Brownstone Institute
The Many Layers of the Canada-India Diplomatic Dispute

From the Brownstone Institute
BY
Canada–India relations have been trapped in a downward spiral following an explosive statement in Parliament by Prime Minister (PM) Justin Trudeau on September 18. He alleged involvement of Indian agents in the June 18 killing of Hardeep Singh Nijjar, a prominent British Columbian (BC) Sikh leader who was on India’s most wanted watchlist.
India has rejected the charge as “absurd” and denounced Canada as a “safe haven” for “terrorists, extremists and organized crime”—language normally reserved for Pakistan.
To understand the unexpected diplomatic tensions between the two Commonwealth parliamentary democracies, we need to recall the historical context, the democratic backsliding in both countries even while each prides itself on being a leading exemplar of democracy, and the shifting global order in which the existing normative architecture is simultaneously challenged by voices from the Global South and being reconfigured by hard-nosed geopolitical calculations.
Historical Baggage on Both Sides
Canada’s first major disillusionment with independent India was the latter’s refusal to frame its approach to world affairs through the West’s moral lens in the three Indochina control commissions set up after the Geneva Agreements of 1954, which India chaired and which was the subject of my PhD dissertation.
There has been similar long-simmering resentment in Ottawa at the perceived ‘betrayal’ by India when it used Canadian-supplied reactors to conduct a nuclear test in 1974, adding insult to injury by calling it a “peaceful nuclear explosion.” Pierre Trudeau, the current PM’s father who was PM in 1968–79 and 1980–84, was also irritated by Indian PM Indira Gandhi’s propensity to moralize.
Today it is Indians who are put off by the younger Trudeau’s virtue-signalling self-righteousness over race and gender-obsessed identity politics. Nothing illustrates this better than his bizarre apology on September 27 for the way in which 98-year-old Ukrainian-Canadian Yaroslav Hunka was honoured by Canada’s Parliament on September 22, in the presence of visiting President Volodymyr Zelensky, with a standing ovation.
It turns out he had fought as part of a Ukrainian Waffen-SS unit against the Soviet Union that was a Western ally at the time in World War II. As well as causing grave offence to Holocaust victims and Jews, Trudeau said in a belated apology: “It also hurt Polish people, Roma people, 2SLGTBQI+ people [don’t ask: I can’t be bothered], disabled people, racialized people” [another woke linguistic innovation of the Trudeau government].
Sikhs number around 25 million in India and are spread all over the country but concentrated in Punjab. Although just under two percent of India’s total population they are the majority community in Punjab. In a Pew Research Survey in 2021, a stunning 95 percent of them said they were extremely proud of their Indian identity; 70 percent said anyone who disrespects India is not a good Sikh; and only 14 percent said Sikhs face significant discrimination in India.
The armed insurgency for Khalistan as a separate homeland for Sikhs died out in India thirty years ago but left a bitter legacy. The Indian Army assault on the Golden Temple in Amritsar—the holiest site for all Sikhs—and the killing of 3,000 Sikhs in the pogrom following Indira Gandhi’s assassination by Sikh bodyguards in 1984 inflamed anti-India passions among Sikhs that remain raw, around the world as well as in India.
Numbering 770,000, Sikhs account for two percent of Canada’s population—a higher proportion than in India—and a little under half of Indo-Canadians. Canada is home to 5 percent of diaspora Indians and 13 percent of Indian overseas students who make up 40 percent of foreign students in Canada. It accounts for 5 percent of India’s foreign tourists but under 0.7 percent of its trade and foreign investment.
Canada-based Sikh extremists blew up an Air India plane in 1985 killing 329 people: the biggest mass murder in Canadian history. In 1982, India’s request to extradite Talwinder Singh Parmar was reportedly rebuffed by Canada. He was one of the architects of the Air India bombing.
Trudeau’s 2018 India Trip
An early indication that Trudeau is a show-pony who lacks policy nous and political street-smarts came with his week-long trip to India in February 2018. It was a PR disaster at home because it looked like an extended family vacation at taxpayer expense, and a political disaster in India. He was ridiculed for the occasional demonstration of Bhangra dancing skills and nonstop display of sartorial splendour more suited to lavish Bollywood wedding scenes than quotidian Indian lifestyle.
More seriously, Jaspal Atwal, convicted in Canada of attempting to kill a visiting Indian cabinet minister in 1986, posed with Trudeau’s wife in Mumbai and was invited to the official dinner at the Canadian High Commission in New Delhi. National security adviser Daniel Jean mooted the conspiracy theory that Atwal’s presence was arranged by factions within the Indian government. Trudeau backed him.
India’s Farmers’ Protest, 2020–21
In September 2020, the Modi government passed three farm reform laws to open up the agricultural sector to market forces and discipline, encourage scale economies by creating a national market, deregulate trade in agricultural produce, and facilitate private investment. Farmers worried that the reforms would leave them vulnerable to large and predatory agri-conglomerates.
