Crime
ICE: 662,000 criminal foreign nationals to be deported are living free nationwide
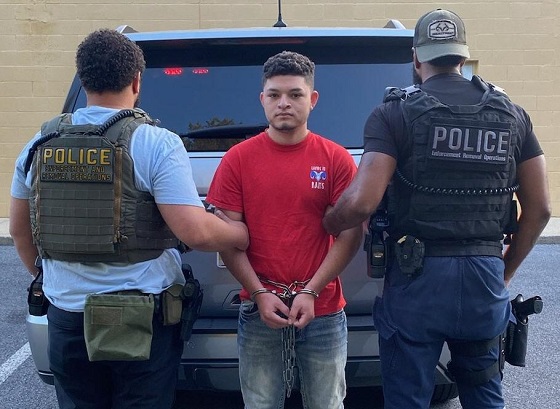

ICE-ERO Baltimore Fugitive Operations agents arrested and removed 19-year-old Guatemalan national Henry Argueta-Tobar, who was illegally in the country and convicted of raping a Maryland resident.
From The Center Square
By
387,000 criminal noncitizens arrested by ICE between fiscal 2021 and 2023
More than 660,000 criminal foreign nationals identified to be deported by U.S. Customs and Immigration Enforcement are freely living in communities nationwide.
Among them are those convicted or charged with violent crimes, including homicide, sexual assault and kidnapping, according to information released in response to a congressional request.
ICE was requested to provide information about the number of noncitizens on its docket for removal who are convicted or charged with a crime. As of July 21, 2024, “there were 662,566 noncitizens with criminal histories on ICE’s national docket, which includes those detained by ICE, and on the agency’s non-detained docket. Of those, 435,719 are convicted criminals, and 226,847 have pending criminal charges,” ICE Deputy Director Patrick Lechleitner said.
This includes criminal foreign nationals convicted of, or charged with, homicide (14,914), sexual assault (20,061), assault (105,146), kidnapping (3,372), and commercialized sexual offenses, including sex trafficking (3,971).
An additional 60,268 are on the list for burglary/larceny/robbery; 126,343 for traffic offenses including driving under the influence (DUIs) and 16,820 for weapons offenses.
ICE’s national docket refers to illegal foreign nationals who were apprehended by Border Patrol agents who then turn them over to ICE. Despite having a confirmed documented criminal history, ICE released them into the United States.
Lechleitner notes that some local jurisdictions “have reduced their cooperation with ICE, to include refusal to honor ICE detainer requests, even for noncitizens who have been convicted of serious felonies and pose an ongoing threat to public safety” due to their so-called “sanctuary city” policies. “However, ‘sanctuary’ policies can end up shielding dangerous criminals, who often victimize those same communities,” he said.
Because of local jurisdictions refusing to cooperate with ICE, the agency lifted detainers for 24,796 known criminals and released them into the U.S., he said. The data is from Oct. 1, 2020, through July 22, 2024.
Among them, state and local law enforcement agencies refused to comply with 23,591 detainer requests; 1,205 detainer requests were lifted “due to insufficient notice to ICE.”
Also during this period, ICE Enforcement and Removal Operations issued 2,897 detainers that were declined by state or local law enforcement agencies even after the subject of the detainer request had a subsequent apprehension by ICE ERO, according to the report.
Lechleitner also notes that “most noncitizens who are convicted of homicide are typically not eligible for release from ICE custody under §236(c) of the Immigration and Nationality Act” but “ICE officers may use their discretion in making custody determinations and release noncitizens with conditions.” He says these determinations are made on a “case-by-case basis.”
In response, U.S. House Committee on Homeland Security Chairman Mark Green, R-TN, said, “It may be shocking to hear that the Biden-Harris administration is actively releasing tens of thousands of criminal illegal aliens into our communities, but their own numbers conclusively prove this to be the case.
