COVID-19
We all want this crisis to end. Read this. Then find a mask and put it on when you go out in public

This is article is abridged for your convenience.
Public use of masks to control the coronavirus pandemic
(Originally published March 29 by Longrich Paleo Lab)
Nicholas R. Longrich, PhD
Department of Biology and Biochemistry, University of Bath, Bath, United Kingdom
The Longrich Paleontology Lab is part of the Milner Centre for Evolution at the University of Bath. We use fossils to understand large-scale evolutionary change in organisms and ecosystems.
The US and UK governments, as well as the World Health Organization, currently advise against the use of masks by the public to fight the ongoing Coronavirus Disease 19 (COVID-19) pandemic (1). But could they be wrong?
The governments of China, South Korea, Hong Kong, Viet Nam, Czechia, Slovakia, Bosnia and Taiwan all recommend that the public wear masks to slow the spread of the coronavirus. In some countries, like Japan, masks aren’t officially recommended, but are still widely used by the public. Many countries treat masks as a strategic resource. China has ramped up production of facemasks, converting Foxconn factories that once made iPhones to make face masks. Taiwan has also ramped up the production of facemasks, prohibited their export, and implemented price controls and rationing. It’s hard to see how both approaches could be right. Increasingly, advice against the use of face masks has been questioned (1) (2) (3), including by the head of China’s CDC (4). Austria has recently moved to make mask wearing in public obligatory, and in the United States, the CDC is now debating their use.
Common sense, scientific studies, but perhaps most of all the success of countries using masks to fight the coronavirus suggest that masks may make a difference. There are fewer scientific studies available to guide decision making than we might like, and the evidence is not always clear-cut. However, decision-making in a crisis requires that decisions be made in the absence of perfect clarity. What is clear is that the exponential mathematics of pandemics mean that even if masks are of limited benefit in reducing infection rates, masks could make a large difference over time, potentially slowing the pace of the pandemic, limiting its spread, saving lives, and finally, letting countries to restart the economies that their people depend on for their livelihoods.

Figure produced by Johns Hopkins University using data from Worldometers on March 29.
Masks protect you from others, others from you
It seems sensible to assume that any barrier between two people’s airways reduces the chance of an air-borne virus being transmitted between them. Masks worn by infected people catch some fraction of virus-laden respiratory droplets that are released by breathing and coughing. Perhaps just as important, breathing through a mask slows and deflects air as it is exhaled, potentially reducing the distance that viral droplets travel as aerosols.
Meanwhile, masks worn by uninfected people catch a fraction of the virus they’d otherwise inhale. If both infected and uninfected people wear masks, then these effects multiply. For example, hypothetically, if an infected person’s mask reduces the amount of virus spread by 75%, and the uninfected person’s mask reduces it by another 75%, then the total reduction of the virus spread is 94%.
It’s still possible that this reduction isn’t enough to prevent infection. However, masks could still protect people— because dosage matters. Lower dosing of virus means infection takes longer to build up, giving the immune system time to mount a response.
The immune system fights viruses, like a farmer trying to remove weeds from his field. How difficult those weeds will be to control depends on how many seeds there are. 1000 seeds in a field might not be a challenge, but 1,000,000 or 100 million make weeding far more difficult. In the same way, even when masks fail to prevent infection, by lowering the initial dose of virus they could conceivably make the difference between mild symptoms and a severe illness requiring hospitalization, or even leading to death.

