Alberta
UCP MLA leading charge to streamline foreign credential recognition in Alberta

MLA Dyck launches campaign on foreign credential recognition system
Grande Prairie MLA Nolan Dyck has launched a campaign called Better for Newcomers to gather feedback on the province’s foreign credential recognition system.
The campaign follows debate around Bill 203, the Foreign Credential Advisory Committee Act, which MLA Dyck tabled in the winter and is currently before the legislature. If passed, Bill 203 would create an Alberta Foreign Credential Advisory Committee that would advocate for and make recommendations to create a more streamlined and efficient foreign credential recognition system for newcomers.
“Alberta has done some tremendous work when it comes to recognizing foreign credentials in a faster and better way, but I believe we can still do more. This is a critical issue, not just for newcomers, but for all Albertans, and our economy at large,” MLA Dyck said. “I’m encouraging all Albertans who have an interest in this subject to visit BetterforNewcomers.ca and fill out a short survey on Bill 203 and Alberta’s foreign credential recognition system. Together, we can make the system even better for newcomers.”
Several key economic sectors such as health care, construction, manufacturing, and internet technology are expected to have a labour shortage of over 3,000 workers by 2030. Bill 203, if passed, would help Alberta proactively address the labour challenges industries are facing.
“Everywhere I go, from Grande Prairie to Medicine Hat, I’m hearing the same thing: Alberta’s economy is growing and diversifying, but we need more skilled workers to keep moving forward,” MLA Dyck said. “Bill 203, if passed, would position Alberta as a leader in recognizing and harnessing the potential of newcomers, bolstering Alberta’s competitiveness and economic growth for generations to come.”
Alberta
Alberta Provincial Police – New chief of Independent Agency Police Service

Sat Parhar has been appointed as the first chief of the Independent Agency Police Service, marking the next step toward a new municipal policing option.
The appointment of a new chief for the Independent Agency Police Service (IAPS) marks the next step in giving municipalities a new option for local policing and builds on the work already underway for the agency to assume the police-like duties currently carried out by the Alberta Sheriffs. The IAPS will empower municipalities to adopt strategies that effectively respond to their specific safety concerns, enhancing public safety across the province.
Chief Parhar brings more than 25 years of policing experience, including senior roles with the Calgary Police Service, most recently as deputy chief. His frontline policing experience and deep understanding of Alberta’s complex and diverse public safety landscape positions him to lead the agency as it takes shape and begins its work as a new municipal policing option, keeping communities safe.
Once operational, the agency will strengthen Alberta’s existing policing model and complement the province’s current police services, which includes the RCMP, Indigenous policing services and municipal police. It will help fill gaps and ensure law enforcement resources are deployed efficiently to meet Alberta’s evolving public safety needs and improve law enforcement response times, particularly in rural communities.
“Appointing Chief Sat Parhar is a key milestone in Alberta’s plan to give municipalities a real choice in how their communities are kept safe. This is about building a modern police service that reflects the priorities of Albertans, strengthens local decision-making, and ensures every corner of our province, especially rural areas, can count on responsive, effective law enforcement. With his decades of experience and deep understanding of Alberta’s policing landscape, he is the right leader to bring this vision to life.”
“This appointment signifies a significant step forward in our efforts to establish a more robust, community-focused policing model that is better equipped to meet the unique needs of our local residents. Under Chief Parhar’s visionary leadership, we are confident that we will develop a modern, efficient police service that not only enhances public safety but also aligns closely with the priorities and values of Albertans. His experience and commitment are vital in shaping an IAPS that is responsive, transparent, and dedicated to fostering trust and collaboration within the community, ultimately ensuring a safer and more connected society for all.”
Chief Parhar’s immediate priorities will be to hire an executive team and commence organizational planning such as developing key recruitment, training and other operational policies. Chief Parhar’s appointment is the first step of many to establishing the IAPS.
“It’s an honour to take on this role and help shape a modern police service built for Alberta. My focus from day one will be on setting high standards for professionalism, building strong relationships with our partners and ensuring this service reflects the needs and priorities of the communities we serve.”
The Independent Agency Police Service was formally created through regulation following the passing of Public Safety Statutes Amendment Act, 2024. The agency will operate as an independent Crown corporation, and will be renamed the Alberta Sheriffs Police Service, with its head office located in Calgary. The IAPS will be operationally independent from the provincial government with civilian oversight, consistent with all police services in Alberta.
“When it comes to policing, municipalities like ours deserve a choice – especially when the current system leaves us disadvantaged simply because of our size. We look forward to learning more about what that alternative will look like once an Alberta police agency is fully established and the options are clear. For us, this is about fairness, sustainability, and ensuring municipalities have access to policing solutions that reflect both their needs and their realities.”
Quick facts
- The regulation establishes the IAPS Provincial Corporation and its governance structure including board of directors, board of director powers, financial responsibilities and accountabilities.
Related news
- Expanding municipal police service options (April 7, 2024)
Alberta
Pierre Poilievre – Per Capita, Hardisty, Alberta Is the Most Important Little Town In Canada

From Pierre Poilievre
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoOttawa Funded the China Ferry Deal—Then Pretended to Oppose It
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoNew Peer-Reviewed Study Affirms COVID Vaccines Reduce Fertility
-

 MAiD2 days ago
MAiD2 days agoCanada’s euthanasia regime is not health care, but a death machine for the unwanted
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoThe permanent CO2 storage site at the end of the Alberta Carbon Trunk Line is just getting started
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoWorld Economic Forum Aims to Repair Relations with Schwab
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta’s government is investing $5 million to help launch the world’s first direct air capture centre at Innisfail
-
 Business2 days ago
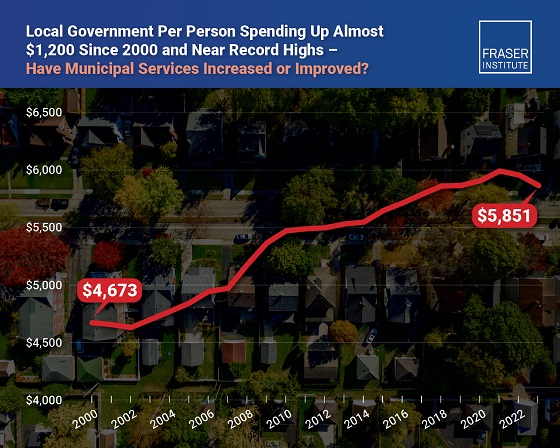
Business2 days agoMunicipal government per-person spending in Canada hit near record levels
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoA new federal bureaucracy will not deliver the affordable housing Canadians need