“This defies all common sense. Under President Biden and his ‘border czar,’ Vice President Harris, DHS law enforcement has been directed to mass-release illegal aliens whom they know have criminal convictions or are facing charges for serious crimes – and these dangerous, destructive individuals are making their way into every city and state in this country. How many more Americans need to die or be victimized before this administration is forced to abide by the laws they swore to uphold?
“This is madness. It is something no civilized, well-functioning society should tolerate.”
Texas Gov. Greg Abbott said the number was “shocking.”
“If accurate, it means that almost 10%” of the criminal illegal foreign nationals released into the country by the Biden-Harris administration “are criminals. It also debunks the narrative that illegal immigrants are less likely to commit crime. We can’t survive four more years of this.”
More than 387,000 criminal noncitizens were arrested by ICE ERO agents in fiscal years 2021 through 2023, The Center Square first reported.
The majority arrested were citizens of Mexico, Nicaragua, Columbia and Venezuela.
The majority of arrests occurred in Dallas and Houston, Texas, according to an ICE online statistical dashboard. The most common arrests are of those convicted of DUIs, drug possession, and assault and criminal (non-civil) traffic offenses like hit-and-run or leaving the scene of an accident, ICE says.
Additionally, a separate data point shows that U.S. Customs and Border Protection and Border Patrol apprehensions of criminal noncitizens totaled nearly 54,000 since fiscal 2021, according to CBP data as of Sept. 16. The majority were for illegal entry and reentry and DUIs.
Crime
CBSA Bust Uncovers Mexican Cartel Network in Montreal High-Rise, Moving Hundreds Across Canada-U.S. Border

A court document cited by La Presse in prior reporting on the case.
The conviction targets Edgar Gonzalez de Paz, 37, a Mexican national identified in court evidence as a key organizer in a Montreal-based smuggling network that La Presse documented in March through numerous legal filings.
According to the Canada Border Services Agency, Gonzalez de Paz’s guilty plea acknowledges that he arranged a clandestine crossing for seven migrants on January 27–28, 2024, in exchange for money. He had earlier been arrested and charged with avoiding examination and returning to Canada without authorization.
Breaking the story in March, La Presse reported: “A Mexican criminal organization has established itself in Montreal, where it is making a fortune by illegally smuggling hundreds of migrants across the Canada-U.S. border. Thanks to the seizure of two accounting ledgers, Canadian authorities have gained unprecedented access to the group’s secrets, which they hope to dismantle in the coming months.”
La Presse said the Mexico-based organization ran crossings in both directions — Quebec to the United States and vice versa — through roughly ten collaborators, some family-linked, charging $5,000 to $6,000 per trip and generating at least $1 million in seven months.
The notebooks seized by CBSA listed clients, guarantors, recruiters in Mexico, and accomplices on the U.S. side. In one April 20, 2024 interception near the border, police stopped a vehicle registered to Gonzalez de Paz and, according to evidence cited by La Presse, identified him as one of the “main organizers,” operating without legal status from a René-Lévesque Boulevard condo that served as headquarters.
Seizures included cellphones, a black notebook, and cocaine. A roommate’s second notebook helped authorities tally about 200 migrants and more than $1 million in receipts.
“This type of criminal organization is ruthless and often threatens customers if they do not pay, or places them in a vulnerable situation,” a CBSA report filed as evidence stated, according to La Presse.
The Montreal-based organization first appeared on the radar in a rural community of about 400 inhabitants in the southern Montérégie region bordering New York State, La Presse reported, citing court documents.
On the U.S. side of the line, in the Swanton Sector (Vermont and adjoining northern New York and New Hampshire), authorities reported an exceptional surge in 2022–2023 — driven largely by Mexican nationals rerouting via Canada — foreshadowing the Mexican-cartel smuggling described in the CBSA case.
Gonzalez de Paz had entered Canada illegally in 2023, according to La Presse. When officers arrested him, CBSA agents seized 30 grams of cocaine, two cellphones, and a black notebook filled with handwritten notes. In his apartment, they found clothing by Balenciaga, a luxury brand whose T-shirts retail for roughly $1,000 each.
