Automotive
Electric vehicle mandates mean misery all around

From the Fraser Institute
By Matthew Lau
The latest news of slowing demand for electric vehicles highlight the profound hazards of the federal government’s Soviet-style mandate that 100 per cent of new light-duty vehicles sold must be electric or plug-in hybrid by 2035 (with interim targets of 20 per cent by 2026 and 60 per cent by 2030, with steep penalties for dealers missing these targets).
The targets were wild to begin with—as Manhattan Institute senior fellow Mark P. Mills observed, bans on conventional vehicles and mandated switches to electric mean, in jurisdictions such as Canada, “consumers will need to adopt EVs at a scale and velocity 10 times greater and faster than the introduction of any new model of car in history.”
Indeed, when the Trudeau government announced its mandate last December, conventional vehicles accounted for 87 per cent of the market, and today the mandated switch to electric looks even more at odds with actual consumer preferences. According to reports, Tesla will cut its global workforce by more than 10 per cent (or more than 14,000 employees) due to slowing electric vehicle demand.
In Canada, a Financial Post headline reads, “‘Tall order to ask the average Canadian’: EVs are twice as hard to sell today.” Not only has Tesla’s quarterly sales declined, Ford Motor Co. announced in April it will delay the start of electric vehicle production at its Oakville plant by two years, from 2025 to 2027.
According to research from global data and analytics firm J.D. Power, it now takes 55 days to sell an electric vehicle in Canada, up from 22 days in the first quarter of 2023 and longer than the 51 days it takes a gasoline-powered car to sell. This is the result, some analysts suggest, of a lack of desirable models and high consumer prices—and despite federal subsidies to car buyers of up to $5,000 per electric vehicle and additional government subsidies in six provinces, as high as $7,000 in Quebec.
Similarly in the United States, the Wall Street Journal reports that on average, electric vehicles and plug-in hybrids sit in dealer lots longer than gasoline-powered cars and hybrids. Again, that’s despite heavy government pressure to switch to electric—the Biden administration mandated two-thirds of new vehicles sold must be electric by 2032.
In both Canada and the U.S., politicians banning consumers from buying vehicles they want and instead forcing them to buy the types of vehicles that run contrary to their preferences, call to mind famed philosopher Adam Smith’s “man of system,” described in his 1759 book, The Theory of Moral Sentiments.
The man of system, Smith explained, “is apt to be very wise in his own conceit” and “seems to imagine that he can arrange the different members of a great society with as much ease as the hand arranges the different pieces upon a chess–board.” But people are not chess pieces to be moved around by a hand from above; they have their own agency and if pushed by the “man of system” in a direction opposite to where they want to go, the result will be misery and “society must be at all times in the highest degree of disorder.”
That nicely sums up the current government effort to mandate electric vehicles contrary to consumer preferences. The vehicle market is in a state of disorder as the government tries to force people to buy the types of cars many of them do not want, and the outcomes are miserable all around.
Author:
Automotive
Politicians should be honest about environmental pros and cons of electric vehicles

From the Fraser Institute
By Annika Segelhorst and Elmira Aliakbari
According to Steven Guilbeault, former environment minister under Justin Trudeau and former member of Prime Minister Carney’s cabinet, “Switching to an electric vehicle is one of the most impactful things Canadians can do to help fight climate change.”
And the Carney government has only paused Trudeau’s electric vehicle (EV) sales mandate to conduct a “review” of the policy, despite industry pressure to scrap the policy altogether.
So clearly, according to policymakers in Ottawa, EVs are essentially “zero emission” and thus good for environment.
But is that true?
Clearly, EVs have some environmental advantages over traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. Unlike cars with engines that directly burn fossil fuels, EVs do not produce tailpipe emissions of pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide, and do not release greenhouse gases (GHGs) such as carbon dioxide. These benefits are real. But when you consider the entire lifecycle of an EV, the picture becomes much more complicated.
Unlike traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, battery-powered EVs and plug-in hybrids generate most of their GHG emissions before the vehicles roll off the assembly line. Compared with conventional gas-powered cars, EVs typically require more fossil fuel energy to manufacture, largely because to produce EVs batteries, producers require a variety of mined materials including cobalt, graphite, lithium, manganese and nickel, which all take lots of energy to extract and process. Once these raw materials are mined, processed and transported across often vast distances to manufacturing sites, they must be assembled into battery packs. Consequently, the manufacturing process of an EV—from the initial mining of materials to final assembly—produces twice the quantity of GHGs (on average) as the manufacturing process for a comparable gas-powered car.
