Automotive
Current EV strategy charging ahead to failure

 Written By Dan McTeague
Written By Dan McTeague
For years now I’ve been saying that electric vehicles, and EV mandates, are bad for Canada.
Back in 2020, when the then-CEO of Toyota, Akio Toyoda, voiced his concerns that governments were moving too fast in their push for an all-electric car market when there were other good options available which didn’t require the same multi-billion dollar infrastructure overhaul or increase in electricity generation, I asked why we weren’t listening to a man who knows his own business.
When Europe found itself in an energy crisis in the winter of 2022, and the Swiss government asked its citizens to avoid driving their EVs, even considering an outright ban, to protect their fragile electricity grid, I said that with our already-strained grid we were seeing our future playing out before us in Switzerland and mandates or no, consumers just wouldn’t stand for it.
And more recently, as stories have piled up of EVs’ vulnerability to the cold — “We got a bunch of dead robots out here,” as one frustrated EV owner put it, surrounded by frozen EVs that had run out of juice while waiting for a charge in a cold snap — I’ve asked over and over again, why on earth our government is trying to force the large scale adoption of an automobile technology which functions so poorly in a normal Canadian winter.
I take no pleasure in being proved right, but nearly every day brings about a new story of EVs failing to meet the lofty expectations our leaders have set for them.
- Recent headlines have trumpeted the difficulties EV drivers are having getting their cars fixed, because so few mechanics know how to work on them.
- People are finding that the resale value of their EV is falling at a much faster rate than their neighbour’s reliable internal combustion engine vehicle.
- Rental car companies like Hertz have been taking major losses after over-investing in EVs, that no one wants to rent. Apparently people don’t like the idea of pinning their vacation on a car they might not be able to charge.
- And major auto manufacturers have been significantly scaling back their annual EV production, despite impending mandates which will force consumers to buy their product in just over a decade.
Even with the generous government subsidies handed to Ford in order to produce made-in-Canada electric SUVs, that company has decided to push their release date for the vehicles back two years — a decision that means layoffs for the majority of the 2,700 workers at the plant, according to the Globe and Mail. GM has followed suit, with recent reports claiming that they are “having a second look” at plans to build EV motors at their plant in St. Catherines, Ontario.
Those companies are beginning to accept reality, something various nations around the world have started to do, as well. The U.K., Germany, Italy, and other European countries, as well as the U.S., have had resistance to EV mandates play a big role in their politics lately. The Biden campaign was even forced to issue a statement saying, “There is no ‘EV mandate,’” after Donald Trump predicted to Detroit autoworkers that the White House’s pro-EV policies would put them out of work.
In the face of all of this, the Trudeau government continues to double down, reaffirming mandates and shovelling more and more tax dollars into the EV fire.
They should know better.
And maybe they do.
But maybe the dollars and the promises to their activist friends have just gotten so big that they feel like they can’t change course now.
Or maybe they are just too stubborn to admit that people like me were right all along, that they bet big and they bet wrong. And they can’t say they weren’t warned.
Buckle up.
Dan McTeague is President of Canadians for Affordable Energy
Automotive
Ford’s EV Fiasco Fallout Hits Hard