Fearing price volatility and loss of stable income, many Sikh farmers launched a mass protest that included blocking traffic in and out of Delhi with trucks and farm vehicles. “Canada will always be there to defend the right of peaceful protest,” Trudeau unnecessarily and unhelpfully declared on November 30. When India denounced the “ill-informed” remark, Trudeau doubled down and urged “dialogue.” Modi capitulated to the farmers in December 2021 and the protest ended peacefully.
Setbacks to Democracy in India and Canada
Both countries’ leaders are open to charges of violating liberal democratic norms and the rule of law. Modi, for pandering to militant Hinduism, eroding minority rights, muzzling the media and silencing critics. Trudeau, because of a reputation for being an unserious dilettante who never grew up or into the leader of a G7 country.
I have previously criticised India’s growing democratic deficit on Modi’s watch, decried efforts to erode Muslims’ equality of Indian citizenship, and warned of the danger of turning India into a Hindu Pakistan. In addition, however, for many of us who were and remain shocked and appalled at the extent of Canada’s assault on citizens’ rights and liberties in its lockdown, mask, and vaccine mandates, there is an undeniable element of schadenfreude at Trudeau’s fall from the virtue signallers’ pedestal.
In early 2022, Canada’s truckers became icons of a larger struggle for freedom and liberty against growing state power that transcended Canada. The Freedom Convoy was the largest, longest, and noisiest honk-fest of a demonstration against a Canadian government in decades. It was mostly peaceful, good-humoured, supported by large numbers of Canadians and also inspired other countries to take up the cause, including America and Australia.
Yet, the world’s emoter-in-chief solemnly intoned in Parliament on February 9 that the truckers were “trying to blockade our economy, our democracy and our fellow citizens’ daily lives.” Trudeau refused to meet and talk to them (“dialogue” for thee, Mr Modi, but not for me). The government froze the protestors’ bank accounts and of anyone linked with the protests, without due process, appeals process, or court order.
On February 21, Parliament approved the declaration of emergency and authorized Trudeau to use force against the protestors. Justice Minister David Lametti boasted: “We took measures that had been applied to terrorism and applied them to other illegal activity.” Western leaders responded with studied silence. Trudeau revoked the emergency on the 23rd, proving they weren’t needed in the first place. His hypocrisy vis-à-vis his support for India’s farm protests was duly noted in India.
We Know You are Guilty. Now Help Us Prove It.
Canada has levelled grave charges against a friendly government without tabling any supporting evidence. Trudeau’s choice of words was curious. Canada’s security agencies, he said, were “actively pursuing credible allegations of a potential link” to Indian agents, not credible “evidence” of “involvement.” In effect Trudeau said to Modi: We believe you are guilty. Now help us prove it. In any joint investigation, both sides will want to protect sources and methods, limiting the scope for collaboration.
The statement covers an extraordinarily wide range of possibilities. At its most innocuous, some Indian embassy personnel might have held meetings with third persons who were in contact with the killers. At its most serious, Indian agents were the prime organizers of the hit on Nijjar or were themselves the assassins.
Key questions for outsiders are: At which point in the continuum should Canadian agencies expect to be informed by the Indians of what was happening? Which is the threshold of unacceptable complicity by Indian agents? Which is the crossover point at which Canada moves from behind-the-scenes efforts to resolve the differences and goes public with the charge of Indian involvement?
Having chosen to raise the allegation in Parliament, the onus is on Trudeau to convince India, allies, and Canadians, not on Modi to prove the negative. Arindam Bagchi, a foreign ministry spokesman, says India is “willing to look at any specific information that is provided to us. But so far, we have not received any.” The failure to provide more detail and evidence has generated disquiet even in Canada with the opposition leader, the centre-left Globe and Mail and the centre-right National Post all saying that Canadians deserve the full truth.
The correct procedure would have been to let the police complete investigations, charge alleged killers, provide evidence of official complicity in the form of forensic analysis, witness testimony, CCTV and/or surveillance photo, audio and video corroboration, and only then request Indian assistance in joint investigations and, if required, extradition to facilitate court proceedings in Canada.
Instead, Trudeau has patented a unique blend of lack of due diligence and incompetent governance. The latest manifestation of this was the Hunka fiasco. The kerfuffle has underlined the dangers of diaspora politics, the lax standards of background checks on migrants, and the keystone cops nature of the Trudeau government’s foreign policy competence. This too has magnified the international and domestic damage from the tiff with India.
“Tails You Lose:” If We Didn’t Do It, You Are Wrong
It is clear from what has been said publicly that Canadian intelligence agencies do not, at this stage, believe that this was a direct Indian hit squad operating on Canadian soil. If they had become aware of an independent plot to kill Nijjar, in light of Canada’s decades-long inaction against Canada-based financing and training for terrorist and criminal actions on Indian targets, Indian officers might have felt no obligation to warn the relevant Canadian agencies.
Only the naïve would believe the Five Eyes club of Anglosphere countries (Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the UK, and the US) doesn’t conduct human and electronic surveillance and share intelligence. David Cohen, US ambassador to Canada, confirmed that “shared intelligence among Five Eyes partners” had informed Trudeau of possible Indian involvement. As India’s global interests and national capabilities grow, it too will invest in increasing intelligence gathering and covert operational infrastructures. But democracies do not perpetrate acts of violence on one another’s citizens and territory.
