Canadian Energy Centre
Completing Trans Mountain, Indigenous LNG: What to watch in Canadian energy in 2024

Workers lay pipe during construction of the Trans Mountain pipeline expansion on farmland in Abbotsford, B.C., on May 3, 2023. CP Images photo
From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Deborah JaremkoActivity promises to highlight Canada’s position as a world supplier of choice
It’s going to be a big year for Canadian energy, with major milestones anticipated that will transform Canada from a supplier with a single customer (the United States) to a global player.
Global demand for oil and gas is expected to stay strong in the decades ahead as the world works to reduce emissions, still supplying nearly half of energy needs in 2050, according to the International Energy Agency.
Activity in 2024 promises to highlight Canada’s position as a supplier of choice with a leading approach to reducing emissions and engaging Indigenous communities.
Here are five things to watch.
5. Start-Up Activities for LNG Canada

Construction of the LNG Canada export terminal is now more than 90 per cent complete. Photo courtesy LNG Canada
Against the backdrop of surging liquefied natural gas (LNG) demand – Asia’s consumption hit a record 26.6 million tonnes in December – Canada’s first LNG export terminal is preparing for start-up.
LNG Canada will have among the world’s lowest emissions for LNG supply, at 0.15 tonnes of CO2 equivalent per tonne of LNG, less than half the global average.
This year, the terminal at Kitimat, B.C. will test and fine-tune equipment and the process of producing LNG will begin, the company says.
The start-up program will take more than one year to complete.
Moving into the final stages at LNG Canada follows the recent completion of the Coastal GasLink Pipeline, connecting natural gas supply from northeast B.C.
4. Progress Toward Oil Sands Net Zero

The Pathways Alliance has extensive work underway on the environmental program for its proposed CCS project, involving 135 experts ranging from aquatic and wildlife biologists to archeologists and paleontologists who have spent more than 1,600 hours in the field working to minimize environmental disturbance. Photo courtesy Pathways Alliance
Major regulatory applications are expected in 2024 for one of the world’s largest proposed carbon capture and storage (CCS) networks, located in Canada’s oil sands.
The project would connect CO2 captured at an initial 14 oil sands facilities by pipeline to a shared hub for storage deep underground.
It is the foundation of the plan by the Pathways Alliance – companies representing 95 per cent of oil sands production – to reduce emissions from operations by nearly one third by 2030 on the way to net zero by 2050.
Pathways has said that after regulatory approvals are complete, CO2 injection and storage could begin by late 2026.
3. Growth in Indigenous Ownership

