligence capabilities with organized crime networks and proxies such as Mexican cartels to exploit Canadian systems. The Bureau has analyzed Chrustie’s comments and connected them to broader findings in its investigations into transnational crime and state-sponsored influence operations.
At the heart of Chrustie’s warning is a shift in how adversaries like China and Iran operate. No longer relying solely on spies or cyberattacks, they are weaponizing organized crime—leveraging fentanyl trafficking, corruption, and influence operations to destabilize democracies.
“Hybrid warfare is the blending of military and non-military means to weaken or destabilize a target,” Chrustie explained. “For hostile states, transnational crime is a tool—just like cyberattacks or disinformation. China, Russia, Iran, North Korea—the CRINKs—use TOC to raise money, create chaos, and undermine our institutions. TOC is no longer just criminal—it’s geopolitical.”
Fentanyl, in this context, is not only a public health catastrophe but a deliberate weapon.
“It’s about destabilizing communities, overwhelming public services, and hollowing out social cohesion,” he said. “Just like the Soviets used propaganda and the KGB used disinformation, modern adversaries use drugs, money laundering, and crime networks to erode their adversaries from within.”
This erosion now extends beyond physical harms into the social and political realm. Chrustie pointed to radical protest movements and the rise in antisemitic incidents on Canadian campuses as evidence of convergence between TOC and foreign influence operations.
“These aren’t disconnected trends,” he said. “The same threat actors behind fentanyl and money laundering are often involved in radicalization efforts. Iranian networks, for example, have long been tied to money laundering and extremist financing. And those networks are not operating in isolation. They’re aligned with China and the Mexican cartels.”
Chrustie argued that radical activism and identity-based polarization are being amplified not just by ideology, but by illicit foreign-backed financing and digital manipulation. “We’re talking about convergence,” he said. “These networks exploit every vulnerability—from public health to political discourse. Failing to connect the dots between TOC, extremism, and foreign interference means we’re always reacting too late.”
Central to this strategy is fentanyl—a substance whose reach now extends far beyond Canadian borders. “There’s no denying the scale of fentanyl production in Canada. It far outpaces our internal consumption,” he said. “We know Canadian labs are supplying Australia in large quantities. And we don’t know how much is crossing into the U.S.—because we’re not meaningfully tracking it. That lack of visibility alone is a serious national security concern.”
Seizures at the border are not the solution, Chrustie argued, because they’re not the full picture. “The U.S. has robust systems for this. Canada doesn’t,” he said. “So pointing to low seizures as proof of safety is misleading—it really just tells us what we’re not seeing.”
And what we’re not seeing, he says, includes deeply compromised infrastructure. “They exploit Canada’s weaknesses, especially in places like Vancouver, where strategic assets such as ports, shipping companies and supply chain infrastructure are key hybrid warfare targets,” he said. “The intent is to target North America through Vancouver-based assets, because it’s a lower-risk operating environment.”
The financial flows enabling this system are equally opaque—and equally dangerous. Chrustie cited the HSBC cartel laundering scandal, which led to a $1.9 billion U.S. settlement, as a historic warning that was never heeded. “The same cartel networks that emerged through the HSBC probe are engaged in Canada today,” he said.
“At one point, more encrypted communication companies linked to TOC and terrorist financers were based in Vancouver than anywhere else in the world,” he added. “These platforms were used globally—by cartels, arms traffickers, terrorists, state proxies. That tells you all you need to know about how Canada is perceived by adversaries.”
So why is Canada such a prime target? Chrustie identifies four layers of failure: strategy, structure, systems, and culture.
“We lack a cohesive, public national security strategy,” he said. “Unlike the United States or Australia, Canada doesn’t clearly define TOC as a strategic national threat. We don’t have a single, unified doctrine coordinating our federal agencies—police, intelligence, border services, foreign affairs. And TOC thrives in those gaps.”
