National
BC election officials still need to count 65k ballots in virtual tie between Conservatives, NDP

From LifeSiteNews
“Final count process for B.C.’s provincial election is scheduled to begin on October 26 and will conclude on October 28.”
Election officials in the province of British Columbia now say there are 65,000 ballots yet to be counted, up from 45,000 following last Saturday’s election that has the Conservative Party and the reigning New Democratic Party in a virtual tie.
In an election count update Thursday, Elections B.C. says during its “screening process” it now estimates that “approximately 65,000 ballots will be counted as part of final count,” which is significantly more than the original 45,000 estimate.
According to Elections B.C., the “final count process for B.C.’s provincial election is scheduled to begin on October 26 and will conclude on October 28.”
It is estimated that on October 27, the final mail-in- ballot counts will be complete. There are recounts underway in two ridings as well, which were remarkably close between the NDP and Conservatives.
Elections B.C. says the “final count” will involve three distinct processes, “counting mail-in ballots, counting absentee ballots, and recounts of ballots counted on election night.”
Final results will be made available on its social media channels and website.
As reported by LifeSiteNews, initial counts show the B.C. Conservatives under leader John Rustad with 45 seats, while the ruling NDP under Premier David Eby have 46 seats. A party needs 47 seats to form a majority government in the province. The Green Party appears to have won 2 seats, meaning should the seat count remain as is, the distant third party will effectively hold the balance of power.
Rustad won his seat easily, beating out his NDP rival with 68 percent of the vote. His win was the first time since 1978 that a Conservative has won a seat in the B.C. legislature.
It hasn’t been since 1991, the last year B.C. was ruled by the Social Credit Party under Premier Bill Vander Zalm, that the province has been under the control of parties other than the NDP or Liberals.
B.C.’s Conservative Party shot up in popularity after the former Liberal Party of the province, under its new name B.C. United, lagged in the polls. Then B.C. United decided shortly before the election to pull all its candidates and throw its support behind the Conservatives.
Rustad, a former Liberal MLA, also gained popularity for promising to restore order and oppose the woke policies popularized under the NDP.
As reported by LifeSiteNews, Rustad, just days before the election, condemned sexually explicit material in school libraries and indicated that he would remove them if elected.
Rustad has also come out in opposition to the use of often-sterilizing puberty blockers for gender-confused children and has condemned SOGI 123, a nationwide program pushing LGBT ideology in schools under the label of “inclusivity.”
Business
Clean energy transition price tag over $150 billion and climbing, with very little to show for it
From the Fraser Institute
By Jake Fuss, Julio Mejía, Elmira Aliakbari, Karen Graham and Jock Finlayson
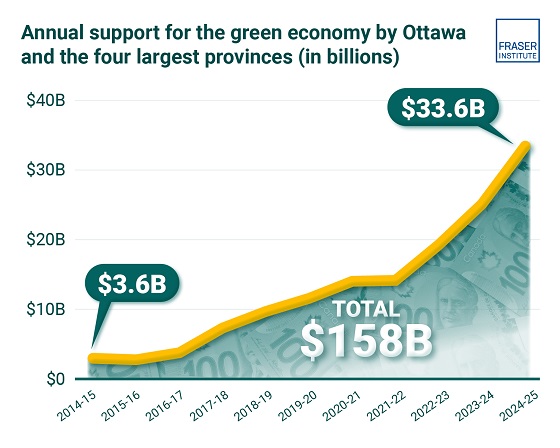
Ottawa and the four biggest provinces have spent (or foregone revenues) of at least $158 billion to create at most 68,000 “clean” jobs since 2014
Despite the hype of a “clean” economic transition, governments in Ottawa and in the four largest provinces have spent or foregone revenues of more than $150 billion (inflation-adjusted) on low-carbon initiatives since 2014/15, but have only created, at best, 68,000 clean jobs, according to two new studies published by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian public policy think-tank.
