Alberta
Edmonton company releases a world first NFT project
Edmonton based; Score G Productions, launched a first of its kind in the world NFT (non-fungible token) project on April 17th. It’s called, Creative Hustler Key. Creative Hustler Key gives buyers through a one-time payment, a lifetime all-access passkey to the Score G Productions. This includes access to a full community of content producers, executive producers, exclusive 3-D NFT artwork, exclusive videos, and even monthly members only access to online workshops featuring creative content producers from around the world. The Creative Hustler Key NFT even offers chances to win access to live in-production sets, access to their studios during editing and post-production, and chances to win tickets and trips to future red-carpet movie premier events. There’s more in the works too. Basically, buyers will get access to Score G Productions’ impressive Rolodex and industry knowledge.
There are only 999 pass keys for sale, once gone, it will never be expanded, with the promise of no copycat versions of this Creative Hustler Key to ever be started by their team.

Adam and Machete during inmate #1: The Rise of Danny Trejo
We asked Score G Productions founder, father of three, married to his high school sweetheart, Edmonton based Adam Scorgie why he’d take on such a huge undertaking when they are already successful in the film production industry? Scorgie replied, “We get calls, emails and social media posts asking us to help people all the time. People approach us at public events, asking for mentorship, internships, contact access, script readings, it is all kind of overwhelming.” Continuing, “I wish I had people I could have called when I was starting out. I knew what I wanted to do, but I knew no one and knew nothing.” Explaining, “This is our pay it forward move. I want to help as many people as possible, in any way I can.”
A huge personal belief for Scorgie is explained, “I like to do things in and as a team; this will be a world’s first team like this. Extremely unique.”
The now, world-wide known and highly respect filmmaker with an extensive library of finished and in-production projects never planned on being a film producer, he in fact, never went to film school. He did however, go to acting school in New York and had credits in voice, as dancer, movie and soap opera acting credits. Things were looking up and moving along nicely.

But then his father, Buddy, got sick, very quickly. At 23, he dropped his dreams of Hollywood fame and fortune, moving back to Kelowna where he was born and raised to take over his dad’s business, Cheetah’s Show Lounge & Bar. Kelowna’s only stripper bar. “I went from 23 to 35 in like six months!” the forced adult entertainment entrepreneur said.
His father passed away after a short health battle.
Then things got “really tough”. A lawsuit was filed against his father’s estate, he had a new partner in the business. While he tried to keep the clothes on his own back and his business afloat; Adam noticed a lot of his patrons, high school friends, same age as himself with cash pouring out of their pockets and stacked high on their tables in the VIP section. They all had 70+ thousand-dollar trucks, 50k Harleys, houses and more. He asked them, what the hell they were all doing to become so rich, so fast? They all said, “We are in the Union, you should join us.”
This was in the height of the multi-billion-dollar BC Bud days. The “Union” was code for underground pot grower for organized crime rings being done at arm’s length. While Adam admits, he did come close to joining the “Union”, he ended up selling his share in the stripper club and put every last cent he had, plus some extra money borrowed from his stepdad into making a full-length documentary movie with his new partner, Vancouver director Brett Harvey. The film was called, The Union: The Business Behind Getting High and it quickly gained a cult following around the world.
And the rest is history! If only it was that easy. Scorgie laughs while reminiscing, “People said I was nuts. I have heard that a lot over the years, especially for just living in Edmonton and not Hollywood.”
He fully expects people to say this again about this unique NFT rollout. Being young and ahead of the curve is nothing new for Adam and his team. Scorgie expands, “We didn’t have any money for PR marketing firms or to pay agents to promote us. So, we did it all on Facebook and other social media platforms.” Continuing, “We had 1.2 million followers on Facebook alone. “Today every production has huge teams of social media specialists, with very expensive detailed marketing plans for social media promotions long before any production even gets close to post-production.”
Scorgie remembers one meeting with Hollywood executives when they were shopping a world-wide release of the final cut of the Union. One said, “Oh isn’t that cute, you have a Facebook page.” Then they saw the Union page had over a million followers for the indie production. Adding, “That got their attention. No one is laughing at us anymore.” Finishing, “And years from now, no one will be over this new NFT project.”

