Business
Bad Research Still Costs Good Money

I have my opinions about which academic research is worth funding with public money and which isn’t. I also understand if you couldn’t care less about what I think. But I expect we’ll all share similar feelings about research that’s actually been retracted by the academic journals where it was published.
Globally, millions of academic papers are published each year. Many – perhaps most – were funded by universities, charitable organizations, or governments. It’s estimated that hundreds of thousands of those papers contain serious errors, irreproducible results, or straight-up plagiarized or false content.
Not only are those papers useless, but they clog up the system and slow down the real business of science. Keeping up with the serious literature coming out in your field is hard enough, but when genuine breakthroughs are buried under thick layers of trash, there’s no hope.
The Audit is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Society doesn’t need those papers and taxpayers shouldn’t have to pay for their creation. The trick, however, is figuring out how to identify likely trash before we approve a grant proposal.
I just discovered a fantastic tool that can help. The good people behind the Retraction Watch site also provide a large dataset currently containing full descriptions and metadata for more than 60,000 retracted papers. The records include publication authors, titles, and subjects; reasons for the retractions; and any institutions with which the papers were associated.
Using that information, I can tell you that 798 of those 60,000 papers have an obvious Canadian connection. Around half of those papers were retracted in the last five years – so the dataset is still timely.
There’s no single Canadian institution that’s responsible for a disproportionate number of clunkers. The data contains papers associated with 168 Canadian university faculties and 400 hospital departments. University of Toronto overall has 26 references, University of British Columbia has 18, and McMaster and University of Ottawa both have nine. Research associated with various departments of Toronto’s Sick Children’s Hospital combined account for 27 retractions.
To be sure, just because your paper shows up on the list doesn’t mean you’ve done anything wrong. For example, while 20 of the retractions were from the Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada, those were all pulled because they were out of date. That’s perfectly reasonable.
I focused on Canadian retractions identified by designations like Falsification (38 papers), Plagiarism (41), Results Not Reproducible (21), and Unreliable (130). It’s worth noting that some of those papers could have been flagged for more than one issue.
Of the 798 Canadian retractions, 218 were flagged for issues of serious concern. Here are the subjects that have been the heaviest targets for concerns about quality:
You many have noticed that the total of those counts comes to far more than 218. That’s because many papers touch on multiple topics.
For those of you keeping track at home, there were 1,263 individual authors involved in those 218 questionable papers. None of them had more than five such papers and only a very small handful showed up in four or five cases. Although there would likely be value in looking a bit more closely at their publishing histories.
This is just about as deep as I’m going to dig into this data right now. But the papers I’ve identified are probably just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to lousy (and expensive) research. So we’ve got an interest in identifying potentially problematic disciplines or institutions. And, thanks to Retraction Watch, we now have the tools.
Kyle Briggs over at CanInnovate has been thinking and writing about these issues for years. He suggests that stemming the crippling flow of bad research will require a serious realigning of the incentives that currently power the academic world.
That, according to Briggs, is most likely to happen by forcing funding agencies to enforce open data requirements – and that includes providing access to the programming code used by the original researchers. It’ll also be critical to truly open up access to research to allow meaningful crowd-sourced review.
Those would be excellent first steps.
The Audit is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
Business
Your $350 Grocery Question: Gouging or Economics?

Dr. Sylvain Charlebois, a visiting scholar at McGill University and perhaps better known as the Food Professor, has lamented a strange and growing trend among Canadians. It seems that large numbers of especially younger people would prefer a world where grocery chains and food producers operated as non-profits and, ideally, were owned by governments.
Sure, some of them have probably heard stories about the empty shelves and rationing in Soviet-era food stores. But that’s just because “real” communism has never been tried.
In a slightly different context, University of Toronto Professor Joseph Heath recently responded to an adjacent (and popular) belief that there’s no reason we can’t grow all our food in publicly-owned farms right on our city streets and parks:
“Unfortunately, they do have answers, and anyone who stops to think for a minute will know what they are. It’s not difficult to calculate the amount of agricultural land that is required to support the population of a large urban area (such as Tokyo, where Saitō lives). All of the farms in Japan combined produce only enough food to sustain 38% of the Japanese population. This is all so obvious that it feels stupid even to be pointing it out.”
Sure, food prices have been rising. Here’s a screenshot from Statistics Canada’s Consumer Price Index price trends page. As you can see, the 12-month percentage change of the food component of the CPI is currently at 3.4 percent. That’s kind of inseparable from inflation.