Once an EV is on the road, its carbon footprint depends on how the electricity used to charge its battery is generated. According to a report from the Canada Energy Regulator (the federal agency responsible for overseeing oil, gas and electric utilities), in British Columbia, Manitoba, Quebec and Ontario, electricity is largely produced from low- or even zero-carbon sources such as hydro, so EVs in these provinces have a low level of “indirect” emissions.
However, in other provinces—particularly Alberta, Saskatchewan and Nova Scotia—electricity generation is more heavily reliant on fossil fuels such as coal and natural gas, so EVs produce much higher indirect emissions. And according to research from the University of Toronto, in coal-dependent U.S. states such as West Virginia, an EV can emit about 6 per cent more GHG emissions over its entire lifetime—from initial mining, manufacturing and charging to eventual disposal—than a gas-powered vehicle of the same size. This means that in regions with especially coal-dependent energy grids, EVs could impose more climate costs than benefits. Put simply, for an EV to help meaningfully reduce emissions while on the road, its electricity must come from low-carbon electricity sources—something that does not happen in certain areas of Canada and the United States.
Finally, even after an EV is off the road, it continues to produce emissions, mainly because of the battery. EV batteries contain components that are energy-intensive to extract but also notoriously challenging to recycle. While EV battery recycling technologies are still emerging, approximately 5 per cent of lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in EVs, are actually recycled worldwide. This means that most new EVs feature batteries with no recycled components—further weakening the environmental benefit of EVs.
So what’s the final analysis? The technology continues to evolve and therefore the calculations will continue to change. But right now, while electric vehicles clearly help reduce tailpipe emissions, they’re not necessarily “zero emission” vehicles. And after you consider the full lifecycle—manufacturing, charging, scrapping—a more accurate picture of their environmental impact comes into view.
Automotive
The $50 Billion Question: EVs Never Delivered What Ottawa Promised
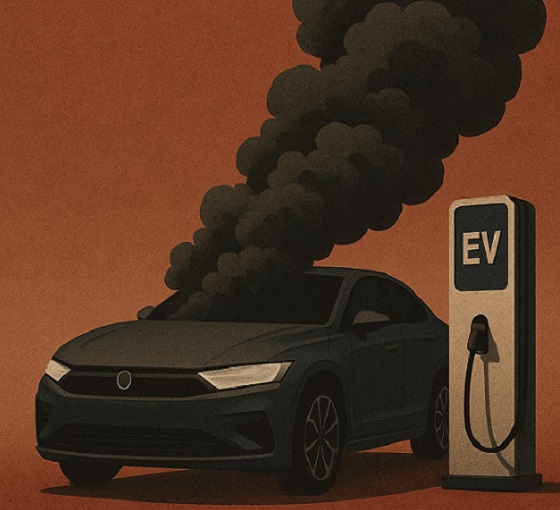

Beware of government promises that arrive gift-wrapped in moral certainty.
The pattern repeats across the sector: subsidies extracted, production scaled back, workers laid off, taxpayers absorbing losses while executives collect bonuses and move on, and politicians pretend that it never happened. CBC isn’t asking Justin Trudeau, Katherine McKenna or Steven Guilbeault any questions about it. They are not asking Mark Carney.
Buy an electric vehicle, they said, and you will save the planet, no questions asked. Justin Trudeau and several of his ministers proclaimed it from podiums. Environmental activists, often cabinet members, chanted it at rallies. Automotive executives leveraged it to extract giant subsidies. For over a decade, the message never wavered: until $50 billion in public money disappeared into corporate failures, and the economic wreckage became impossible to ignore.
Prime Minister Mark Carney, himself a spokesperson for the doomsday culture, inherited the policy disaster from Trudeau and still clings to the wreckage. The 2026 EV sales target sits suspended, a grudging acknowledgment that reality refused to cooperate with radical predictions and Ottawa’s mandates. Yet the 2030 and 2035 targets remain federal law, monuments to a central-planning exercise that delivered the opposite of what it promised.
Their claims were never quite true. Electric vehicles were pure good. They were marketed as unconditionally cleaner than conventional cars, a transformation so obviously beneficial that questioning it invited accusations of climate denial. Government messaging suggested switching to an EV meant immediate environmental virtue. The nuance, the conditions, and the caveats were conveniently omitted from the government sales pitch that justified tens of billions of your money into subsidies for foreign EV manufacturing and corporate advancement.
The Reality Ottawa Is Hiding
Research documented the conditional nature of EV benefits for over a decade, yet Ottawa proceeded as if the complexity didn’t exist. Studies from China, where coal dominates electricity generation, showed as early as 2010 that EVs in coal-dependent regions had “very limited benefits” in reducing emissions compared to gasoline vehicles. In Northern China, where electricity generation is over 80% coal-based, EVs could produce lifecycle emissions comparable to or even higher than those of conventional cars. A 2015 Chinese study found that EVs generated lifecycle emissions that were only 18% lower than those of gasoline vehicles, compared to 40-70% reductions in regions with cleaner grids.