“Governments, activists and special interest groups have been making a lot of claims about the opportunities of a clean economic transition, but after a decade of policy interventions and more than $150 billion in taxpayers’ money, the results are
extremely underwhelming,” said Elmira Aliakbari, director of natural resource studies and co-author of The Fiscal Cost of Canada’s Low-Carbon Economy.
The study finds that since 2014/15, the federal government and provincial governments in the country’s four largest provinces (Ontario, Quebec, Alberta and British Columbia) combined have spent and foregone revenues of $158 billion (inflation adjusted to 2024 dollars) trying to create clean jobs, as defined by Statistics Canada’s Environmental and Clean Technology Products Economic Account.
Importantly, that cost estimate is conservative since it does not account for an exhaustive list of direct government spending and it does not measure the costs from Canada’s other six provinces, municipalities, regulatory costs and other economic
costs because of the low-carbon spending and tax credits.
A second study, Sizing Canada’s Clean Economy, finds that there was very little change over the 2014 to 2023 period in terms of the share of the total economy represented by the clean economy. For instance, in 2014, the clean economy represented 3.1 per cent of GDP compared to 3.6 per cent in 2023.
“The evidence is clear—the much-hyped clean economic transition has failed to fundamentally transform Canada’s $3.3 trillion economy,” said study co-author and Fraser Institute senior fellow Jock Finlayson.
State of the Green Economy
- The Fiscal Cost of Canada’s Low-Carbon Economy documents spending initiatives by the federal government and the governments of Ontario, British Columbia, Alberta, and Quebec since 2014 to promote the low-carbon economy, as well as how much revenue they have foregone through offering tax credits.
- Overall, the combined cost of spending and tax credits supporting a low-carbon economy by the federal government and the four provincial governments is estimated at $143.6 billion from 2014–15 to 2024–25, in nominal terms. When adjusted for inflation, the total reaches $158 billion in 2024 dollars.
- These estimates are based on very conservative assumptions, and they do not cover every program area or government-controlled expenditure related to the low-carbon economy and/or reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Sizing Canada’s Green Economy assesses the composition, growth, share of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) output, and employment of Canada’s “clean economy” from 2014 to 2023.
- Canada’s various environmental and clean technology industries collectively have accounted for between 3.07% and 3.62% of all-industry GDP over the 10-year period from 2014 to 2023. While it has grown, the sector as a whole has not been expanding at a pace that meaningfully exceeds the growth of the overall Canadian economy, despite significant policy attention and mounting public subsidies.
- The clean economy represents a respectable and relatively stable share of Canada’s $3.3 trillion economy. However, it remains a small part of Canada’s broader industrial mix, it is not a major source of export earnings, and it is not about to supplant the many other industries that underpin the country’s prosperity and dominate its international exports.
Addictions
The Shaky Science Behind Harm Reduction and Pediatric Gender Medicine


