Food
RFK Jr.’s War on Toxic Baby Formula and Junk Food Begins
Long-needed reforms start now.
The following is an editorialized version of a thread that originally appeared on the American Values X page. It was republished and edited with permission. Click here to read the original thread.
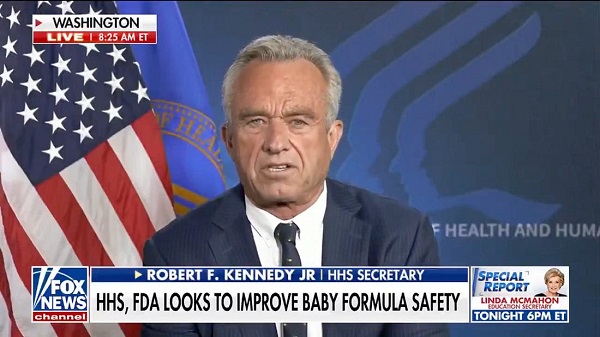
For the first time in over two decades, baby formula in the U.S. is getting a serious safety overhaul. On Thursday, Secretary Kennedy announced, alongside HHS and the FDA, “Operation Stork Speed,” a major initiative aimed at improving the safety and nutritional quality of infant formula.
“We’re gonna review the formulations for the first time since 1998 and do comprehensive tests to make sure this is the healthiest product that our kids can have,” Kennedy announced.
But that’s just the beginning. Kennedy is also taking on the growing concerns around cell phone use in schools—something he says is hurting kids on multiple levels.
“There are many other countries in the world that have banned cell phones in our schools.”
“Cell phones also produce electric magnetic radiation, which has been shown to do neurological damage to kids when it’s around them all day.”
“Cell phone use and social media use on the cell phone has been directly connected with depression, poor performance in schools, suicidal ideation, and with substance abuse.”
Kennedy is also tackling what he sees as one of the biggest flaws in how America approves food ingredients. He’s targeting the GRAS (“Generally Recognized As Safe”) loophole that’s allowed questionable substances to enter our food supply for years.
“We are going to get rid of the GRAS standards for new products. We’re going to go back and review all of these old ingredients to make sure that they are safe, and we’re going to encourage these companies to get rid of them as quickly as possible,” Kennedy said.
And when it comes to food safety, Kennedy says it’s time for the U.S. to catch up with the rest of the world.
“In this country, food ingredients are innocent till proven guilty.”
“In Europe and other countries they have to prove themselves safe before you add them, and we ought to have that kind of protection for American citizens.”
It’s a refreshing sight to see Secretary Kennedy take a wrecking ball to the status quo. From cracking down on harmful ingredients in baby formula to general food safety, he’s sending a clear message that the health and safety of America’s children come first.
Thanks for reading.
If you value the work being published here, upgrading your subscription is the most powerful way to support it.
The more this Substack earns, the more we can expand the team, improve quality,
and create the best reader experience possible.
Agriculture
Cloned foods are coming to a grocer near you

This article supplied by Troy Media.
And you may never find out if Health Canada gets its way
Cloned-animal foods could soon enter Canada’s food supply with no labels identifying them as cloned and no warning to consumers—a move that risks public trust.
According to Health Canada’s own consultation documents, Ottawa intends to remove foods derived from cloned animals from its “novel foods” list, the process that requires a pre-market safety review and public disclosure. Health Canada defines “novel
foods” as products that haven’t been commonly consumed before or that use new production processes requiring extra safety checks.
From a regulatory standpoint, this looks like an efficiency measure. From a consumer-trust standpoint, it’s a miscalculation.
Health Canada argues that cloned animals and their offspring are indistinguishable from conventional ones, so they should be treated the same. The problem isn’t the science—it’s the silence. Canadians are not being told that the rules for a controversial technology are about to change. No press release, no public statement, just a quiet update on a government website most citizens will never read.
Cloning in agriculture means producing an exact genetic copy of an animal, usually for breeding purposes. The clones themselves rarely end up on dinner plates, but their offspring do, showing up in everyday products such as beef, milk or pork. The benefits are indirect: steadier production, fewer losses from disease or more uniform quality.
But consumers see no gain at checkout. Cloning is expensive and brings no visible improvement in taste, nutrition or price.
Shoppers could one day buy steak from the offspring of a cloned cow without any way of knowing, and still pay the same, if not more, for it.
Without labels identifying cloned origin, potential efficiencies stay hidden upstream. When products born from new technologies are mixed with conventional ones, consumers lose their ability to differentiate, reward innovation or make an informed choice. In the end, the industry keeps the savings while shoppers see none.
And it isn’t only shoppers left in the dark. Exporters could soon pay the price too. Canada exports billions in beef and pork annually, including to the EU. If cloned origin products enter the supply chain without labelling, Canadian exporters could face additional scrutiny or restrictions in markets where cloning is not accepted. A regulatory shortcut at home could quickly become a market barrier abroad.
This debate comes at a time when public trust in Canada’s food system is already fragile. A 2023 survey by the Canadian Centre for Food Integrity found that only 36 per cent of Canadians believe the food industry is “heading in the right direction,” and fewer than half trust government regulators to be transparent.
Inserting cloned foods quietly into the supply without disclosure would only deepen that skepticism.
This is exactly how Canada became trapped in the endless genetically modified organism (GMO) debate. Two decades ago, regulators and companies quietly introduced a complex technology without giving consumers the chance to understand it. By denying transparency, they also denied trust. The result was years of confusion, suspicion and polarization that persist today.
Transparency shouldn’t be optional in a democracy that prides itself on science based regulation. Even if the food is safe, and current evidence suggests it is, Canadians deserve to know how what they eat is produced.
The irony is that this change could have been handled responsibly. Small gestures like a brief notice, an explanatory Q&A or a commitment to review labelling once international consensus emerges would have shown respect for the public and preserved confidence in our food system.
Instead, Ottawa risks repeating an old mistake: mistaking regulatory efficiency for good governance. At a time when consumer trust in food pricing, corporate ethics and government oversight is already fragile, the last thing Canada needs is another quiet policy that feels like a secret.
Cloning may not change the look or taste of what’s on your plate, but how it gets there should still matter.
Dr. Sylvain Charlebois is a Canadian professor and researcher in food distribution and policy. He is senior director of the Agri-Food Analytics Lab at Dalhousie University and co-host of The Food Professor Podcast. He is frequently cited in the media for his insights on food prices, agricultural trends, and the global food supply chain.
Troy Media empowers Canadian community news outlets by providing independent, insightful analysis and commentary. Our mission is to support local media in helping Canadians stay informed and engaged by delivering reliable content that strengthens community connections and deepens understanding across the country.
Business
The painful return of food inflation exposes Canada’s trade failures