“Our institutions are siloed,” he continued. “Policing is on the front line, but CSIS, CBSA, military and CSE aren’t always integrated. Right now, the RCMP is expected to shoulder most of the burden. But that’s unsustainable. We need an all-agency model.”
Canada’s legal and regulatory systems are another weak point. “Our legal system is designed for a domestic, rule-of-law environment. It’s ill-suited to confront global adversaries who don’t play by those rules,” Chrustie said. “Disclosure rules from Stinchcombe, Charter constraints, and evidentiary burdens mean that complex prosecutions often fall apart or never proceed.”
Finally, Chrustie warned that Canadian political culture is its most underappreciated vulnerability. “Canadians are culturally indifferent to national security,” he said. “We’ve taken a maternalistic approach—shielding the public from harsh realities, hoping to avoid panic or xenophobia. But that silence has allowed foreign actors to operate here with little resistance.”
“The historical paternalist approach of governments and bureaucrats—‘we won’t discuss these issues in public, we are the experts’—that thinking is outdated,” he said. “China, Russia, Iran and North Korea are the biggest fans of that mindset.”
Asked what a real solution looks like, Chrustie offered a sweeping and urgent framework: a national strategy naming hostile states and TOC as geopolitical threats; centralized agency coordination; intelligence-led disruption operations with allies abroad; and legal reforms enabling proactive countermeasures.
“We either need carve-outs with enhanced powers for TOC-related and foreign threat investigations—or we rely more on foreign-facing disruption efforts and accept that prosecutions are secondary,” he said.
He also emphasized grassroots engagement. “The solutions are in the communities, not in the siloed offices of governments,” Chrustie said. “We need to engage business leaders, civic organizations, educators, and diaspora communities. We need to build national resilience—not just enforce laws after the damage is done.”
His closing warning was as stark as his opening diagnosis.
“Canada is a saturated and vulnerable target,” he said. “And until we stop treating this as a criminal justice problem and start treating it as an integrated national security emergency, we will continue to lose ground.”
“There is no room for spectators.”
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
Crime
Vancouver police seize fentanyl and grenade launcher in opioid-overdose crisis zone

Vancouver police say they have seized a grenade launcher, four guns, and nearly 500 grams of fentanyl and other hard drugs from a fortified Downtown Eastside rooming house that was allegedly feeding a synthetic opioid supply line through the city’s most drug-ravaged blocks.
“Task Force Barrage has come to an end, but our work to curb violence and disrupt organized crime in the Downtown Eastside continues,” Sergeant Steve Addison said, adding “the proliferation of violence and weapons in some residential buildings continues to put the neighbourhood at risk.”
The latest investigation began November 13, when a 42-year-old man suffered serious injuries in an assault near Carrall Street and East Cordova and was taken to hospital. Officers followed leads to a rooming house at 50 East Cordova Street, in the heart of a street-level open drug market that has become notorious in photos and news clips around the world.
On November 18, police say they uncovered a stockpile of illicit drugs, guns and weapons in three rooms of the East Cordova building. According to Addison, there are signs that parts of the property, which is supposed to house low-income residents, were repurposed as a hub to store weapons and distribute contraband throughout the neighbourhood, with some areas “fortified with countersurveillance measures to avoid detection from law enforcement.”
Items seized include four firearms, two imitation guns, a grenade launcher, a firearm suppressor, seven machetes, four flare guns, bullwhips, baseball bats, body armour, handcuffs and ammunition. Officers also seized 486 grams of fentanyl, cannabis, Dilaudid pills and methamphetamine – a quantity police say represents more than 2,500 single doses.
Meanwhile, in a separate update posted November 26 — the day before VPD announced the Cordova Street raid — Vancouver Fire Rescue Services said that on Tuesday, November 21, firefighters responded to 54 overdoses, the highest single-day total in the department’s history. The service said it averaged about 16 overdose calls per day in May, but that figure has surged in recent weeks, and during the most recent income-assistance week, firefighters were averaging roughly 45 overdose responses per day.
