Fraser Institute
Canada can solve its productivity ‘emergency’—we just need politicians on board

From the Fraser Institute
By Jake Fuss
Policymakers are slowly acknowledging the problem, but their proposed solutions are troubling.
According to Carolyn Rogers, senior deputy governor of the Bank of Canada, it’s time to “break the glass” and respond to Canada’s productivity “emergency.” Unfortunately, the country is unlikely to solve this issue any time soon as politicians are doubling down on the policy status quo rather than making sorely needed reforms.
Worker productivity—the level of output in the economy per hour worked—is a crucial indicator of a country’s underlying economic performance. When productivity increases, we not only increase our output and efficiency, but worker wages typically rise as well.
According to Statistics Canada, the country’s productivity dropped for six consecutive quarters before eking out a small gain in the final quarter of 2023. Rogers is right, this is an emergency, and it’s unsurprising that living standards for Canadians are falling alongside our productivity. Since the second quarter of 2022 (when it peaked post-COVID), inflation-adjusted per-person GDP (a common indicator of living standards) declined from $60,178 to $58,111 by the end of 2023—and declined during five of those six quarters, now sitting below where it was at the end of 2014.
Policymakers are slowly acknowledging the problem, but their proposed solutions are troubling. Federal Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland, for instance, recently emphasized the importance of making “investments in productivity and growth.” Yet, the federal government increased taxes on capital gains in its recent budget, which will disincentivize investment in Canada. Usually, when a politician says the word “investment” this is a fancy way of saying we need more government spending.
And in fact, more government spending appears to be the popular solution to every problem for most governments in Canada these days. Canadian premiers and the prime minister already support this approach in health care even though it’s been tried for decades. The result? In 2023, the longest wait times for health care on record despite having the most expensive system (as a share of GDP) among high-income universal health-care countries.
And now, these same policymakers are advocating for the same approach to boost productivity—that is, throw taxpayer money at the problem and hope it will somehow go away.
But there’s hope—governments have other options. For starters, governments from coast to coast could eliminate interprovincial trade barriers, which limit productivity improvements by (among other things) shielding inefficient local businesses from competition from businesses in other provinces. Governments also effectively prohibit the entry of foreign-owned competitors in crucial industries such as telecommunications and air travel. There’s less incentive for Canadian firms to innovate or improve when there’s no threat to shake things up.
Moreover, if governments reduced regulatory red tape and subsequent compliance costs, firms could allocate more resources towards training their workers, investing in equipment, and producing new and better products. And if governments reduced tax rates on families and businesses, they could make Canada more attractive to productive businesses, high-skilled workers and investors. Our current relatively high tax rates on capital gains, personal income and businesses income discourage capital investment and scare away the best and brightest scientists, engineers, doctors and entrepreneurs.
The Trudeau government, and other governments in Canada, seemingly want to spend their way out of our productivity emergency. While some level of government spending can help improve productivity, continued spending increases reallocate resources from the private sector to the government sector, which is by nature less productive. Governments should impose credible restraints (i.e. fiscal rules) on the growth of government spending to prevent this crowding out of private-sector investment.
There are plenty of ways Canada can boost productivity. We just need policymakers to be on board.
Author:
Energy
National media energy attacks: Bureau chiefs or three major Canadian newspapers woefully misinformed about pipelines

