Business
Carney must tell Canadians how much “changing” the carbon tax will cost

Taxpayers are demanding to know how much Liberal Party leadership candidate Mark Carney’s carbon tax will cost after he admitted he would “change” the policy rather than scrapping the tax.
“After Carney led Canadians to believe he was getting rid of the carbon tax, now he says he’s going to ‘change’ it, so how much will his relabeled carbon tax cost?” said Franco Terrazzano, CTF Federal Director. “We know the cost of Carney’s carbon tax won’t be zero, so how much extra will people have to pay when they fill up at the gas station or pay their heating bills?”
Carney clarified his plans for the carbon tax in Kelowna, British Columbia, on Wednesday.
“The issue wasn’t, to coin a phrase, whether to ‘axe the tax,’ the issue was how to change it,” Carney said. “So in changing the carbon tax … We are making the large companies pay for everybody.”
Currently, the federal carbon tax costs about 17 cents per litre of gasoline, 21 cents per litre of diesel and 15 cents per cubic metre of natural gas. The carbon tax is set to increase on April 1.
The Parliamentary Budget Officer has repeatedly reported the carbon tax costs the average family hundreds of dollars more than the rebates they get back.
“Taxpayers have a simple question for Carney: What will happen to gas prices and home heating bills under his plan?” Terrazzano said. “Whether the carbon tax is up front or hidden, Canadians can’t afford to pay more to fuel up their cars, heat their homes and buy groceries.”
Carney is proposing to eliminate the visibility of the carbon tax on things like home heating bills, but to still hit businesses with the carbon tax.
Carney’s plan would cancel the carbon tax rebates and instead “create a system of incentives to reward Canadians” for making environmentally approved purchases.
“Carbon taxes on refineries make gas more expensive, carbon taxes on utilities make home heating more expensive and carbon taxes on fertilizer plants increase costs for farmers and that makes groceries more expensive,” said Kris Sims, CTF Alberta Director. “Conservative Party Leader Pierre Poilievre is promising to scrap the carbon tax and that will cut the price of gas by 17 cents per litre. Now Carney needs to be honest about how much his changed carbon tax will cost.”
Alberta
Falling resource revenue fuels Alberta government’s red ink

From the Fraser Institute
By Tegan Hill
According to this week’s fiscal update, amid falling oil prices, the Alberta government will run a projected $6.4 billion budget deficit in 2025/26—higher than the $5.2 billion deficit projected earlier this year and a massive swing from the $8.3 billion surplus recorded in 2024/25.
Overall, that’s a $14.8 billion deterioration in Alberta’s budgetary balance year over year. Resource revenue, including oil and gas royalties, comprises 44.5 per cent of that decline, falling by a projected $6.6 billion.
Albertans shouldn’t be surprised—the good times never last forever. It’s all part of the boom-and-bust cycle where the Alberta government enjoys budget surpluses when resource revenue is high, but inevitably falls back into deficits when resource revenue declines. Indeed, if resource revenue was at the same level as last year, Alberta’s budget would be balanced.
Instead, the Alberta government will return to a period of debt accumulation with projected net debt (total debt minus financial assets) reaching $42.0 billion this fiscal year. That comes with real costs for Albertans in the form of high debt interest payments ($3.0 billion) and potentially higher taxes in the future. That’s why Albertans need a new path forward. The key? Saving during good times to prepare for the bad.
The Smith government has made some strides in this direction by saving a share of budget surpluses, recorded over the last few years, in the Heritage Fund (Alberta’s long-term savings fund). But long-term savings is different than a designated rainy-day account to deal with short-term volatility.
Here’s how it’d work. The provincial government should determine a stable amount of resource revenue to be included in the budget annually. Any resource revenue above that amount would be automatically deposited in the rainy-day account to be withdrawn to support the budget (i.e. maintain that stable amount) in years when resource revenue falls below that set amount.
It wouldn’t be Alberta’s first rainy-day account. Back in 2003, the province established the Alberta Sustainability Fund (ASF), which was intended to operate this way. Unfortunately, it was based in statutory law, which meant the Alberta government could unilaterally change the rules governing the fund. Consequently, by 2007 nearly all resource revenue was used for annual spending. The rainy-day account was eventually drained and eliminated entirely in 2013. This time, the government should make the fund’s rules constitutional, which would make them much more difficult to change or ignore in the future.
According to this week’s fiscal update, the Alberta government’s resource revenue rollercoaster has turned from boom to bust. A rainy-day account would improve predictability and stability in the future by mitigating the impact of volatile resource revenue on the budget.
Business
Higher carbon taxes in pipeline MOU are a bad deal for taxpayers