At present, the geographical focus of India’s external intelligence agency, the Research and Analysis Wing, is its own neighbourhood and the tools of its tradecraft are bribery and blackmail. Although some would like to copy the example of Israel’s Mossad, for now RAW lacks the training, assets, and authority to kill enemies of the state sheltering in foreign lands. (It may act through domestic rivals.)
Modi has been willing to expand the limits of the militarily possible against hostile militant groups based in Myanmar and Pakistan. But India is not believed to have sanctioned state killings even in Pakistan, despite public pressure to do so.
In a conversation at the Council on Foreign Relations in New York on September 26, eight days on from Trudeau’s public accusation, rather than duck and weave, India’s Foreign Minister Subrahmanyam Jaishankar was unequivocal in saying that India had told Canada that assassinations is not government policy, but that it would look into specific and relevant information provided by Ottawa. His denials have been firm enough that if he is gaslighting, he will pay a high individual reputational price, which adds to the presumption of credibility to his statement.
There is an additional political calculation. On the one hand, at best India would have only a rudimentary capability to carry out such missions in Canada. Although possible, it’s highly implausible. On the other hand, after Edward Snowden’s revelations of the US as a surveillance state and the international headlines about how the National Security Agency had eavesdropped on then-German Chancellor Angela Merkel’s and other European leaders’ conversations for decades, India would be stupid to believe it could escape detection by a Five Eyes country with sophisticated human and signals intelligence capabilities. The risk of seriously damaging relations with all five countries seems too high for state sanction of Nijjar’s murder. It could also fatally undermine India’s international campaign against Pakistan as a state sponsor of terrorism.
The failure to provide more detail and evidence has generated disquiet within Canada. The opposition Conservative Party is comfortably ahead in polls. The latest poll would see it winning 179 of the 338 seats, to the Liberal’s 103. Opposition leader Pierre Poilievre has urged Trudeau to reveal more details. His support for a tough response was qualified with “If true.” He also contrasted Trudeau’s softer actions in earlier dealings with China that had held two Canadian citizens hostage for many months. Both the centre-left Globe and Mail and the centre-right National Post say Canadians deserve the full truth.
India in turn holds fast to the allegation that Canadian authorities have been soft on diaspora terrorism, too tolerant of anti-Indian activities and rhetoric because of the electoral importance of the concentrated Sikh vote in BC and Ontario. Trudeau has been surprisingly indifferent to the sensitivity of the Sikh factor in Canada–India relations and unwilling to vigorously target terrorist financing from Canada. During Trudeau’s 2018 trip to India Amarinder Singh, Punjab’s Sikh premier (2002–07, 2017–21), gave him a list of wanted terrorist fugitives that included Nijjar’s name. Nothing happened.
As noted by Omer Aziz, a former foreign policy adviser to Trudeau, diaspora-courting domestic politics often distorts foreign policy priorities. Trudeau’s minority government is reliant on the support of the New Democratic Party (NDP) to stay in power. Its Sikh leader Jagmeet Singh is viewed in India as “a known Khalistan promoter and supporter:” a sympathiser at best and an activist at worst. His public statements in response to an alleged Indian link to Nijjar’s killing referenced acts of “violence, persecution,” “torture and even death” by Indian authorities. This will not assuage India’s concerns that Trudeau is captive to domestic diaspora politics.
Many Canadians feel growing unease at migrant communities importing the troubles of their homeland into Canada. In a widely-circulated video, Gurpatwant Singh Pannun, Nijjar’s US-based lawyer, has urged Hindu Indo-Canadians to go back to India. Disinterest in policies to encourage and assist immigrant groups to adopt cultural norms and core political values of their new country can, for some groups, create isolated, self-contained parallel worlds in which they import all the prejudices and conflicts from their home countries.
Trudeau is going to have to put up or shut up. He has gone too far on a limb to survive prevarication and backtracking. If the allegations are not substantiated, he will damage his standing in Canada and internationally and worsen already strained relations with India.
Attention will focus on the foreign policy risks of diaspora communities and Canada’s lukewarm efforts to rein in their excesses. Allies will not be happy at being put in the middle of a bilateral spat to which Trudeau has contributed by failing to recognize the complexities and magnitude of India’s internal security challenges and not taking its concerns seriously.
Nijjar was a shady character who entered Canada illegally on a false passport in 1997. Eleven days after his claim to refugee status was rejected, he married a woman who sponsored him for immigration. That too was rejected, indicating a marriage of convenience. There is also an undated video (at about the 18-minute mark), of uncorroborated authenticity, of him at a training camp somewhere in BC with an illegal assault rifle. Despite this background, he was granted citizenship in 2015. This doesn’t seem like a mature and responsible approach to conferring citizenship.
An intra-Sikh quarrel in Canada, and in particular the occasionally violent “gurdwara [Sikh temple] politics” in BC, is another possible explanation for his murder. Indian intelligence had linked Nijjar to a hit on a local Sikh rival last year, raising the question: was he killed in a tit-for-tat assassination in the civil war?
