Agriculture
How Canadian Dairy Farms Can Adjust to New Dairy Demand
How Canadian Dairy Farms Can Adjust to New Dairy Demand
Many changes occurred around the world as a result of the coronavirus pandemic. In Canada, while schools and businesses closed, consumers flocked to the supermarkets to buy essentials.
Perishable goods flew off the shelves, resulting in limits being placed on items like dairy and poultry. The standard distribution system schedule put in place for dairy products could not keep up with buyers’ increased shopping.
While retail demand from grocers skyrocketed, orders from the foodservice industry plummeted. This has resulted in unforeseen fluctuations in the dairy market.
Hotels, restaurants, schools and eateries are closed or operating at limited capacity. As a result, there is now an enormous surplus of milk that has nowhere to go. Farmers are not equipped with storage spaces to accommodate the excess supply. Unlike agriculture products like potatoes, milk has to be sold immediately or risk spoilage.
Cows will continue producing milk, regardless of fluctuations in the market. While farmers have the option to reduce the size of their herd or change diet or nutrition, these things could prove detrimental when the market stabilizes.
The Supply Management System
A supply management system controls production quotas and imports for Canadian dairy, chicken, turkey and eggs. It was established in the1970s to coordinate production and demand while simultaneously controlling imports. By operating under this method, prices are stabilized for both producers and consumers.
A national agency represents each industry, and they are in charge of setting production levels that match provincial demand. Farmers in each province are allocated production quotas that are meant to prevent surpluses or shortages.
The original quotas were based on consumer needs pre-pandemic. As a result of these unforeseen events, farmers must now adjust to the new Canadian dairy demand. Here are four main ways farmers can adapt to the changing times.
- Dump the Milk
Producers say that discarding raw milk is inevitable at this stage. Farmers are reporting that they have been asked to take turns dumping milk. Although they’re paid for it, the waste could amount to as much as 5 million litres every week.
This disposal method is unsustainable and should only be utilized while the market is above capacity. Cows must continue to be milked to keep them comfortable and healthy, and production must continue to ensure product availability in retail stores.
- Donate to Food Banks
Rather than dumping milk, some farmers have begun donating to food banks to support Canadians in need. While this is a positive form of dispersing the milk surplus, it has the potential to overwhelm food banks that may not have the storage capacity to support this influx.
Additionally, the raw milk provided from farmers must be processed, which complicates the standard donation process.
- Improve Operations
Dairy farmers should focus on improving operations to become more efficient and cost-effective. Many producers have begun investing in updated equipment and robotics to save time and money. Competition is set to increase as a result of import growth projected for the next decade. To maintain a market edge, operations should be improved and simplified wherever possible.
- Expand or Retire
In 2019, the Canadian federal government announced an aid package valued at $1.75 billion to compensate supply-managed dairy producers over an eight-year period. The Dairy Direct Payment Program is one part of this aid package and provides $345 million payments as compensation during 2019 and 2020.
The aid package was proposed as a result of import shifts. The Canadian government has opened part of its domestic market to foreign producers as part of several free-trade negotiations. To adapt to increased competition from foreign products, Canadian producers should plan to expand their operations or retire. Larger farms will be able to sustain demand while simultaneously upgrading their methods to be constantly improving.
Smaller producers may not be able to afford the necessary production updates to keep up with competitors.
Future Demand
These are unprecedented circumstances. As schools, businesses and restaurants reopen, dairy demand will increase. With indoor capacity requirements and shifts in consumer trends, consumption levels will undoubtedly continue to fluctuate.
While farmers should take steps to dispose of surplus responsibly, they should not halt production or decrease their operation size.
Read more from Emily Folk

I’m Emily Folk, and I grew up in a small town in Pennsylvania. Growing up I had a love of animals, and after countless marathons of watching Animal Planet documentaries, I developed a passion for ecology and conservation. You can read more of my work by clicking this link: Conservation Folks.
Canadian Federal Government Taking Measures to Reduce Impact of COVID-19 on Agriculture
Agriculture
The Climate Argument Against Livestock Doesn’t Add Up

