Business
Timeline: Panama Canal Politics, Policy, and Tensions
 By Greg Collard and James Rushmore
By Greg Collard and James Rushmore
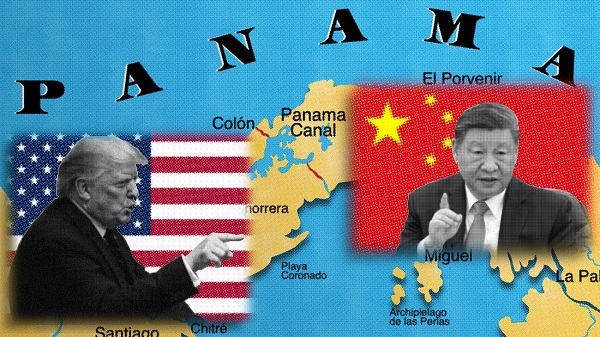
Hegseth’s visit to Panama includes strongly-worded speeches directed at China
While the trade war with China plays out, another war of political rhetoric is heating up again over the Panama Canal.
Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth was in Panama this week, and pointed out America’s military presence and joint training exercises with Panamanians. Though he said the U.S. doesn’t seek war and that “war with China is certainly not inevitable,” he had a strong military message for the CCP:
Racket News is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Our relationship is growing in part to meet communist China’s rising challenge. China-based companies continue to control critical infrastructure in the canal area that gives China the potential to conduct surveillance activities across Panama. This makes Panama and the United States less secure, less prosperous, and less sovereign.
He said “China will not weaponize this canal,” and it will stay that way “through the deterrent power of the strongest, most effective, and most lethal fighting force in the world.”
Hegseth followed up Wednesday with a similar message to the Central American Security Conference.
The era of capitulating to coercion by the communist Chinese is over. They’re growing an adversarial control of strategic land and critical infrastructure in this hemisphere cannot and will not stand. To accomplish this, our countries cannot face these shared threats alone. We have to face them together. America will confront, will deter, and if necessary defeat these threats alongside all of you, our close and valued partners. Our mission is simple: achieve peace through strength through an America first approach. We’re doing this by restoring the warrior ethos, rebuilding our military and reestablishing deterrence.
Obviously, that didn’t go over well with China. Its embassy in Panama accuses the U.S. of hypocrisy as it “repeats ad nauseam the ‘Chinese interference and influence.’” It noted the U.S. invaded Panama in 1989 and asked: “Who represents the real threat to the Channel? People will make their own judgment.”
(In making that judgment, a reminder that the U.S. still controlled the Panama Canal in 1989, and Panama was run by dictator Manuel Noriega who had been indicted in the U.S. on drug crimes. He was also a former CIA informant, and American officials knew about his crimes — which included helping Pablo Escobar — for years before doing anything about it).
China’s influence over the Canal has grown since 2017, when Panama severed ties with Taiwan and established diplomatic relations with China. A Chinese company controls the largest port on the Atlantic side of the Canal, and a Hong Kong company, CK Hutchinson, controls ports on both ends of the Canal. Last month, BlackRock, an American investment firm, reached a deal to buy CK Hutchinson’s ports, but that deal could be in jeopardy of falling through. Chinese firms are also building a bridge across the Canal.
President Trump has said the U.S. should have never given up the canal to Panama, which occurred on Dec. 31, 1999, as agreed to in treaties that President Carter signed in 1977 and won Senate approval the following year.
While critics place a lot of blame on Carter, Presidents Nixon and Ford started the negotiations. There was bipartisan support to reach a deal (there was even a tentative deal in place in 1967, but a coup in Panama ended those negotiations) because there were tensions and sometimes violence between locals and Americans. The audio below is from a 1976 NBC story that describes life inside the barbed wire fence that surrounded the Canal Zone: “Its 40,000 American residents, both military and civilian, enjoy a suburban lifestyle.” Panamanians on the other side of the fence were resentful.
Ronald Reagan changed the political debate over the Canal during his primary challenge to Ford in 1976. Opposition to any deal with Panama became the focus of his campaign. Reagan says in the ad below: “We bought it, we paid for it, and General Torrijos (Panama’s dictator) should be told we’re going to keep it.”
