Fraser Institute
Canadian generosity hits lowest point in 20 years
From the Fraser Institute
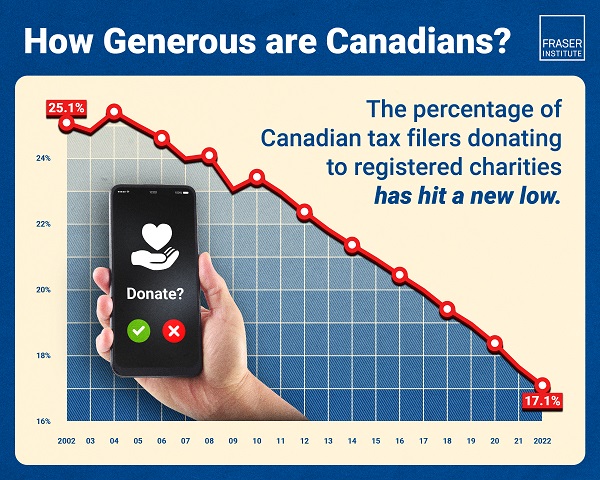
The number of Canadians donating to charity—as a percentage of all tax filers—is at the lowest point in 20 years, finds a new study published by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian public policy think-tank.
“The holiday season is a time to reflect on charitable giving, and the data shows Canadians are consistently less charitable every year, which means charities face greater challenges to secure resources to help those in need,” said Jake Fuss, director of Fiscal Studies at the Fraser Institute and co-author of Generosity in Canada: The 2024 Generosity Index.
The study finds that the percentage of Canadian tax filers donating to charity during the 2022 tax year—just 17.1 per cent—is the lowest proportion of Canadians donating since at least 2002.
Canadians’ generosity peaked at 25.4 per cent of tax-filersdonating in 2004, before declining in subsequent years.
Nationally, the total amount donated to charity by Canadian tax filers has also fallen from 0.61 per cent of income in 2002 to 0.50 per cent of income in 2022.
The study finds that Manitoba had the highest percentage of tax filers that donated to charity among the provinces (19.3 per cent) during the 2022 tax year while New Brunswick had the lowest (14.7 per cent).
Likewise, Manitoba also donated the highest percentage of its aggregate income to charity among the provinces (0.71 per cent) while Quebec donated the lowest (0.26 per cent).
“A smaller proportion of Canadians are donating to registered charities than what we saw in previous decades, and those who are donating are donating less,” said Fuss.
“This decline in generosity in Canada undoubtedly limits the ability of Canadian charities to improve the quality of life in their communities and beyond,” said Grady Munro, policy analyst and co-author.

NOTE: Table based on 2022 tax year, the most recent year of comparable data in Canada
Generosity in Canada: The 2024 Generosity Index
- Manitoba had the highest percentage of tax filers that donated to charity among the provinces (19.3%) during the 2022 tax year while New Brunswick had the lowest (14.7%).
- Manitoba also donated the highest percentage of its aggregate income to charity among the provinces (0.71%) while Quebec donated the lowest (0.26%).
- Nationally, the percentage of Canadian tax filers donating to charity has fallen over the last decade from 22.4% in 2012 to 17.1% in 2022.
- The percentage of aggregate income donated to charity by Canadian tax filers has also decreased from 0.55% in 2012 to 0.50% in 2022.
- This decline in generosity in Canada undoubtedly limits the ability of Canadian charities to improve the quality of life in their communities and beyond.
Business
Ottawa’s gun ‘buyback’ program will cost billions—and for no good reason