Shane Fennessey
One of Scorgie’s closest friends and partner in Score G Productions, Shane Fennessey, explains more about the Creative Hustler Key project, “There is nothing in the world like what we just launched by offering a real, hands-on community of successful high-quality, award-winning professionals from the film production industry.” Adding, “NFT’s are known for exclusive digital images and video, yes with us you still get exclusive 3-D images that took months to produce and exclusive videos with the purchase of these keys.” Continuing, “What is truly different and very exciting is that this is a utility driven NFT project, a place where professionals will collaborate. It has long-term value too. We are young. As long as we are a business, these keys never expire” Adding, “There are no annual renewal fees, you own the Keys, you can sell them for the going price any time in the future, you can even add them to your estate, they are yours.”
Expanding on the added values of the only 999 keys available, Fennessey says, “We know how to apply for grants, we know where the grants are, we know how to fund-raise for the next project.” Continuing, “We know all the tax credits and other forms of how to finance projects. We are going to share all of this and even more knowledge that we have about this industry.”
In closing Fennessey said, “We love the idea of opening doors for new young Creative Hustlers.” Asked if it will it sell out, “Most likely and very quickly we expect, with no outside advertising or media coverage 10% of the 999 keys sold in just the first 2-hours of the Sunday release.”
Details for how to get involved can be found here; https://creativehustlerkey.com/
Score G Production’s main catalogue;
- Bisping. The Michael Bisping Story (2022)
- Connor McDavid: Whatever It Takes (2020)
- Inmate #1: The Rise of Danny Trejo, (2020)
- Over a Barrel (2019)
- Tough Guy: The Bob Probert Story (2019)
- The Bailey Experience (2019)
- Making Coco: The Grant Fuhr Story (2018)
- Chasing Evel: The Robbie Knievel Story (2017)
- Juarez 2045. A scripted movie. (2017)
- Ice Guardians (2016)
- Soul on Ice: Past, Present and Future (2015)
- The Culture High (2014
- The Good Son: The Life of Ray Boom Boom Mancini (2013)
- I Am Bruce Lee (2012)
- The Union: The Business Behind Getting High (2007)
Alberta
Alberta project would be “the biggest carbon capture and storage project in the world”

Pathways Alliance CEO Kendall Dilling is interviewed at the World Petroleum Congress in Calgary, Monday, Sept. 18, 2023.THE CANADIAN PRESS/Jeff McIntosh
From Resource Works
Carbon capture gives biggest bang for carbon tax buck CCS much cheaper than fuel switching: report
Canada’s climate change strategy is now joined at the hip to a pipeline. Two pipelines, actually — one for oil, one for carbon dioxide.
The MOU signed between Ottawa and Alberta two weeks ago ties a new oil pipeline to the Pathways Alliance, which includes what has been billed as the largest carbon capture proposal in the world.
One cannot proceed without the other. It’s quite possible neither will proceed.
The timing for multi-billion dollar carbon capture projects in general may be off, given the retreat we are now seeing from industry and government on decarbonization, especially in the U.S., our biggest energy customer and competitor.
But if the public, industry and our governments still think getting Canada’s GHG emissions down is a priority, decarbonizing Alberta oil, gas and heavy industry through CCS promises to be the most cost-effective technology approach.
New modelling by Clean Prosperity, a climate policy organization, finds large-scale carbon capture gets the biggest bang for the carbon tax buck.
Which makes sense. If oil and gas production in Alberta is Canada’s single largest emitter of CO2 and methane, it stands to reason that methane abatement and sequestering CO2 from oil and gas production is where the biggest gains are to be had.
A number of CCS projects are already in operation in Alberta, including Shell’s Quest project, which captures about 1 million tonnes of CO2 annually from the Scotford upgrader.
What is CO2 worth?
Clean Prosperity estimates industrial carbon pricing of $130 to $150 per tonne in Alberta and CCS could result in $90 billion in investment and 70 megatons (MT) annually of GHG abatement or sequestration. The lion’s share of that would come from CCS.
To put that in perspective, 70 MT is 10% of Canada’s total GHG emissions (694 MT).
The report cautions that these estimates are “hypothetical” and gives no timelines.
All of the main policy tools recommended by Clean Prosperity to achieve these GHG reductions are contained in the Ottawa-Alberta MOU.
One important policy in the MOU includes enhanced oil recovery (EOR), in which CO2 is injected into older conventional oil wells to increase output. While this increases oil production, it also sequesters large amounts of CO2.
Under Trudeau era policies, EOR was excluded from federal CCS tax credits. The MOU extends credits and other incentives to EOR, which improves the value proposition for carbon capture.
Under the MOU, Alberta agrees to raise its industrial carbon pricing from the current $95 per tonne to a minimum of $130 per tonne under its TIER system (Technology Innovation and Emission Reduction).
The biggest bang for the buck
Using a price of $130 to $150 per tonne, Clean Prosperity looked at two main pathways to GHG reductions: fuel switching in the power sector and CCS.
Fuel switching would involve replacing natural gas power generation with renewables, nuclear power, renewable natural gas or hydrogen.
“We calculated that fuel switching is more expensive,” Brendan Frank, director of policy and strategy for Clean Prosperity, told me.
Achieving the same GHG reductions through fuel switching would require industrial carbon prices of $300 to $1,000 per tonne, Frank said.
Clean Prosperity looked at five big sectoral emitters: oil and gas extraction, chemical manufacturing, pipeline transportation, petroleum refining, and cement manufacturing.
“We find that CCUS represents the largest opportunity for meaningful, cost-effective emissions reductions across five sectors,” the report states.