While police have not publicly linked the East Cordova seizure to any specific cartel, the mix of fentanyl, fortified real estate and a small armoury of weapons closely tracks the profile of a separate, high-profile British Columbia case in which provincial authorities say a Sinaloa Cartel–aligned cell embedded itself just south of Vancouver.
In that case, a civil forfeiture lawsuit alleged a Sinaloa Cartel–linked fentanyl and cocaine trafficking group set up in a multi-million-dollar mansion near the U.S. border, capable of negotiating major cocaine import deals with Ismael Garcia—known as “El Mayo”—the reputed Sinaloa Cartel chief. According to the filings, the Canada-based syndicate involved at least three men, and belonged to a violent drug trafficking organization that “used and continues to use violence, or threats of violence, to achieve its aims.”
Investigators alleged the Surrey-based group trafficked ketamine, methamphetamine, Xanax, oxycodone, MDMA and fentanyl. “As part of these efforts, the drug trafficking organization has agreed to, and made arrangements to, purchase cocaine from the Cártel de Sinaloa in Mexico,” the filings stated. They added: “the Sinaloa Cartel is a terrorist entity, and the government of Canada listed it as such on February 20, 2025.”
RCMP said they uncovered a substantial cache of weapons and narcotics during a search of the Surrey property on 77th Avenue on September 23, 2024. Opioids seized from the mansion included 400 grams of counterfeit Xanax, 810 oxycodone pills, 5.5 grams of fentanyl and nearly a kilogram of Ecstasy. The province is now seeking forfeiture of the house, which sits about 20 minutes from the Peace Arch border crossing north of Seattle.
Court submissions detailed an arsenal of 23 weapons – ten handguns, two sawed-off shotguns, two hunting rifles, seven assault rifles (two reportedly fitted with screw-on suppressors), and a speargun – alongside about 3.5 kilograms of ketamine and methamphetamine hidden in a compartment in one suspect’s room, hundreds of counterfeit alprazolam pills, a stash of oxycodone, and nearly CAD 15,000 in bundled cash “not consistent with standard banking practices.”
Viewed together, the Downtown Eastside raid and the Surrey mansion case sketch out different ends of what appears to be the same continuum, ultimately pointing to senior criminal leaders in Mexico and China.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Crime
B.C.’s First Money-Laundering Sentence in a Decade Exposes Gaps in Global Hub for Chinese Drug Cash

Port Coquitlam Mayor Brad West met with Biden Secretary of State Antony Blinken in 2023, to discuss Canada’s enforcement gap on fentanyl money laundering.
Chinese underground-banking conviction is a baby step in a jurisdiction that some experts see as North America’s center of gravity for transnational crime.
In a milestone that is staggering for its rarity in a jurisdiction regarded as a global nexus of Chinese transnational money laundering that facilitates fentanyl trafficking for Mexican and Iranian gangs, British Columbia’s anti-gang unit has finally secured its first money laundering sentencing in a decade.
On Monday, a B.C. Supreme Court judge sentenced 37-year-old Richmond resident Alexandra Joie Chow to 18 months in jail for laundering the proceeds of crime, following a six-year investigation that targeted illegal Chinese underground casinos and unlicensed money transfer businesses in Metro Vancouver. The court also ordered the forfeiture of cash and bank drafts seized during the probe, the Combined Forces Special Enforcement Unit of B.C. (CFSEU) says.
Chow’s case marks the first time in roughly ten years that a money-laundering investigation in British Columbia has actually resulted in a sentencing — a remarkable data point in a province where hundreds of billions have washed through casinos, banks and real estate, according to The Bureau’s estimates, yet almost no one has been successfully prosecuted for the underlying financial crime.
