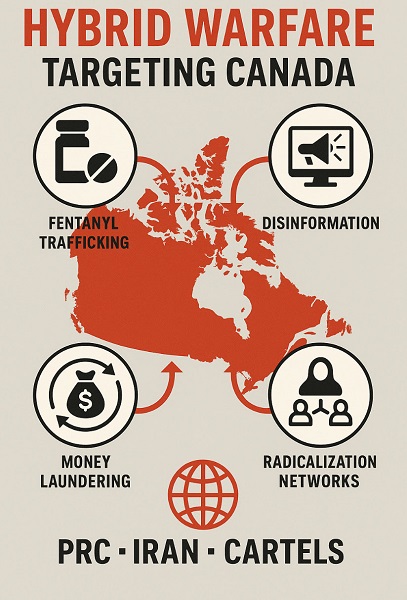
As Ottawa faces mounting pressure from Washington to respond to fentanyl trafficking, human smuggling, and terror threats stemming from a convergence of Chinese Communist operatives and transnational mafias from Mexico and Iran, a fresh assessment of Canada’s policing strategy and governance reveals the stunning absence of a “Criminal Intelligence Committee to deal with a number of intelligence policy and related issues”—while simultaneously raising troubling doubts about the RCMP’s capacity to prioritize, analyze, and target serious threats free from political influence.
The Bureau’s comparative analysis is based on a sweeping 2024 external review of the RCMP’s response to the pandemic-era “freedom convoy,” which suggests Canada’s federal police force—working for “clients” who do not understand or value how intelligence should shape decision-making—bent under severe political pressure, compromising its intelligence collection and reporting integrity, and helping execute an unprecedented crackdown on citizens’ financial freedoms during the winter 2022 protests in Ottawa.
The 92-page report, produced under a post-operation initiative called Project Natterjack, paints a portrait of intelligence breakdowns, governance failure, and inappropriate political influence—particularly from senior officials in Prime Minister Justin Trudeau’s government. The review, first obtained by The Canadian Press under the Access to Information Act, included survey responses from 1,641 RCMP officers and personnel deployed during the protests, which paralyzed downtown Ottawa and disrupted key international border crossings.
Yet an element overlooked in previous analyses of Natterjack may be its most damning: the complete absence of an organizing vision across Canada’s security and intelligence arms.
This structural vacuum comes at a time when the national security threats facing Canada are increasingly hybridized—blending terrorism, organized crime, election interference, cyber warfare, and financial infiltration. These are precisely the kinds of threats Washington is now pressing Ottawa to address, including investigations into fentanyl superlabs and hostile networks tied to the Chinese Communist Party, Mexican cartels, and Iranian and Russian threat actors.
Amid what the U.S. government sees as a growing vulnerability that Ottawa has failed to address in coordination with Washington under Trudeau’s Liberals, the Natterjack report highlights a deeply relevant structural failure in Canadian policing.
“Many interviewees expressed a level of concern that beyond the informal networks that loosely bind criminal, tactical, and strategic analysts from a variety of law enforcement and security and intelligence agencies, there is not a recognized national body that comes together to advocate, address and advance issues in criminal analysis,” the report states. “The absence of a Criminal Intelligence Committee to deal with a number of intelligence policy and related issues appears glaringly missing and should be explored.”
Regarding the “freedom convoy,” the review’s most serious suggestion is that RCMP intelligence officers felt pressured to present the protests through the lens of “ideologically motivated violent extremism”—a national security framework typically reserved for terrorism investigations. Intelligence teams were subjected to hourly briefing demands from federal officials and were forced to issue rapid assessments under tight timelines, with resulting reports often presenting skewed or misattributed findings.
“Interviewees also indicated that there were issues with information and intelligence that was disseminated to external Government of Canada agencies,” the report states. “Specifically, some Government of Canada partners would misrepresent the information or misattribute third-party information as RCMP information… Interviewees and survey respondents felt immense pressure from the Government of Canada to be briefed on a regular basis… in particular when briefings were requested on an hourly basis.”
As the review notes bluntly: “When there is that much pressure to produce a report within an hour or a few hours’ time, it is not productive.”
