Business
Americans Say Government Is Corrupt and Inefficient but Are Lukewarm About DOGE

Democrats seem willing to tolerate a lot to get a larger government, but Republicans aren’t much better
Americans think government is wasteful when it’s not outright fraudulent and abusive. That should create a welcoming environment for the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) and its mission to cut fat out of federal agencies on the way to (hopefully) reducing the state and balancing the budget. But support for DOGE is lukewarm. Unsurprisingly in these politically fractured times, cost-cutting efforts are a lot more popular with Republicans than Democrats, but polling suggests the division isn’t just one of partisanship. The DOGE is running up against fundamental disagreements over the role of government and the people who staff it—and the price people are willing to pay for a less-obnoxious government.
Corrupt and Inefficient Government, but Iffy Support for DOGE
Last year, Pew Research polling found that 56 percent of Americans say government is “almost always wasteful and inefficient.” The Babbie Centre at Chapman University reported that “nearly 2/3 of Americans fear that our government is run by corrupt officials.” And last month, A.P.-NORC researchers found 70 percent of Americans believe corruption is a major problem in the federal government, 65 percent say the same of inefficiency, and 59 percent see red tape—including regulations and bureaucracy—as a major problem.
Yet DOGE draws just a 39 percent “favorable” rating in the latest The Economist/YouGov poll, a bare three points ahead of “unfavorable” at 36 percent (25 percent picked “don’t know”). A poll this month from Trafalgar Group found 49 percent approving of the cost-cutting efforts of DOGE and Elon Musk, with 44 percent disapproving (7 percent were undecided). That’s more support than opposition in both cases, but you’d expect greater enthusiasm from a public that overwhelmingly considers government to be corrupt and wasteful (with plenty of evidence to support that position).
Part of the explanation, of course, is partisanship. Anything done by officials from one of the major parties is bound to be booed by the opposition, no matter what. As Gallup’s Jeffrey M. Jones pointed out in 2022, “generally speaking, Republicans and Democrats are more inclined to say the government has too much power when the president is from the other party, and less inclined when a president from their own party is in the White House.” That tribalism likely extends to cutting government as well, even if the cuts apply to agencies controlled for the moment by political enemies. Sure enough, both Trafalgar and The Economist/YouGov found far greater support for DOGE among Republicans than among Democrats (independents split the difference).
Democrats Want More Government, Flaws and All
But there are also real differences in attitudes toward the role of the state. The same Pew poll that reported widespread belief in the wastefulness and inefficiency of government also found that 49 percent of respondents “would prefer a smaller government providing fewer services” while 48 percent “would rather have a bigger government providing more services.” And the partisan divide here isn’t just tribal, it’s ideological. Despite fluctuations depending on who is in power, Republicans have overwhelmingly favored a smaller government providing fewer services since polling on the issue began in 1976 (support for bigger government peaked among them at about one-third in 1988 and 2004). Democratic support for larger, more active government grew from 49 percent in 1976 to 74 percent now.
Democrats in the A.P.-NORC poll were just slightly kinder than Republicans in their opinions on government corruption, efficiency, and red tape; majorities agree the federal government is corrupt and inefficient, while a 47 percent plurality says that red tape is a major problem. Given the overwhelming belief that government is corrupt and wasteful, but iffy support for DOGE, it’s fair to conclude that at least some Democrats are willing to put up with those concerns as the price of a larger state.
Partisan disagreement over the role of government also applies to trust in the people who staff the federal bureaucracy. These are the people the Trump administration offered buyouts and seeks to reduce in number, much like the Clinton administration did in the 1990s. Support for reducing the federal workforce depends, to a large extent, on agreement that those workers are part of the problem—or at least that we’d be better off with fewer of them. That’s not a universal opinion.
“Just 38% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents express a great deal or a fair amount of confidence in federal career employees,” Pew Research noted last week. That’s down 10 points from 2018. “In contrast, 72% of Democrats and Democratic leaners say they have confidence in career government employees – 7 points higher than in 2022, but on par with 2018 levels.”
