Economy
If Canadian families spent and borrowed like the federal government, they would be $427,759 in debt

From the Fraser Institute
By Grady Munro and Jake Fuss
If the median Canadian family spent and borrowed like the federal government, they would already be $427,759 in debt and continuing to borrow, finds a new study published today by the Fraser Institute.
“If the median family in Canada spent and borrowed like the federal government, they would be in serious financial trouble,” said Grady Munro, a Fraser Institute policy analyst and co-author of Understanding the Scale of Canada’s Federal Deficit.
The $39.8 billion deficit expected by Ottawa in 2024/25 represents the 17th consecutive annual federal deficit, with continued deficits expected into the foreseeable future, eventually resulting in higher taxes for Canadians.
Continuous annual borrowing by Ottawa to finance increased spending has driven federal total debt from 53.0 per cent of the economy ($1.1 trillion) in 2014/15 up to an expected 69.8 per cent ($2.1 trillion) in 2024/25.
To put this into perspective, the study’s analysis offers an example of what a median family’s household finances would look like if they were to spend and borrow like the federal government in 2024.
The study found that the median Canadian family in 2024 would spend $109,982 while only earning $101,821, meaning that it would borrow $8,161 just to pay for its normal spending. This $8,000-plus in additional debt is on top of the $427,759 in existing debt the family would already hold based on previous borrowing.
Illustrative of the burden of debt, $11,066 of the family’s income, representing almost 11 per cent, would be spent on just the interest costs of existing debt.
“Unlike most households, where debt is often offset by assets such as a home or investments, the federal government has little in the way of assets to offset its enormous debt,” said Jake Fuss, director of fiscal policy at the Fraser Institute and coauthor. “And it’s important to note that this government debt burden on Canadian families does not include the burden of provincial and municipal government debt, which depending on one’s location, can be significant.”

- For many years the federal government’s approach to government finances has relied on spending-driven deficits and a growing debt burden, causing a deterioration in the state of federal finances.
- While deficits can sometimes be justified in certain circumstances, perpetual spending-driven deficits have become the norm rather than a temporary exception for the federal government. The $39.8 billion deficit expected in 2024/25 is the 17th consecutive annual deficit, and deficits are expected to continue into the foreseeable future.
- Deficits have helped drive federal gross debt from 53.0% of the economy ($1.1 trillion) in 2014/15 up to an expected 69.8% ($2.1 trillion) in 2024/25.
- This increase in the level of federal debt comes with costs and will result in higher taxes on Canadians.
- It may be hard to comprehend the scale of the deficits and debt, so to contextualize the current state of federal finances this bulletin provides an example of what a median family’s household budget would look like in 2024 if it managed its finances the way the federal government does.
- The median family earning $101,821 in 2024 would be spending $109,982 if it spent the way the federal government does. To cover the difference, it would put $8,161 on a credit card, despite already being $427,759 in debt.
- Of the total amount spent, $11,066 would go towards interest on the debt his year. Simply put, a Canadian family that chose to spend like the federal government would be in financial trouble.
Authors:
Business
Is affirming existing, approved projects truly the best we can do in Canada?

