Artificial Intelligence
Poll: Despite global pressure, Americans want the tech industry to slow down on AI
From The Deep View
| A little more than a year ago, the Future of Life Institute published an open letter calling for a six-month moratorium on the development of AI systems more powerful than GPT-4. Of course, the pause never happened (and we didn’t seem to stumble upon superintelligence in the interim, either) but it did elicit a narrative from the tech sector that, for a number of reasons, a pause would be dangerous. | |
|
|
| As the Pause AI organization themselves put it: “We might end up in a world where the first AGI is developed by a non-cooperative actor, which is likely to be a bad outcome.” | |
| But new polling shows that American voters aren’t buying it. | |
| The details: A recent poll conducted by the Artificial Intelligence Policy Institute (AIPI) — and first published by Time — found that Americans would rather fall behind in that global race than skimp on regulation. | |
|
|
| The polling additionally found that 50% of voters surveyed think the U.S. should use its position in the AI race to prevent other countries from building powerful AI systems by enforcing “safety restrictions and aggressive testing requirements.” | |
| Only 23% of Americans polled believe that the U.S. should eschew regulation in favor of being the first to build a more powerful AI. | |
|
|
| This comes as federal regulatory efforts in the U.S. remain stalled, with the focus shifting to uneven state-by-state regulation. | |
| Previous polling from the AIPI has found that a vast majority of Americans want AI to be regulated and wish the tech sector would slow down on AI; they don’t trust tech companies to self-regulate. | |
| Colson has told me in the past that the American public is hyper-focused on security, safety and risk mitigation; polling published in May found that “66% of U.S. voters believe AI policy should prioritize keeping the tech out of the hands of bad actors, rather than providing the benefits of AI to all.” | |
|
|
| Underpinning all of this is a layer of hype and an incongruity of definition. It is not clear what “extremely powerful” AI means, or how it would be different from current systems. | |
| Unless artificial general intelligence is achieved (and agreed upon in some consensus definition by the scientific community), I’m not sure how you measure “more powerful” systems. As current systems go, “more powerful” doesn’t mean much more than predicting the next word at slightly greater speeds. | |
|
|
| Do people want development to slow down, or deployment? | |
| To once again call back Helen Toner’s comment of a few weeks: how is AI affecting your life, and how do you want it to affect your life? | |
| Regulating a hypothetical is going to be next to impossible. But if we establish the proper levels of regulation to address the issues at play today, we’ll be in a better position to handle that hypothetical if it ever does come to pass. |
Artificial Intelligence
AI is accelerating the porn crisis as kids create, consume explicit deepfake images of classmates

From LifeSiteNews
“Ten years ago it was sexting and nudes causing havoc in classrooms,” writes Sally Weale in a chilling new report at the Guardian. “Today, advances in artificial intelligence (AI) have made it child’s play to generate deepfake nude images or videos, featuring what appear to be your friends, your classmates, even your teachers. This may involve removing clothes, getting an image to move suggestively or pasting someone’s head on to a pornographic image.”
I have been covering the rise of the next horrific manifestation of our collective porn crisis here at LifeSiteNews since 2019, when I warned that the rise of “deepfakes” would inevitably result in people making artificial pornography of their peers. Just a few years later, I reported on stories of middle-schoolers making deepfake pornography of kids they attended class with; last year, I reported on the rise of “nudify” apps that can digitally undress people in photographs, and the trauma, bullying, and inevitable sexual blackmail that has resulted.
The Guardian report reveals how swiftly this crisis is escalating. One teacher described an incident in which a teenage boy took out his phone, chose a social media image of a girl from a neighboring school, and used the “nudify” app to digitally remove her clothes. The teacher was shocked to see that the boy wasn’t even hiding his actions, because he didn’t see what he was doing as shocking, or even shameful. “It worries me that it’s so normalized,” she said. Other students reported the boy, his parents were contacted, and the police were called. The victimized girl was not even told.
The crisis is global. “In Spain last year, 15 boys in the south-western region of Extremadura were sentenced to a year’s probation after being convicted of using AI to produce fake naked images of their female schoolmates, which they shared on WhatsApp groups,” Weale writes. “About 20 girls were affected, most of them aged 14, while the youngest was 11.”
A similar situation unfolded in Australia, where 50 high school students had deepfake images distributed; in the United States, 30 female students in New Jersey discovered that “pornographic images of them had been shared among their male classmates on Snapchat.”