Fuel switching requires higher carbon prices than CCUS.
Measures like energy efficiency and methane abatement are included in Clean Prosperity’s calculations, but again CCS takes the biggest bite out of Alberta’s GHGs.
“Efficiency and (methane) abatement are a portion of it, but it’s a fairly small slice,” Frank said. “The overwhelming majority of it is in carbon capture.”

From left, Alberta Minister of Energy Marg McCuaig-Boyd, Shell Canada President Lorraine Mitchelmore, CEO of Royal Dutch Shell Ben van Beurden, Marathon Oil Executive Brian Maynard, Shell ER Manager, Stephen Velthuizen, and British High Commissioner to Canada Howard Drake open the valve to the Quest carbon capture and storage facility in Fort Saskatchewan Alta, on Friday November 6, 2015. Quest is designed to capture and safely store more than one million tonnes of CO2 each year an equivalent to the emissions from about 250,000 cars. THE CANADIAN PRESS/Jason Franson
Credit where credit is due
Setting an industrial carbon price is one thing. Putting it into effect through a workable carbon credit market is another.
“A high headline price is meaningless without higher credit prices,” the report states.
“TIER credit prices have declined steadily since 2023 and traded below $20 per tonne as of November 2025. With credit prices this low, the $95 per tonne headline price has a negligible effect on investment decisions and carbon markets will not drive CCUS deployment or fuel switching.”
Clean Prosperity recommends a kind of government-backstopped insurance mechanism guaranteeing carbon credit prices, which could otherwise be vulnerable to political and market vagaries.
Specifically, it recommends carbon contracts for difference (CCfD).
“A straight-forward way to think about it is insurance,” Frank explains.
Carbon credit prices are vulnerable to risks, including “stroke-of-pen risks,” in which governments change or cancel price schedules. There are also market risks.
CCfDs are contractual agreements between the private sector and government that guarantees a specific credit value over a specified time period.
“The private actor basically has insurance that the credits they’ll generate, as a result of making whatever low-carbon investment they’re after, will get a certain amount of revenue,” Frank said. “That certainty is enough to, in our view, unlock a lot of these projects.”
From the perspective of Canadian CCS equipment manufacturers like Vancouver’s Svante, there is one policy piece still missing from the MOU: eligibility for the Clean Technology Manufacturing (CTM) Investment tax credit.
“Carbon capture was left out of that,” said Svante co-founder Brett Henkel said.
Svante recently built a major manufacturing plant in Burnaby for its carbon capture filters and machines, with many of its prospective customers expected to be in the U.S.
The $20 billion Pathways project could be a huge boon for Canadian companies like Svante and Calgary’s Entropy. But there is fear Canadian CCS equipment manufacturers could be shut out of the project.
“If the oil sands companies put out for a bid all this equipment that’s needed, it is highly likely that a lot of that equipment is sourced outside of Canada, because the support for Canadian manufacturing is not there,” Henkel said.
Henkel hopes to see CCS manufacturing added to the eligibility for the CTM investment tax credit.
“To really build this eco-system in Canada and to support the Pathways Alliance project, we need that amendment to happen.”
Resource Works News
Alberta
Alberta Next Panel calls for less Ottawa—and it could pay off