The message was effective. Reagan won 24 states, and Ford didn’t secure the GOP nomination until the Republican National Convention.
Today’s debate over the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal was not a campaign issue in 2024. Trump first complained about passage rates charged to the Navy and U.S. shipping companies in two December 21 social media posts. Trump wrote that if the situation does not improve, “we will demand that the Panama Canal be returned to us, in full, and without question. To the Officials of Panama, please be guided accordingly!”
He repeated those criticisms and threats in a speech the following day:
It was not given for the benefit of others by a token of cooperation, but it was given to Panama and to the people of Panama, but it has provisions. You gotta treat us fairly, and they haven’t treated us fairly. If the principles, both moral and legal, of this magnanimous gesture of giving are not followed, then we demand that the Panama Canal be returned to the United States of America in full, quickly and without question.
Congresswoman Debbie Wasserman Schultz called that “preposterous.” House Minority Leader Hakeem Jeffries also dismissed the idea of regaining control of the Panama Canal.
But Democratic Congressman Jared Moskowitz said Trump has a point. He dismissed the idea of taking the Canal by force, but said “the United States reasserting its history in the Panama Canal is actually a good, important, strategic issue.”
At a hearing in January, Senate Commerce Committee Chairman Ted Cruz voiced concern about the bridge that Chinese firms are building across the Canal.
The partially-completed bridge gives China the ability to block the Canal without warning, and the ports give China ready observation posts to time that action. This situation poses acute risks to U.S. national security.
A witness at that hearing, George Mason international law professor Eugene Kontorovich, testified that the presence of a Chinese company essentially means the Chinese military has a presence in the Canal.
In a communist regime, distinctions between private and government-owned firms are not as absolute or clear-cut as in a Western liberal society. This is particularly the case for the People’s Republic of China (PRC), which has an official doctrine known as “Military-Civilian Fusion,” a top-level strategy of the CCP Central Committee since 2019.
Here’s a timeline of key events in the history of the Panama Canal leading up to this week’s speeches from Hegseth.
January 22, 1903
The U.S. and Colombia, which controlled what is now Panama, agree to a treaty that gives the U.S. rights to the land to build the Canal in return for $10 million and $250,000 annually. However, Colombia’s congress rejects the deal.
November 3, 1903
With the backing of the U.S., Panama declares its independence from Colombia.
November 18, 1903
The U.S. and Panama sign the Hay-Bunau-Varilla Treaty, which establishes the Panama Canal Zone and “grants to the United States all the rights, power and authority within the zone.” The treaty has the same financial terms that Colombia’s Congress rejected. It’s ratified by the Senate and approved by President Theodore Roosevelt in February 1904.
August 15, 1914
The Panama Canal opens to shipping.
January 9, 1964
Panamanian rioters invade the Canal Zone and attempt to substitute the U.S. flag with a Panamanian one. The riots last three days, killing 22 Panamanians and four U.S. troops.
September 7, 1977
President Jimmy Carter and Panamanian dictator Omar Torrijos sign the Torrijos-Carter Treaties. Panama will take control of the Canal on Dec. 31, 1999. President Carter says:
This agreement thus forms a new partnership to ensure that this vital waterway, so important to all of us, will continue to be well-operated, safe, and open to shipping by all nations now and in the future. Under these accords, Panama will play an increasingly important role in the operation and defense of the Canal during the next 23 years, and after that, the United States will still be able to counter any threat to the Canal’s neutrality and openness for use.
Panama gains control of the Canal. Army Secretary Louis Caldera, the head of the U.S. delegation at the handover ceremony, says:
The United States could not aspire to be a good neighbor to Latin America and continue occupying and dividing the territory of a country considered a friend.
December 21, 2024
On Truth Social, President-elect Trump slams Panama for charging the United States “exorbitant prices and rates of passage” to use the Canal. He claims that China is influencing the canal’s management, before adding, “This complete ‘rip-off’ of our Country will immediately stop.”