Trudeau’s star power has faded. He has been buffeted by allegations of Chinese interference in Canada’s last election and criticised for the tardiness and softness of his response.
Payment on the Covid-era economic shutdowns and subsidies has come due in the form of inflationary pressures. Carson Jerema, a National Post editor, writes that at a time of sinking popularity, almost “everything this government does is calculated for political gain.” Creating “an international incident” with the allegation that India “is behind the murder of a Canadian citizen could be exactly the point.”
Nevertheless, if an uncooperative India is proven guilty in the world court of public opinion, it will deserve unqualified condemnation.
“Heads We Win:” If We Did It, We Are Right
States using targeted assassination as an instrument of national security policy is rare but not unknown, especially by major powers. President Barack Obama ordered assassination-by-drones of several suspected anti-American terrorists in the Afghanistan–Pakistan badlands. Most of those killed were not high-value targets in whose names the strikes were justified, but low-level combatants and civilians (16 percent of those killed in drone strikes 2004–12, according to data compiled by the New American Foundation).
Moreover, Obama also ordered a hit—without any due process of trial and conviction—of Anwar al-Awlaki, an American of Yemeni descent. Awlaki’s 16-year-old son was killed in a follow-up strike.
I have no doubt whatsoever that Obama had no intention of capturing Osama bin Laden alive. For practical purposes it was a targeted assassination whose morality did not trouble too many people, all things considered. For major powers, including Western powers, lethal action against grave threats based in foreign jurisdictions, if it is operationally feasible, will be judged to be morally permissible if the government is persistently unable or unwilling to take effective action.
Many Indians are exasperated with Trudeau’s pandering to diaspora “vote bank” politics. An editorial in the Indian Express concluded: “Trudeau appears to be engaging in toxic domestic politics by playing to the extremist fringe of the Sikh diaspora.” Amarinder Singh dismisses Trudeau’s allegations of Indian involvement in the killing and non-cooperation in the investigation as “a classic case of the pot calling the kettle black.” He adds: “It is common knowledge that Nijjar was killed because of rivalry over local gurdwara [Sikh temple] politics.”
Thus the net result is that Canada too finds itself in the international spotlight as a safe haven for extremists who use Canada as a base of operations against the interests of their countries of origin. Another example from South Asia is the presence in Canada of significant numbers of Sri Lankans and their role, often under coercion from activists, in financing the Tamil Tigers in that country’s civil war.
Modi has cultivated a strongman persona as a muscular nationalist. In the unlikely event that it is confirmed that India executed a successful hit on a wanted alleged terrorist in Canada, international reputational costs notwithstanding, it would give a big boost to his popularity leading into next year’s elections. In the context of how Western-based diaspora communities can encourage covert operations and military interventions, as in Iraq in 2003, it could also cement India’s reputation in the Global South as a country able and willing to stand up for its interests.
The Moral Rebalancing in a Shifting Global Order
Canada’s mainstream media would appear to be blind, still, to the grave global damage caused to the country’s liberal democracy brand and the international cynicism when Trudeau invokes commitment to the rule of law and human rights. In an editorial, the Globe and Mail noted that Canada’s “embarrassed allies” have essentially “averted their gaze” and refused to voice strong public condemnation of India. In the geopolitical reordering underway, the Globe explained: “The U.S. is clearly prepared to swallow Mr. Modi’s well-documented assaults on liberal democratic values.”
It’s past time that Western commentators woke up and smell the coffee. The era of the West being the arbiter of the moral compass for itself and for everyone else is over. The new assertiveness of several prominent countries among the rest reflects a self-confidence rooted in a position of strength.
In sharp contrast with Trudeau’s lightweight persona, Jaishankar has a deserved reputation for intellectual depth and gravitas to go with this his decades of experience as a career diplomat and then an articulate (but not angry) champion of India’s non-Western (but not anti-Western) perspectives. All these traits, plus the easy manner in which he connects to a policy audience in Washington, can be seen in this video of his interactive conversation at the Hudson Institute in Washington on September 29.
Jaishankar has been polite but firm in calling out the double standards of Western countries for their criticisms of India’s stance on the Ukraine war. In India’s annual statement to the UN General Assembly on September 26, he decried the reality that “it is still a few nations who shape the agenda and seek to define the norms.” Rule-makers cannot go on subjugating rule-takers indefinitely and we must not “countenance that political convenience determines responses to terrorism, extremism and violence.” Jaishankar’s pointed remarks on the persisting imbalances in the global order would have played well throughout the Global South.
Canada’s Soft Power Righteousness Has Collided with India’s Growing Hard Power Geopolitical Heft
So far, as noted by the Washington Post and also by Canada’s main national newspaper the Globe and Mail, Canada’s allies have offered only tepid support while attempting to walk the tightrope between an old ally and a growing strategic partner. Canada is a dependable ally but not a first-tier global power nor one with realistic alternatives to continued national security dependence on the US. Its soft-power credentials are a liability when the world has pivoted into a hard-power moment.