While Chow’s case in itself is relatively small in dollar terms, it followed the catastrophic collapse of the RCMP’s E-Pirate probe into a Richmond underground bank called Silver International, which was alleged to have laundered over $1 billion through a network of Chinese Triad leaders known as “Sam Gor” or “The Company” — a scheme that moved drug cash collected in Chinese diasporas across North and Latin America, cycling the funds back to hundreds of accounts in China, in part through lending gang cash to Asian high-rollers who washed massive sums through B.C. government casinos.
The collapse of E-Pirate raised significant concerns in Washington around Canada’s capacity to prosecute fentanyl money laundering and trafficking. Vancouver-area Mayor Brad West has told The Bureau that the failure of Canadian authorities to secure convictions in that case was explicitly noted in 2023 by senior figures in the Biden administration, including Secretary of State Antony Blinken, in discussions about Canada’s role in North American drug trafficking.
Chow pleaded guilty in February 2025 to one count of laundering proceeds of crime after prosecutors alleged she was part of an underground loan-sharking and money-services scheme that operated in the Lower Mainland. Her plea came almost two years after B.C.’s Joint Illegal Gaming Investigation Team first announced charges.
The trail to that conviction began in August 2019, when B.C.’s Joint Illegal Gaming Investigation Team (JIGIT) quietly launched an investigation into the alleged loan-sharking and money-laundering activities of a man and a woman. Investigators believed the suspects were charging criminal interest rates and operating an unlicensed money services business.
Over the course of the probe, police say they developed evidence that the suspects allegedly laundered more than $828,000 in Canadian cash. On November 5, 2021, JIGIT executed a series of search warrants on properties in Richmond and Burnaby, as well as three vehicles associated to the investigation.
The searches resulted in the seizure of a number of items believed to be tied to money laundering and loan-sharking, including score sheets with client names and payment due dates, four cellular phones, two bank drafts totaling $50,000, and $10,680 in Canadian currency and three high-end vehicles.
Two years later, on November 1, 2023, the B.C. Prosecution Service approved four sets of charges against Chow: money laundering, possessing proceeds of crime, and entering into agreements to receive criminal-rate interest — classic loan-sharking. No other individuals were ultimately charged in the case.
As CFSEU-BC media officer Sgt. Sarbjit Sangha put it in the unit’s statement Monday, this is “the first time in a decade that a money laundering investigation in British Columbia has resulted in a sentencing,” and it “underscores the impact of collaborative investigative work” and JIGIT’s mandate to tackle illegal gaming tied to organized crime, loan-sharking and sophisticated bookmaking.
The scale of the enforcement gap this case exposes is critical to understanding current irritants between Washington and Ottawa, and the Trump administration’s leverage of tariffs on Canada. That campaign of economic pressure, some U.S. and Canadian officials have informed The Bureau, apparently extends from deep concerns in both the Biden and Trump administrations over Ottawa’s lack of meaningful action against massive money laundering through Canada’s financial system — including the TD Bank fentanyl money laundering case prosecuted in the Tri-State area, which exposed transactions similar to those revealed in the Chow investigation in Richmond.
The Cullen Commission into money laundering in B.C. found that by 2014, casinos in the province were accepting nearly $1.2 billion in cash transactions of $10,000 or more in a single year, many involving patrons who showed classic indicators of criminal cash — bricks of small bills delivered in bags by couriers closely watched by organized-crime investigators. JIGIT itself was created as part of the province’s response to that crisis. In a 2021 presentation to the Cullen Commission, then-Unit Commander Staff Sgt. Joel Hussey explained that JIGIT’s money-laundering and loan-sharking probes were focused on “top-tier” organized criminals exploiting casinos and banks, particularly at Richmond’s River Rock Casino Resort, Vancouver’s Parq Casino and Burnaby’s Grand Villa, where investigators saw the most entrenched high-roller criminal activity.