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
I’ve written frequently here in recent years about the financial fiasco that has hit Ford Motor Company and other big U.S. carmakers who made the fateful decision to go in whole hog in 2021 to feed at the federal subsidy trough wrought on the U.S. economy by the Joe Biden autopen presidency. It was crony capitalism writ large, federal rent seeking on the grandest scale in U.S. history, and only now are the chickens coming home to roost.
Ford announced on Monday that it will be forced to take $19.5 billion in special charges as its management team embarks on a corporate reorganization in a desperate attempt to unwind the financial carnage caused by its failed strategies and investments in the electric vehicles space since 2022.
Cancelled is the Ford F-150 Lightning, the full-size electric pickup that few could afford and fewer wanted to buy, along with planned introductions of a second pricey pickup and fully electric vans and commercial vehicles. Ford will apparently keep making its costly Mustang Mach-E EV while adjusting the car’s features and price to try to make it more competitive. There will be a shift to making more hybrid models and introducing new lines of cheaper EVs and what the company calls “extended range electric vehicles,” or EREVs, which attach a gas-fueled generator to recharge the EV batteries while the car is being driven.
Dear Readers:
As a nonprofit, we are dependent on the generosity of our readers.
Please consider making a small donation of any amount here.
Thank you!
“The $50k, $60k, $70k EVs just weren’t selling; We’re following customers to where the market is,” Farley said. “We’re going to build up our whole lineup of hybrids. It’s gonna be better for the company’s profitability, shareholders and a lot of new American jobs. These really expensive $70k electric trucks, as much as I love the product, they didn’t make sense. But an EREV that goes 700 miles on a tank of gas, for 90% of the time is all-electric, that EREV is a better solution for a Lightning than the current all-electric Lightning.”
It all makes sense to Mr. Farley, but one wonders how much longer the company’s investors will tolerate his presence atop the corporate management pyramid if the company’s financial fortunes don’t turn around fast.
To Ford’s and Farley’s credit, the company has, unlike some of its competitors (GM, for example), been quite transparent in publicly revealing the massive losses it has accumulated in its EV projects since 2022. The company has reported its EV enterprise as a separate business unit called Model-E on its financial filings, enabling everyone to witness its somewhat amazing escalating EV-related losses since 2022:
• 2022 – Net loss of $2.2 billion
• 2023 – Net loss of $4.7 billion
• 2024 – Net loss of $5.1 billion
Add in the company’s $3.6 billion in losses recorded across the first three quarters of 2025, and you arrive at a total of $15.6 billion net losses on EV-related projects and processes in less than four calendar years. Add to that the financial carnage detailed in Monday’s announcement and the damage from the company’s financial electric boogaloo escalates to well above $30 billion with Q4 2025’s damage still to be added to the total.
Ford and Farley have benefited from the fact that the company’s lineup of gas-and-diesel powered cars have remained strongly profitable, resulting in overall corporate profits each year despite the huge EV-related losses. It is also fair to point out that all car companies were under heavy pressure from the Biden government to either produce battery electric vehicles or be penalized by onerous federal regulations.
Now, with the Trump administration rescinding Biden’s harsh mandates and canceling the absurdly unattainable fleet mileage requirements, Ford and other companies will be free to make cars Americans actually want to buy. Better late than never, as they say, but the financial fallout from it all is likely just beginning to be made public.
- David Blackmon is an energy writer and consultant based in Texas. He spent 40 years in the oil and gas business, where he specialized in public policy and communications.
Automotive
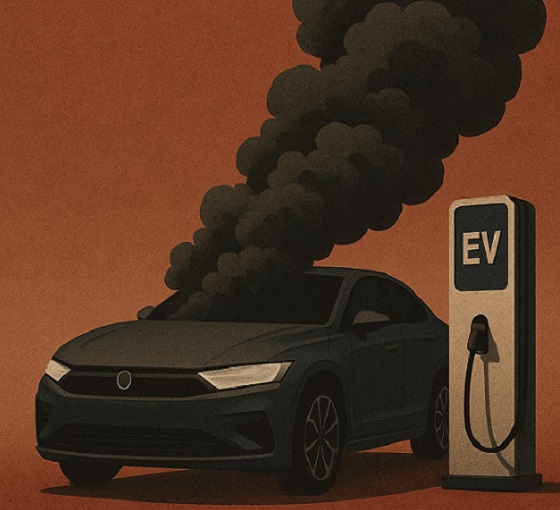
Politicians should be honest about environmental pros and cons of electric vehicles

