Energy
No calling in sick or waiting for a nice day – The grid has to perform on the worst of them
From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
By Terry Etam
Saturday night, the middle of the cold snap, was something to be endured
Saturday night, the middle of the cold snap, was something to be endured. Things break at -36 degrees. A quick run to the grocery store was rerouted by a fleet of city vehicles tearing up the street in a considerable manner, most likely chasing a broken water main or some such. Imagine being without water on a night like that.
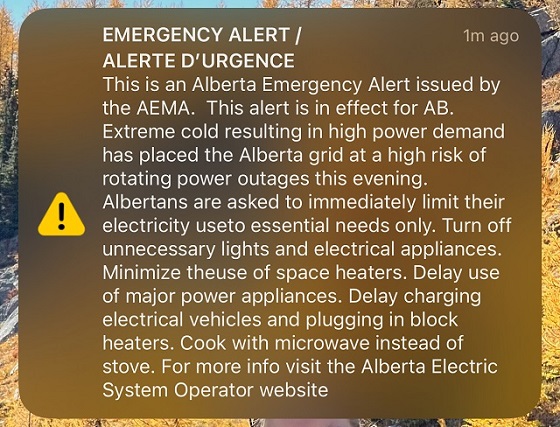
Half an hour later it got worse – the provincial grid operator issued an alert for people to “immediately limit their electrical use to essential needs only.”
Keep in mind the staggering circumstance, and location, of that alert: Alberta. Even the province’s biggest naysayer would have to admit that the province is an energy juggernaut, blessed with resources most of the world can only dream of, including and especially energy.
If power consumption levels were not reduced, there could have been rolling blackouts. Anyone care to imagine what that would have been like at -35 degree temperatures?
Hopefully every single voter in Canada, and the US for that matter, is paying attention. The false prophecies of utopian energy transitions visions are, quite clearly, dangerously false.
The media feeds you dumbed-down pablum; don’t take it at face value. Instead of listening to blathering about “new installed capacity”, pay attention to actual output. In extreme cold, wind and solar output fall to zero, or very close. It doesn’t matter if there are a billion gigawatts of ‘capacity’ installed.
Everyone needs to understand the fundamental issue that was best described by Nassim Taleb via his turkey analogy. A turkey has 364 days of a very good life, followed by one very bad day come Thanksgiving. It is the bad day that matters, not 364 good ones. A deadly day is a deadly day.
It’s the same with renewables penetration, and how it makes the news ‘on the good days’. Activists and simplistic policymakers (but I repeat myself) tout how a particular jurisdiction may have at such and such a time sourced “xx percent” of power from renewables. Yay, look at the progress, marching ever higher. But it’s not what it sounds like. It doesn’t matter if a country or state or province gets 80% of its power from solar at the peak of a good sunny day, nor if 80% comes from wind on a particularly windy day. Those are misleading numbers, because the system must be fully capable of meeting peak demand every day, and not just ‘on a good day’.
According to AESO, the provincial grid operator, Alberta has 4,481 MW of wind power capacity. At the peak of last weekend’s deepfreeze, it was producing about 1/3 of one percent of that total. Not just useless, but far worse: useless when needed exactly the most.
What matters is: how does the system perform at peak times – what is going to show up on demand?
Just like everyone else that’s trying to bring rationality to this conversation, I need also point out that wind and solar are welcome additions, in moderate amounts, sited where they do the least damage, and as supplements to a grid.
But that’s where the conversation needs to get serious. The real danger out there are people that want an energy transition so badly, or are employed as ‘climate architects’ such that their career depends on it, who sweep some mighty big things under the rug.
“We just need more storage, then wind and solar will be able to carry the load.” Not possible, not if batteries are the vision. Imagine a day’s worth of battery power supply for the entire province. Or two days. The cost would be off the charts, and, then after two days of ‘usage’, how would the batteries get recharged if the cold spell persisted more than a few days? Is that the kind of backup anyone would accept? We’ll have power again if the wind picks up strongly and consistently for the next week, if not, well, good luck?