In a follow-up post, Trump adds:
December 22, 2024
While delivering a speech in Phoenix, Trump asks, “Has anyone ever heard of the Panama Canal? Because we’re being ripped off at the Panama Canal like we’re being ripped off everywhere else.”
When an audience member suggests taking back the Canal, Trump responds, “That’s a good idea.”
Panamanian President Jose Raul Mulino responds to Trump in a video he posts on X:
Mulino also issues a written statement, citing the Torrijos-Carter Treaties: “Every square meter of the Panama Canal and its adjacent area belong to PANAMA, and will continue to be. The sovereignty and independence of our country are not negotiable.”
He adds that passage rates are determined by “market conditions, international competition, operating costs and the maintenance and modernization needs of the interoceanic waterway,” and insists upon the Canal’s “permanent neutrality” and “open and safe operation for all nations.” He also rejects the notion that China wields any special influence over the Canal: “The Canal has no direct or indirect control from China, nor the European Union, nor the United States or any other power.”
Trump’s response:
Trump also shares an AI-generated image with the following caption:
December 23, 2024
Panamanian protesters gather outside the U.S. embassy to protest Trump.
Among the chants: “Get out invading gringo” and “Trump, animal, leave the Canal alone.”
They burn an American flag and set fire to an image of Trump.
“Donald Trump and his imperial delusion cannot claim even a single centimeter of land in Panama,” says one protester.
December 25, 2024
Trump posts the following Christmas message:
Minutes later, he announces that Miami-Dade County Commissioner Kevin Marino Cabrera will serve as the next U.S. ambassador to Panama, “a Country that is ripping us off on the Panama Canal, far beyond their wildest dreams.”
December 26, 2024
Panamian President Murino holds a press conference to send a message to Trump that the Canal is not for sale.
The Canal is Panamanian and belongs to Panamanians. There’s no possibility of opening any kind of conversation around this reality, which has cost the country blood, sweat and tears.
He also denies Trump’s claim that the Chinese military has any presence in the Canal, saying, “There are no Chinese soldiers in the Canal, for the love of God.”
January 7, 2025
During a press conference at Mar-a-Lago, Trump refuses to rule out using military force to acquire the Panama Canal. He claims that it was “built for our military” and “is vital to our country.” He once again argues that the Canal is “being operated by China.”
January 9, 2025
Republican Congressman Dusty Johnson of South Dakota introduces the Panama Canal Repurchase Act of 2025, which authorizes the President and the Secretary of State to “initiate and conduct negotiations with appropriate counterparts of the Government of the Republic of Panama to reacquire the Panama Canal.”
Panama Canal Administrator Ricaurte Vásquez tells the Associated Press that the Canal cannot charge lower rates to U.S. ships. He speaks of his desire to “maintain the established rules,” insists that the Canal is a neutral economic zone, and says that the Chinese companies operating in its ports have no special influence over how the Canal is run.
January 20, 2025
During his inauguration address, President Trump describes how “American ships [that use the Panama Canal] are being severely overcharged and not treated fairly in any way, shape, or form.” He repeats his assertion that China controls the Canal and closes with the following: “We gave it to Panama, and we’re taking it back.”
Trump’s comments prompt another statement from Mulino in which he says, “The Canal was not a concession from anyone.”
Panama also sends the statement to the U.N. Security Council.
February 2, 2025
Secretary of State Marco Rubio arrives in Panama City to meet with Mulino.
Mulino attempts to assuage Rubio’s concerns about Chinese influence by announcing that Panama would allow its membership in China’s Belt and Road Initiative to expire. He also vows to allow more U.S. investments in Panama.
Later that day, Trump reiterates his interest in obtaining the Canal. He tells reporters that “something very powerful is going to happen” if Panama does not cede control over the waterway.
Secretary of State Rubio is in Panama right now, and we’re talking about the Panama Canal. What they’ve done is terrible. They violated the agreement. They’re not allowed to violate the agreement.
China is running the Panama Canal. That was not given to China; that was given to Panama, foolishly. But they violated the agreement, and we’re going to take it back, or something very powerful is going to happen.