The mother of one student in Australia said that “her daughter was so horrified by the sexually explicit images that she vomited.” In the United Kingdom, the problem has exploded overnight:
A new poll of 4,300 secondary school teachers in England, carried out by Teacher Tapp on behalf of the Guardian, found that about one in 10 were aware of students at their school creating “deepfake, sexually explicit videos” in the last academic year. Three-quarters of these incidents involved children aged 14 or younger, while one in 10 incidents involved 11-year-olds, and 3% were younger still, illustrating just how easy the technology is to access and use. Among participating teachers, 7% said they were aware of a single incident, and 1% said it had happened twice, while a similar proportion said it had happened three times or more in the last academic year. Earlier this year, a Girlguiding survey found that one in four respondents aged 13 to 18 had seen a sexually explicit deepfake image of a celebrity, a friend, a teacher or themselves.
Predictably, teachers are also being targeted. Girls and women are left shattered by this victimization. Laura Bates, author of The New Age of Sexism: How the AI Revolution Is Reinventing Misogyny, writes: “It feels like someone has taken you and done something to you and there is nothing you can do about it. Watching a video of yourself being violated without your consent is an almost out-of-body experience.” Boys, meanwhile, are engaging in criminal behavior often without even knowing it. In the world they have grown up in, pornography is normal – and this is merely the next step.
The experts that Weale interviews are, as usual, at a loss of what can be done about this crisis. They emphasize education, while admitting that this is the equivalent of taking a water pistol to a raging forest fire. They are skeptical that guidelines or bans around technology at school will help. Understandably, educators are demoralized and even despairing. Pornography and sexting have already transformed schools. Deepfake pornography is now making an already ugly crisis far more personal, and there is no indication that the problem can be stopped without dramatic action.
The only genuine solution was put forward by Dame Rachel de Souza, the children’s commissioner for England. She has advocated that “nudification apps such as ClothOff” be simply banned. “Children have told me they are frightened by the very idea of this technology even being available, let alone used,” de Souza stated. De Souza is correct. The solution to the porn crisis is both tremendously difficult, but extraordinarily simple: we must simply make this content – and these apps – illegal.
The good news is that the first step in this direction has already been taken in the U.K. On November 3, the government tabled the Crime and Policing Bill in Parliament. It includes an amendment criminalizing pornography featuring strangulation or suffocation – usually referred to as “choking” – with legal requirements for tech platforms to block this content from U.K. users.
This is the first time a genre of pornography has been criminalized on the basis that even if it is consensual, it genuinely harms society. That is an encouraging precedent, because it applies to virtually all hardcore pornography – and certainly to the “nudification” apps that are set to make middle school a hyper-sexualized hell for women and girls.
The porn industry is destroying society. We must destroy it first.
Artificial Intelligence
The Emptiness Inside: Why Large Language Models Can’t Think – and Never Will

This is a special preview article from the:
Early attempts at artificial intelligence (AI) were ridiculed for giving answers that were confident, wrong and often surreal – the intellectual equivalent of asking a drunken parrot to explain Kant. But modern AIs based on large language models (LLMs) are so polished, articulate and eerily competent at generating answers that many people assume they can know and, even
better, can independently reason their way to knowing.
This confidence is misplaced. LLMs like ChatGPT or Grok don’t think. They are supercharged autocomplete engines. You type a prompt; they predict the next word, then the next, based only on patterns in the trillions of words they were trained on. No rules, no logic – just statistical guessing dressed up in conversation. As a result, LLMs have no idea whether a sentence is true or false or even sane; they only “know” whether it sounds like sentences they’ve seen before. That’s why they often confidently make things up: court cases, historical events, or physics explanations that are pure fiction. The AI world calls such outputs
“hallucinations”.
But because the LLM’s speech is fluent, users instinctively project self-understanding onto the model, triggered by the same human “trust circuits” we use for spotting intelligence. But it is fallacious reasoning, a bit like hearing someone speak perfect French and assuming they must also be an excellent judge of wine, fashion and philosophy. We confuse style for substance and
we anthropomorphize the speaker. That in turn tempts us into two mythical narratives: Myth 1: “If we just scale up the models and give them more ‘juice’ then true reasoning will eventually emerge.”
Bigger LLMs do get smoother and more impressive. But their core trick – word prediction – never changes. It’s still mimicry, not understanding. One assumes intelligence will magically emerge from quantity, as though making tires bigger and spinning them faster will eventually make a car fly. But the obstacle is architectural, not scalar: you can make the mimicry more
convincing (make a car jump off a ramp), but you don’t convert a pattern predictor into a truth-seeker by scaling it up. You merely get better camouflage and, studies have shown, even less fidelity to fact.
Myth 2: “Who cares how AI does it? If it yields truth, that’s all that matters. The ultimate arbiter of truth is reality – so cope!”