“Sure we can handle an all-EV world because users can charge at night.” I’ve seen this argument now and then, based on some simplistic studies that show, correctly, that financial enticements can get people to charge EVs at off peak hours. But that’s a red herring in the world we are headed for, “electrify everything”. If we do electrify even half of what we could, then peak demand will still go way up, as will our life-perched dependency on it. More EVs just mean more load. And not all EVs will shift to night charging; it is some pretty weak thinking to imagine that all EV owners will have that optionality, or live in a place that allows it, or won’t be travelling, etc. And remember that the feds’ plan is for all vehicles to be electrified. So maybe J. Consumer in suburbia can shift his EV to night charging, but what about a fleet of city buses, or Uber drivers, or forklifts, or taxis, or…the list is endless.
“We can switch to heat pumps.” This one takes the cake. Heat pumps will exacerbate the problem at the exact worst time – when it is coldest, and when power demand is highest, and when the grid is maxed out. It is the opposite of proponents who say EVs can charge at off peak hours – heat pumps will be called into full service precisely at peak hours. Taleb’s turkey again: a mass-heat-pump system will be wonderful on many days, but on the very worst day, all goes black. And cold.
There is no joy in this silly debate we seem to be in with ideologues, particularly when the threat of rolling blackouts is announced by the grid operator. But there is also no time to waste indulging people who want to rewire the grid with “well academic studies say this should work.” Set up your own commune somewhere and experiment for a few years and at least one winter cold snap, then let us know how it goes.
Wishful thinking doesn’t turn many wrenches, nor does it heat homes. Wishful thinking is not what an energy system can or should be built on. Energy is life or death in extreme weather. Ideology is the last thing that should be involved in energy supply, and yet we are up to our ears in it, a situation that is becoming dangerous.
People can see this. They may not understand how grids (and energy) work, but they know when something smells bad. That’s why federal government support is at such lows, and why distrust in the media is at such highs. Political scientists telling you “Don’t worry, we know how to design a new grid” are no match for the likes of, for example, real-world experiences such as this relayed by a gentleman named John Wright on LinkedIn: “Currently out at our cabin trying to help out our heat pumps (we run three geothermal units and they are running full out with auxiliary/ supplemental heating coils engaged). We have two propane fireplaces burning full time in addition to all the firewood that we’re also splitting and burning, and all of the burners on the cooktop are on. It’s probably about +12.5° C inside here vs -36°C outside…Everyone seems to ignore the fact that heat pumps are a huge draw on the power grid. Our power bill could easily be $1500.00 to $2000.00 for January…By the way, the power consumption and poor performance is the same in the summer when it is +36°C here.”
And finally, it is important to note that the gradual but persistent undermining of the hydrocarbon industry will have massive consequences, because hydrocarbons underpin everything we use and do. Governmental and media animosity will drive away capital (don’t wonder why dividends are such a popular thing in the oil and gas sector – capital flight in full view) and ultimately weaken a pillar of our economy. Until nuclear energy is ubiquitous, or some technological breakthrough happens, we need reliable, baseload power, which at this time in history means hydrocarbons, here and around the world. That baseload is not guaranteed, it is not a right, it is not going to be sustained if capital is chased away from it.
Voters, it’s up to you. Demand more from your politicians, but also demand better conversations from the entire energy industry as well. We owe you that.
Terry Etam is a columnist with the BOE Report, a leading energy industry newsletter based in Calgary. He is the author of The End of Fossil Fuel Insanity. You can watch his Policy on the Frontier session from May 5, 2022 here.
Daily Caller
Trump Floats Reimbursing Oil Companies If They Put Up Big Bucks In Venezuela


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
Following the removal of socialist dictator Nicolás Maduro, President Donald Trump said the U.S. government might reimburse oil companies that invest in Venezuela.
In a Monday afternoon phone interview, Trump told NBC News’ Kristen Welker that an expansion of the U.S. oil industry in the South American nation could be “up and running” in less than a year and a half, but this would require “a lot of money.” Hours after announcing Maduro’s capture Saturday, Trump said in a press conference that the U.S. is going to “run” Venezuela until there could be “a safe, proper and judicious transition” — a remark that sparked much discussion over exactly what will come next for the country.