So, if we’re to believe what members of the public tell researchers, majorities of Americans across partisan divides think the federal government is corrupt and inefficient. But a fair number of those who hold this position—Democrats, in particular—are confident that the people employed by the federal government aren’t responsible for that corruption and efficiency. Those problems appear from somewhere, perhaps as a miasma emanating from the swamp that D.C. was in years past. Also, many of those concerned that corruption and inefficiency plague the government are willing to put up with those handicaps so that the corrupt and inefficient government can play a larger role in our lives.
Republicans Also Want Their Expensive Goodies
Of course, consistency and logic aren’t necessarily common features of public opinion. As I’ve noted before, Republicans and Democrats may disagree when it comes to broad philosophical statements about the size and role of government, but when it comes to specifics, there’s more that unites them than divides them. Majorities of partisans of both parties as well as of independents want more federal spending on Social Security, Education, and Medicare, according to A.P.-NORC. A majority of Democrats also want more to be spent on Medicaid and assistance to the poor, while a majority of Republicans similarly want more dedicated to border security and the military.
Social Security is almost a quarter of federal spending all by itself, while Medicare, Medicaid, and other health care are slightly more, by the Cato Institute’s reckoning. National defense is about 13 percent, as is income security, with interest on federal debt right behind. DOGE faces quite an uphill battle to succeed in its mission to slash the size and cost of federal government.
DOGE faces obstacles from Democrats who recognize that the government is corrupt and inefficient but want more of it anyway. It also faces a challenge in Republicans and independents who say they want less government but don’t want to surrender their favorite boondoggles.
Americans are lukewarm about DOGE because they’re torn about its mission. Sure, they have a low opinion of the federal government, but they might be willing to put up with its deep flaws so long as it delivers their goodies.
|
|
|
Automotive
The high price of green virtue

By Jerome Gessaroli for Inside Policy
Reducing transportation emissions is a worthy goal, but policy must be guided by evidence, not ideology.
In the next few years, the average new vehicle in British Columbia could reach $80,000, not because of inflation, but largely because of provincial and federal climate policy. By forcing zero-emission-vehicle (ZEV) targets faster than the market can afford, both governments risk turning climate ambition into an affordability crisis.
EVs are part of the solution, but mandates that outpace market acceptance risk creating real-world challenges, ranging from cold-weather travel to sparse rural charging to the cost and inconvenience for drivers without home charging. As Victoria and Ottawa review their ZEV policies, the goal is to match ambition with evidence.
Introduced in 2019, BC’s mandate was meant to accelerate electrification and cut emissions from light-duty vehicles. In 2023, however, it became far more stringent, setting the most aggressive ZEV targets in North America. What began as a plan to boost ZEV adoption has now become policy orthodoxy. By 2030, automakers must ensure that 90 per cent of new light-duty vehicles sold in BC are zero-emission, regardless of what consumers want or can afford. The evidence suggests this approach is out of step with market realities.
The province isn’t alone in pursuing EV mandates, but its pace is unmatched. British Columbia, Quebec, and the federal government are the only ones in Canada with such rules. BC’s targets rise much faster than California’s, the jurisdiction that usually sets the bar on green-vehicle policy, though all have the same goal of making every new vehicle zero-emission by 2035.
According to Canadian Black Book, 2025 model EVs are about $17,800 more expensive than gas-powered vehicles. However, ever since Ottawa and BC removed EV purchase incentives, sales have fallen and have not yet recovered. Actual demand in BC sits near 16 per cent of new vehicle sales, well below the 26 per cent mandate for 2026. To close that gap, automakers may have to pay steep penalties or cut back on gas-vehicle sales to meet government goals.