March 4, 2025
A consortium led by BlackRock announces that it will purchase CK Hutchison’s holdings in the Panama Ports Company, which owns and operates two ports on each side of the canal. CK Hutchison is owned by Hong Kong billionaire Li Ka-shing, and it reportedly felt “political pressure to exit the ports business.” The deal is worth over $19 billion.
Trump references the deal during his address to the joint session of Congress that evening (1:19:50 of the video below).

March 5, 2025
In an X post, Mulino denies Trump’s implication that the BlackRock deal lays the groundwork for a U.S. takeover of the Canal. He accuses Trump of lying.
March 13, 2025
NBC News reports that the Trump administration plans to bolster the U.S. military presence in Panama. Military officials tell NBC that, while the goal is to eventually reclaim control over the Canal, a U.S. invasion remains unlikely.
March 20, 2025
The Chinese government threatens to block CK Hutchison from selling its controlling interest in the two Panama Canal ports to BlackRock.
April 7, 2025
A Panamanian government investigation finds that CK Hutchison owes the country’s government over $300 million in fees because it did not properly renew its contract to operate its two ports along the Canal. This development has the potential to delay or even jeopardize the company’s deal with BlackRock.
Later that night, Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth arrives in Panama. He will speak at the reopening of an American port and address the Central American Security Conference. He is the first secretary of defense to visit Panama in two decades.
April 8, 2025
Hegseth meets with Mulino and Panama Canal Authority Administrator Ricaurte Vazquez.
They release a joint statement that says they agree to “strengthen bilateral Canal security cooperation,” guarantee “the expedited transit of warships and auxiliary vessels of the Republic of Panama and the United States, improve bilateral cyber cooperation,” and allocate Army Corps of Engineers resources towards ensuring the Canal’s sustainability. They also announce that they will move toward adopting a new mechanism for U.S. payment of Canal tolls and charges. The Defense Secretary praises Mulino for withdrawing Panama from the Belt and Road Initiative.
Panama’s version of their joint statement includes an additional detail: It says that Hegseth “recognized Panama’s leadership and inalienable sovereignty over the Panama Canal and its adjacent areas.”
Racket News is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Business
Trump makes impact on G7 before he makes his exit

Trump Rips Into Obama and Trudeau at G7 for a “Very Big Mistake” on Russia
At the G7 in Canada, President Trump didn’t just speak—he delivered a headline-making indictment.
Standing alongside Canada’s Prime Minister, he directly blasted Barack Obama and Justin Trudeau, accusing them of committing a “very big mistake” by booting Russia out of the G8. He warned that this move didn’t deter conflict—it unleashed it, and he insists it paved the way for the war in Ukraine.
Before the working sessions began, the two leaders fielded questions. The first topic: the ongoing trade negotiations between the U.S. and Canada. Trump didn’t hesitate to point out that the issue wasn’t personal—it was philosophical.
“It’s not so much holding up. I think we have different concepts,” Trump said. “I have a tariff concept, Mark [Carney] has a different concept, which is something that some people like.”
He made it clear that he prefers a more straightforward approach. “I’ve always been a tariff person. It’s simple, it’s easy, it’s precise and it just goes very quickly.”
Carney, he added, favors a more intricate framework—“also very good,” Trump said. The goal now, according to Trump, is to examine both strategies and find a path forward. “We’re going to look at both and we’re going to come out with something hopefully.”
When asked whether a deal could be finalized in a matter of days or weeks, Trump didn’t overpromise, but he left the door open. “It’s achievable but both parties have to agree.”
Then the conversation took an unexpected turn.
Standing next to Canada’s Prime Minister, whose predecessor helped lead that push, Trump argued that isolating Moscow may have backfired. “The G7 used to be the G8,” he said, pointing to the moment Russia was kicked out.
He didn’t hold back. “Barack Obama and a person named Trudeau didn’t want to have Russia in, and I would say that was a mistake because I think you wouldn’t have a war right now if you had Russia in.”