This article supplied by Troy Media.
Canadians are feeling the pinch as Ottawa’s trade blunders and a weak dollar drive grocery bills higher
Almost a year ago, Canada’s Food Price Report projected that food inflation in 2025 would range between three and five per cent. We now stand squarely at four.
For consumers, it’s been a bruising year. After months of relative calm, grocery prices have surged again since spring, driven by tariffs, weather disruptions and a weakening Canadian dollar.
Between March and September, food inflation jumped sharply across several everyday staples. Coffee and tea prices rose by nearly 15 percentage points, sugar and confectionery climbed by more than three, while beef and condiments each increased by about one.
These aren’t luxury goods—they’re breakfast-table essentials. Canadians are paying more for their morning coffee, family barbecues and pantry staples than they were just six months ago.
When compared with other G7 countries, Canada’s performance stands out—and not in a good way. Japan currently faces the highest food inflation rate at 7.2 per cent, followed by the United Kingdom at 5.1 per cent. Canada sits third at 3.8 per cent, the only G7 country to post three consecutive monthly increases. Italy follows closely at 3.7 per cent, while the United States, Germany and France are all below Canada at 3.2, 2.9 and 1.7 per cent, respectively. For an advanced, food-producing nation, this is not a comfortable position.
Much of the renewed pressure can be traced back to trade policy. The counter tariffs introduced in March, combined with new U.S. measures, have quietly inflated costs across the entire food chain. Tariffs are by nature inflationary: they disrupt market efficiencies, raise input prices and trigger retaliatory actions that make goods more expensive on both sides of the border. What begins as a political statement quickly becomes an economic burden, felt most acutely in grocery aisles.
The loonie’s recent weakness has only made matters worse. Since January, the Canadian dollar has fallen significantly against the U.S. dollar, amplifying the cost of imported products such as coffee, cocoa and processed foods. For a country that imports roughly $70 billion in food annually, currency depreciation functions like a silent tax on every grocery bill.
As we move into the winter months, these forces show few signs of easing. Transportation costs remain high, retailers are passing along supplier increases and consumers are already adapting by trading down or buying less. While overall inflation is moderating elsewhere in the world, Canada’s food sector is moving in the opposite direction.
Prime Minister Mark Carney recently remarked that his government will be judged by the prices Canadians pay at the grocery store. On that score, Canadians are indeed paying attention. Tariffs, trade friction and a soft currency have all converged to make food more expensive. Voters are noticing.
In a world where food inflation is once again a global problem, Canada’s return to the top of the G7 pack is an unenviable distinction.
Dr. Sylvain Charlebois is a Canadian professor and researcher in food distribution and policy. He is senior director of the Agri-Food Analytics Lab at Dalhousie University and co-host of The Food Professor Podcast. He is frequently cited in the media for his insights on food prices, agricultural trends, and the global food supply chain.
Troy Media empowers Canadian community news outlets by providing independent, insightful analysis and commentary. Our mission is to support local media in helping Canadians stay informed and engaged by delivering reliable content that strengthens community connections and deepens understanding across the country.
-

 espionage2 days ago
espionage2 days agoU.S. Charges Three More Chinese Scholars in Wuhan Bio-Smuggling Case, Citing Pattern of Foreign Exploitation in American Research Labs
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCarney budget doubles down on Trudeau-era policies
-

 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoCrown still working to put Lich and Barber in jail
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCarney’s Deficit Numbers Deserve Scrutiny After Trudeau’s Forecasting Failures
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoKazakhstan joins Abraham Accords, Trump says more nations lining up for peace
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCarney budget continues misguided ‘Build Canada Homes’ approach
-

 Energy17 hours ago
Energy17 hours agoCanada Cannot Become an Energy Superpower With its Regulatory Impediments
-

 armed forces15 hours ago
armed forces15 hours agoIt’s time for Canada to remember, the heroes of Kapyong