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
Livestock contribute far less to emissions than activists claim, and eliminating them would weaken nutrition, resilience and food security
The war on livestock pushed by Net Zero ideologues is not environmental science; it’s a dangerous, misguided campaign that threatens global food security.
The priests of Net Zero 2050 have declared war on the cow, the pig and the chicken. From glass towers in London, Brussels and Ottawa, they argue that cutting animal protein, shrinking herds and pushing people toward lentils and lab-grown alternatives will save the climate from a steer’s burp.
This is not science. It is an urban belief that billions of people can be pushed toward a diet promoted by some policymakers who have never worked a field or heard a rooster at dawn. Eliminating or sharply reducing livestock would destabilize food systems and increase global hunger. In Canada, livestock account for about three per cent of total greenhouse gas emissions, according to Environment and Climate Change Canada.
Activists speak as if livestock suddenly appeared in the last century, belching fossil carbon into the air. In reality, the relationship between humans and the animals we raise is older than agriculture. It is part of how our species developed.
Two million years ago, early humans ate meat and marrow, mastered fire and developed larger brains. The expensive-tissue hypothesis, a theory that explains how early humans traded gut size for brain growth, is not ideology; it is basic anthropology. Animal fat and protein helped build the human brain and the societies that followed.
Domestication deepened that relationship. When humans raised cattle, sheep, pigs and chickens, we created a long partnership that shaped both species. Wolves became dogs. Aurochs, the wild ancestors of modern cattle, became domesticated animals. Junglefowl became chickens that could lay eggs reliably. These animals lived with us because it increased their chances of survival.
In return, they received protection, veterinary care and steady food during drought and winter. More than 70,000 Canadian farms raise cattle, hogs, poultry or sheep, supporting hundreds of thousands of jobs across the supply chain.
Livestock also protected people from climate extremes. When crops failed, grasslands still produced forage, and herds converted that into food. During the Little Ice Age, millions in Europe starved because grain crops collapsed. Pastoral communities, which lived from herding livestock rather than crops, survived because their herds could still graze. Removing livestock would offer little climate benefit, yet it would eliminate one of humanity’s most reliable protections against environmental shocks.
Today, a Maasai child in Kenya or northern Tanzania drinking milk from a cow grazing on dry land has a steadier food source than a vegan in a Berlin apartment relying on global shipping. Modern genetics and nutrition have pushed this relationship further. For the first time, the poorest billion people have access to complete protein and key nutrients such as iron, zinc, B12 and retinol, a form of vitamin A, that plants cannot supply without industrial processing or fortification. Canada also imports significant volumes of soy-based and other plant-protein products, making many urban vegan diets more dependent on long-distance supply chains than people assume. The war on livestock is not a war on carbon; it is a war on the most successful anti-poverty tool ever created.
And what about the animals? Remove humans tomorrow and most commercial chickens would die of exposure, merino sheep would overheat under their own wool and dairy cattle would suffer from untreated mastitis (a bacterial infection of the udder). These species are fully domesticated. Without us, they would disappear.
Net Zero 2050 is a climate target adopted by federal and provincial governments, but debates continue over whether it requires reducing livestock herds or simply improving farm practices. Net Zero advocates look at a pasture and see methane. Farmers see land producing food from nothing more than sunlight, rain and grass.
So the question is not technical. It is about how we see ourselves. Does the Net Zero vision treat humans as part of the natural world, or as a threat that must be contained by forcing diets and erasing long-standing food systems? Eliminating livestock sends the message that human presence itself is an environmental problem, not a participant in a functioning ecosystem.
The cow is not the enemy of the planet. Pasture is not a problem to fix. It is a solution our ancestors discovered long before anyone used the word “sustainable.” We abandon it at our peril and at theirs.
Dr. Joseph Fournier is a senior fellow at the Frontier Centre for Public Policy. An accomplished scientist and former energy executive, he holds graduate training in chemical physics and has written more than 100 articles on energy, environment and climate science.
Agriculture
End Supply Management—For the Sake of Canadian Consumers