This wasn’t just a jab at past leaders. Trump was drawing a direct line from that decision to the war in Ukraine. According to him, expelling Russia took away any real chance at diplomacy before things spiraled.
“They threw Russia out, which I claimed was a very big mistake even though I wasn’t in politics then, I was loud about it.” For Trump, diplomacy doesn’t mean agreement—it means keeping adversaries close enough to negotiate.
“It was a mistake in that you spent so much time talking about Russia, but he’s no longer at the table. It makes life more complicated. You wouldn’t have had the war.”
Then he made it personal. Trump compared two timelines—one with him in office, and one without. “You wouldn’t have a war right now if Trump were president four years ago,” he said. “But it didn’t work out that way.”
Before reporters could even process Trump’s comments on Russia, he shifted gears again—this time turning to Iran.
Asked whether there had been any signs that Tehran wanted to step back from confrontation, Trump didn’t hesitate. “Yeah,” he said. “They’d like to talk.”
The admission was short but revealing. For the first time publicly, Trump confirmed that Iran had signaled interest in easing tensions. But he made it clear they may have waited too long.
“They should have done that before,” he said, referencing a missed 60-day negotiation window. “On the 61st day I said we don’t have a deal.”
Even so, he acknowledged that both sides remain under pressure. “They have to make a deal and it’s painful for both parties but I would say Iran is not winning this war.”
Then came the warning, delivered with unmistakable urgency. “They should talk and they should talk IMMEDIATELY before it’s too late.”
Eventually, the conversation turned back to domestic issues: specifically, immigration and crime.
He confirmed he’s directing ICE to focus its efforts on sanctuary cities, which he accused of protecting violent criminals for political purposes.
He pointed directly at major Democrat-led cities, saying the worst problems are concentrated in deep blue urban centers. “I look at New York, I look at Chicago. I mean you got a really bad governor in Chicago and a bad mayor, but the governor is probably the worst in the country, Pritzker.”
And he didn’t stop there. “I look at how that city has been overrun by criminals and New York and L.A., look at L.A. Those people weren’t from L.A. They weren’t from California most of those people. Many of those people.”
According to Trump, the crime surge isn’t just a local failure—it’s a direct consequence of what he called a border catastrophe under President Biden. “Biden allowed 21 million people to come into our country. Of that, vast numbers of those people were murderers, killers, people from gangs, people from jails. They emptied their jails into the U.S. Most of those people are in the cities.”
“All blue cities. All Democrat-run cities.”
He closed with a vow—one aimed squarely at the ballot box. Trump said he’ll do everything in his power to stop Democrats from using illegal immigration to influence elections.
“They think they’re going to use them to vote. It’s not going to happen.”
Just as the press corps seemed ready for more, Prime Minister Carney stepped in.
The momentum had clearly shifted toward Trump, and Carney recognized it. With a calm smile and hands slightly raised, he moved to wrap things up.
“If you don’t mind, I’m going to exercise my role, if you will, as the G7 Chair,” he said. “Since we have a few more minutes with the president and his team. And then we actually have to start the meeting to address these big issues, so…”
Trump didn’t object. He didn’t have to.
By then, the damage (or the impact) had already been done. He had steered the conversation, dropped one headline after another, and reshaped the narrative before the summit even began.
By the time Carney tried to regain control, it was already too late.
Wherever Trump goes, he doesn’t just attend the event—he becomes the event.
Thanks for reading! This post took time and care to put together, and we did our best to give this story the coverage it deserved.
If you like my work and want to support me and my team and help keep this page going strong, the most powerful thing you can do is sign up for the email list and become a paid subscriber.
Your monthly subscription goes further than you think. Thank you so much for your support.
This story was made possible with the help of Overton —I couldn’t have done it without him.
If you’d like to support his growing network, consider subscribing for the month or the year. Your support helps him expand his team and cover more stories like this one.
We both truly appreciate your support!
Business
The CBC is a government-funded giant no one watches

This article supplied by Troy Media.
