Addictions
Field of death: Art project highlights drug crisis’ impact on tradespeople

City Counsellor Ron Kerr’s Blue Hat Memorial Project at the Tyee Spit in Campbell River, B.C., April 2025. | Courtesy of Ron Kerr
By Alexandra Keeler
The drug crisis is really a men’s mental health crisis, says Ron Kerr, the artist and city councillor behind a visually staggering project
Fifty thousand flags blanket the north end of Tyee Spit in Campbell River, B.C. — a staggering visual memorial to the lives lost in Canada’s opioid crisis since it was declared a public health emergency in 2016.
Called the Blue Hat Memorial Project, the installation spans nearly the length of a football field. It features 36,000 blue flags to represent the men and boys killed by toxic drugs, and 14,000 purple flags for women and girls.
“The actual installation does something you can’t do by just reading [about it],” said Ron Kerr, the artist behind the project. Kerr is also a city councillor in Campbell River, a city of 38,000 on the northeast coast of Vancouver Island.
“You’re visually seeing it, and it’s going right to your heart and creating an emotional response,” he said.
The installation’s name is a reference to the blue hard hats worn by newcomers or trainees on blue-collar job sites. Kerr says one of his aims is to draw attention to how the drug crisis has acutely affected working-class men. Between one-third and half of the individuals who died of opioid poisoning worked in the skilled trades, according to public health data.
Kerr, who has worked closely with tradesmen as an artist and advocate in men’s peer support groups, describes many of these tradesmen as “functional addicts” — employed, seemingly stable individuals who privately use drugs to manage pain or depression without others noticing.
“They are doing drugs at home or in their garage, and people don’t even know that they are [because] they’re functional, they’re working,” he said. “They’re able to control their depression or occupational injury through opiate drugs.”
Tradespeople are especially vulnerable to developing substance use disorders due to the physical demands, long hours and high injury rates associated with their work. Many use stimulants to stay alert or opioids to manage pain or cope with isolation in remote jobs.
“There is an expectation to get out the next day and get to work, no matter how you’re feeling,” said Kerr. “Self-medication is the easiest way to do it — a slippery slope from Tylenol to prescription drugs.”
A 2021 survey by the Construction Industry Rehabilitation Plan found that one in three B.C. construction workers reported problematic substance use. More than two-thirds screened positive for PTSD.
Loneliness is another major driver. Experts say men often avoid seeking help due to stigma, leading to further isolation.
“The opposite of addiction is connection,” said Kerr. “Men don’t have a place to go when they can’t deal with their issues, so they self-medicate.”
A pattern flipped
When Kerr first launched the installation in August 2024, he and a team of volunteers initially planted only blue flags. But in response to questions like, “Where are the women?”, he added purple flags this year.
“It was a blending — to give them their due,” he said.
Kerr’s installation sits on the unceded territory of the Liǧʷiłdax̌ʷ people, including the Wei Wai Kum Nation, a nation of nearly 1,000 people.
Wei Wai Kum’s chief, Chris Roberts, told Canadian Affairs he does not want the project’s focus on men to overshadow other key trends.
In B.C., Indigenous people die from drug poisoning at nearly seven times the rate of the general population. And within many Indigenous communities, the gendered pattern is at odds with national trends: women are dying at even higher rates than men.
“The opioid crisis has significantly affected my community as well, and it continues to — we are overrepresented as Indigenous people,” Roberts said.
“In our case, the gender split is much more balanced,” he added.
 |
An aerial view of the Blue Hat Memorial Project in Campbell River, B.C., April 2025. | Courtesy of Ron Kerr
‘Inadequate recovery’
Currently, Campbell River — the overdose epicentre of northern Vancouver Island — has only one aging recovery centre.
“[The city is] a hub for the whole North Island, but we have very little in terms of recovery,” said Kerr. “[There is] just one inadequate recovery centre in a 50-60 year old house with tiny rooms.”
Kerr is critical of how B.C. has implemented harm reduction strategies. He says policies such as drug decriminalization and safer supply were launched without the recovery infrastructure needed to make them effective.
“[Portugal] legalized drugs too, but the most important thing was that they provided the recovery services for them — they went all in,” said Kerr. “In this province, they just haven’t spent the money and time on doing that.”
Kerr also worries too many resources have gone to safer supply programs, without offering drug users a way out.
“When you get a person in full-blown addiction, and you’re giving them all the drugs they need, the food they need, and the clothes and shelter, what’s going to stop them from carrying on?” he said.
Subscribe for free to get BTN’s latest news and analysis – or donate to our investigative journalism fund.