From the Fraser Institute
By Annika Segelhorst and Elmira Aliakbari
According to Steven Guilbeault, former environment minister under Justin Trudeau and former member of Prime Minister Carney’s cabinet, “Switching to an electric vehicle is one of the most impactful things Canadians can do to help fight climate change.”
And the Carney government has only paused Trudeau’s electric vehicle (EV) sales mandate to conduct a “review” of the policy, despite industry pressure to scrap the policy altogether.
So clearly, according to policymakers in Ottawa, EVs are essentially “zero emission” and thus good for environment.
But is that true?
Clearly, EVs have some environmental advantages over traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. Unlike cars with engines that directly burn fossil fuels, EVs do not produce tailpipe emissions of pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide, and do not release greenhouse gases (GHGs) such as carbon dioxide. These benefits are real. But when you consider the entire lifecycle of an EV, the picture becomes much more complicated.
Unlike traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, battery-powered EVs and plug-in hybrids generate most of their GHG emissions before the vehicles roll off the assembly line. Compared with conventional gas-powered cars, EVs typically require more fossil fuel energy to manufacture, largely because to produce EVs batteries, producers require a variety of mined materials including cobalt, graphite, lithium, manganese and nickel, which all take lots of energy to extract and process. Once these raw materials are mined, processed and transported across often vast distances to manufacturing sites, they must be assembled into battery packs. Consequently, the manufacturing process of an EV—from the initial mining of materials to final assembly—produces twice the quantity of GHGs (on average) as the manufacturing process for a comparable gas-powered car.
Once an EV is on the road, its carbon footprint depends on how the electricity used to charge its battery is generated. According to a report from the Canada Energy Regulator (the federal agency responsible for overseeing oil, gas and electric utilities), in British Columbia, Manitoba, Quebec and Ontario, electricity is largely produced from low- or even zero-carbon sources such as hydro, so EVs in these provinces have a low level of “indirect” emissions.
However, in other provinces—particularly Alberta, Saskatchewan and Nova Scotia—electricity generation is more heavily reliant on fossil fuels such as coal and natural gas, so EVs produce much higher indirect emissions. And according to research from the University of Toronto, in coal-dependent U.S. states such as West Virginia, an EV can emit about 6 per cent more GHG emissions over its entire lifetime—from initial mining, manufacturing and charging to eventual disposal—than a gas-powered vehicle of the same size. This means that in regions with especially coal-dependent energy grids, EVs could impose more climate costs than benefits. Put simply, for an EV to help meaningfully reduce emissions while on the road, its electricity must come from low-carbon electricity sources—something that does not happen in certain areas of Canada and the United States.
Finally, even after an EV is off the road, it continues to produce emissions, mainly because of the battery. EV batteries contain components that are energy-intensive to extract but also notoriously challenging to recycle. While EV battery recycling technologies are still emerging, approximately 5 per cent of lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in EVs, are actually recycled worldwide. This means that most new EVs feature batteries with no recycled components—further weakening the environmental benefit of EVs.
So what’s the final analysis? The technology continues to evolve and therefore the calculations will continue to change. But right now, while electric vehicles clearly help reduce tailpipe emissions, they’re not necessarily “zero emission” vehicles. And after you consider the full lifecycle—manufacturing, charging, scrapping—a more accurate picture of their environmental impact comes into view.
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoCanada’s New Green Deal
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoCanada’s recent economic growth performance has been awful
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta’s huge oil sands reserves dwarf U.S. shale
-

 Indigenous2 days ago
Indigenous2 days agoResidential school burials controversy continues to fuel wave of church arsons, new data suggests
-

 armed forces2 days ago
armed forces2 days agoOttawa’s Newly Released Defence Plan Crosses a Dangerous Line
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoSaskatchewan woman approved for euthanasia urged to seek medical help in Canada rather than US
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoCOP30 finally admits what resource workers already knew: prosperity and lower emissions must go hand in hand
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoCanadian gov’t considers sharing census data on gender-confused children