 By Kris Sims
By Kris Sims
The CBC is draining taxpayer money while Canadians tune out. It’s time to stop funding a media giant that’s become a political pawn
The CBC is a taxpayer-funded failure, and it’s time to pull the plug. Yet during the election campaign, Prime Minister Mark Carney pledged to pump another $150 million into the broadcaster, even as the CBC was covering his campaign. That’s a blatant conflict of interest, and it underlines why government-funded journalism must end.
The CBC even reported on that announcement, running a headline calling itself “underfunded.” Think about that. Imagine being a CBC employee asking Carney questions at a campaign news conference, while knowing that if he wins, your employer gets a bigger cheque. Meanwhile, Conservative Leader Pierre Poilievre has pledged to defund the CBC. The broadcaster is literally covering a story that determines its future funding—and pretending there’s no conflict.
This kind of entanglement isn’t journalism. It’s political theatre. When reporters’ paycheques depend on who wins the election, public trust is shattered.
And the rot goes even deeper. In the Throne Speech, the Carney government vowed to “protect the institutions that bring these cultures and this identity to the world, like CBC/RadioCanada.” Before the election, a federal report recommended nearly doubling the CBC’s annual funding. Former heritage minister Pascale St-Onge said Canada should match the G7 average of $62 per person per year—a move that would balloon the CBC’s budget to $2.5 billion annually. That would nearly double the CBC’s current public funding, which already exceeds $1.2 billion per year.
To put that in perspective, $2.5 billion could cover the annual grocery bill for more than 150,000 Canadian families. But Ottawa wants to shovel more cash at an organization most Canadians don’t even watch.
St-Onge also proposed expanding the CBC’s mandate to “fight disinformation,” suggesting it should play a formal role in “helping the Canadian population understand fact-based information.” The federal government says this is about countering false or misleading information online—so-called “disinformation.” But the Carney platform took it further, pledging to “fully equip” the CBC to combat disinformation so Canadians “have a news source
they know they can trust.”
That raises troubling questions. Will the CBC become an official state fact-checker? Who decides what qualifies as “disinformation”? This isn’t about journalism anymore—it’s about control.
Meanwhile, accountability is nonexistent. Despite years of public backlash over lavish executive compensation, the CBC hasn’t cleaned up its act. Former CEO Catherine Tait earned nearly half a million dollars annually. Her successor, Marie Philippe Bouchard, will rake in up to $562,700. Bonuses were scrapped after criticism—but base salaries were quietly hiked instead. Canadians struggling with inflation and rising costs are footing the bill for bloated executive pay at a broadcaster few of them even watch.
The CBC’s flagship English-language prime-time news show draws just 1.8 per cent of available viewers. That means more than 98 per cent of TV-viewing Canadians are tuning out. The public isn’t buying what the CBC is selling—but they’re being forced to pay for it anyway.
Government-funded journalism is a conflict of interest by design. The CBC is expensive, unpopular, and unaccountable. It doesn’t need more money. It needs to stand on its own—or not at all.
Kris Sims is the Alberta Director for the Canadian Taxpayers Federation
Troy Media empowers Canadian community news outlets by providing independent, insightful analysis and commentary. Our mission is to support local media in helping Canadians stay informed and engaged by delivering reliable content that strengthens community connections and deepens understanding across the country.
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoLast day and last chance to win this dream home! Support the 2025 Red Deer Hospital Lottery before midnight!
-

 conflict2 days ago
conflict2 days ago“Evacuate”: Netanyahu Warns Tehran as Israel Expands Strikes on Iran’s Military Command
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoKananaskis G7 meeting the right setting for U.S. and Canada to reassert energy ties
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCarney’s Honeymoon Phase Enters a ‘Make-or-Break’ Week
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoCould the G7 Summit in Alberta be a historic moment for Canadian energy?
-

 Aristotle Foundation2 days ago
Aristotle Foundation2 days agoThe Canadian Medical Association’s inexplicable stance on pediatric gender medicine
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta announces citizens will have to pay for their COVID shots
-

 conflict1 day ago
conflict1 day agoIsrael bombs Iranian state TV while live on air
