From the Fraser Institute
By Gary Mauser
The government told Cape Bretoners they had two weeks to surrender their firearms to qualify for reimbursement or “buyback.” The pilot project netted a grand total of 22 firearms.
Five years after then-prime minister Justin Trudeau banned more than 100,000 types of so-called “assault-style firearms,” the federal government recently made the first attempt to force Canadians to surrender these firearms.
It didn’t go well.
The police chief in Cape Breton, Nova Scotia, volunteered to run a pilot “buyback” project, which began last month. The government told Cape Bretoners they had two weeks to surrender their firearms to qualify for reimbursement or “buyback.” The pilot project netted a grand total of 22 firearms.
This failure should surprise no one. Back in 2018, a survey of “stakeholders” warned the government that firearms owners wouldn’t support such a gun ban. According to Prime Minister Carney’s own Privy Council Office the “program faces a risk of non-compliance.” And federal Public Safety Minister Gary Anandasangaree was recently recorded admitting that the “buyback” is a partisan maneuver, and if it were up to him, he’d scrap it. What’s surprising is Ottawa’s persistence, particularly given the change in the government and the opportunity to discard ineffective policies.
So what’s really going on here?
One thing is for certain—this program is not, and never has been, about public safety. According to a report from the federal Department of Justice, almost all guns used in crimes in Canada, including in big cities such as Toronto, are possessed illegally by criminals, with many smuggled in from the United States. And according to Ontario’s solicitor general, more than 90 per cent of guns used in crimes in the province are illegally imported from the U.S. Obviously, the “buyback” program will have no effect on these guns possessed illegally by criminals.
Moreover, Canadian firearms owners are exceptionally law-abiding and less likely to commit murder than other Canadians. That also should not be surprising. To own a firearm in Canada, you must obtain a Possession and Acquisition Licence (PAL) from the RCMP after initial vetting and daily monitoring for possible criminal activity. Between 2000 and 2020, an average of 12 PAL-holders per year were accused of homicide, out of approximately two million PAL-holders. During that same 10-year period, the PAL-holder firearms homicide rate was 0.63 (per 100,000 PAL-holders) compared to 0.72 (per 100,000 adult Canadians)—that’s 14 per cent higher than the rate for PAL-holders.
In other words, neither the so-called “assault-style firearms” nor their owners pose a threat to the public.
And the government’s own actions belie its claims. If these firearms are such a threat to Canadians, why slow-roll the “buyback” program? If inaction increased the likelihood of criminality by law-abiding firearms owners, why wait five years before launching a pilot program in a small community such as Cape Breton? And why continue to extend the amnesty period for another year, which the government did last month at the same time its pilot project netted a mere 22 firearms?
To ask those questions is to answer them.
Another question—how much will the “buyback” program cost taxpayers?
The government continues to block any attempt to disclose the full financial costs (although the Canadian Taxpayers Federation has launched a lawsuit to try to force the government to honour its Access to Information Act request). But back in 2020 the Trudeau government said it would cost $200 million to compensate firearms owners (although the Parliamentary Budget Officer said compensation costs could reach $756 million). By 2024, the program had spent $67.2 million—remember, that’s before it collected a single gun. The government recently said the program’s administrative costs (safe storage, destruction of hundreds of thousands of firearms, etc.) would reach an estimated $1.8 billion. And according to Carney’s first budget released in November, his government will spend $364 million on the program this fiscal year—at a time of massive federal deficits and debt.
This is reminiscent of the Chretien government’s gun registry fiasco, which wound up costing more than $2 billion even after then-justice minister Allan Rock promised the registry program would “almost break even” after an $85 million initial cost. The Harper government finally scrapped the registry in 2012.
As the Carney government clings to the policies of its predecessor, Canadians should understand the true nature of Ottawa’s gun “buyback” program and its costs.
Business
Recent price declines don’t solve Toronto’s housing affordability crisis