Kerr wants his installation to draw attention to the need for more recovery-oriented solutions, such as treatment centres and housing. In particular, he points to a lack of affordable or free housing for people to live in after initial recovery.
“What you need is a good, clear off-ramp,” said Kerr. “They need to have recovery options that are either affordable or free so they can get off the road that they’re on.”
Chief Roberts agrees. Wei Wai Kai Nation is currently converting the former Tsạkwạ’lutạn resort into a 40-bed healing centre that will combine medical care with culture-based recovery.
“We’ve made investments to acquire properties and assets where people can go and reconnect with the land, the territory and their identity as a Ligwilda’xw person,” Roberts said.
Kerr says he will consider the Blue Hat Memorial a success if it leads to more funding and momentum for these types of recovery-oriented services.
The Blue Hat Memorial remains in Campbell River until the end of April. But Kerr, who previously re-created the installation in Nanaimo and West Vancouver, says he remains committed to doing more projects.
“I’ve got no expectation of senior government to come along and do this without a groundswell of grassroots people saying ‘we need this,’ and pushing government to do it,” said Kerr.
“I’m going to keep having the installation until that happens.”
This article was produced through the Breaking Needles Fellowship Program, which provided a grant to Canadian Affairs, a digital media outlet, to fund journalism exploring addiction and crime in Canada. Articles produced through the Fellowship are co-published by Break The Needle and Canadian Affairs.
Subscribe to Break The Needle.
Our content is always free – but if you want to help us commission more high-quality journalism, consider getting a voluntary paid subscription.
Addictions
Canada must make public order a priority again

A Toronto park
Public disorder has cities crying out for help. The solution cannot simply be to expand our public institutions’ crisis services
[This editorial was originally published by Canadian Affairs and has been republished with permission]
This week, Canada’s largest public transit system, the Toronto Transit Commission, announced it would be stationing crisis worker teams directly on subway platforms to improve public safety.
Last week, Canada’s largest library, the Toronto Public Library, announced it would be increasing the number of branches that offer crisis and social support services. This builds on a 2023 pilot project between the library and Toronto’s Gerstein Crisis Centre to service people experiencing mental health, substance abuse and other issues.
The move “only made sense,” Amanda French, the manager of social development at Toronto Public Library, told CBC.
Does it, though?
Over the past decade, public institutions — our libraries, parks, transit systems, hospitals and city centres — have steadily increased the resources they devote to servicing the homeless, mentally ill and drug addicted. In many cases, this has come at the expense of serving the groups these spaces were intended to serve.
For some communities, it is all becoming too much.
Recently, some cities have taken the extraordinary step of calling states of emergency over the public disorder in their communities. This September, both Barrie, Ont. and Smithers, B.C. did so, citing the public disorder caused by open drug use, encampments, theft and violence.
In June, Williams Lake, B.C., did the same. It was planning to “bring in an 11 p.m. curfew and was exploring involuntary detention when the province directed an expert task force to enter the city,” The Globe and Mail reported last week.
These cries for help — which Canadian Affairs has also reported on in Toronto, Ottawa and Nanaimo — must be taken seriously. The solution cannot simply be more of the same — to further expand public institutions’ crisis services while neglecting their core purposes and clientele.
Canada must make public order a priority again.
Without public order, Canadians will increasingly cease to patronize the public institutions that make communities welcoming and vibrant. Businesses will increasingly close up shop in city centres. This will accelerate community decline, creating a vicious downward spiral.
We do not pretend to have the answers for how best to restore public order while also addressing the very real needs of individuals struggling with homelessness, mental illness and addiction.
But we can offer a few observations.
First, Canadians must be willing to critically examine our policies.
Harm-reduction policies — which correlate with the rise of public disorder — should be at the top of the list.
The aim of these policies is to reduce the harms associated with drug use, such as overdose or infection. They were intended to be introduced alongside investments in other social supports, such as recovery.
But unlike Portugal, which prioritized treatment alongside harm reduction, Canada failed to make these investments. For this and other reasons, many experts now say our harm-reduction policies are not working.
“Many of my addiction medicine colleagues have stopped prescribing ‘safe supply’ hydromorphone to their patients because of the high rates of diversion … and lack of efficacy in stabilizing the substance use disorder (sometimes worsening it),” Dr. Launette Rieb, a clinical associate professor at the University of British Columbia and addiction medicine specialist recently told Canadian Affairs.
Yet, despite such damning claims, some Canadians remain closed to the possibility that these policies may need to change. Worse, some foster a climate that penalizes dissent.