The mandate also allows domestic automakers to meet their targets by purchasing credits from companies, such as Tesla, which hold surplus credits, transferring millions of dollars out of the country simply to comply with provincial rules. But even that workaround is not sustainable. As both federal and provincial mandates tighten, credit supplies will shrink and costs will rise, leaving automakers more likely to limit gas-vehicle sales.
It may be climate policy in intent, but in reality, it acts like a luxury tax on mobility. Higher new-vehicle prices are pushing consumers toward used cars, inflating second-hand prices, and keeping older, higher-emitting vehicles on the road longer. Lower-income and rural households are hit hardest, a perverse outcome for a policy meant to reduce emissions.
Infrastructure is another obstacle. Charging-station expansion and grid upgrades remain far behind what is needed to support mass electrification. Estimates suggest powering BC’s future EV fleet alone could require the electricity output of almost two additional Site C dams by 2040. In rural and northern regions, where distances are long and winters are harsh, drivers are understandably reluctant to switch. Beyond infrastructure, changing market and policy conditions now pose additional risks to Canada’s EV goals.
Major automakers have delayed or cancelled new EV models and battery-plant investments. The United States has scaled back or reversed federal and state EV targets and reoriented subsidies toward domestic manufacturing. These shifts are likely to slow EV model availability and investment across North America, pushing both British Columbia and Ottawa to reconsider how realistic their own targets are in more challenging market conditions.
Meanwhile, many Canadians are feeling the strain of record living costs. Recent polling by Abacus Data and Ipsos shows that most Canadians view rising living costs as the country’s most pressing challenge, with many saying the situation is worsening. In that climate, pressing ahead with aggressive mandates despite affordability concerns appears driven more by green ideology than by evidence. Consumers are not rejecting EVs. They are rejecting unrealistic timelines and unaffordable expectations.
Reducing transportation emissions is a worthy goal, but policy must be guided by evidence, not ideology. When targets become detached from real-world conditions, ideology replaces judgment. Pushing too hard risks backlash that can undo the very progress we are trying to achieve.
Neither British Columbia nor the federal government needs to abandon its clean-transportation objectives, but both need to adjust them. That means setting targets that match realistic adoption rates, as EVs become more affordable and capable, and allowing more flexible compliance based on emissions reductions rather than vehicle type. In simple terms, the goal should be cutting emissions, not forcing people to buy a specific type of car. These steps would align ambition with reality and ensure that environmental progress strengthens, rather than undermines, public trust.
With both Ottawa and Victoria reviewing their EV mandates, their next moves will show whether Canadian climate policy is driven by evidence or by ideology. Adjusting targets to reflect real-world affordability and adoption rates would signal pragmatism and strengthen public trust in the country’s clean-energy transition.
Jerome Gessaroli is a senior fellow at the Macdonald-Laurier Institute and leads the Sound Economic Policy Project at the BC Institute of British Columbia
Business
Carney shrugs off debt problem with more borrowing

Ottawa, we’ve got some problems.
The first problem is government debt is spiralling out of control because government spending is spiralling out of control. The second problem is no one within government is taking the first problem seriously.
Prime Minister Mark Carney’s first budget shows Ottawa will borrow about $80 billion this year.
Massive government borrowing means debt interest charges cost taxpayers more than $1 billion every week.
That’s enough money to build a brand-new hospital every week, but that money is going to the bond fund managers on Bay Street to pay interest on the government credit card.
Or think about it this way the next time you’re standing in the check-out line:
Every dollar you pay in federal sales tax goes to pay interest on the debt.
The government’s own non-partisan, independent budget watchdog pulled the fire alarm back in September.
“The current path we’re on in terms of federal debt as the share of the economy is unsustainable,” the Parliamentary Budget Officer said.
Here are other ways the PBO described the government’s financial situation:
Stupefying. Shocking. Something is going to break. Everybody should be concerned.
That’s how the PBO described the situation when he projected the deficit to be $10 billion lower than Carney’s deficit in Budget 2025.