But it’s just possible that there’s more going on here than greedy corporate price gouging.
It should be obvious that grocery retailers are subject to volatile supply chain costs. According to Statistics Canada, as of June 2025, for example, the price of “livestock and animal products” had increased by 130 percent over their 2007 prices. And “crops” saw a 67 percent increase over that same period. Grocers also have to lay out for higher packaging material costs that include an extra 35 percent (since 2021) for “foam products for packaging” and 78 percent more for “paperboard containers”.
In the years since 2012, farmers themselves had to deal with 49 percent growth in “commercial seed and plant” prices, 46 percent increases in the cost of production insurance, and a near-tripling of the cost of live cattle.
So should we conclude that Big Grocery is basically an industry whose profits are held to a barely sustainable minimum by macro economic events far beyond their control? Well that’s pretty much what the Retail Council of Canada (RCC) claims. Back in 2023, Competition Bureau Canada published a lengthy response from the RCC to the consultation on the Market study of retail grocery.
The piece made a compelling argument that food sales deliver razor-thin profit margins which are balanced by the sale of more lucrative non-food products like cosmetics.
However, things may not be quite as simple as the RCC presents them. For instance:
- While it’s true that the large number of supermarket chains in Canada suggests there’s little concentration in the sector, the fact is that most independents buy their stock as wholesale from the largest companies.
- The report pointed to Costco and Walmart as proof that new competitors can easily enter the market, but those decades-old well-financed expansions prove little about the way the modern market works. And online grocery shopping in Canada is still far from established.
- Consolidated reporting methods would make it hard to substantiate some of the report’s claims of ultra-thin profit margins on food.
- The fact that grocers are passing on costs selectively through promotional strategies, private-label pricing, and shrinkflation adjustments suggests that they retain at least some control over their supplier costs.
- The claim that Canada’s food price inflation is more or less the same as in other peer countries was true in 2022. But we’ve since seen higher inflation here than, for instance, in the U.S.
Nevertheless, there’s vanishingly little evidence to support claims of outright price gouging. Rising supply chain costs are real and even high-end estimates of Loblaw, Metro, and Sobeys net profit margins are in the two to five percent range. That’s hardly robber baron territory.
What probably is happening is some opportunistic margin-taking through various selective pricing strategies. And at least some price collusion has been confirmed.
How much might such measures have cost the average Canadian family? A reasonable estimate places the figure at between $150 and $350 a year. That’s real money, but it’s hardly enough to justify gutting the entire free market in favor of some suicidal system of central planning and control.
Business
The Grocery Greed Myth