“A tremendous amount of money will have to be spent, and the oil companies will spend it, and then they’ll get reimbursed by us or through revenue,” Trump said in his interview with Welker, referring to rebuilding the beleaguered oil infrastructure in post-Maduro Venezuela.
The president did not specify how much money is required for oil companies to upgrade the infrastructure, NBC News reported. Trump previously said he was going to “have our very large United States oil companies, the biggest anywhere in the world, go in, spend billions of dollars, fix the badly broken infrastructure and start making money for the country.”
“It’ll be a very substantial amount of money [that] will be spent,” Trump added in his interview with Welker. “But they’ll [the oil companies will] do very well. And the country will do well.”
Trump told the NBC News host that Venezuela producing oil is “good for the United States because it keeps the price of oil down.”
He also told Welker that his administration did not brief oil companies before carrying out the surprise attack that deposed Maduro.The companies, though, “were absolutely aware that we were thinking about doing something.”
Welker, on NBC News’ “Meet The Press” Sunday, asked Secretary of State Marco Rubio, “Why does the United States need to take over the Venezuelan oil industry?”
“We don’t need to. We don’t need Venezuela’s oil,” Rubio said. “We have plenty of oil in the United States. What we’re not going to allow is for the oil industry in Venezuela to be controlled by adversaries of the United States.”
“Why does China need their oil? Why does Russia need their oil? Why does Iran need their oil?” the Secretary of State asked. “They’re not even in this continent. This is the Western Hemisphere. This is where we live.”
Also on Sunday, a Venezuelan man in Buenos Aires, Argentina went viral while celebrating the end of the Mauro regime, after he pushed back against critics who said the U.S. is only interested in Venezuela due to its status as an oil-producing country.
“Those who say that the U.S. is only interested in our oil, I ask you: What do you think the Russians and the Chinese wanted here? The recipe for arepas?” the man asked in Spanish, naming a popular street food in Venezuelan cuisine. “Impossible.”
Energy
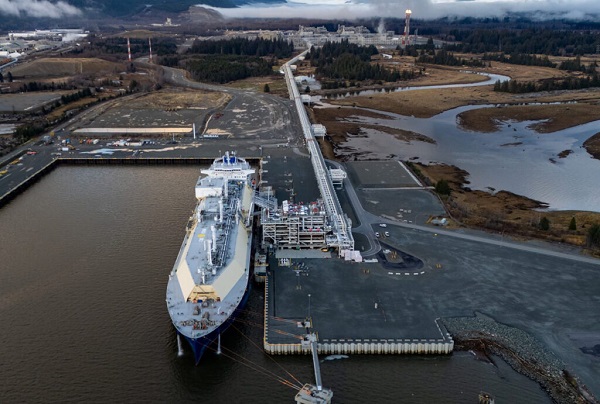
The global math: Why exporting Canadian energy is a climate win

From Resource Works
New report finds that displacing coal and foreign gas with Canadian LNG could lower global emissions by 70 megatonnes a year
Canada’s energy policy debate has become trapped in a polarization that feels dangerously disconnected from global reality.
On one side, we have a domestic conversation focused intensely on our own emissions ledger—counting every tonne produced within our borders as a liability. On the other side is the global reality: a world hungry for energy, often turning to the dirtiest sources available to keep the lights on and economies growing.
I’ve long argued that we cannot solve a global problem like climate change by wearing blinders that restrict our view to the 49th parallel. Recently, on the Power Struggle podcast, I sat down with Mark Cameron to discuss the hard data that backs this up.
Cameron is a fellow at the Public Policy Forum and the co-author of a new report Refuel: What Canadian LNG and Oil Exports Could Mean for Global Emissions. The numbers tell a story that might surprise those who view energy exports solely as a climate negative.
Flipping the script on emissions
The central finding of the Refuel report challenges the orthodoxy that “more production equals more pollution.” When we look at the global picture, the opposite appears to be true.
“The headline news is that if Canada was to increase its LNG exports by [47 million tonnes a year] and if we are exporting primarily into Asian markets, there would be a net reduction in emissions of about 40 to 70 megatonnes per year,” Cameron told me.