Models suggest masks could work to control pandemics
Of course, it’s possible that masks might have only limited benefit in stopping the spread of COVID-19— for any number of reasons. Masks might provide limited protection, because they are less effective than suggested by some studies, because people misuse them, because of shortages of effective masks like surgical masks and N-95s— or all of these.
But to understand how they could still make a difference, we have to consider masks in the context of small reductions in viral transmission rates. Consider how epidemics grow— exponentially. Allowed to spread unchecked, one case of Covid-19 becomes 2.5 (assuming for this model an R0 of 2.5), each case causing 2.5 more, and so on. Over the course of 15 reproductive cycles, each taking 7 days, or about 3 months in total, one case becomes 2.5 x 2.5 x 25… or 2.5^15 = 931,323 cases (Fig. 1).
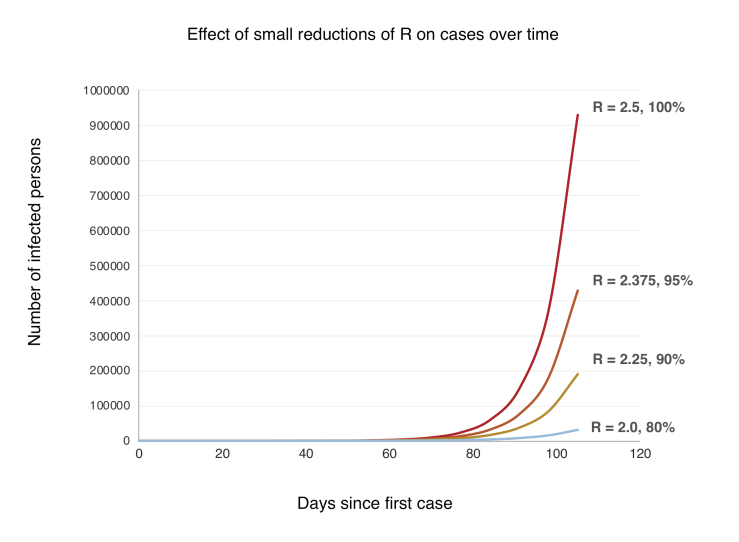
Figure 1. A simple model showing exponential growth in an uncontained outbreak over time (generation time = 7 days, R0 = 2.5) and with small reductions in the reproductive rate R.
Now, let’s suppose widespread use of masks cuts the growth rate by just 10%. Each person now infects 2.25 others, who infect 2.25 others, and so on. Over 15 cycles, 2.25^15 = 191,751 cases. An 80% reduction. Understanding this exponential growth explains how the virus caught the world by surprise even as the pandemic was monitored in real time. Exponential growth just doesn’t make sense, until you do the numbers, and even, they’re still hard to believe. But another counterintuitive aspect of exponential growth is that small decreases in the exponent greatly slow growth. A 10% increase in the exponent can have a massive effect, but even a limited intervention, with a 10% decrease over time, pays large dividends (Fig. 1).
These are very, very simple models. But sophisticated modeling also shows large scale use of masks could slow, even stop pandemics. A 2010 study found that above a certain threshold, widespread use of effective masks can reduce the reproductive number (R) of an influenza virus below 1, and the pandemic stops (25). If face masks were highly effective (well-designed, used properly and consistently), then public use of masks could stop a flu pandemic if used by just 50% of people. If masks were less effective, more than half the population would have to wear them to stop the pandemic. If masks were highly ineffective, they could flatten the curve of the epidemic, but wouldn’t stop it (25). We don’t know which model is most accurate. But does it even matter? In the context of the current pandemic, any of these scenarios would be a huge win.

Real world experience suggests masks work in pandemics
The most compelling evidence of the potential effectiveness of masks in the fight against COVID-19 comes from their use in the real world. Places that have controlled their coronavirus epidemics most effectively – China, South Korea, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Vietnam, Singapore, Kuwait, Czechia, Slovakia, Japan- use masks (Fig. 2). Aside from China, which was the epicenter of the pandemic and so played catchup in developing and implementing its strategy, virtually all of the worst outbreaks are in Western countries that officially advise against mask use, and where there is little culture or practice of mask wearing.
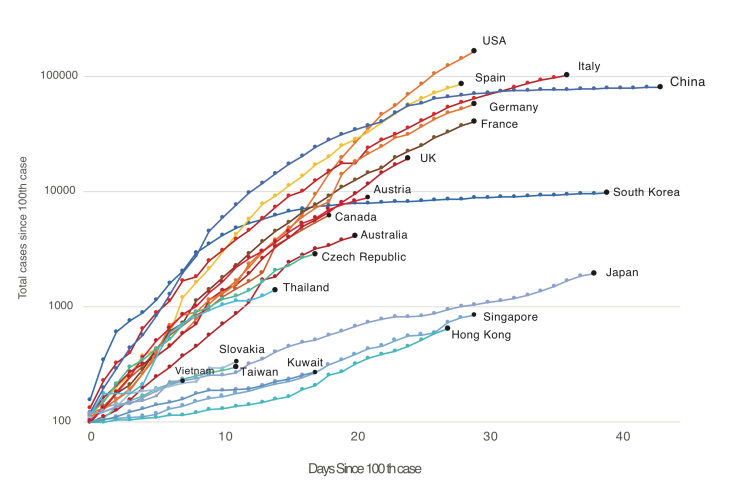
Figure 2. Western countries (US, Canada, Australia, UK, Western Europe) versus countries and territories using masks as part of official government or in practice policy (China, South Korea, Japan, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Vietnam, Thailand, Kuwait, Slovakia, Czech Republic, in blues and greens). Countries with official or unofficial policies of mask usage have controlled the outbreak far better than those without. Note that Austria currently uses masks but has only revised its official policy recently.
Places like China, South Korea, Taiwan, Vietnam, Kuwait, Czechia and Singapore differ greatly in political organization, ranging from communism to democracies, and also in their level of economic development and population density. And strikingly, these countries also differ in their suppression strategies. China implemented a lockdown of Wuhan, shut down industry nationwide, implemented temperature checks and social distancing, tested extensively— and employed masks. Korea responded with an aggressive testing and contact tracing—and masks. Japan has done far less extensive testing than Korea, but shut down schools and large gatherings— and used masks. The pandemic management strategies used by these countries far more diverse than has been appreciated. Arguably one of the few things all these successes share is widespread wearing of masks. And on the other hand, one common factor shared by the pandemic suppression strategies of the US, Canada, the UK and Europe is the decision to discourage the use of masks by the public. This evidence doesn’t prove, but it does very strongly hint that masks are a critical part of these country’s suppression strategies. And by watching countries like Austria that have recently revised their policies, we can test this idea.