From Resource Works
For major projects, what is old is new again
Prime Minister Mark Carney’s second wave of “nation-building projects” sounds transformative: six new energy and mining proposals, plus a northern corridor, added to the first tranche unveiled in September, and included in the freshly passed federal budget for the fiscal year.
Together, Ottawa says, they amount to more than $116 billion in investment and are central to “realizing Canada’s full potential as an energy superpower.” That is the pitch in the federal news release.
Look closely, though, and a different picture emerges. For major projects, what is old is new again. Almost every file now being “fast-tracked” was already on the books, sometimes for a decade or more.
The new referrals to the Major Projects Office (MPO) are all familiar: the Nisga’a-led Ksi Lisims LNG terminal on B.C.’s north coast; BC Hydro’s North Coast Transmission Line; Canada Nickel’s Crawford project near Timmins; Nouveau Monde Graphite’s Matawinie mine north of Montréal; Northcliff’s Sisson tungsten project in New Brunswick; and the Inuit-owned Iqaluit Nukkiksautiit hydro project in Nunavut. The “Northwest Critical Conservation Corridor” in B.C. and the Yukon is added as a long-range concept.
Long timelines and longstanding obstacles
None of these is a fresh idea. As the Globe and Mail notes in a project-by-project rundown, Ksi Lisims has been in development for years and already faces two Federal Court challenges from nearby First Nations and opposition from Wet’suwet’en hereditary leaders who fought Coastal GasLink. The North Coast Transmission Line was identified in 2023, with B.C. legislation to fast-track it and term-sheet co-ownership deals with First Nations already in place. The Sisson mine has been stalled at the pre-construction stage for more than a decade, despite earlier approvals and new public money to update its feasibility study.
Iqaluit hydro is hardly a novelty either. As Globe reporting shows, dam concepts near the city have been studied since the mid-2000s, with the current Inuit-owned proposal building on that earlier work and backed by federal engineering funds. The Crawford nickel project was acquired in 2019 and has spent years lining up investors and a complex financing stack, documented in both CBC and Financial Post coverage. Matawinie received its Quebec authorization in 2021, has an impact-benefit agreement with the local Atikamekw Nation and now enjoys federal price-floor guarantees on graphite.
The first tranche, announced in September, follows the same pattern. LNG Canada Phase 2 in Kitimat, new nuclear at Darlington, Contrecoeur container capacity at the Port of Montréal, McIlvenna Bay in Saskatchewan and the Red Chris expansion in B.C. were all in various stages of planning long before Carney entered office. The MPO is not inventing a new project pipeline; it is trying to accelerate the one Ottawa already had.
Acceleration is the point — and industry welcomes it
Acceleration is, to be fair, the point. The Calgary-based MPO, led by former Trans Mountain head Dawn Farrell, is designed to run permits in parallel, not one after another, and to coordinate financing through bodies like the Canada Infrastructure Bank and Canada Growth Fund. Farrell told CBC that work which might have taken “five or six more years” could be cut to roughly two. In a country where large projects regularly die of regulatory exhaustion, that is significant.
Industry likes the signal. Canada Nickel CEO Mark Selby says MPO referral “puts us in the fast lane,” even without the more controversial “national interest” label in Bill C-5 that would allow cabinet to set aside parts of the Fisheries Act, Species at Risk Act or Impact Assessment Act. Inuit proponents of the Iqaluit project welcome Carney’s description of their hydro plan as a breakthrough for Arctic sovereignty, replacing millions of litres of diesel.
But a superpower strategy this is not
Still, if this is what becoming an “energy superpower” looks like, it is a modest start.
Notably absent from Carney’s list is any new oil pipeline. Alberta Premier Danielle Smith has spent months pushing a concept for a bitumen pipeline from the oil sands to the northern B.C. coast, doing provincial groundwork in the hope a private proponent will one day take it over. A BBC report sets out the feud with B.C. Premier David Eby, who dismisses the idea as “fictional” and “political” and insists no company wants it, accusing Smith of jeopardizing B.C.’s LNG ambitions. Smith has called that stance “un-Canadian.”
Western frustration is growing. In the National Post, Whitecap Resources chief executive Grant Fagerheim warns of “fury from Alberta and Saskatchewan” if a pipeline to tidewater is never prioritized and argues producers are tired of a U.S.-dominated system where Canadian barrels sell at a discount while others capture the margins. He favours an energy corridor carrying oil, gas, power and rail, not just more rhetoric about nation-building.