India is the anchor of the West’s Indo-Pacific strategy. Canada is outside both the Quad and AUKUS as the main bulwarks of the emerging anti-China resistance front. More than putting India in the dock, Christopher Sands, director of the Canada Institute at the Woodrow Wilson Center in Washington, told the BBC that Trudeau’s allegations have exposed Canada’s “moment of weakness.”
Jaishankar is in great demand at the world’s major foreign policy platforms and used his trip to the opening of the UN General Assembly to speak to multiple influential audiences in the US. As a result, for the first time, key American audiences will have been exposed to the decades-long Indian complaint about the operating space that has been given to extremist and criminal elements from India by a very permissive Canada that has its own political compulsions.
Jaishankar noted at the Hudson Institute event that while most Indians know this, not many Americans do. His comment about the relative knowledge and ignorance of Indians and Americans is illustrated in this video podcast on September 29 of an in-house discussion at the Woodrow Wilson Center. At around the 10-minute mark, Sands, an American, recalls the 1985 Air India bombing only to make two astonishing gaffes. He says it was a Montreal-Bombay flight over the Pacific and “almost all” the victims were Indian citizens. In fact Air India flight 182 was blown up over the Irish Sea en route from Montreal to Delhi via London.
The overwhelming majority of passengers were Canadian citizens and residents, albeit of Indian ancestry. But in the Canadian collective consciousness this seems to be remembered as a bombing in which the victims were mainly Indians, not Canadians.
The bigger picture that has been in existence for some considerable time provides the necessary context to the current Canadian charges. As a vibrant democracy, India doesn’t need lessons from others on the meaning of free speech. But freedom of speech does not extend to “incitement to violence.” That’s not a defence but “an abuse of freedom,” Jaishankar insisted.
It is not therefore simply a matter of other countries overriding their normative principles to accommodate policy to geopolitics. Rather, India is gaining some sympathy for its charge that Canada too has a case to answer and needs to put its own house in order. In other words, as far as Western democracies are concerned, ignoring the problem of migrant communities engaged in hostile activities in home countries is not a long-term solution to the policy dilemma.
Brownstone Institute
The Unmasking of Vaccine Science
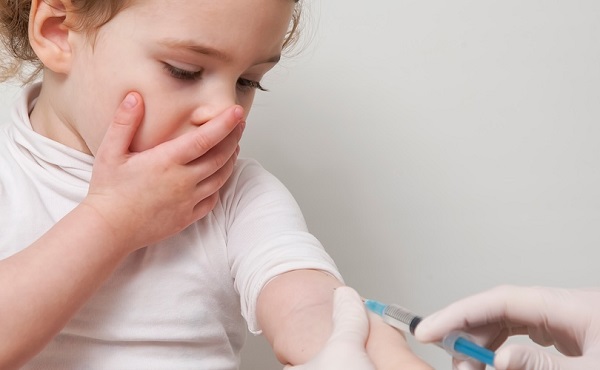
From the Brownstone Institute
By
I recently purchased Aaron Siri’s new book Vaccines, Amen. As I flipped though the pages, I noticed a section devoted to his now-famous deposition of Dr Stanley Plotkin, the “godfather” of vaccines.
I’d seen viral clips circulating on social media, but I had never taken the time to read the full transcript — until now.
Siri’s interrogation was methodical and unflinching…a masterclass in extracting uncomfortable truths.
A Legal Showdown
In January 2018, Dr Stanley Plotkin, a towering figure in immunology and co-developer of the rubella vaccine, was deposed under oath in Pennsylvania by attorney Aaron Siri.
The case stemmed from a custody dispute in Michigan, where divorced parents disagreed over whether their daughter should be vaccinated. Plotkin had agreed to testify in support of vaccination on behalf of the father.
What followed over the next nine hours, captured in a 400-page transcript, was extraordinary.
Plotkin’s testimony revealed ethical blind spots, scientific hubris, and a troubling indifference to vaccine safety data.
He mocked religious objectors, defended experiments on mentally disabled children, and dismissed glaring weaknesses in vaccine surveillance systems.
A System Built on Conflicts
From the outset, Plotkin admitted to a web of industry entanglements.
He confirmed receiving payments from Merck, Sanofi, GSK, Pfizer, and several biotech firms. These were not occasional consultancies but long-standing financial relationships with the very manufacturers of the vaccines he promoted.
Plotkin appeared taken aback when Siri questioned his financial windfall from royalties on products like RotaTeq, and expressed surprise at the “tone” of the deposition.
Siri pressed on: “You didn’t anticipate that your financial dealings with those companies would be relevant?”
Plotkin replied: “I guess, no, I did not perceive that that was relevant to my opinion as to whether a child should receive vaccines.”
The man entrusted with shaping national vaccine policy had a direct financial stake in its expansion, yet he brushed it aside as irrelevant.
Contempt for Religious Dissent
Siri questioned Plotkin on his past statements, including one in which he described vaccine critics as “religious zealots who believe that the will of God includes death and disease.”
Siri asked whether he stood by that statement. Plotkin replied emphatically, “I absolutely do.”
Plotkin was not interested in ethical pluralism or accommodating divergent moral frameworks. For him, public health was a war, and religious objectors were the enemy.