By Adam Zivo
Both are shaped by radical LGBTQ activism and questionable evidence.
Over the past decade, North America embraced two disastrous public health movements: pediatric gender medicine and “harm reduction” for drug use. Though seemingly unrelated, these movements are actually ideological siblings. Both were profoundly shaped by extremist LGBTQ activism, and both have produced grievous harms by prioritizing ideology over high-quality scientific evidence.
While harm reductionists are known today for championing interventions that supposedly minimize the negative effects of drug consumption, their movement has always been connected to radical “queer” activism. This alliance began during the 1980s AIDS crisis, when some LGBTQ activists, hoping to reduce HIV infections, partnered with addicts and drug-reform advocates to run underground needle exchanges.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
In the early 2000s, after the North American AIDS epidemic was brought under control, many HIV organizations maintained their relevance (and funding) by pivoting to addiction issues. Despite having no background in addiction medicine, their experience with drug users in the context of infectious diseases helped them position themselves as domain experts.
These organizations tended to conceptualize addiction as an incurable infection—akin to AIDS or Hepatitis C—and as a permanent disability. They were heavily staffed by progressives who, influenced by radical theory, saw addicts as a persecuted minority group. According to them, drug use itself was not the real problem—only society’s “moralizing” norms.
These factors drove many HIV organizations to lobby aggressively for harm reduction at the expense of recovery-oriented care. Their efforts proved highly successful in Canada, where I am based, as HIV researchers were a driving force behind the implementation of supervised consumption sites and “safer supply” (free, government-supplied recreational drugs for addicts).
From the 2010s onward, the association between harm reductionism and queer radicalism only strengthened, thanks to the popularization of “intersectional” social justice activism that emphasized overlapping forms of societal oppression. Progressive advocates demanded that “marginalized” groups, including drug addicts and the LGBTQ community, show enthusiastic solidarity with one another.
These two activist camps sometimes worked on the same issues. For example, the gay community is struggling with a silent epidemic of “chemsex” (a dangerous combination of drugs and anonymous sex), which harm reductionists and queer theorists collaboratively whitewash as a “life-affirming cultural practice” that fosters “belonging.”
For the most part, though, the alliance has been characterized by shared tones and tactics—and bad epistemology. Both groups deploy politicized, low-quality research produced by ideologically driven activist-researchers. The “evidence-base” for pediatric gender medicine, for example, consists of a large number of methodologically weak studies. These often use small, non-representative samples to justify specious claims about positive outcomes. Similarly, harm reduction researchers regularly conduct semi-structured interviews with small groups of drug users. Ignoring obvious limitations, they treat this testimony as objective evidence that pro-drug policies work or are desirable.
Gender clinicians and harm reductionists are also averse to politically inconvenient data. Gender clinicians have failed to track long-term patient outcomes for medically transitioned children. In some cases, they have shunned detransitioners and excluded them from their research. Harm reductionists have conspicuously ignored the input of former addicts, who generally oppose laissez-faire drug policies, and of non-addict community members who live near harm-reduction sites.
Both fields have inflated the benefits of their interventions while concealing grievous harms. Many vulnerable children, whose gender dysphoria otherwise might have resolved naturally, were chemically castrated and given unnecessary surgeries. In parallel, supervised consumption sites and “safer supply” entrenched addiction, normalized public drug use, flooded communities with opioids, and worsened public disorder—all without saving lives.
In both domains, some experts warned about poor research practices and unmeasured harms but were silenced by activists and ideologically captured institutions. In 2015, one of Canada’s leading sexologists, Kenneth Zucker, was fired from the gender clinic he had led for decades because he opposed automatically affirming young trans-identifying patients. Analogously, dozens of Canadian health-care professionals have told me that they feared publicly criticizing aspects of the harm-reduction movement. They thought doing so could invite activist harassment while jeopardizing their jobs and grants.
By bullying critics into silence, radical activists manufactured false consensus around their projects. The harm reductionists insist, against the evidence, that safer supply saves lives. Their idea of “evidence-based policymaking” amounts to giving addicts whatever they ask for. “The science is settled!” shout the supporters of pediatric gender medicine, though several systematic reviews proved it was not.
Both movements have faced a backlash in recent years. Jurisdictions throughout the world are, thankfully, curtailing irreversible medical procedures for gender-confused youth and shifting toward a psychotherapy-based “wait and see” approach. Drug decriminalization and safer supply are mostly dead in North America and have been increasingly disavowed by once-supportive political leaders.
Harm reductionists and queer activists are trying to salvage their broken experiments, occasionally by drawing explicit parallels between their twin movements. A 2025 paper published in the International Journal of Drug Policy, for example, asserts that “efforts to control, repress, and punish drug use and queer and trans existence are rising as right-wing extremism becomes increasingly mainstream.” As such, there is an urgent need to “cultivate shared solidarity and action . . . whether by attending protests, contacting elected officials, or vocally defending these groups in hostile spaces.”
How should critics respond? They should agree with their opponents that these two radical movements are linked—and emphasize that this is, in fact, a bad thing. Large swathes of the public understand that chemically and surgically altering vulnerable children is harmful, and that addicts shouldn’t be allowed to commandeer public spaces. Helping more people grasp why these phenomena arose concurrently could help consolidate public support for reform and facilitate a return to more restrained policies.
Adam Zivo is director of the Canadian Centre for Responsible Drug Policy.
For the full experience, please upgrade your subscription and support a public interest startup.
We break international stories and this requires elite expertise, time and legal costs.
-

 Alberta6 hours ago
Alberta6 hours agoFrom Underdog to Top Broodmare
-
 Media1 day ago
Media1 day agoCarney speech highlights how easily newsrooms are played by politicians
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoThe painful return of food inflation exposes Canada’s trade failures
-
 Business8 hours ago
Business8 hours agoPaying for Trudeau’s EV Gamble: Ottawa Bought Jobs That Disappeared
-

 Business11 hours ago
Business11 hours agoCBC uses tax dollars to hire more bureaucrats, fewer journalists
-

 National9 hours ago
National9 hours agoElection Officials Warn MPs: Canada’s Ballot System Is Being Exploited
-

 Economy3 hours ago
Economy3 hours agoIn his own words: Stunning Climate Change pivot from Bill Gates. Poverty and disease should be top concern.
-

 Addictions5 hours ago
Addictions5 hours agoThe Shaky Science Behind Harm Reduction and Pediatric Gender Medicine