Yet the province’s record in actually getting such cases to the finish line has been abysmal. The most notorious example remains E-Pirate, the massive RCMP investigation that targeted Silver International, a Richmond underground bank alleged to be moving over $1 billion a year in drug and casino cash for Chinese and Mexican cartels and Middle Eastern networks. That case collapsed in 2018–2019 after federal prosecutors mistakenly exposed a confidential informant, leading to a stay of charges despite years of work and huge evidence seizures.
International bodies such as the Financial Action Task Force later used E-Pirate as a case study, describing a “professional” Richmond-hub laundering network that allegedly used B.C. casinos and real estate to clean and move drug proceeds on a global scale. Cullen’s final report, released in 2022, concluded that sophisticated money-laundering networks were moving “staggering amounts” of illicit funds through B.C., while law-enforcement and regulatory agencies failed to respond in a timely or coordinated way.
Whether Chow’s 18-month sentence becomes a template for future Vancouver Model prosecutions — or remains an isolated success in a province still struggling to hold money launderers to account — will be the next test for B.C.’s anti-gang and financial-crime enforcement regime.
Those questions are not just academic in Ottawa. As The Bureau has previously reported, senior officials in Washington — Democrats and Republicans alike — have for years warned that Canada’s failure to deliver sustained proceeds-of-crime prosecutions, and its lack of a RICO-style racketeering law, has turned the country into a structural weak point in North America’s fight against cartel-linked fentanyl networks.
As reported previously by The Bureau, in a high-level meeting in 2023, according to Vancouver-area Mayor Brad West, a longstanding critic of transnational drug networks in his province, Secretary of State Antony Blinken stressed that Washington believes Beijing is effectively weaponizing fentanyl against North Americans—and that Canada stands out as a worrisome weak link in the global supply chain.
West, reflecting on his encounter with Blinken, argued that only bold legislative change, coupled with a willingness to challenge entrenched legal barriers, can dispel the U.S. government’s unease over Canada’s approach. “Secretary Blinken specifically noted the lack of a RICO-style law in Canada,” West said. “He talked about how, in the United States, that law had been used to take down large portions of the mafia. Then he looked at us—one of America’s closest allies—and saw a very concerning weak link.”
According to West, Blinken pointed to China’s role in funneling precursor chemicals into fentanyl labs. He warned that China’s government, if inclined, could stem the flow but has little interest in doing so. “He was incredibly candid,” West recalled. “He confirmed the connection between the Chinese Communist Party, the triads, and the Mexican cartels, telling me these groups are working together—and it’s Canada where they’re finding a safe operating base.”
Blinken also conveyed to West that U.S. agencies had grown hesitant to share certain intelligence with their Canadian counterparts. “He told me that U.S. intelligence and law enforcement are withholding some evidence because they don’t believe we’ll act on it,” West explained. “They’ve lost confidence.”
West added that in ongoing communications, he had learned American officials are shocked that major figures in Asian organized crime “seem to have so much access to our political class. They’re basically saying, ‘What’s going on in Canada?’”
A major concern, according to West, is how known criminals manage to appear at political events or fundraisers with little oversight. “It’s not necessarily that politicians are complicit, but our political structures have weak guardrails,” West said. “The Americans see pictures of transnational criminals mingling at official gatherings and find it baffling.”
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoRecent price declines don’t solve Toronto’s housing affordability crisis
-

 MAiD20 hours ago
MAiD20 hours agoFrom Exception to Routine. Why Canada’s State-Assisted Suicide Regime Demands a Human-Rights Review
-

 MAiD2 days ago
MAiD2 days agoHealth Canada report finds euthanasia now accounts for over 5% of deaths nationwide
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoTech Mogul Gives $6 Billion To 25 Million Kids To Boost Trump Investment Accounts
-

 Automotive2 days ago
Automotive2 days agoPower Struggle: Governments start quietly backing away from EV mandates
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoUnceded is uncertain
-

 Business18 hours ago
Business18 hours agoCarney government should privatize airports—then open airline industry to competition
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoNew Chevy ad celebrates marriage, raising children