He also admitted to using human foetal cells in vaccine production — specifically WI-38, a cell line derived from an aborted foetus at three months’ gestation.
Siri asked if Plotkin had authored papers involving dozens of abortions for tissue collection. Plotkin shrugged: “I don’t remember the exact number…but quite a few.”
Plotkin regarded this as a scientific necessity, though for many people — including Catholics and Orthodox Jews — it remains a profound moral concern.
Rather than acknowledging such sensitivities, Plotkin dismissed them outright, rejecting the idea that faith-based values should influence public health policy.
That kind of absolutism, where scientific aims override moral boundaries, has since drawn criticism from ethicists and public health leaders alike.
As NIH director Jay Bhattacharya later observed during his 2025 Senate confirmation hearing, such absolutism erodes trust.
“In public health, we need to make sure the products of science are ethically acceptable to everybody,” he said. “Having alternatives that are not ethically conflicted with foetal cell lines is not just an ethical issue — it’s a public health issue.”
Safety Assumed, Not Proven
When the discussion turned to safety, Siri asked, “Are you aware of any study that compares vaccinated children to completely unvaccinated children?”
Plotkin replied that he was “not aware of well-controlled studies.”
Asked why no placebo-controlled trials had been conducted on routine childhood vaccines such as hepatitis B, Plotkin said such trials would be “ethically difficult.”
That rationale, Siri noted, creates a scientific blind spot. If trials are deemed too unethical to conduct, then gold-standard safety data — the kind required for other pharmaceuticals — simply do not exist for the full childhood vaccine schedule.
Siri pointed to one example: Merck’s hepatitis B vaccine, administered to newborns. The company had only monitored participants for adverse events for five days after injection.
Plotkin didn’t dispute it. “Five days is certainly short for follow-up,” he admitted, but claimed that “most serious events” would occur within that time frame.
Siri challenged the idea that such a narrow window could capture meaningful safety data — especially when autoimmune or neurodevelopmental effects could take weeks or months to emerge.
Siri pushed on. He asked Plotkin if the DTaP and Tdap vaccines — for diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis — could cause autism.
“I feel confident they do not,” Plotkin replied.
But when shown the Institute of Medicine’s 2011 report, which found the evidence “inadequate to accept or reject” a causal link between DTaP and autism, Plotkin countered, “Yes, but the point is that there were no studies showing that it does cause autism.”
In that moment, Plotkin embraced a fallacy: treating the absence of evidence as evidence of absence.
“You’re making assumptions, Dr Plotkin,” Siri challenged. “It would be a bit premature to make the unequivocal, sweeping statement that vaccines do not cause autism, correct?”
Plotkin relented. “As a scientist, I would say that I do not have evidence one way or the other.”
The MMR
The deposition also exposed the fragile foundations of the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine.
When Siri asked for evidence of randomised, placebo-controlled trials conducted before MMR’s licensing, Plotkin pushed back: “To say that it hasn’t been tested is absolute nonsense,” he said, claiming it had been studied “extensively.”
Pressed to cite a specific trial, Plotkin couldn’t name one. Instead, he gestured to his own 1,800-page textbook: “You can find them in this book, if you wish.”
Siri replied that he wanted an actual peer-reviewed study, not a reference to Plotkin’s own book. “So you’re not willing to provide them?” he asked. “You want us to just take your word for it?”
Plotkin became visibly frustrated.
Eventually, he conceded there wasn’t a single randomised, placebo-controlled trial. “I don’t remember there being a control group for the studies, I’m recalling,” he said.
The exchange foreshadowed a broader shift in public discourse, highlighting long-standing concerns that some combination vaccines were effectively grandfathered into the schedule without adequate safety testing.
In September this year, President Trump called for the MMR vaccine to be broken up into three separate injections.
The proposal echoed a view that Andrew Wakefield had voiced decades earlier — namely, that combining all three viruses into a single shot might pose greater risk than spacing them out.
Wakefield was vilified and struck from the medical register. But now, that same question — once branded as dangerous misinformation — is set to be re-examined by the CDC’s new vaccine advisory committee, chaired by Martin Kulldorff.
The Aluminium Adjuvant Blind Spot
Siri next turned to aluminium adjuvants — the immune-activating agents used in many childhood vaccines.
When asked whether studies had compared animals injected with aluminium to those given saline, Plotkin conceded that research on their safety was limited.
Siri pressed further, asking if aluminium injected into the body could travel to the brain. Plotkin replied, “I have not seen such studies, no, or not read such studies.”
When presented with a series of papers showing that aluminium can migrate to the brain, Plotkin admitted he had not studied the issue himself, acknowledging that there were experiments “suggesting that that is possible.”
Asked whether aluminium might disrupt neurological development in children, Plotkin stated, “I’m not aware that there is evidence that aluminum disrupts the developmental processes in susceptible children.”
Taken together, these exchanges revealed a striking gap in the evidence base.
Compounds such as aluminium hydroxide and aluminium phosphate have been injected into babies for decades, yet no rigorous studies have ever evaluated their neurotoxicity against an inert placebo.