“Many doctors who initially supported ‘safe supply’ no longer provide it but do not wish to talk about it publicly for fear of reprisals,” Rieb said.
Second, Canadians must look abroad — well beyond the United States — for policy alternatives.
As The Globe and Mail reported in August, Canada and the U.S. have been far harder hit by the drug crisis than European countries.
The article points to a host of potential factors, spanning everything from doctors’ prescribing practices to drug trade flows to drug laws and enforcement.
For example, unlike Canada, most of Europe has not legalized cannabis, the article says. European countries also enforce their drug laws more rigorously.
“According to the UN, Europe arrests, prosecutes and convicts people for drug-related offences at a much higher rate than that of the Americas,” it says.
Addiction treatment rates also vary.
“According to the latest data from the UN, 28 per cent of people with drug use disorders in Europe received treatment. In contrast, only 9 per cent of those with drug use disorders in the Americas received treatment.”
And then there is harm reduction. No other country went “whole hog” on harm reduction the way Canada did, one professor told The Globe.
If we want public order, we should look to the countries that are orderly and identify what makes them different — in a good way.
There is no shame in copying good policies. There should be shame in sticking with failed ones due to ideology.
Our content is always free – but if you want to help us commission more high-quality journalism,
consider getting a voluntary paid subscription.
Addictions
No, Addicts Shouldn’t Make Drug Policy

By Adam Zivo
Canada’s policy of deferring to the “leadership” of drug users has proved predictably disastrous. The United States should take heed.
[This article was originally published in City Journal, a public policy magazine and website published by the Manhattan Institute for Policy Research]
Progressive “harm reduction” advocates have insisted for decades that active users should take a central role in crafting drug policy. While this belief is profoundly reckless—akin to letting drunk drivers set traffic laws—it is now entrenched in many left-leaning jurisdictions. The harms and absurdities of the position cannot be understated.
While the harm-reduction movement is best known for championing public-health interventions that supposedly minimize the negative effects of drug use, it also has a “social justice” component. In this context, harm reduction tries to redefine addicts as a persecuted minority and illicit drug use as a human right.
This campaign traces its roots to the 1980s and early 1990s, when “queer” activists, desperate to reduce the spread of HIV, began operating underground needle exchanges to curb infections among drug users. These exchanges and similar efforts allowed some more extreme LGBTQ groups to form close bonds with addicts and drug-reform advocates. Together, they normalized the concept of harm reduction, such that, within a few years, needle exchanges would become officially sanctioned public-health interventions.
The alliance between these more radical gay rights advocates and harm-reduction proponents proved enduring. Drug addiction remained linked to HIV, and both groups shared a deep hostility to the police, capitalism, and society’s “moralizing” forces.
In the 1990s, harm-reduction proponents imitated the LGBTQ community’s advocacy tactics. They realized that addicts would have greater political capital if they were considered a persecuted minority group, which could legitimize their demands for extensive accommodations and legal protections under human rights laws. Harm reductionists thus argued that addiction was a kind of disability, and that, like the disabled, active users were victims of social exclusion who should be given a leading role in crafting drug policy.
These arguments were not entirely specious. Addiction can reasonably be considered a mental and physical disability because illicit drugs hijack users’ brains and bodies. But being disabled doesn’t necessarily mean that one is part of a persecuted group, much less that one should be given control over public policy.
More fundamentally, advocates were wrong to argue that the stigma associated with drug addiction was senseless persecution. In fact, it was a reasonable response to anti-social behavior. Drug addiction severely impairs a person’s judgement, often making him a threat to himself and others. Someone who is constantly high and must rob others to fuel his habit is a self-evident danger to society.
Despite these obvious pitfalls, portraying drug addicts as a persecuted minority group became increasingly popular in the 2000s, thanks to several North American AIDS organizations that pivoted to addiction work after the HIV epidemic subsided.
In 2005, the Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network published a report titled “Nothing about us without us.” (The nonprofit joined other groups in publishing an international version in 2008.) The 2005 report included a “manifesto” written by Canadian drug users, who complained that they were “among the most vilified and demonized groups in society” and demanded that policymakers respect their “expertise and professionalism in addressing drug use.”
The international report argued that addiction qualified as a disability under international human rights treaties, and called on governments to “enact anti-discrimination or protective laws to reduce human rights violations based on dependence to drugs.” It further advised that drug users be heavily involved in addiction-related policy and decision-making bodies; that addict-led organizations be established and amply funded; and that “community-based organizations . . . increase involvement of people who use drugs at all levels of the organization.”