Investigators have linked this case to another incident at the same address involving a man named Mario Alberto Perez Gutierrez, a resident of the same condo as early as 2023.
Perez Gutierrez was accompanied by several men known to Canadian authorities for cocaine trafficking, receiving stolen goods, armed robbery, or loitering in the woods near the American border, according to a Montreal Police Service (SPVM) report filed as evidence.
The CBSA argued before the immigration tribunal that Gonzalez de Paz belonged to a group active in human and drug trafficking — “activities usually orchestrated by Mexican cartels.”
As The Bureau has previously reported, Justin Trudeau’s Liberal Cabinet was warned in 2016 that lifting visa requirements for Mexican visitors would “facilitate travel to Canada by Mexicans with criminal records,” potentially including “drug smugglers, human smugglers, recruiters, money launderers and foot soldiers.”
CBSA “serious-crime” flags tied to Mexican nationals rose sharply after the December 2016 visa change. Former CBSA officer Luc Sabourin, in a sworn affidavit cited by The Bureau, alleged that hundreds of cartel-linked operatives entered Canada following the visa lift.
The closure of Roxham Road in 2023 altered migrant flows and increased reliance on organized smugglers — a shift reflected in the ledger-mapped Montreal network and a spike in U.S. northern-border encounters.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Crime
Public Execution of Anti-Cartel Mayor in Michoacán Prompts U.S. Offer to Intervene Against Cartels

“I don’t want to be just another mayor on the list of those executed”
On the first night of November, during Day of the Dead celebrations, the independent, anti-cartel mayor of Uruapan in Michoacán, Carlos Manzo, was assassinated in the heart of his city during a public festival. His bloody murder has underscored the deadly risks faced by local officials who may lack adequate protection from a state that critics say is corroded by corruption and penetrated by powerful cartel networks that, in some regions, have supplanted government authority. The killing intensifies urgent questions about political and police corruption, cartel impunity, and the scope of U.S.–Mexico security cooperation — with a response from the U.S. State Department today offering to “deepen security cooperation with Mexico.”
Manzo, a fiercely outspoken anti-cartel mayor who took office in 2024 as Uruapan’s first independent leader, was gunned down as he stood before crowds at the annual Day of the Dead candlelight celebration. Witnesses said gunfire erupted shortly after Manzo appeared onstage, holding his young son moments before the attack. The festival, known locally as the Festival de las Velas, drew hundreds of families to Uruapan’s central plaza — now transformed into the scene of Mexico’s latest high-profile political assassination, and a catalyst for nationwide outrage, as online protests surged and citizens called for demonstrations against cartel violence.
According to early reports, at least two suspects have been detained and one attacker was killed on site. Authorities asserted — despite the success of the attack — that Manzo had been under National Guard protection since December 2024, with additional reinforcements added in May 2025 following credible threats to his life.
In Washington today, the killing drew political reaction. “My thoughts are with the family and friends of Carlos Manzo, mayor of Uruapan, Michoacán, Mexico, who was assassinated at a public Day of the Dead celebration last night. The United States stands ready to deepen security cooperation with Mexico to wipe out organized crime on both sides of the border,” Deputy Secretary of State Christopher Landau, the former U.S. ambassador to Mexico, said in a statement shared online.
Federal Security Minister Omar García Harfuch said the gunmen “took advantage of the vulnerability of a public event” to carry out the attack, despite a standing security perimeter.
President Claudia Sheinbaum condemned the killing as a “vile” assault on democracy and vowed there would be “zero impunity.” Her administration convened an emergency security meeting and pledged that the investigation would reach the “intellectual authors” of the crime. Yet the murder has already ignited outrage across Mexico over the government’s failure to protect local officials in cartel-dominated states such as Michoacán, where extortion, assassinations, and territorial disputes continue to erode basic governance.