This issue returned to the spotlight in September 2025, when President Trump pledged to remove aluminium from vaccines, and world-leading researcher Dr Christopher Exley renewed calls for its complete reassessment.
A Broken Safety Net
Siri then turned to the reliability of the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) — the primary mechanism for collecting reports of vaccine-related injuries in the United States.
Did Plotkin believe most adverse events were captured in this database?
“I think…probably most are reported,” he replied.
But Siri showed him a government-commissioned study by Harvard Pilgrim, which found that fewer than 1% of vaccine adverse events are reported to VAERS.
“Yes,” Plotkin said, backtracking. “I don’t really put much faith into the VAERS system…”
Yet this is the same database officials routinely cite to claim that “vaccines are safe.”
Ironically, Plotkin himself recently co-authored a provocative editorial in the New England Journal of Medicine, conceding that vaccine safety monitoring remains grossly “inadequate.”
Experimenting on the Vulnerable
Perhaps the most chilling part of the deposition concerned Plotkin’s history of human experimentation.
“Have you ever used orphans to study an experimental vaccine?” Siri asked.
“Yes,” Plotkin replied.
“Have you ever used the mentally handicapped to study an experimental vaccine?” Siri asked.
“I don’t recollect…I wouldn’t deny that I may have done so,” Plotkin replied.
Siri cited a study conducted by Plotkin in which he had administered experimental rubella vaccines to institutionalised children who were “mentally retarded.”
Plotkin stated flippantly, “Okay well, in that case…that’s what I did.”
There was no apology, no sign of ethical reflection — just matter-of-fact acceptance.
Siri wasn’t done.
He asked if Plotkin had argued that it was better to test on those “who are human in form but not in social potential” rather than on healthy children.
Plotkin admitted to writing it.
Siri established that Plotkin had also conducted vaccine research on the babies of imprisoned mothers, and on colonised African populations.
Plotkin appeared to suggest that the scientific value of such studies outweighed the ethical lapses—an attitude that many would interpret as the classic ‘ends justify the means’ rationale.
But that logic fails the most basic test of informed consent. Siri asked whether consent had been obtained in these cases.
“I don’t remember…but I assume it was,” Plotkin said.
Assume?
This was post-Nuremberg research. And the leading vaccine developer in America couldn’t say for sure whether he had properly informed the people he experimented on.
In any other field of medicine, such lapses would be disqualifying.
A Casual Dismissal of Parental Rights
Plotkin’s indifference to experimenting on disabled children didn’t stop there.
Siri asked whether someone who declined a vaccine due to concerns about missing safety data should be labelled “anti-vax.”
Plotkin replied, “If they refused to be vaccinated themselves or refused to have their children vaccinated, I would call them an anti-vaccination person, yes.”
Plotkin was less concerned about adults making that choice for themselves, but he had no tolerance for parents making those choices for their own children.
“The situation for children is quite different,” said Plotkin, “because one is making a decision for somebody else and also making a decision that has important implications for public health.”
In Plotkin’s view, the state held greater authority than parents over a child’s medical decisions — even when the science was uncertain.
The Enabling of Figures Like Plotkin
The Plotkin deposition stands as a case study in how conflicts of interest, ideology, and deference to authority have corroded the scientific foundations of public health.
Plotkin is no fringe figure. He is celebrated, honoured, and revered. Yet he promotes vaccines that have never undergone true placebo-controlled testing, shrugs off the failures of post-market surveillance, and admits to experimenting on vulnerable populations.
This is not conjecture or conspiracy — it is sworn testimony from the man who helped build the modern vaccine program.
Now, as Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy, Jr. reopens long-dismissed questions about aluminium adjuvants and the absence of long-term safety studies, Plotkin’s once-untouchable legacy is beginning to fray.
Republished from the author’s Substack
Brownstone Institute
Bizarre Decisions about Nicotine Pouches Lead to the Wrong Products on Shelves

From the Brownstone Institute
A walk through a dozen convenience stores in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, says a lot about how US nicotine policy actually works. Only about one in eight nicotine-pouch products for sale is legal. The rest are unauthorized—but they’re not all the same. Some are brightly branded, with uncertain ingredients, not approved by any Western regulator, and clearly aimed at impulse buyers. Others—like Sweden’s NOAT—are the opposite: muted, well-made, adult-oriented, and already approved for sale in Europe.
Yet in the United States, NOAT has been told to stop selling. In September 2025, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued the company a warning letter for offering nicotine pouches without marketing authorization. That might make sense if the products were dangerous, but they appear to be among the safest on the market: mild flavors, low nicotine levels, and recyclable paper packaging. In Europe, regulators consider them acceptable. In America, they’re banned. The decision looks, at best, strange—and possibly arbitrary.
What the Market Shows
My October 2025 audit was straightforward. I visited twelve stores and recorded every distinct pouch product visible for sale at the counter. If the item matched one of the twenty ZYN products that the FDA authorized in January, it was counted as legal. Everything else was counted as illegal.