This is a special preview article from the:
U.S. President Donald Trump’s trade policy is often chaotic and punitive. But on one point, he is right: Canada’s agricultural supply management system has to go. Not because it is unfair to the United States, though it clearly is, but because it punishes Canadians. Supply management is a government-enforced price-fixing scheme that limits consumer choice, inflates grocery bills, wastes food, and shields a small, politically powerful group of producers from competition—at the direct expense of millions of households.
And yet Ottawa continues to support this socialist shakedown. Last week, Prime Minister Mark Carney told reporters supply management was “not on the table” in negotiations for a renewed United States-Mexico-Canada Trade Agreement, despite U.S. negotiators citing it as a roadblock to a new deal.
Supply management relies on a web of production quotas, fixed farmgate prices, strict import limits, and punitive tariffs that can approach 300 percent. Bureaucrats decide how much milk, chicken, eggs, and poultry Canadians farmers produce and which farmers can produce how much. When officials misjudge demand—as they recently did with chicken and eggs—farmers are legally barred from responding. The result is predictable: shortages, soaring prices, and frustrated consumers staring at emptier shelves and higher bills.
This is not a theoretical problem. Canada’s most recent chicken production cycle, ending in May 2025, produced one of the worst supply shortfalls in decades. Demand rose unexpectedly, but quotas froze supply in place. Canadian farmers could not increase production. Instead, consumers paid more for scarce domestic poultry while last-minute imports filled the gap at premium prices. Eggs followed a similar pattern, with shortages triggering a convoluted “allocation” system that opened the door to massive foreign imports rather than empowering Canadian farmers to respond.
Over a century of global experience has shown that central economic planning fails. Governments are simply not good at “matching” supply with demand. There is no reason to believe Ottawa’s attempts to manage a handful of food categories should fare any better. And yet supply management persists, even as its costs mount.
Those costs fall squarely on consumers. According to a Fraser Institute estimate, supply management adds roughly $375 a year to the average Canadian household’s grocery bill. Because lower-income families spend a much higher proportion of their income on food, the burden falls most heavily on them.
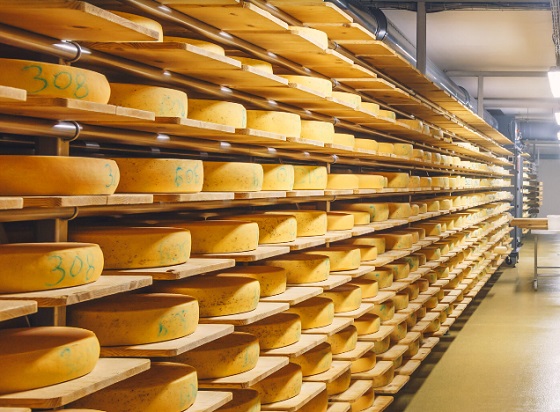
The system also strangles consumer choice. European countries produce thousands of varieties of high-quality cheeses at prices far below what Canadians pay for largely industrial domestic products. But our import quotas are tiny, and anything above them is hit with tariffs exceeding 245 percent. As a result, imported cheeses can cost $60 per kilogram or more in Canadian grocery stores. In Switzerland, one of the world’s most eye-poppingly expensive countries, where a thimble-sized coffee will set you back $9, premium cheeses are barely half the price you’ll find at Loblaw or Safeway.
Canada’s supply-managed farmers defend their monopoly by insisting it provides a “fair return” for famers, guarantees Canadians have access to “homegrown food” and assures the “right amount of food is produced to meet Canadian needs.” Is there a shred of evidence Canadians are being denied the “right amount” of bread, tuna, asparagus or applesauce? Of course not; the market readily supplies all these and many thousands of other non-supply-managed foods.
Like all price-fixing systems, Canada’s supply management provides only the illusion of stability and security. We’ve seen above what happens when production falls short. But perversely, if a farmer manages to get more milk out of his cows than his quota, there’s no reward: the excess must be
dumped. Last year alone, enough milk was discarded to feed 4.2 million people.
Over time, supply management has become less about farming and more about quota ownership. Artificial scarcity has turned quotas into highly valuable assets, locking out young farmers and rewarding incumbents.
Why does such a dysfunctional system persist? The answer is politics. Supply management is of outsized importance in Quebec, where producers hold a disproportionate share of quotas and are numerous enough to swing election results in key ridings. Federal parties of all stripes have learned the cost of crossing this lobby. That political cowardice now collides with reality. The USMCA is heading toward mandatory renegotiation, and supply management is squarely in Washington’s sights. Canada depends on tariff-free access to the U.S. market for hundreds of billions of dollars in exports. Trading away a deeply-flawed system to secure that access would make economic sense.
Instead, Ottawa has doubled down. Not just with Carney’s remarks last week but with Bill C-202, which makes it illegal for Canadian ministers to reduce tariffs or expand quotas on supply-managed goods in future trade talks. Formally signalling that Canada’s negotiating position is hostage to a tiny domestic lobby group is reckless, and weakens Canada’s hand before talks even begin.
Food prices continue to rise faster than inflation. Forecasts suggest the average family will spend $1,000 more on groceries next year alone. Supply management is not the only cause, but it remains a major one. Ending it would lower prices, expand choice, reduce waste, and reward entrepreneurial farmers willing to compete.
If Donald Trump can succeed in forcing supply management onto the negotiating table, he will be doing Canadian consumers—and Canadian agriculture—a favour our own political class has long refused to deliver.
The original, full-length version of this article was recently published in C2C Journal. Gwyn Morgan is a retired business leader who was a director of five global corporations.
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day agoTent Cities Were Rare Five Years Ago. Now They’re Everywhere
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin6 hours ago
Bruce Dowbiggin6 hours agoBe Careful What You Wish For In 2026: Mark Carney With A Majority
-

 International14 hours ago
International14 hours agoNo peace on earth for ISIS: Trump orders Christmas strikes after Christian massacres
-

 Fraser Institute15 hours ago
Fraser Institute15 hours agoCarney government sowing seeds for corruption in Ottawa
-

 Daily Caller14 hours ago
Daily Caller14 hours agoUS Halts Construction of Five Offshore Wind Projects Due To National Security
-

 Alberta15 hours ago
Alberta15 hours agoAlberta Next Panel calls for less Ottawa—and it could pay off
-

 Energy14 hours ago
Energy14 hours agoWhile Western Nations Cling to Energy Transition, Pragmatic Nations Produce Energy and Wealth
-

 Opinion1 day ago
Opinion1 day agoPope Leo XIV’s Christmas night homily