From the Fraser Institute
By Tegan Hill
Last Friday, less than a week before Christmas, the Smith government quietly released the final report from its Alberta Next Panel, which assessed Alberta’s role in Canada. Among other things, the panel recommends that the federal government transfer some of its tax revenue to provincial governments so they can assume more control over the delivery of provincial services. Based on Canada’s experience in the 1990s, this plan could deliver real benefits for Albertans and all Canadians.
Federations such as Canada typically work best when governments stick to their constitutional lanes. Indeed, one of the benefits of being a federalist country is that different levels of government assume responsibility for programs they’re best suited to deliver. For example, it’s logical that the federal government handle national defence, while provincial governments are typically best positioned to understand and address the unique health-care and education needs of their citizens.
But there’s currently a mismatch between the share of taxes the provinces collect and the cost of delivering provincial responsibilities (e.g. health care, education, childcare, and social services). As such, Ottawa uses transfers—including the Canada Health Transfer (CHT)—to financially support the provinces in their areas of responsibility. But these funds come with conditions.
Consider health care. To receive CHT payments from Ottawa, provinces must abide by the Canada Health Act, which effectively prevents the provinces from experimenting with new ways of delivering and financing health care—including policies that are successful in other universal health-care countries. Given Canada’s health-care system is one of the developed world’s most expensive universal systems, yet Canadians face some of the longest wait times for physicians and worst access to medical technology (e.g. MRIs) and hospital beds, these restrictions limit badly needed innovation and hurt patients.
To give the provinces more flexibility, the Alberta Next Panel suggests the federal government shift tax points (and transfer GST) to the provinces to better align provincial revenues with provincial responsibilities while eliminating “strings” attached to such federal transfers. In other words, Ottawa would transfer a portion of its tax revenues from the federal income tax and federal sales tax to the provincial government so they have funds to experiment with what works best for their citizens, without conditions on how that money can be used.
According to the Alberta Next Panel poll, at least in Alberta, a majority of citizens support this type of provincial autonomy in delivering provincial programs—and again, it’s paid off before.
In the 1990s, amid a fiscal crisis (greater in scale, but not dissimilar to the one Ottawa faces today), the federal government reduced welfare and social assistance transfers to the provinces while simultaneously removing most of the “strings” attached to these dollars. These reforms allowed the provinces to introduce work incentives, for example, which would have previously triggered a reduction in federal transfers. The change to federal transfers sparked a wave of reforms as the provinces experimented with new ways to improve their welfare programs, and ultimately led to significant innovation that reduced welfare dependency from a high of 3.1 million in 1994 to a low of 1.6 million in 2008, while also reducing government spending on social assistance.
The Smith government’s Alberta Next Panel wants the federal government to transfer some of its tax revenues to the provinces and reduce restrictions on provincial program delivery. As Canada’s experience in the 1990s shows, this could spur real innovation that ultimately improves services for Albertans and all Canadians.
-

 Energy22 hours ago
Energy22 hours agoWhy Japan wants Western Canadian LNG
-

 Business19 hours ago
Business19 hours agoMainstream media missing in action as YouTuber blows lid off massive taxpayer fraud
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoWhat Do Loyalty Rewards Programs Cost Us?
-

 Business21 hours ago
Business21 hours agoLand use will be British Columbia’s biggest issue in 2026
-
 International10 hours ago
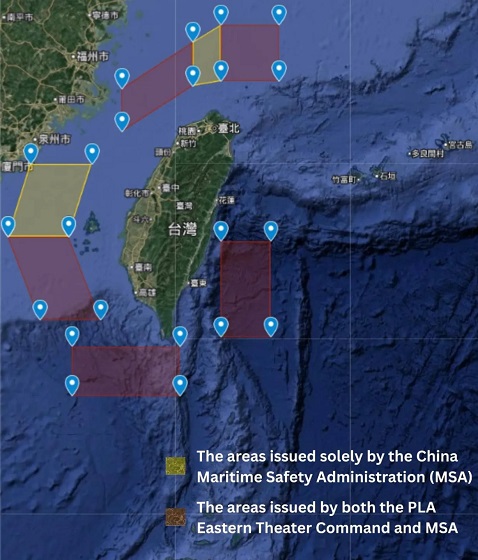
International10 hours agoChina Stages Massive Live-Fire Encirclement Drill Around Taiwan as Washington and Japan Fortify
-

 Haultain Research1 day ago
Haultain Research1 day agoSweden Fixed What Canada Won’t Even Name
-

 Energy10 hours ago
Energy10 hours agoRulings could affect energy prices everywhere: Climate activists v. the energy industry in 2026
-

 Digital ID9 hours ago
Digital ID9 hours agoThe Global Push for Government Mandated Digital IDs And Why You Should Worry