Eva Clayton, back left, President of the Nisga’a Lisims Government (joint venture owner of the proposed Ksi Lisims LNG project), Crystal Smith, back right, Haisla Nation Chief Councillor (joint venture owner of proposed Cedar LNG project), and Karen Ogen, front right, CEO of the First Nations LNG Alliance pose for a photograph on the HaiSea Wamis zero-emission tugboat outside the LNG2023 conference, in Vancouver, B.C., Monday, July 10, 2023. CP Images photo
The rising tide of Indigenous ownership in Canadian energy is likely to continue growing in 2024.
From LNG terminals to oil and gas pipelines, natural gas-fired power plants and CCS projects to reduce emissions, more Indigenous communities are taking on a leadership role.
Since 2022, more than 75 First Nations and Métis communities in Alberta and British Columbia have agreed to ownership stakes in energy projects including the Coastal GasLink pipeline and major oil sands transportation networks.
Indigenous loan guarantee programs like those offered by the Alberta Indigenous Opportunities Corporation (AIOC) are helping communities invest.
So far, the AIOC has underwritten more than $500 million in loan guarantees. This year it has $3 billion of support available, up from $2 billion in 2023.
Details of a proposed national loan guarantee program to help facilitate Indigenous equity ownership in major resource projects are also expected in the federal budget this spring.
2. Green Light for Cedar LNG
Owners of the world’s first Indigenous-led LNG project – a floating terminal at Kitimat, B.C. –plan to make the final decision to proceed within the next three months.
Cedar LNG, owned jointly by the Haisla Nation and Pembina Pipeline Corporation, would have capacity to export three million tonnes of LNG per year, primarily to Asian markets.
With emissions intensity of 0.08 tonnes of CO2 equivalent per tonne of LNG, it would be one of the lowest carbon footprint LNG projects in the world.
In early January, the partners reached the critical milestone of selecting the primary contractors to engineer, build and deliver the floating LNG unit.
A final investment decision is now expected in the first quarter of 2024.
1. Completion of the Trans Mountain Pipeline Expansion
After more than 12 years in the making, Canada’s first large-scale access to growing global oil markets is now weeks away from completion.
The existing Trans Mountain pipeline system from Edmonton, Alberta to Burnaby, B.C. runs consistently at maximum capacity with producers seeking more export space than is available.
The expansion will increase service by about 600,000 barrels per day, bringing more Canadian oil to customers around the world, primarily on the U.S. west coast and Asia.
After the recent resolution of a regulatory delay, Trans Mountain can now proceed with the last two per cent of construction.
The company anticipates oil will flow on the expanded line before the end of March.
Alberta
‘Weird and wonderful’ wells are boosting oil production in Alberta and Saskatchewan
From the Canadian Energy Centre
Multilateral designs lift more energy with a smaller environmental footprint
A “weird and wonderful” drilling innovation in Alberta is helping producers tap more oil and gas at lower cost and with less environmental impact.
With names like fishbone, fan, comb-over and stingray, “multilateral” wells turn a single wellbore from the surface into multiple horizontal legs underground.
“They do look spectacular, and they are making quite a bit of money for small companies, so there’s a lot of interest from investors,” said Calin Dragoie, vice-president of geoscience with Calgary-based Chinook Consulting Services.
Dragoie, who has extensively studied the use of multilateral wells, said the technology takes horizontal drilling — which itself revolutionized oil and gas production — to the next level.
“It’s something that was not invented in Canada, but was perfected here. And it’s something that I think in the next few years will be exported as a technology to other parts of the world,” he said.
Dragoie’s research found that in 2015 less than 10 per cent of metres drilled in Western Canada came from multilateral wells. By last year, that share had climbed to nearly 60 per cent.
Royalty incentives in Alberta have accelerated the trend, and Saskatchewan has introduced similar policy.
Multilaterals first emerged alongside horizontal drilling in the late 1990s and early 2000s, Dragoie said. But today’s multilaterals are longer, more complex and more productive.
The main play is in Alberta’s Marten Hills region, where producers are using multilaterals to produce shallow heavy oil.
Today’s average multilateral has about 7.5 horizontal legs from a single surface location, up from four or six just a few years ago, Dragoie said.
One record-setting well in Alberta drilled by Tamarack Valley Energy in 2023 features 11 legs stretching two miles each, for a total subsurface reach of 33 kilometres — the longest well in Canada.
By accessing large volumes of oil and gas from a single surface pad, multilaterals reduce land impact by a factor of five to ten compared to conventional wells, he said.
The designs save money by skipping casing strings and cement in each leg, and production is amplified as a result of increased reservoir contact.
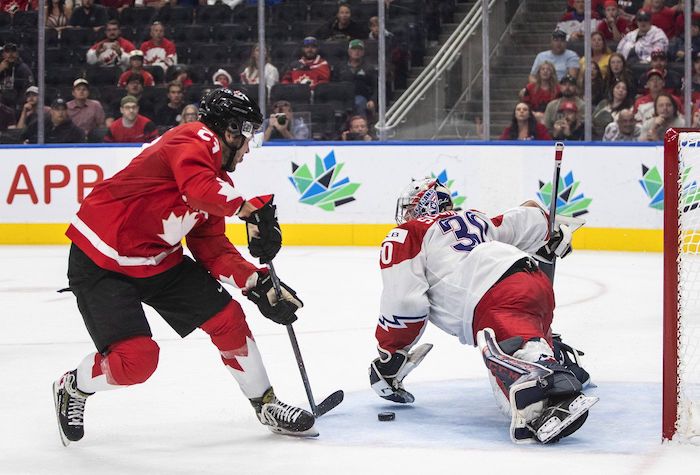
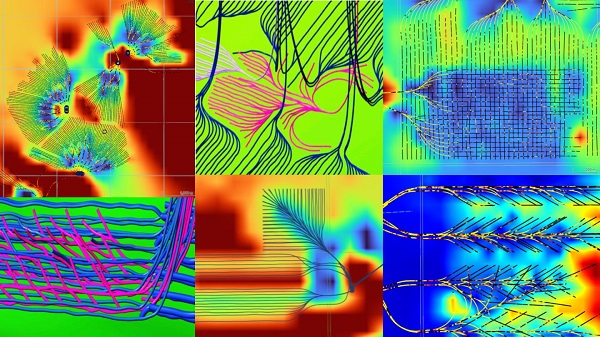
Here are examples of multilateral well design. Images courtesy Chinook Consulting Services.
Parallel
Fishbone
Fan
Waffle
Stingray
Frankenwells
Alberta
How economic corridors could shape a stronger Canadian future