What kind of mask? Surgical masks as good as N95s; are improvised masks better than nothing?
Would cloth masks work? Research into the effectiveness of cloth masks is limited (34). Existing research shows homemade masks are- unsurprisingly- inferior to surgical masks. However, they appear to be better than nothing. One laboratory study found homemade masks were half as effective as surgical masks in filtering particles (35). Another study found homemade masks made from various materials stopped virus aerosols, but less well than surgical masks (36). A surgical mask stopped 90% of viral aerosol particles, a dish towel, 72%, linen, 62%, and a cotton T-shirt, 51% (36).
Conclusions
Strong scientific evidence and rational arguments exist for the widespread, public use of facemasks. The principle behind facemasks- they reduce the amount of virus exhaled by infected people, and inhaled by uninfected- suggest they should be a primary tool in combating any respiratory virus. Scientific research, including experimental studies, retrospective studies of the SARS epidemic, hospital studies of COVID-19, and modeling studies, all suggests masks are likely to be effective in controlling the pandemic. Most importantly, the experience of countries using masks against SARS and the current coronavirus pandemic imply that they are effective when used by the public. However, modeling studies and the real-world experience of countries like China and South Korea suggests that neither masks, nor anything else, provides a magic bullet against a pandemic. So strategies should not rely on any single intervention, but rather a wide range of interventions, potentially including masks. Further research and open debate on the effectiveness of masks and other strategies are urgently needed.
(Originally published March 29 by Longrich Paleo Lab) Nicholas R. Longrich, PhD
Albertans are encouraged to wear cloth masks in public. Some easy tips and links on “How To” make your own mask with and or without sewing machines.
Flames GM Brad Treliving does what he can to be ready for NHL reboot
COVID-19
A new study proves, yet again, that the mRNA Covid jabs should NEVER have been approved for young people.

2.7 million Spanish children and teenagers. ZERO Covid deaths.
Here’s some news from Spanish researchers: contrary to what American health bureaucrats said for years to justify the increasingly insane mRNA “vaccine” experiment, Covid doesn’t kill kids.
—
(More facts, fewer guesses. For pennies a day.)
—
Yes, making categorical statements like “Covid doesn’t kill kids” is foolish.
Look hard enough, and there will be an exception, perhaps a child terminally ill with cancer pushed over the edge by Covid.
But the Spanish study, which was peer-reviewed and published in The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal, proves yet again that Covid’s risk is too low to measure — not just not to healthy children, but to all children. It is the strongest evidence yet that the oft-repeated claim that Covid has killed 2,100 American children is fiction.¹
The researchers examined medical records from 2.7 million Spanish children and teenagers from mid-2021 through the end of 2022, a period in which the Omicron variant infected almost everyone worldwide with Covid. The vast majority of those kids and adolescents, about 2.2 million, had not been vaccinated.
Yet none of those 2.7 million died of Covid.
None. As in zero.
—
(Good thing we closed the schools!)
(SOURCE)
—
There really isn’t much more to say about the paper, except that the authors couldn’t find any difference for Covid hospitalization rates between vaccinated and unvaccinated kids under 12.
For adolescents 12-17, they calculated about 38,000 mRNA jabs were required to avoid one Covid hospitalization — an absurdly high number given the known short-term side effects of the shots and the potential long-term risks of exposing young people to mRNA.
At this point, any physician who recommends Covid jabs for kids (as a handful, mostly in blue states, still are) should be sued for malpractice.
—
One final note: this week’s immigration articles have gotten a LOT of likes and comments, more than any recent Covid or mRNA pieces. More new subscribers too.
I expect that will be true again today, though I hope you’ll prove me wrong. I understand. We all have moved on.
But when studies like this new one come out, covering them is crucial.
Nearly 1.5 billion people received mRNA Covid jabs worldwide, including perhaps 100 million kids and teenagers in the United States, Canada, Japan, Europe, and elsewhere. And the American public health establishment and legacy media outlets continue to push mRNA on children and fight even modest efforts to tighten restrictions on mRNA Covid jabs.
Witness the furious pushback Food and Drug Administration chief medical officer Dr. Vinay Prasad received in late November after he reported FDA reviewers found Covid shots had killed children.
So, even as I write about immigration, healthcare fraud, and other topics vital to you, I believe I have a duty to continue to update the factual record about the mRNAs. Duty is not too strong a word. In June 2023, I covered a paper from South Korean researchers about cardiac deaths of young adults who had received the mRNA jabs.
It is no exaggeration to say no one else — no other journalist or scientist covering Covid or the jabs — paid attention to that paper at the time . But now, in the wake of Prasad’s bombshell memo, I’ve again raised that paper. Even the mRNA fanatics at the Atlantic have been forced to acknowledge it.
It’s impossible to know if these articles will matter today, tomorrow, or years from now. But as long as the mRNA companies and their public health handmaidens keep pushing this troubled technology, I’ll keep trying to build the most complete possible record.
—
(And I hope you will support me.)
(More facts, fewer guesses. For pennies a day.)
That 2,100 death figure, which the American Academy of Pediatrics loves to quote, appears to come from a 2023 paper from the National Academy of Medicine paper that in turn relies on Centers for Disease Control data. But the CDC figures no distinction between “with” and “from” Covid deaths, which are particularly important in groups at low baseline risk from Covid. Further, the fact that the number hasn’t been updated in almost three years suggests that the people quoting it know it’s nonsense and don’t want to double-check it, much less try to update it.
What, kids just stopped dying from Covid in 2023 after getting mowed down during the first three years of the epidemic?
|
|||
|
|||||
|
|||||
| Independent, citizen-funded journalism |
COVID-19
Judge denies Canadian gov’t request to take away Freedom Convoy leader’s truck