Let that sink in. By increasing our economic output and shipping more product abroad, we could lower global emissions by an amount roughly equivalent to taking millions of cars off the road.
It comes down to displacement. The energy we export doesn’t vanish into a void; it replaces other, often dirtier, forms of power generation.
“In some of those markets, you’re displacing coal,” Cameron explained. “Coal obviously is about twice the emissions in generating electricity as LNG. So to the extent that you’re displacing coal, you’re getting a clear emissions reduction.”
The Canadian advantage
This isn’t just about the inherent chemistry of gas versus coal. It is also about the specific quality of the gas produced in Western Canada. Not all liquefied natural gas (LNG) is created equal.
Canada’s geography and technology provide a distinct edge over competitors regarding carbon intensity.
“Canadian LNG, because it has cooler temperatures, shorter shipping times to Asia, more electric drive in its production, is actually about 35 per cent lower in emissions than LNG that would be shipped from, say, the U.S. Gulf Coast,” Cameron said.
When we debate blocking a Canadian project, we act as if the alternative is zero consumption. But the alternative is often gas from the Gulf Coast—which requires more energy to cool in the hot southern climate and takes longer to ship—or worse, coal.
Asian markets know this. They are looking for reliability and lower carbon intensity.
“We want to have a certain percentage of LNG, and we want a certain percentage of that coming from Canada because it’s a stable market and it has a particularly low emissions intensity,” Cameron noted.
The reality of substitution
This brings us to the concept of “carbon leakage.” It is a harsh economic reality that if Canada steps out of the market, we don’t save the planet—we simply cede market share to those with lower environmental standards.
“If the LNG is not coming from Canada, it’s going to come from somewhere else,” Cameron said bluntly. “It’s going to come from the U.S. or Qatar or Australia, or it would be displaced by coal or another energy source. So when you look at all those things in balance, it does look like Canadian LNG is a net positive for the climate.”
Progress in the oilsands
While LNG often dominates the “transition fuel” conversation, the report also addresses the oilsands. The narrative there has often ignored massive strides in efficiency.
“That emissions intensity is coming down. It’s come down by about 30 per cent in the last 20 years,” Cameron said.
He pointed to operational fuel switching as a key driver of this progress.
“Canadian oilsands was using petroleum coke, essentially coal, to generate the steam for the oilsands production. That is almost entirely shifted to natural gas.”
The long game
Finally, we must address the timeline. Critics argue that building LNG infrastructure locks us into fossil fuels. But the transition is a decades-long process.
“There is going to be LNG demand,” Cameron said. “We don’t know exactly how much, but there’s going to be LNG demand for the next four or five, six decades.”
Furthermore, natural gas is a fundamental building block of modern civilization, used for fertilizer and chemical production, not just electricity.
“If we can produce the cleanest LNG in the world, we’re actually doing global climate a favour by building those projects,” Cameron added.
If we retreat from the world stage, we aren’t taking the moral high ground; we are merely outsourcing the emissions to countries with a heavier carbon footprint. A Canada that exports more is a Canada that contributes to a cleaner world.
Watch the video on Power Struggle
- Power Struggle audio and transcript
- Mark Cameron on LinkedIn
- Stewart Muir on X
- Stewart Muir on LinkedIn
Power Struggle on social media:
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day agoIs Canada still worth the sacrifice for immigrants?
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin1 day ago
Bruce Dowbiggin1 day agoThe Olympic Shutout: No Quebec Players Invited For Canada
-

 Canadian Energy Centre1 day ago
Canadian Energy Centre1 day agoFive reasons why 2026 could mark a turning point for major export expansions
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoNetwork of Nonprofits with Marxist and CCP Ties, and Elected Socialists Race to Counter Washington’s Narrative of the Maduro Raid
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoTrump’s Venezuela Geopolitical Earthquake Shakes up Canada’s Plans as a “Net Zero” Energy Superpower
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoPolicy uncertainty continues to damage Canada’s mining potential
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoTrump’s Venezuela Move: A $17 Trillion Reset of Global Geopolitics and a Pivotal Shift in US Energy Strategy
-

 Environment1 day ago
Environment1 day agoLeft-wing terrorists sabotage German power plant, causing massive power outage