Taken together, the findings paint a sobering portrait of a federal police force struggling to preserve its independence and credibility under political strain. While officers were deployed to confront a disruptive but largely peaceful protest, critics inside and outside government have pointed to the RCMP’s relative inaction toward far more dangerous networks—namely, fentanyl trafficking cartels, Chinese underground banking structures linked to the same political influence operations involved in federal election interference, intelligence-connected money laundering syndicates, and hostile state-sponsored actors operating inside Canada.
One telling passage indicating a scramble within RCMP command to produce findings on ideological extremism—whether fully valid or not—reads: “Ideologically Motivated Criminal Intelligence Team and the Joint Intelligence Group were both operating to provide the strategic threat picture, and reaching in directly to the Divisions for intelligence updates. As such, some interviewees noted that they were inundated by requests for intelligence updates from different intelligence teams at National Headquarters.”
In parallel, the federal cabinet invoked the Emergencies Act—suspending civil liberties and activating sweeping enforcement powers that allowed financial institutions to freeze protestors’ bank accounts. Between February 15 and 23, 2022, the RCMP’s Federal Policing Criminal Operations Financial Crimes Unit made 57 disclosures to banks and other institutions, targeting 62 individuals and 17 businesses for asset freezes.
The report pointedly states: “The act of participating in a demonstration is not in itself a form of ideologically motivated violent extremism.” Yet that nuance appeared largely lost amid the political urgency to classify the protests as a national threat.
Interviewees also noted limitations in their ability to disseminate protected information and intelligence to certain external agencies and private financial institutions. Specifically, they indicated that encryption was not consistently available across these external channels.
Perhaps most revealingly, the review found that senior officials—referred to as intelligence “clients”—did not appear to value intelligence or allow it to meaningfully guide decision-making during the crisis. “Interviewees and survey respondents expressed the need to educate intelligence clients on the value of intelligence and how it can be used for decision making,” the report notes. “Interviewees noted that the role of intelligence was not valued during the convoy-related events.” The admission sits uneasily beside the broader findings: that RCMP intelligence was not only shaped to support a political narrative that exaggerated the role of ideological extremism in the protests, but ultimately sidelined when it failed to serve that narrative.
The report also paints a picture that fits with a serious assertion previously conveyed to The Bureau by an RCMP source: that in the days following the convoy’s dispersal, investigators felt they were pressured to reconstruct investigative timelines to match political expectations—to sustain a national security narrative even when the underlying evidence did not necessarily meet threshold.
The Emergencies Act was revoked after just nine days. In January 2024, a federal judge ruled that the Trudeau government’s invocation of the Act was both unnecessary and unlawful, concluding that the legal threshold for a national emergency had not been met.
According to the review, RCMP officials shared protected personal information with financial institutions using processes that lacked consistent legal oversight. The Office of the Privacy Commissioner raised formal concerns, citing the RCMP’s reliance on open-source and social media research to flag individuals—many of whom had no demonstrated connection to criminal activity.
The Natterjack review further confirms that RCMP intelligence operations during the protests were defined by duplication, confusion, and political interference. At least three separate intelligence units—the Ideologically Motivated Criminal Intelligence Team, the Combined Intelligence Group, and the Joint Intelligence Group—were simultaneously tasked with protest reporting, resulting in overlapping and sometimes circular intelligence products. RCMP sources said the structure was unsustainable and exacerbated by National Headquarters’ failure to provide unified command or governance.
Meanwhile, on Sunday, in a televised interview that sent shockwaves through Washington, Ottawa, and Victoria, FBI Director Kash Patel warned that a new axis of global threat actors—consisting of Chinese Communist Party operatives, Iranian proxies, and Mexican cartel networks—is exploiting Canada’s lax border enforcement, immigration systems, and critical infrastructure in Vancouver to move fentanyl and terror suspects into the United States.
“Where’s all the fentanyl coming from still? Where are all the narco traffickers going to keep bringing this stuff into the country? The northern border,” Patel said. “Our adversaries have partnered up with the CCP and others—Russia, Iran—on a variety of different criminal enterprises. And they’re going and they’re sailing around to Vancouver and coming in by air.”
Patel’s public assessment aligns disturbingly well with the key findings of a Bureau investigation first published in August 2024. That report, based on testimony and documentary evidence from former Canada Border Services Agency officer Luc Sabourin, warned that systemic corruption and compromised enforcement at Canada’s ports of entry had already created the kind of vulnerabilities now cited by the FBI.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
If you enjoy The Bureau, share it with your friends and earn rewards when they subscribe.
Invite Friends
Related