Volvo began publishing transparent lifecycle assessments for its first EV in 2019, making it the first major automaker to document the significant upfront emissions from battery production publicly. Their 2021 C40 Recharge report, released during the COP26 climate summit in Glasgow, revealed that manufacturing an EV produces 70% more emissions than building a comparable conventional vehicle. But there are no CBC reports about that. The Volvo report showed that an EV charged on a coal-heavy global grid required 68,000 to 110,000 miles of driving to break even with a conventional car, potentially more than half the vehicle’s usable lifetime. For drivers with low annual mileage in regions with dirty electricity grids, that breakeven point could take six to nine years to reach, if ever.
Battery manufacturing location proved enormously consequential. Production in China, powered by coal, generates 60-85% higher emissions than manufacturing in Europe or the United States. Yet Canadian subsidies flowed to companies regardless of where batteries were made or where vehicles would be charged. The federal government committed over $50 billion without requiring the environmental due diligence that should precede such massive public investment.
The Canadian government never acknowledged Volvo’s findings. Not once. A search of federal policy documents, ministerial statements, and environmental assessments from 2019 forward reveals no mention of the lifecycle complexities Volvo documented. Ottawa’s silence on inconvenient research speaks loudly about how ideology trumped evidence in shaping EV policy.
You want to build a pipeline in Canada. There will be 8 to 10 years of red tape and environmental impact assessments. But if you say you want to make EVs, Laurentian provincial premiers and the feds will bend over backwards. They handed over billions while the economy and social conditions in their cities decayed.
The environmental promise was conditional: clean electricity grids, high annual mileage, manufacturing in regions with low-carbon energy, and vehicles driven long enough to offset the massive carbon debt from battery production. Remove those conditions, and the environmental case collapses. The subsidies, however, remained unconditional.
The Subsidies Flow, The Companies Fail
Corporate casualties now litter the landscape. Northvolt received $240 million in federal subsidies to build a Quebec battery plant before filing for bankruptcy protection in November. Lion Electric, Quebec’s homegrown EV manufacturer, burned through $100 million in government support before announcing massive layoffs and production cuts. Arrival, which secured subsidies for its electric van facility, collapsed entirely, leaving taxpayers with nothing but broken promises.
Stellantis and LG Energy Solution extracted $15 billion, the most extensive corporate handout in Canadian history, for their Windsor battery plant. Volkswagen secured $13 billion for St. Thomas. Provincial governments layered on additional incentives. The public investment dwarfed any plausible return, yet the money kept flowing based on environmental claims the government either never bothered to verify or suppressed from its own documents and reports.
Despite this flood of subsidies and regulatory coercion, Canadian consumers rejected the offering. Even with massive incentives, EVs accounted for only 15% of new vehicle sales in 2024, far short of the mandated 20% target for 2026, let alone the 60% demanded by 2030. When federal subsidies ended in early 2025, sales collapsed to 9%, revealing the limited consumer demand. Dealer lots overflow with unsold inventory. Manufacturers scaled back production plans. The market spoke; Ottawa is only half listening.
The GM plant in Oshawa serves as a cautionary tale. Thousands of jobs lost. Promises of green manufacturing jobs evaporated. Workers who believed government assurances that EV mandates would secure their livelihoods found themselves unemployed as companies redirected production or collapsed entirely. The pattern repeats across the sector: subsidies extracted, production scaled back, workers laid off, taxpayers absorbing losses while executives collect bonuses and move on, and politicians pretend that it never happened. CBC isn’t asking Justin Trudeau, Katherine McKenna or Steven Guilbeault any questions about it. They are not asking Mark Carney.
The Central Planning Failure
The EV disaster illustrates why economies run by political offices never succeed. Friedrich Hayek observed that “The curious task of economics is to demonstrate to men how little they really know about what they imagine they can design.” Politicians and bureaucrats in Ottawa do not possibly possess the dispersed knowledge embedded in millions of individual economic decisions. But they think that they do.
Markets aggregate information that no central planner can access. Consumer preferences for vehicle range, charging convenience, and total cost of ownership. Regional variations in electricity generation and the pace of grid decarbonization. Battery technology improvements and supply chain vulnerabilities. Resource constraints and mining capacity. These factors interact in ways too complex for any cabinet planning committee to comprehend, yet Ottawa presumed to mandate outcomes a generation in advance.
