Crime
ICE: 662,000 criminal foreign nationals to be deported are living free nationwide
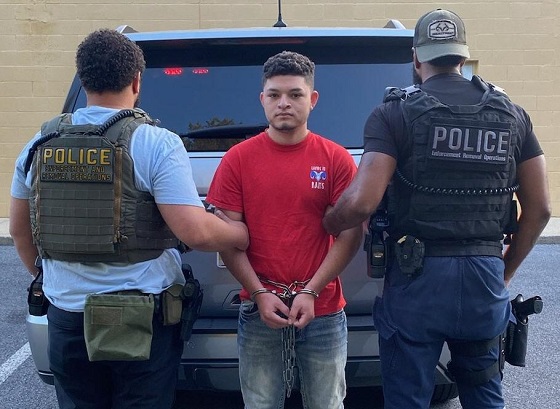

ICE-ERO Baltimore Fugitive Operations agents arrested and removed 19-year-old Guatemalan national Henry Argueta-Tobar, who was illegally in the country and convicted of raping a Maryland resident.
From The Center Square
By
387,000 criminal noncitizens arrested by ICE between fiscal 2021 and 2023
More than 660,000 criminal foreign nationals identified to be deported by U.S. Customs and Immigration Enforcement are freely living in communities nationwide.
Among them are those convicted or charged with violent crimes, including homicide, sexual assault and kidnapping, according to information released in response to a congressional request.
ICE was requested to provide information about the number of noncitizens on its docket for removal who are convicted or charged with a crime. As of July 21, 2024, “there were 662,566 noncitizens with criminal histories on ICE’s national docket, which includes those detained by ICE, and on the agency’s non-detained docket. Of those, 435,719 are convicted criminals, and 226,847 have pending criminal charges,” ICE Deputy Director Patrick Lechleitner said.
This includes criminal foreign nationals convicted of, or charged with, homicide (14,914), sexual assault (20,061), assault (105,146), kidnapping (3,372), and commercialized sexual offenses, including sex trafficking (3,971).
An additional 60,268 are on the list for burglary/larceny/robbery; 126,343 for traffic offenses including driving under the influence (DUIs) and 16,820 for weapons offenses.
ICE’s national docket refers to illegal foreign nationals who were apprehended by Border Patrol agents who then turn them over to ICE. Despite having a confirmed documented criminal history, ICE released them into the United States.
Lechleitner notes that some local jurisdictions “have reduced their cooperation with ICE, to include refusal to honor ICE detainer requests, even for noncitizens who have been convicted of serious felonies and pose an ongoing threat to public safety” due to their so-called “sanctuary city” policies. “However, ‘sanctuary’ policies can end up shielding dangerous criminals, who often victimize those same communities,” he said.
Because of local jurisdictions refusing to cooperate with ICE, the agency lifted detainers for 24,796 known criminals and released them into the U.S., he said. The data is from Oct. 1, 2020, through July 22, 2024.
Among them, state and local law enforcement agencies refused to comply with 23,591 detainer requests; 1,205 detainer requests were lifted “due to insufficient notice to ICE.”
Also during this period, ICE Enforcement and Removal Operations issued 2,897 detainers that were declined by state or local law enforcement agencies even after the subject of the detainer request had a subsequent apprehension by ICE ERO, according to the report.
Lechleitner also notes that “most noncitizens who are convicted of homicide are typically not eligible for release from ICE custody under §236(c) of the Immigration and Nationality Act” but “ICE officers may use their discretion in making custody determinations and release noncitizens with conditions.” He says these determinations are made on a “case-by-case basis.”
In response, U.S. House Committee on Homeland Security Chairman Mark Green, R-TN, said, “It may be shocking to hear that the Biden-Harris administration is actively releasing tens of thousands of criminal illegal aliens into our communities, but their own numbers conclusively prove this to be the case.
“This defies all common sense. Under President Biden and his ‘border czar,’ Vice President Harris, DHS law enforcement has been directed to mass-release illegal aliens whom they know have criminal convictions or are facing charges for serious crimes – and these dangerous, destructive individuals are making their way into every city and state in this country. How many more Americans need to die or be victimized before this administration is forced to abide by the laws they swore to uphold?
“This is madness. It is something no civilized, well-functioning society should tolerate.”
Texas Gov. Greg Abbott said the number was “shocking.”
“If accurate, it means that almost 10%” of the criminal illegal foreign nationals released into the country by the Biden-Harris administration “are criminals. It also debunks the narrative that illegal immigrants are less likely to commit crime. We can’t survive four more years of this.”