While the international report suggested that addicts could serve as effective policymakers, it also presented them as incapable of basic professionalism. In a list of “do’s and don’ts,” the authors counseled potential employers to pay addicts in cash and not to pass judgment if the money were spent on drugs. They also encouraged policymakers to hold meetings “in a low-key setting or in a setting where users already hang out,” and to avoid scheduling meetings at “9 a.m., or on welfare cheque issue day.” In cases where addicts must travel for policy-related work, the report recommended policymakers provide “access to sterile injecting equipment” and “advice from a local person who uses drugs.”
The international report further asserted that if an organization’s employees—even those who are former drug users—were bothered by the presence of addicts, then management should refer those employees to counselling at the organization’s expense. “Under no circumstances should [drug addicts] be reprimanded, singled out or made to feel responsible in any way for the triggering responses of others,” stressed the authors.
Reflecting the document’s general hostility to recovery, the international report emphasized that former drug addicts “can never replace involvement of active users” in public policy work, because people in recovery “may be somewhat disconnected from the community they seek to represent, may have other priorities than active users, may sometimes even have different and conflicting agenda, and may find it difficult to be around people who currently use drugs.”
Subscribe for free to get BTN’s latest news and analysis – or donate to our investigative journalism fund.
The messaging in these reports proved highly influential throughout the 2000s and 2010s. In Canada, federal and provincial human rights legislation expanded to protect active addicts on the basis of disability. Reformers in the United States mirrored Canadian activists’ appeals to addicts’ “lived experience,” albeit with less success. For now, American anti-discrimination protections only extend to people who have a history of addiction but who are not actively using drugs.
The harm reduction movement reached its zenith in the early 2020s, after the Covid-19 pandemic swept the world and instigated a global spike in addiction. During this period, North American drug-reform activists again promoted the importance of treating addicts like public-health experts.
Canada was at the forefront of this push. For example, the Canadian Association of People Who Use Drugs released its “Hear Us, See Us, Respect Us” report in 2021, which recommended that organizations “deliberately choose to normalize the culture of drug use” and pay addicts $25-50 per hour. The authors stressed that employers should pay addicts “under the table” in cash to avoid jeopardizing access to government benefits.
These ideas had a profound impact on Canadian drug policy. Throughout the country, public health officials pushed for radical pro-drug experiments, including giving away free heroin-strength opioids without supervision, simply because addicts told researchers that doing so would be helpful. In 2024, British Columbia’s top doctor even called for the legalization of all illicit drugs (“non-medical safer supply”) primarily on the basis of addict testimonials, with almost no other supporting evidence.
For Canadian policymakers, deferring to the “lived experiences” and “leadership” of drug users meant giving addicts almost everything they asked for. The results were predictably disastrous: crime, public disorder, overdoses, and program fraud skyrocketed. Things have been less dire in the United States, where the harm reduction movement is much weaker. But Americans should be vigilant and ensure that this ideology does not flower in their own backyard.
Subscribe to Break The Needle.
Our content is always free – but if you want to help us commission more high-quality journalism,
consider getting a voluntary paid subscription.
-
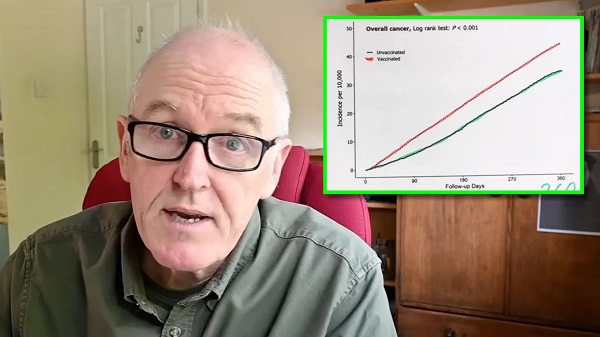
 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoDevastating COVID-19 Vaccine Side Effect Confirmed by New Data: Study
-

 Red Deer1 day ago
Red Deer1 day agoThe City of Red Deer’s Financial Troubles: Here Are The Candidates I Am Voting For And Why.
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTrump and Carney full of warm compliments but still no trade deal between Canada and U.S.
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoCanada Post is failing Canadians—time to privatize it
-

 Haultain Research2 days ago
Haultain Research2 days agoInclusion and Disorder: Unlearned Lessons from Palestinian Protests
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoGovernment distorts financial picture with definition of capital
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day ago‘We’re Really, Really Close’: Freed Gaza Hostages, Relatives Have High Hopes For Trump’s Peace Plan
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoFinance Minister ducks deficit questions, talks down to critics, and rebrands reckless spending as ‘transparency’.