Northern ambitions lag behind rhetoric
Another gap is the North. The Indigenous-led Arctic Gateway partnership, Manitoba and Ottawa are already spending heavily on the Hudson Bay Railway and planning new storage and loading systems to expand the Port of Churchill for grain, potash, critical minerals and Arctic resupply. Carney talks up a “huge host of opportunities” in northern Manitoba, but Churchill sits only on the MPO’s lower-profile “transformative strategies” list, with a full plan now pushed out to 2026.
Meanwhile, the one project that has fundamentally shifted Canada’s oil export position is the long-delayed Trans Mountain expansion. As Resource Works points out, TMX now sends diluted bitumen from Burnaby to Asia, shrinking the old “captive discount” and giving Canada genuine leverage in global markets. But TMX predates Carney’s government by more than a decade and only exists because Ottawa nationalized a struggling private pipeline to get it built.
Evolution, not revolution
Carney’s major-projects push is real, and for the companies involved, the prospect of faster permits and clearer federal backing is very good news. Yet for a government that talks about mobilizing a trillion dollars and remaking Canada as an energy superpower, the current list is evolutionary rather than revolutionary. For now, Ottawa is mostly trying to build what was already on the drawing board. The tougher choices on pipelines, ports and interprovincial trade still lie in front of it.
Headline photo credit to THE CANADIAN PRESS/Adrian Wyld
Business
Taxpayers paying wages and benefits for 30% of all jobs created over the last 10 years
From the Fraser Institute
By Jason Childs
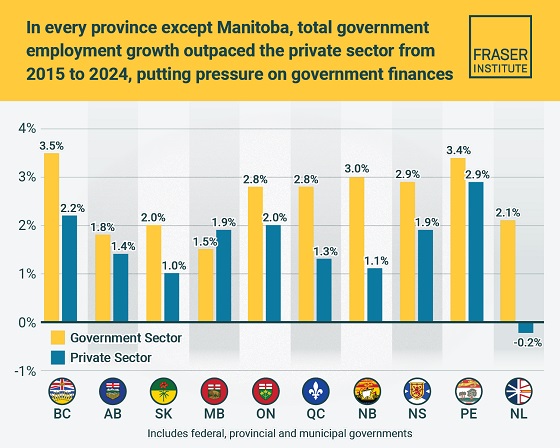
From 2015 to 2024, the government sector in Canada—including federal, provincial and municipal—added 950,000 jobs, which accounted for roughly 30 per cent of total employment growth in the country, finds a new study published today by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian public policy think-tank.
“In Canada, employment in the government sector has skyrocketed over the last 10 years,” said Jason Childs, a professor of economics at the University of Regina, senior fellow at the Fraser Institute and author of Examining the Growth of Public-Sector Employment Since 2015.
Over the same 10-year period (2015-2024), government-sector employment grew at an annual average rate of 2.7 per cent compared to only 1.7 per cent for the private sector. The study also examines employment growth by province. Government employment (federal, provincial, municipal) grew at a higher annual rate than the private sector in every province except Manitoba over the 10-year period.
The largest gaps between government-sector employment growth compared to the private sector were in Newfoundland and Labrador, New Brunswick, Quebec and British Columbia. The smallest gaps were in Alberta and Prince Edward Island.
“The larger government’s share of employment, the greater the ultimate burden on taxpayers to support government workers—government does not pay for itself,” Childs said.
A related study (Measuring the Cost to Canadians from the Growth in Public Administration, also authored by Childs) finds that, from 2015 to 2024, across all levels of government in Canada, the number of public administrators (many of who
work in government ministries, agencies and other offices that do not directly provide services to the public) grew by more than 328,000—or 3.5 per cent annually (on average).
“If governments want to reduce costs, they should look closely at the size of their public administration,” Childs said.
Examining the Growth of Public Sector Employment Since 2015
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta to protect three pro-family laws by invoking notwithstanding clause
-
 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoCDC’s Autism Reversal: Inside the Collapse of a 25‑Year Public Health Narrative
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoCanada is failing dismally at our climate goals. We’re also ruining our economy.
-

 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days ago‘Modern-Day Escobar’: U.S. Says Former Canadian Olympian Ran Cocaine Pipeline with Cartel Protection and a Corrupt Toronto Lawyer
-

 Crime1 day ago
Crime1 day agoCocaine, Manhunts, and Murder: Canadian Cartel Kingpin Prosecuted In US
-

 Health1 day ago
Health1 day agoBREAKING: CDC quietly rewrites its vaccine–autism guidance
-

 Alberta21 hours ago
Alberta21 hours agoPremier Smith explains how private clinics will be introduced in Alberta
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoTens of thousands are dying on waiting lists following decades of media reluctance to debate healthcare