From the Fraser Institute
These three allegedly well informed national opinion-shapers are incredibly ignorant of national energy realities.
In a recent episode of CPAC PrimeTime Politics, three bureau chiefs from three major Canadian newspapers discussed the fracas between Alberta Premier Danielle Smith and Prime Minister Mark Carney. The Smith government plans to submit a proposal to Ottawa to build an oil pipeline from Alberta to British Columbia’s north coast. The episode underscored the profound disconnect between these major journalistic gatekeepers and the realities of energy policy in Canada.
First out of the gate, the Globe and Mail’s Robert Fife made the (false) argument that we already have the Trans Mountain pipeline expansion (TMX), which is only running at 70 per cent, so we don’t need additional pipelines. This variant of the “no market case” argument misunderstands both the economics of running pipelines and the reality of how much oilsands production can increase to supply foreign markets if—and only if—there’s a way to get it there.
In reality, since the TMX expansion entered service, about 80 per cent of the system’s capacity is reserved for long-term contracts by committed shippers, and the rest is available on a monthly basis for spot shippers who pay higher rates due largely to government-imposed costs of construction. From June 2024 to June 2025, committed capacity was fully utilized each month, averaging 99 per cent utilization. Simply put, TMX is essentially fully subscribed and flowing at a high percentage of its physical capacity.
And the idea that we don’t need additional capacity is also silly. According to S&P Global, Canadian oilsands production will reach a record annual average production of 3.5 million barrels per day (b/d), and by 2030 could top 3.9 million b/d (that’s 500,000 b/d higher than 2024). Without pipeline expansion, this growth may not happen. Alberta’s government, which is already coordinating with pipeline companies such as Enbridge, hopes to see oilsands production double in coming years.
Next, Mia Rabson, Ottawa deputy bureau chief of the Canadian Press, implied that Smith’s proposal is not viable because it comes from government, not the private sector. But Rabson neglected to say that it would be foolish for any company to prepare a very expensive project proposal in light of current massive regulatory legislative barriers (tanker ban off B.C. coast, oil and gas emission cap, etc.). Indeed, proposal costs can run into the billions.
Finally, Joel-Denis Bellavance, Ottawa bureau chief of La Presse, opined that a year ago “building a pipeline was not part of the national conversation.” Really? On what planet? How thick is the bubble around Quebec? Is it like bulletproof Perspex? This is a person helping shape Quebec opinion on pipelines in Western Canada, and if we take him at his word, he doesn’t know that pipelines and energy infrastructure have been on the agenda for quite some time now.
If these are the gatekeepers of Canadian news in central Canada, it’s no wonder that the citizenry seems so woefully uninformed about the need to build new pipelines, to move Alberta oil and gas to foreign markets beyond the United States, to strengthen Canada’s economy and to employ in many provinces people who don’t work in the media.
Business
Canada has fewer doctors, hospital beds, MRI machines—and longer wait times—than most other countries with universal health care
From the Fraser Institute
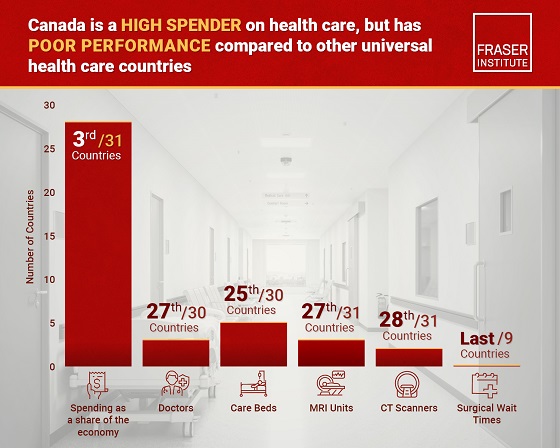
Despite a relatively high level of spending, Canada has significantly fewer doctors, hospital beds, MRI machines and CT scanners compared to other countries with universal health care, finds a new study released today by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian public policy think-tank.
“There’s a clear imbalance between the high cost of Canada’s health-care system and the actual care Canadians receive in return,” said Mackenzie Moir, senior policy
analyst at the Fraser Institute and author of Comparing Performance of Universal Health-Care Countries, 2025.
In 2023, the latest year of available comparable data, Canada spent more on health care (as a percentage of the economy/GDP, after adjusting for population age) than
most other high-income countries with universal health care (ranking 3rd out of 31 countries, which include the United Kingdom, Australia and the Netherlands).
And yet, Canada ranked 27th (of 30 countries) for the availability of doctors and 25th (of 30) for the availability of hospital beds.
In 2022, the latest year of diagnostic technology data, Canada ranked 27th (of 31 countries) for the availability of MRI machines and 28th (of 31) for CT scanners.
And in 2023, among the nine countries with universal health-care systems included in the Commonwealth Fund’s International Health Policy Survey, Canada ranked last for the percentage of patients able to make same- or next-day appointments when sick (22 per cent) and had the highest percentage of patients (58 per cent) who waited two months or more for non-emergency surgery. For comparison, the Netherlands had much higher rates of same- or next-day appointments (47 per cent) and much lower waits of two months or more for non-emergency surgery (20 per cent).
“To improve health care for Canadians, our policymakers should learn from other countries around the world with higher-performing universal health-care systems,”
said Nadeem Esmail, director of health policy at the Fraser Institute.
Comparing Performance of Universal Health Care Countries, 2025
- Of the 31 high-income universal health-care countries, Canada ranks among the highest spenders, but ranks poorly on both the availability of most resources and access to services.
- After adjustments for differences in the age of the population of these 31 countries, Canada ranked third highest for spending as a percentage of GDP in 2023 (the most recent year of comparable data).
- Across 13 indictors measured, the availability of medical resources and timely access to medical services in Canada was generally below that of the average OECD country.
- In 2023, Canada ranked 27th (of 30) for the relative availability of doctors and 25th (of 30) for hospital beds dedicated to physical care. In 2022, Canada ranked 27th (of 31) for the relative availability of Magnetic Resonance Im-aging (MRI) machines, and 28th (of 31) for CT scanners.
- Canada ranked last (or close to last) on three of four indicators of timeliness of care.
- Notably, among the nine countries for which comparable wait times measures are available, Canada ranked last for the percentage of patients reporting they were able to make a same- or next-day appointment when sick (22%).
- Canada also ranked eighth worst for the percentage of patients who waited more than one month to see a specialist (65%), and reported the highest percentage of patients (58%) who waited two months or more for non-emergency surgery.
- Clearly, there is an imbalance between what Canadians get in exchange for the money they spend on their health-care system.
Mackenzie Moir
Senior Policy Analyst, Fraser Institute
-

 Agriculture1 day ago
Agriculture1 day agoFrom Underdog to Top Broodmare
-

 City of Red Deer2 days ago
City of Red Deer2 days agoCindy Jefferies is Mayor. Tristin Brisbois, Cassandra Curtis, Jaelene Tweedle, and Adam Goodwin new Councillors – 2025 Red Deer General Election Results
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin2 days ago
Bruce Dowbiggin2 days agoIs The Latest Tiger Woods’ Injury Also A Death Knell For PGA Champions Golf?
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta’s licence plate vote is down to four
-

 Health1 day ago
Health1 day agoSovereignty at Stake: Why Parliament Must Review Treaties Before They’re Signed
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day ago$15B and No Guarantees? Stellantis Deal explained by former Conservative Shadow Minister of Innovation, Science and Technology
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days ago“Modernization,” They Call It: How Ottawa Redefined Fraud as Progress
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex2 days ago
Censorship Industrial Complex2 days agoCanada’s justice minister confirms ‘hate crimes’ bill applies to online content