Manzo had publicly warned of his fate. “I don’t want to be just another mayor on the list of those executed,” he said earlier this year, as he pressed the federal government for better coordination between municipal and military authorities. For years, Uruapan — an agricultural and trade hub in western Mexico — has been the site of deadly clashes between the Jalisco New Generation Cartel and remnants of the Knights Templar Organization, both vying to control lucrative extortion and drug routes.
The killing of Manzo fits a dark and familiar pattern. In 2025 alone, several mayors in Michoacán, Guerrero, and Tamaulipas have been killed in attacks widely attributed to organized-crime groups. In June, the mayors of Tepalcatepec and Tacámbaro were ambushed and slain while traveling in official convoys. More than 90 local officials have been murdered since 2018 — a rate that analysts say reflects how cartels target municipal governments to ensure political control over territories tied to narcotics, mining, and agriculture. Uruapan, at the heart of Mexico’s avocado belt, is a strategic prize for the cartels that tax every shipment leaving the region.
The mayor’s death also recalls earlier tragedies that scarred the nation. In 2012, Dr. María Santos Gorrostieta Salazar, the former mayor of Tiquicheo, was abducted and murdered after surviving two assassination attempts and defying cartel threats. Her death became emblematic of the dangers faced by reformers who refuse to cooperate with criminal groups. More than a decade later, Manzo’s murder illustrates that little has changed — except the brazenness of the attackers, now willing to strike in front of cameras and families celebrating one of Mexico’s most sacred holidays.
The killing has also reignited long-standing U.S. frustration over Mexico’s inability to stem cartel violence, even as the Trump administration has expanded counter-narcotics operations at the border. Under Trump’s renewed directives, the U.S. has classified several Mexican cartels as foreign terrorist organizations and empowered the Pentagon to develop strike options against high-value targets abroad. A September 2025 joint statement between Washington and Mexico City pledged deeper intelligence sharing and cross-border enforcement initiatives, including efforts to halt arms trafficking southward.
However, Mexico’s government remains deeply wary of any U.S. military involvement on its soil. President Sheinbaum has warned that “Mexico will not stand for an invasion in the name of counter-cartel operations,” rebuffing Republican calls for unilateral action. Her position lays bare a long-standing tension between Mexico’s need for U.S. support and its insistence on sovereignty — a fault line that Manzo’s killing has reignited.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
-

 armed forces2 days ago
armed forces2 days agoIt’s time for Canada to remember, the heroes of Kapyong
-

 Digital ID2 days ago
Digital ID2 days agoCanada moves forward with digital identification for federal benefits seekers
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoUS Nuclear Bomber Fleet Shares Fence With Trailer Park Linked To Chinese Intel-Tied Fraudster
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoSchool defunding petition in Alberta is a warning to parents
-
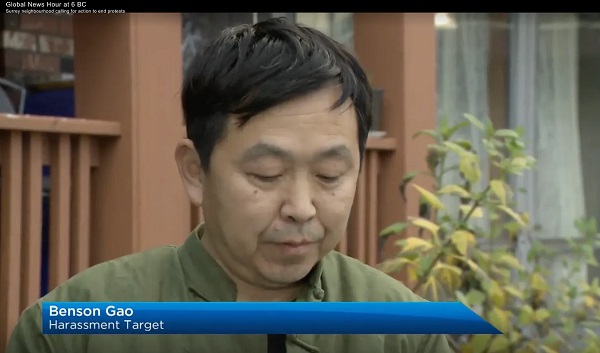
 espionage1 day ago
espionage1 day agoChinese-Owned Trailer Park Beside U.S. Stealth Bomber Base Linked to Alleged Vancouver Repression Case
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoLaura Ingraham Presses Trump On Allowing Flood Of Chinese Students Into US
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoLiberals refuse to disclose the amount of taxpayer dollars headed to LGBT projects in foreign countries
-

 Environment1 day ago
Environment1 day agoThe Myths We’re Told About Climate Change | Michael Shellenberger