The Canadian Taxpayers Federation is criticizing the Memorandum of Understanding between the federal and Alberta governments for including higher carbon taxes.
“Hidden carbon taxes will make it harder for Canadian businesses to compete and will push Canadian entrepreneurs to shift production south of the border,” said Franco Terrazzano, CTF Federal Director. “Politicians should not be forcing carbon taxes on Canadians with the hope that maybe one day we will get a major project built.
“Politicians should be scrapping all carbon taxes.”
The federal and Alberta governments released a memorandum of understanding. It includes an agreement that the industrial carbon tax “will ramp up to a minimum effective credit price of $130/tonne.”
“It means more than a six times increase in the industrial price on carbon,” Prime Minister Mark Carney said while speaking to the press today.
Carney previously said that by “changing the carbon tax … We are making the large companies pay for everybody.”
A Leger poll shows 70 per cent of Canadians believe businesses pass most or some of the cost of the industrial carbon tax on to consumers. Meanwhile, just nine per cent believe businesses pay most of the cost.
“It doesn’t matter what politicians label their carbon taxes, all carbon taxes make life more expensive and don’t work,” Terrazzano said. “Carbon taxes on refineries make gas more expensive, carbon taxes on utilities make home heating more expensive and carbon taxes on fertilizer plants increase costs for farmers and that makes groceries more expensive.
“The hidden carbon tax on business is the worst of all worlds: Higher prices and fewer Canadian jobs.”
-

 Alberta4 hours ago
Alberta4 hours agoFrom Underdog to Top Broodmare
-

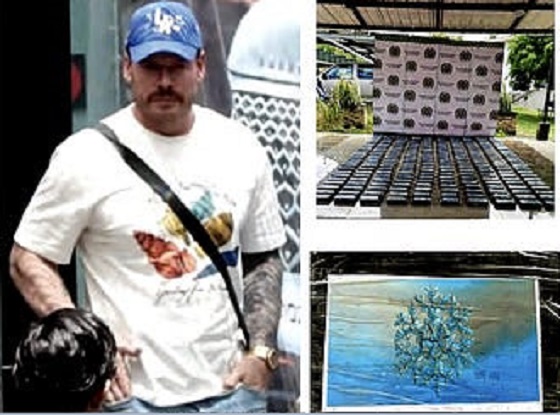
 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days agoB.C.’s First Money-Laundering Sentence in a Decade Exposes Gaps in Global Hub for Chinese Drug Cash
-

 armed forces2 days ago
armed forces2 days ago2025 Federal Budget: Veterans Are Bleeding for This Budget
-

 Banks2 days ago
Banks2 days agoThe Bill Designed to Kill Canada’s Fossil Fuel Sector
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlberta and Ottawa ink landmark energy agreement
-

 Artificial Intelligence2 days ago
Artificial Intelligence2 days agoTrump’s New AI Focused ‘Manhattan Project’ Adds Pressure To Grid
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoAfghan Ex–CIA Partner Accused in D.C. National Guard Ambush
-

 Carbon Tax1 day ago
Carbon Tax1 day agoCanadian energy policies undermine a century of North American integration