How is Carney responding to Canada’s debt crunch? Instead of acting, Carney is obfuscating.
Instead of balancing the budget, Carney promises to balance the operating budget.
Carney isn’t balancing squat when he continues to borrow tens of billions of dollars every year. The closest Carney is willing to get to a balanced budget is a $57 billion deficit in 2029.
Instead of cutting the debt, Carney is changing the budget guardrails.
Even under the Trudeau government, politicians repeatedly promised to keep the debt as a share of the economy going down.
Carney used a sneaky sleight of hand in Budget 2025 to change that guardrail.
Because Carney’s debt will grow faster than Canada’s economy, he’s changing the previous guardrail of a declining debt-to-GDP ratio to a declining “deficit-to-GDP ratio.”
Carney plans to add $324 billion to the debt by 2030. For comparison, former prime minister Justin Trudeau planned to add $154 billion to the debt over those same years.
Instead of cutting spending, Carney muddies the waters with slogans of “spending less to invest more.”
The Carney government wrote Budget 2025 in a way to try to convince Canadians that it will save about $60 billion over five years.
But the government is spending billions of dollars more every year.
The government will spend $581 billion this year. That’s $38 billion more than the government spent last year. The government will spend $644 billion in 2029.
Does that look like saving money to you?
Even if you want to be as charitable as possible, nearly all the savings Carney promises to find occur in future years.
This should give taxpayers flashbacks of the Trudeau era.
Trudeau initially promised to run “modest” deficits and balance the budget in four years. But Trudeau never balanced the budget, he doubled the debt.
Trudeau promised to find $15 billion in savings. But Trudeau never cut spending, he ballooned the bureaucracy and spent billions more.
Here’s the key lesson: When the government promises to start its diet on Monday, Monday never comes.
The government debt problem is serious.
The government is now wasting more money paying interest on the debt than it sends to provinces in health-care transfers. In 2029, thirteen cents of every dollar the government takes will be used to make debt interest payments.
But instead of acting, Carney is trying to convince Canadians that everything is fine.
Instead of acting, Carney is using slogans and changing budget guardrails to paint a rosier picture of government finances.
Carney needs to change course. Shrugging off the debt won’t make things better. Only urgent action to cut spending will.
-

 Digital ID2 days ago
Digital ID2 days agoCanada moves forward with digital identification for federal benefits seekers
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoUS Nuclear Bomber Fleet Shares Fence With Trailer Park Linked To Chinese Intel-Tied Fraudster
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoSchool defunding petition in Alberta is a warning to parents
-
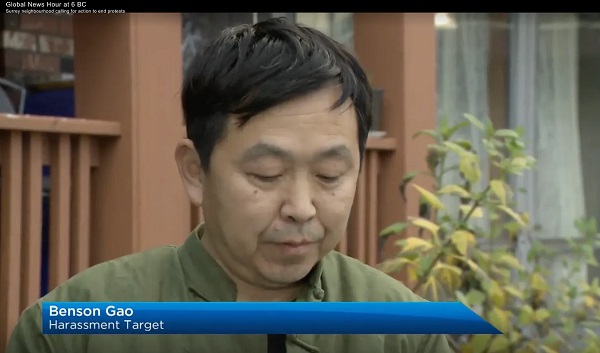
 espionage2 days ago
espionage2 days agoChinese-Owned Trailer Park Beside U.S. Stealth Bomber Base Linked to Alleged Vancouver Repression Case
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoLaura Ingraham Presses Trump On Allowing Flood Of Chinese Students Into US
-

 Environment2 days ago
Environment2 days agoThe Myths We’re Told About Climate Change | Michael Shellenberger
-

 Crime1 day ago
Crime1 day agoCBSA Bust Uncovers Mexican Cartel Network in Montreal High-Rise, Moving Hundreds Across Canada-U.S. Border
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoSpy Agencies Cozied Up To Wuhan Virologist Before Lying About Pandemic