From the Fraser Institute
By Jake Fuss and Austin Thompson
House prices in Toronto are declining. But the city’s affordability crisis is far from over—and government policies will likely make it worse.
While most Torontonians know there’s a crisis, the numbers make it clear. According to our new study, in 2023 (the latest year of available data), a family earning the city’s median after-tax income ($60,510) had to save $216,240 (the equivalent of 42.9 months of its after-tax income) for a 20 per cent downpayment on a typical home of any type (single-detached, semi-detached, condominium). But even if that family could somehow clear this monumental hurdle, it then had to dedicate 110.2 per cent of its after-tax income for monthly mortgage payments ($5,557)—a financial impossibility, unless the family can share housing costs (e.g. live-in tenants) or rely on financial support from elsewhere.
At this point, some long-time Toronto residents might recall their own difficult home purchase and think, “Hasn’t it always been this bad?” But just a decade ago, the hurdles weren’t nearly as high.
For example, in 2014 in Toronto, a 20 per cent downpayment cost 26.4 months of median after-tax family income—not 42.9 months. And the monthly mortgage payment on a typical home purchase required 56.0 per cent of median after-tax family income—not 110.2 per cent. So yes, typical homes have been broadly unaffordable for median-income-earning Toronto families for years, but it’s way worse now.
For Torontonians priced out of homeownership, renting has not offered much relief. In 2023, Toronto had the least affordable rents in Canada. The monthly cost of the median rental unit was $1,750, equal to 34.7 per cent of the median after-tax family income. That’s up from $1,110 (or 27.7 per cent of after-tax income) in 2014.
Fast-forward to today, and Torontonians should view reports of “crashing” home prices in the proper context. Typical home prices peaked at $1.27 million in the first quarter of 2022. By the second quarter of 2025, they had fallen to $1.00 million. That’s a marked decline, but prices remain well above pre-pandemic levels and far beyond the reach of most typical families.
And while the fall in house prices hasn’t been enough to restore affordability, it has caused a steep contraction in homebuilding as builders take a more cautious approach to development at a time when the city still needs more new homes to improve affordability.
This unhealthy dynamic, where price declines weigh heavily on housing construction, is made worse by government policy. Despite hundreds of millions of taxpayer dollars spent on housing initiatives by the federal government, the Ford government and Toronto City Hall, key provincial and municipal policies continue to impose needless costs and restrictions on new housing.
For example, Toronto homebuilders must endure costly wait times of more than two years for municipal approvals—more than three times longer than in Vancouver and seven times longer than in Edmonton. New high-rise developments in Toronto face municipal charges of $134,900 per unit compared to $38,100 in Ottawa and $6,900 in Edmonton. Meanwhile, the Ford government has backed away from several critical recommendations from its own Housing Task Force, which would make it easier to build more and denser housing, such as allowing fourplexes provincewide without special approval.
Of course, federal immigration policy, particularly over the last five years, has increased demand for new homes in Toronto and across the country. But even so, if not for lengthy approval processes, sky-high fees and restrictive land-use policies, many more new homes would be built in Toronto today despite declining prices. Homes only get built when buyers can cover the cost of construction plus a reasonable return on investment for developers. But when governments drive up costs, increase uncertainty and claim a significant share of the final sale price through fees and charges, projects that might otherwise proceed can become financially unviable. The result is less new housing, fewer options for buyers and a slower path to improved affordability.
To help improve housing affordability, Toronto needs a steady flow of new homebuilding. Torontonians should demand faster approvals, lower fees and more sensible rules on what types of homes can be built.
-

 National18 hours ago
National18 hours agoMedia bound to pay the price for selling their freedom to (selectively) offend
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin17 hours ago
Bruce Dowbiggin17 hours agoSometimes An Ingrate Nation Pt. 2: The Great One Makes His Choice
-

 Business6 hours ago
Business6 hours agoRecent price declines don’t solve Toronto’s housing affordability crisis
-

 Daily Caller7 hours ago
Daily Caller7 hours agoTech Mogul Gives $6 Billion To 25 Million Kids To Boost Trump Investment Accounts
-

 Business5 hours ago
Business5 hours agoOttawa’s gun ‘buyback’ program will cost billions—and for no good reason
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoELZABETH MAY HAS IT WRONG: An Alberta to Prince Rupert Oil Pipeline Will Contribute to Greater Global Oil Tanker Safety
-

 National2 days ago
National2 days agoAlberta will use provincial laws to stop Canadian gov’t from trying to confiscate legal firearms
-

 Energy8 hours ago
Energy8 hours agoThe Trickster Politics of the Tanker Ban are Hiding a Much Bigger Reckoning for B.C.