This one is especially dangerous as it stomps on epistemology wearing concrete boots. It effectively claims that the seeming reliability of LLM’s mundane knowledge should be extended to trusting the opaque methods through which it is obtained. But truth has rules. For example, a conclusion only becomes epistemically trustworthy when reached through either: 1) deductive reasoning (conclusions that must be true if the premises are true); or 2) empirical verification (observations of the real world that confirm or disconfirm claims).
LLMs do neither of these. They cannot deduce because their architecture doesn’t implement logical inference. They don’t manipulate premises and reach conclusions, and they are clueless about causality. They also cannot empirically verify anything because they have no access to reality: they can’t check weather or observe social interactions.
Attempting to overcome these structural obstacles, AI developers bolt external tools like calculators, databases and retrieval systems onto an LLM system. Such ostensible truth-seeking mechanisms improve outputs but do not fix the underlying architecture.
The “flying car” salesmen, peddling various accomplishments like IQ test scores, claim that today’s LLMs show superhuman intelligence. In reality, LLM IQ tests violate every rule for conducting intelligence tests, making them a human-prompt engineering skills competition rather than a valid assessment of machine smartness.
Efforts to make LLMs “truth-seeking” by brainwashing them to align with their trainer’s preferences through mechanisms like RLHF miss the point. Those attempts to fix bias only make waves in a structure that cannot support genuine reasoning. This regularly reveals itself through flops like xAI Grok’s MechaHitler bravado or Google Gemini’s representing America’s Founding Fathers as a lineup of “racialized” gentlemen.
Other approaches exist, though, that strive to create an AI architecture enabling authentic thinking:
Symbolic AI: uses explicit logical rules; strong on defined problems, weak on ambiguity;
Causal AI: learns cause-and-effect relationships and can answer “what if” questions;
Neuro-symbolic AI: combines neural prediction with logical reasoning; and
Agentic AI: acts with the goal in mind, receives feedback and improves through trial-and-error.
Unfortunately, the current progress in AI relies almost entirely on scaling LLMs. And the alternative approaches receive far less funding and attention – the good old “follow the money” principle. Meanwhile, the loudest “AI” in the room is just a very expensive parrot.
LLMs, nevertheless, are astonishing achievements of engineering and wonderful tools useful for many tasks. I will have far more on their uses in my next column. The crucial thing for users to remember, though, is that all LLMs are and will always remain linguistic pattern engines, not epistemic agents.
The hype that LLMs are on the brink of “true intelligence” mistakes fluency for thought. Real thinking requires understanding the physical world, persistent memory, reasoning and planning that LLMs handle only primitively or not all – a design fact that is non-controversial among AI insiders. Treat LLMs as useful thought-provoking tools, never as trustworthy sources. And stop waiting for the parrot to start doing philosophy. It never will.
The original, full-length version of this article was recently published as Part I of a two-part series in C2C Journal. Part II can be read here.
Gleb Lisikh is a researcher and IT management professional, and a father of three children, who lives in Vaughan, Ontario and grew up in various parts of the Soviet Union.
-
 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoTrump DOJ seeks to quash Pfizer whistleblower’s lawsuit over COVID shots
-

 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days agoU.S. seizes Cuba-bound ship with illicit Iranian oil history
-
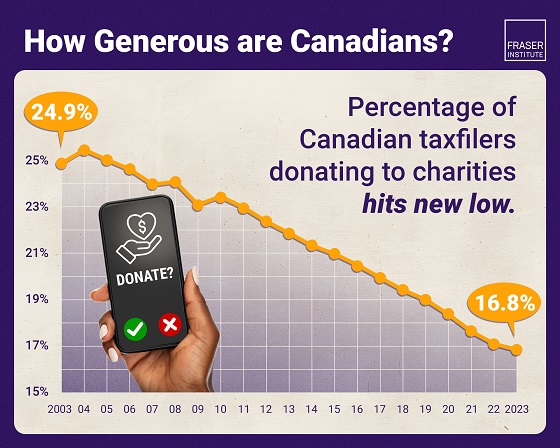
 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoAlbertans give most on average but Canadian generosity hits lowest point in 20 years
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoMarjorie Taylor Greene’s ’60 Minutes’ interview reveals power struggle between populists and RINOs
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin1 day ago
Bruce Dowbiggin1 day agoCarney Hears A Who: Here Comes The Grinch
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoUS Supreme Court Has Chance To End Climate Lawfare
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex2 days ago
Censorship Industrial Complex2 days agoOttawa’s New Hate Law Goes Too Far
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoTaxpayers Federation calls on politicians to reject funding for new Ottawa Senators arena