From LifeSiteNews
A judge ruled that the Ontario Court of Justice is already ‘satisfied’ with Chris Barber’s sentence and taking away his very livelihood would be ‘disproportionate.’
A Canadian judge has dismissed a demand from Canadian government lawyers to seize Freedom Convoy leader Chris Barber’s “Big Red” semi-truck.
On Friday, Ontario Court of Justice Judge Heather Perkins-McVey denied the Crown’s application seeking to forfeit Barber’s truck.
She ruled that the court is already “satisfied” with Barber’s sentence and taking away his very livelihood would be “disproportionate.”
“This truck is my livelihood,” said Barber in a press release sent to LifeSiteNews.
“Trying to permanently seize it for peacefully protesting was wrong, and I’m relieved the court refused to allow that to happen,” he added.
Criminal defense lawyer Marwa Racha Younes was welcoming of the ruling as well, stating, “We find it was the right decision in the circumstances and are happy with the outcome.”
John Carpay, president of the Justice Centre for Constitutional Freedoms (JCCF), said the decision is “good news for all Canadians who cherish their Charter freedom to assemble peacefully.”
READ: Freedom Convoy protester appeals after judge dismissed challenge to frozen bank accounts
“Asset forfeiture is an extraordinary power, and it must not be used to punish Canadians for participating in peaceful protest,” he added in the press release.
As reported recently by LifeSiteNews, the Canadian government claimed that Barber’s truck is an “offence-related property” relating to his involvement in the 2022 protests against Canada’s COVID mandates.
At this time, the court ruling ends any forfeiture proceedings for the time being, however Barber will continue to try and appeal his criminal conviction and house arrest sentence.
Barber’s truck, a 2004 Kenworth long-haul he uses for business, was a focal point in the 2022 protests. He drove it to Ottawa, where it was parked for an extended period of time, but he complied when officials asked him to move it.
On October 7, 2025, after a long trial, Ontario Court Justice Perkins-McVey sentenced Barber and Tamara Lich, the other Freedom Convoy leader, to 18 months’ house arrest. They had been declared guilty of mischief for their roles as leaders of the 2022 protest against COVID mandates, and as social media influencers.
Lich and Barber have filed appeals of their own against their house arrest sentences, arguing that the trial judge did not correctly apply the law on their mischief charges.
Government lawyers for the Crown have filed an appeal of the acquittals of Lich and Barber on intimidation charges.
The pair’s convictions came after a nearly two-year trial despite the nonviolent nature of the popular movement.
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day agoIs Canada still worth the sacrifice for immigrants?
-

 Daily Caller21 hours ago
Daily Caller21 hours agoMinnesota Governor resigns from re-election campaign as massive government frauds revealed
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoPolicy uncertainty continues to damage Canada’s mining potential
-

 International21 hours ago
International21 hours agoMaduro, wife plead not guilty in first court appearance
-

 Courageous Discourse21 hours ago
Courageous Discourse21 hours agoLargest rollback of routine childhood vaccination in U.S. history
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin1 day ago
Bruce Dowbiggin1 day agoThe Olympic Shutout: No Quebec Players Invited For Canada
-

 Business19 hours ago
Business19 hours agoChrystia Freeland Didn’t Leave Power. She Just Took It Somewhere Else
-

 Canadian Energy Centre1 day ago
Canadian Energy Centre1 day agoFive reasons why 2026 could mark a turning point for major export expansions