More than 387,000 criminal noncitizens were arrested by ICE ERO agents in fiscal years 2021 through 2023, The Center Square first reported.
The majority arrested were citizens of Mexico, Nicaragua, Columbia and Venezuela.
The majority of arrests occurred in Dallas and Houston, Texas, according to an ICE online statistical dashboard. The most common arrests are of those convicted of DUIs, drug possession, and assault and criminal (non-civil) traffic offenses like hit-and-run or leaving the scene of an accident, ICE says.
Additionally, a separate data point shows that U.S. Customs and Border Protection and Border Patrol apprehensions of criminal noncitizens totaled nearly 54,000 since fiscal 2021, according to CBP data as of Sept. 16. The majority were for illegal entry and reentry and DUIs.
Crime
France stunned after thieves loot Louvre of Napoleon’s crown jewels
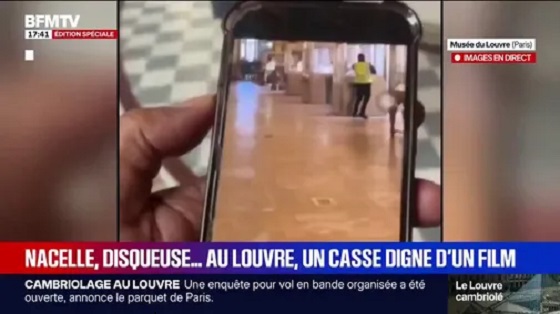
In one of the boldest art crimes in modern French history, a team of masked thieves struck the Louvre Museum in Paris early Sunday, stealing a collection of jewels once belonging to Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. According to French media, the heist unfolded in just ten minutes — between 9:30 and 9:40 a.m. — as three men disguised as construction workers used a mechanical lift and power tools to access a second-floor balcony of the Apollon Gallery, home to some of France’s most treasured artifacts. Police say the burglars shattered a window, smashed glass display cases, and fled on two motor scooters through the heart of Paris as panicked tourists watched officers flood the museum courtyard. Investigators said the group made off with at least nine pieces, including a necklace, brooch, and tiara tied to Napoleon’s imperial court, though forensic teams are still confirming the exact inventory and value. One damaged crown — believed to have belonged to Napoleon’s wife, Empress Eugénie — was later found discarded near the gallery. The French Interior Ministry called the theft “an intolerable attack on our national heritage,” adding that while the jewels’ market value can be calculated, “their historical significance is beyond measure.”
And here are the first images from the Louvre heist — inside the Apollo Gallery, where it all took place.
A man dressed as a construction worker breaks open a display case.
Museum visitors walk by, unaware that a robbery is unfolding right beside them.
How does something so… https://t.co/whDblfNiYY pic.twitter.com/LQv6jCFqs9
— Muse (@xmuse_) October 19, 2025
Authorities are investigating whether the mechanical lift used in the break-in was part of ongoing renovation work at the site, a potential inside assist that could explain how the thieves breached the museum so efficiently. “The suspects appeared to know exactly where they were going,” one investigator told ABC News, noting that the men wore construction vests and hoods to blend in with workers already on site. One suspect reportedly stood guard outside as the others executed the theft with surgical precision. No injuries were reported and no firearms were used, but the crime has rattled both the museum and the French government.
Jordan Bardella, president of France’s right-wing National Rally party, called the episode “a humiliation for our country” and “proof of the state’s decay.” Writing on X, he said, “The Louvre is a global symbol of our culture. This heist, which allowed thieves to steal the Crown Jewels of France, is an intolerable humiliation for our country. How far will the decay of the state go?” The Louvre — which houses masterpieces such as the “Mona Lisa” and the “Venus de Milo” — attracts nearly nine million visitors a year, making it the most visited museum in the world. Yet the theft comes amid growing turmoil inside the institution. Over the summer, staff staged a mass walkout over overcrowding, understaffing, and what unions called a “collapse in basic security.”
Police now fear the stolen artifacts could be melted down or dismantled to erase their trace, destroying centuries of French history in the process. “The risk is that some of the diamonds could be sold individually, which would make reconstituting the jewels nearly impossible,” a source close to the investigation told Le Parisien. As forensic teams comb through security footage and question contractors, France is once again confronting a painful reality — that even in the heart of Paris, its most sacred treasures are not immune to the growing sense of disorder plaguing the country.
Crime
Canadian Sovereignty at Stake: Stunning Testimony at Security Hearing in Ottawa from Sam Cooper