Federal ministers with no experience in automotive manufacturing or battery chemistry presumed to direct the transformation of a trillion-dollar industry. Career bureaucrats drafted regulations determining which vehicles Canadians could purchase years hence, as if they possessed prophetic knowledge of technological development, grid decarbonization rates, consumer preferences, and global supply chains.
The EV mandate attempted to force a technological transition. It was an economic coup. Environmental claims proved conditional at best. Billions in subsidies flowed to failing companies. Taxpayers absorbed losses while corporations extracted rents and walked away. It worked well for the corporations, but the coup failed Canadians and Canadian workers. They are not building back better.
Green ideology provided perfect cover for this overreach. Invoke climate emergency, and fiscal responsibility vanishes. Question subsidies and you’re labelled a denier. Point out that environmental benefits depend on specific conditions, and you’re accused of spreading misinformation. The rhetorical shield, aided and abetted by a complicit media unable to see past its own financial interests, allowed government to bypass scrutiny that should attend any massive industrial policy intervention.
The Trust Deficit
As Canadians learn that EV environmental benefits depend heavily on electricity sources and driving patterns, as they watch subsidized companies collapse, as they discover how thoroughly the promise was oversold and how completely Ottawa ignored contrary evidence, trust in government erodes. This badly needed skepticism will spread beyond EVs and undermine legitimate government functions.
It would be good if future government claims about environmental policy face rising skepticism. Corporations wrapping themselves in green rhetoric may be viewed as con artists. Environmental activists who championed these policies may see their credibility destroyed. When citizens conclude their government systematically misled them about costs, benefits, and basic facts while suppressing inconvenient research, liberal democracy itself suffers. But that may not happen at all in Laurentian LaLa-land or in the Pacific Lotusland.
Over fifty billion dollars are distributed among local and foreign industrialists, while tens of thousands live in tents in Laurentian cities.
The EV debacle demonstrates that overselling policy benefits, suppressing complexity, and using ideology to short-circuit debate produce a backlash far worse than honest acknowledgment of nuance would have. The damage compounds when governments commit billions based on conditional environmental claims they never verified, then remain silent when industry-leading manufacturers publish data revealing those conditions.
The Path Forward
Canada needs a full repeal of the EV mandate and a complete retreat from Ottawa directing market decisions. The EV law must be struck, not merely paused. The 2030 and 2035 targets must be abandoned entirely. No new subsidies for EV production (or any other production). No bailouts for failed battery plants. No additional funds for charging infrastructure. And absolutely no subsidies for conventional or hybrid vehicle production justified by the same environmental complexity that should have prevented EV mandates in the first place.
Let markets determine which technologies Canadians choose. If EVs deliver genuine value for specific consumers in specific circumstances—those with clean electricity grids, high annual mileage, and long vehicle ownership timelines—those consumers will buy them without mandates or subsidies. If hybrids or improved conventional vehicles better serve other consumers’ needs, manufacturers will produce them without government direction.
The aggregated wisdom of millions of economic actors making decisions based on their actual circumstances will produce better outcomes than any planning committee in Ottawa. Some Canadians will find EVs deliver environmental and financial benefits. Others will not. Both conclusions can be correct simultaneously, a nuance Ottawa spent $50 billion refusing to acknowledge.
Markets work because no one has to know everything. Central planning fails because someone must. I wish I could say that Ottawa has learned this lesson the expensive way. Or whether Laurentians will remember it at the next election. Or whether the same politicians and bureaucrats who delivered this disaster will identify the next technology to mandate and subsidize, armed with new promises that reality will eventually expose as conditional at best.
But let’s keep our dreams in check. It seems more likely, given their ideological make-up and propensities for certainty, that low-information Laurentian and Pacific Coast voters will go right for the next green-washed fantasy that the feds and provincial governments will put in front of them, provided it is coiled into a catchy slogan.
Subscribe to Haultain Research.
For the full experience, and to help us bring you more quality research and commentary,
please upgrade your subscription.
-

 Great Reset2 days ago
Great Reset2 days agoViral TikTok video shows 7-year-old cuddling great-grandfather before he’s euthanized
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoChinese Billionaire Tried To Build US-Born Baby Empire As Overseas Elites Turn To American Surrogates
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoSchools should go back to basics to mitigate effects of AI
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoAt Least 15 Killed In Shooting Targeting Jewish Community At Australia’s Bondi Beach, Police Say
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoMajor tax changes in 2026: Report
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoTwo states designate Muslim group as terrorist
-

 Digital ID1 day ago
Digital ID1 day agoCanada releases new digital ID app for personal documents despite privacy concerns
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin1 day ago
Bruce Dowbiggin1 day agoNFL Ice Bowls Turn Down The Thermostat on Climate Change Hysteria