Haultain’s Substack is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support our work, please consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Try it out.
The Justin Trudeau and Jagmeet Singh charges of “greedflation” collapses under scrutiny.
“It’s not okay that our biggest grocery stores are making record profits while Canadians are struggling to put food on the table.” —PM Justin Trudeau, September 13, 2023.
A couple of days after the above statement, the then-prime minister and his government continued a campaign to blame rising food prices on grocery retailers.
The line Justin Trudeau delivered in September 2023, triggered a week of political theatre. It also handed his innovation minister, François-Philippe Champagne, a ready-made role: defender of the common shopper against supposed corporate greed. The grocery price problem would be fixed by Thanksgiving that year. That was two years ago. Remember the promise?
But as Ian Madsen of the Frontier Centre for Public Policy has shown, the numbers tell a different story. Canada’s major grocers have not been posting “record profits.” They have been inching forward in a highly competitive, capital-intensive sector. Madsen’s analysis of industry profit margins shows this clearly.
Take Loblaw. Its EBITDA margin (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) averaged 11.2 per cent over the three years ending 2024. That is up slightly from 10 per cent pre-COVID. Empire grew from 3.9 to 7.6 per cent. Metro went from 7.6 to 9.6. These are steady trends, not windfalls. As Madsen rightly points out, margins like these often reflect consolidation, automation, and long-term investment.
Meanwhile, inflation tells its own story. From March 2020 to March 2024, Canada’s money supply rose by 36 per cent. Consumer prices climbed about 20 per cent in the same window. That disparity suggests grocers helped absorb inflationary pressure rather than drive it. The Justin Trudeau and Jagmeet Singh charges of “greedflation” collapses under scrutiny.
Yet Ottawa pressed ahead with its chosen solution: the Grocery Code of Conduct. It was crafted in the wake of pandemic disruptions and billed as a tool for fairness. In practice, it is a voluntary framework with no enforcement and no teeth. The dispute resolution process will not function until 2026. Key terms remain undefined. Suppliers are told they can expect “reasonable substantiation” for sudden changes in demand. They are not told what that means. But food inflation remains.
This ambiguity helps no one. Large suppliers will continue to settle matters privately. Small ones, facing the threat of lost shelf space, may feel forced to absorb losses quietly. As Madsen observes, the Code is unlikely to change much for those it claims to protect.
What it does serve is a narrative. It lets the government appear responsive while avoiding accountability. It shifts attention away from the structural causes of price increases: central bank expansion, regulatory overload, and federal spending. Instead of owning the crisis, the state points to a scapegoat.
This method is not new. The Trudeau government, of which Carney’s is a continuation, has always shown a tendency to favour symbolism over substance. Its approach to identity politics follows the same pattern. Policies are announced with fanfare, dissent is painted as bigotry, and inconvenient facts are set aside.
The Grocery Code fits this model. It is not a policy grounded in need or economic logic. It is a ritual. It gives the illusion of action. It casts grocers as villains. It gives the impression to the uncaring public that the government is “providing solutions,” and that “it has their backs.” It flatters the state.
Madsen’s work cuts through that illusion. It reminds us that grocery margins are modest, inflation was monetary, and the public is being sold a story.
Canadians deserve better than fables, but they keep voting for the same folks. They don’t think to think that they deserve a government that governs within its limits; a government that accept its role in the crises it helped cause, and restores the conditions for genuine economic freedom. The Grocery Code is not a step in that direction. It was always a distraction, wrapped in a moral pose.
And like most moral poses in Ottawa, it leaves the facts behind.
Haultain’s Substack is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support our work, please consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Try it out.
-

 National1 day ago
National1 day agoCanada’s birth rate plummets to an all-time low
-

 Crime1 day ago
Crime1 day agoPierre Poilievre says Christians may be ‘number one’ target of hate violence in Canada
-

 Opinion13 hours ago
Opinion13 hours agoJordan Peterson needs prayers as he battles serious health issues, daughter Mikhaila says
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex14 hours ago
Censorship Industrial Complex14 hours agoWinnipeg Universities Flunk The Free Speech Test
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoJason Kenney’s Separatist Panic Misses the Point
-
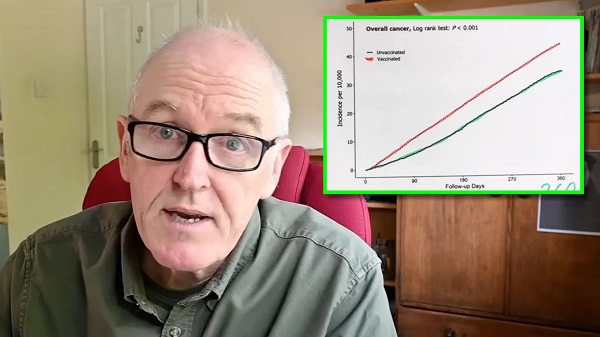
 COVID-199 hours ago
COVID-199 hours agoDevastating COVID-19 Vaccine Side Effect Confirmed by New Data: Study
-

 Automotive1 day ago
Automotive1 day agoBig Auto Wants Your Data. Trump and Congress Aren’t Having It.
-

 Crime12 hours ago
Crime12 hours agoThe Bureau Exclusive: Chinese–Mexican Syndicate Shipping Methods Exposed — Vancouver as a Global Meth Hub

 By
By 