Canada’s Border Vulnerabilities: Confronting Transnational Crime and Legal Failures
The Bureau has chosen to publish the full opening statement of founder Sam Cooper before the House of Commons Standing Committee on Public Safety and National Security, during the session titled “Canada–United States Border Management,” held on Tuesday, October 7, 2025, and webcast live at https://www.ourcommons.ca/
https://www.ourcommons.ca/Committees/en/SECU/Meetings?utm_source=substack&utm_medium=email
I offer these remarks and recommendations with humility. I’m still learning every day. I speak regularly with numerous law-enforcement and security professionals in both the United States and Canada. For over a decade, I’ve focused professionally on the threats that transnational crime poses to Canada’s borders, institutions, and people, alongside deep reporting on our financial and legal vulnerabilities to threat networks that often include ties to hostile state activity. Canada’s recent terror designation of the India-based Bishnoi gang is important. But that particular action recognizes only one facet of the many-sided transnational fentanyl, human-trafficking, Chinese-supplied chemical precursor, weapons-trafficking, terror and extremism threats that I will discuss today.
Across hundreds of interviews with Canadian and U.S. experts, I have come to a conclusion: many Canadians — including citizens, lawmakers, and judges — do not yet fully understand the scope and nature of the problem, and also seem defensive in engaging it. And if we don’t understand it, we cannot solve it.
In these politically divisive times, I hope I can add value by relaying, clearly and fairly, what professionals on both sides of the border are saying about the cultural, legal, and political differences that impede cooperation between the United States and Canada. My reporting has emphasized Canadian enforcement challenges — not to be unduly critical of my homeland, but because I think we should focus first on the levers we control, and reforms we should have already tackled decades ago.
This isn’t my opinion only. As you know, Canadian Association Police Chiefs president Thomas Carrique recently warned that police are being asked to confront a new wave of transnational threats with “outdated and inadequate” laws “never designed to address today’s criminal landscape.” He added that Canada would have been far better positioned to “disrupt” organized crime had Ottawa acted on reforms first recommended in the early 2000s.
As RCMP Assistant Commissioner David Teboul said this year after the discovery of major fentanyl labs in British Columbia — notable for their commercial-grade chemistry equipment and scientific expertise — “There’s a need for legislative reform around how such equipment and precursor chemicals can be obtained.” More border regulations could help, but will not be sufficient absent foundational legal change.
It has long been my experience in discussions with senior U.S. enforcement experts that American and Australian police can collaborate effectively because the two nations are able to authorize wiretaps on dangerous transnational suspects within days. In Canada, that speed is impossible, and it has become a major obstacle.
As former RCMP investigator Calvin Chrustie testified before British Columbia’s Cullen Commission several years ago, due to judicial blockages arising from Charter of Rights rulings, it had become practically impossible to obtain timely wiretaps on Sinaloa Cartel targets in Vancouver. In recent years, such delays in sensitive investigations have undermined cooperation between the RCMP and the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration in major cases of fentanyl trafficking and drug money laundering. In 2017, I was personally alerted to these longstanding concerns about the breakdown in RCMP–DEA cooperation by a U.S. State Department official.
These impeded investigations have involved the upper echelons of Chinese Triads, which maintain deep global leadership in Canada and align with Chinese state-interference networks, as well as senior Iranian and Hezbollah-linked networks operating here. Both networks are engaged in fentanyl trafficking and money laundering in collaboration with Mexican cartels active in Canada.
Canada must urgently reform what it can fix on our side.
My first recommendation is this — there is no “low-hanging fruit.” I have not spoken to a single knowledgeable Canadian officer — current or former — who believes that simply spending more on personnel, equipment, training, or border staffing will solve this. What I hear is that, from ten to twenty years ago, before the evolution of Charter-driven disclosure and delay jurisprudence in Canada, our nations enjoyed a much closer enforcement relationship. Experts point above all to two Supreme Court rulings — Stinchcombe and Jordan — as the core legal obstacles. Our Stinchcombe disclosure standards and Jordan time restrictions, as applied, disincentivize complex, multi-jurisdictional cases and deter U.S. partners from sharing sensitive intelligence that could be exposed in open court. Veterans describe enterprise files stalling for lack of approvals or because specialized techniques are denied. When police and prosecutors anticipate disclosure fights they cannot resource — and trial deadlines they cannot meet — the rational choice is to avoid the fight altogether.
I can explain in greater detail, but without question these rulings have devastated Canada’s ability to prosecute sophisticated organized crime. The result is a vicious circle of non-prosecution and impunity. To deny the need for deep legal reform is to deny the depth of the problem.
To sum up, my reporting at The Bureau has highlighted interlocking failures — legal, political, and bureaucratic — that have turned Canada into a permissive platform for synthetic narcotics and criminal finance, badly misaligning us with our Five Eyes law-enforcement and intelligence partners, and bringing us to the brink of a rupture with the United States.
Thanks for your attention, Chairman and Members.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoClick here to help choose Alberta’s new licence plate design
-

 National1 day ago
National1 day agoDemocracy Watch Renews Push for Independent Prosecutor in SNC-Lavalin Case
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoOver two thirds of Canadians say Ottawa should reduce size of federal bureaucracy
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTrump Admin Blows Up UN ‘Global Green New Scam’ Tax Push, Forcing Pullback
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTrump Blocks UN’s Back Door Carbon Tax
-

 Media1 day ago
Media1 day agoCanada’s top Parliamentary reporters easily manipulated by the PMO’s “anonymous sources”
-

 Red Deer2 days ago
Red Deer2 days agoYour last minute election prep: Common Sense Red Deer talks to the candidates
-

 Agriculture1 day ago
Agriculture1 day agoIs the CFIA a Rogue Agency or Just Taking Orders from a Rogue Federal Government?