Two of the stores told me they had recently received FDA letters and had already removed most illegal stock. The other ten stores were still dominated by unauthorized products—more than 93 percent of what was on display. Across all twelve locations, about 12 percent of products were legal ZYN, and about 88 percent were not.
The illegal share wasn’t uniform. Many of the unauthorized products were clearly high-nicotine imports with flashy names like Loop, Velo, and Zimo. These products may be fine, but some are probably high in contaminants, and a few often with very high nicotine levels. Others were subdued, plainly meant for adult users. NOAT was a good example of that second group: simple packaging, oat-based filler, restrained flavoring, and branding that makes no effort to look “cool.” It’s the kind of product any regulator serious about harm reduction would welcome.
Enforcement Works
To the FDA’s credit, enforcement does make a difference. The two stores that received official letters quickly pulled their illegal stock. That mirrors the agency’s broader efforts this year: new import alerts to detain unauthorized tobacco products at the border (see also Import Alert 98-06), and hundreds of warning letters to retailers, importers, and distributors.
But effective enforcement can’t solve a supply problem. The list of legal nicotine-pouch products is still extremely short—only a narrow range of ZYN items. Adults who want more variety, or stores that want to meet that demand, inevitably turn to gray-market suppliers. The more limited the legal catalog, the more the illegal market thrives.
Why the NOAT Decision Appears Bizarre
The FDA’s own actions make the situation hard to explain. In January 2025, it authorized twenty ZYN products after finding that they contained far fewer harmful chemicals than cigarettes and could help adult smokers switch. That was progress. But nine months later, the FDA has approved nothing else—while sending a warning letter to NOAT, arguably the least youth-oriented pouch line in the world.
The outcome is bad for legal sellers and public health. ZYN is legal; a handful of clearly risky, high-nicotine imports continue to circulate; and a mild, adult-market brand that meets European safety and labeling rules is banned. Officially, NOAT’s problem is procedural—it lacks a marketing order. But in practical terms, the FDA is punishing the very design choices it claims to value: simplicity, low appeal to minors, and clean ingredients.
This approach also ignores the differences in actual risk. Studies consistently show that nicotine pouches have far fewer toxins than cigarettes and far less variability than many vapes. The biggest pouch concerns are uneven nicotine levels and occasional traces of tobacco-specific nitrosamines, depending on manufacturing quality. The serious contamination issues—heavy metals and inconsistent dosage—belong mostly to disposable vapes, particularly the flood of unregulated imports from China. Treating all “unauthorized” products as equally bad blurs those distinctions and undermines proportional enforcement.
A Better Balance: Enforce Upstream, Widen the Legal Path
My small Montgomery County survey suggests a simple formula for improvement.
First, keep enforcement targeted and focused on suppliers, not just clerks. Warning letters clearly change behavior at the store level, but the biggest impact will come from auditing distributors and importers, and stopping bad shipments before they reach retail shelves.
Second, make compliance easy. A single-page list of authorized nicotine-pouch products—currently the twenty approved ZYN items—should be posted in every store and attached to distributor invoices. Point-of-sale systems can block barcodes for anything not on the list, and retailers could affirm, once a year, that they stock only approved items.
Third, widen the legal lane. The FDA launched a pilot program in September 2025 to speed review of new pouch applications. That program should spell out exactly what evidence is needed—chemical data, toxicology, nicotine release rates, and behavioral studies—and make timely decisions. If products like NOAT meet those standards, they should be authorized quickly. Legal competition among adult-oriented brands will crowd out the sketchy imports far faster than enforcement alone.
The Bottom Line
Enforcement matters, and the data show it works—where it happens. But the legal market is too narrow to protect consumers or encourage innovation. The current regime leaves a few ZYN products as lonely legal islands in a sea of gray-market pouches that range from sensible to reckless.
The FDA’s treatment of NOAT stands out as a case study in inconsistency: a quiet, adult-focused brand approved in Europe yet effectively banned in the US, while flashier and riskier options continue to slip through. That’s not a public-health victory; it’s a missed opportunity.
If the goal is to help adult smokers move to lower-risk products while keeping youth use low, the path forward is clear: enforce smartly, make compliance easy, and give good products a fair shot. Right now, we’re doing the first part well—but failing at the second and third. It’s time to fix that.
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlberta’s huge oil sands reserves dwarf U.S. shale
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoCanada’s New Green Deal
-

 Energy22 hours ago
Energy22 hours agoCanada’s sudden rediscovery of energy ambition has been greeted with a familiar charge: hypocrisy
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCOP30 finally admits what resource workers already knew: prosperity and lower emissions must go hand in hand
-

 armed forces1 day ago
armed forces1 day agoOttawa’s Newly Released Defence Plan Crosses a Dangerous Line
-

 Indigenous1 day ago
Indigenous1 day agoResidential school burials controversy continues to fuel wave of church arsons, new data suggests
-

 Business20 hours ago
Business20 hours agoOttawa Pretends To Pivot But Keeps Spending Like Trudeau
-

 Daily Caller21 hours ago
Daily Caller21 hours agoParis Climate Deal Now Decade-Old Disaster