Ship containers are stacked at the Panama Canal Balboa port in Panama City, Saturday, Sept. 20, 2025. The Panama Canals is one of the most significant trade infrastructure projects ever built. CP Images photo
From the Canadian Energy Centre
Q&A with Gary Mar, CEO of the Canada West Foundation
Building a stronger Canadian economy depends as much on how we move goods as on what we produce.
Gary Mar, CEO of the Canada West Foundation, says economic corridors — the networks that connect producers, ports and markets — are central to the nation-building projects Canada hopes to realize.
He spoke with CEC about how these corridors work and what needs to change to make more of them a reality.
CEC: What is an economic corridor, and how does it function?
Gary Mar: An economic corridor is a major artery connecting economic actors within a larger system.
Consider the road, rail and pipeline infrastructure connecting B.C. to the rest of Western Canada. This infrastructure is an important economic corridor facilitating the movement of goods, services and people within the country, but it’s also part of the economic corridor connecting western producers and Asian markets.
Economic corridors primarily consist of physical infrastructure and often combine different modes of transportation and facilities to assist the movement of many kinds of goods.
They also include social infrastructure such as policies that facilitate the easy movement of goods like trade agreements and standardized truck weights.
The fundamental purpose of an economic corridor is to make it easier to transport goods. Ultimately, if you can’t move it, you can’t sell it. And if you can’t sell it, you can’t grow your economy.
CEC: Which resources make the strongest case for transport through economic corridors, and why?
Gary Mar: Economic corridors usually move many different types of goods.
Bulk commodities are particularly dependent on economic corridors because of the large volumes that need to be transported.
Some of Canada’s most valuable commodities include oil and gas, agricultural commodities such as wheat and canola, and minerals such as potash.
CEC: How are the benefits of an economic corridor measured?
Gary Mar: The benefits of economic corridors are often measured via trade flows.
For example, the upcoming Roberts Bank Terminal 2 in the Port of Vancouver will increase container trade capacity on Canada’s west coast by more than 30 per cent, enabling the trade of $100 billion in goods annually, primarily to Asian markets.
Corridors can also help make Canadian goods more competitive, increasing profits and market share across numerous industries. Corridors can also decrease the costs of imported goods for Canadian consumers.
For example, after the completion of the Trans Mountain Expansion in May 2024 the price differential between Western Canada Select and West Texas Intermediate narrowed by about US$8 per barrel in part due to increased competition for Canadian oil.
This boosted total industry profits by about 10 per cent, and increased corporate tax revenues to provincial and federal governments by about $3 billion in the pipeline’s first year of operation.
CEC: Where are the most successful examples of these around the world?
Gary Mar: That depends how you define success. The economic corridors transporting the highest value of goods are those used by global superpowers, such as the NAFTA highway that facilitates trade across Canada, the United States and Mexico.
The Suez and Panama canals are two of the most significant trade infrastructure projects ever built, facilitating 12 per cent and five per cent of global trade, respectively. Their success is based on their unique geography.
Canada’s Asia-Pacific Gateway, a coordinated system of ports, rail lines, roads, and border crossings, primarily in B.C., was a highly successful initiative that contributed to a 48 per cent increase in merchandise trade with Asia from $44 million in 2006 to $65 million in 2015.
China’s Belt and Road initiative to develop trade infrastructure in other countries is already transforming global trade. But the project is as much about extending Chinese influence as it is about delivering economic returns.

Piles of coal awaiting export and gantry cranes used to load and unload containers onto and from cargo ships are seen at Deltaport, in Tsawwassen, B.C., on Monday, September 9, 2024. CP Images photo
CEC: What would need to change in Canada in terms of legislation or regulation to make more economic corridors a reality?
Gary Mar: A major regulatory component of economic corridors is eliminating trade barriers.
The federal Free Trade and Labour Mobility in Canada Act is a good start, but more needs to be done at the provincial level to facilitate more internal trade.
Other barriers require coordinated regulatory action, such as harmonizing weight restrictions and road bans to streamline trucking.
By taking a systems-level perspective – convening a national forum where Canadian governments consistently engage on supply chains and trade corridors – we can identify bottlenecks and friction points in our existing transportation networks, and which investments would deliver the greatest return on investment.
-
 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoCDC’s Autism Reversal: Inside the Collapse of a 25‑Year Public Health Narrative
-

 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days agoCocaine, Manhunts, and Murder: Canadian Cartel Kingpin Prosecuted In US
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoBREAKING: CDC quietly rewrites its vaccine–autism guidance
-

 National2 days ago
National2 days agoPsyop-Style Campaign That Delivered Mark Carney’s Win May Extend Into Floor-Crossing Gambits and Shape China–Canada–US–Mexico Relations
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoHere’s what they don’t tell you about BC’s tanker ban
-

 Great Reset1 day ago
Great Reset1 day agoEXCLUSIVE: A Provincial RCMP Veterans’ Association IS TARGETING VETERANS with Euthanasia
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoBREAKING: Globalist Climate Conference Bursts Into Flames
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin2 days ago
Bruce Dowbiggin2 days agoBurying Poilievre Is Job One In Carney’s Ottawa

















