conflict
U.S. Tells Europe To Handle Its Own Defense

The U.S. is no longer willing to subsidize prosperous countries that won’t defend themselves.
The Trump administration’s foreign policy gambits can be baffling: Why rename the Gulf of Mexico? What is this fixation on annexing Greenland? Does anybody really want to find out what happens if we add Canadians to the U.S. Senate? But the president is right that allies have been allowed to shift the costs of their defense to the United States for decades, and they’ve relied on the U.S. to resolve what are largely European problems. With the U.S. government spending far beyond its means, it’s time for our NATO allies to step up, as U.S. Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth recently suggested.
Blunt Word for Europe
“The United States remains committed to the NATO alliance and to the defense partnership with Europe, full stop,” Hegseth, who served as an infantry officer in Afghanistan and Iraq before taking high-profile roles with Fox News and then with the Trump administration, commented last week at a meeting of the Ukraine Defense Contact Group held in Brussels. “But the United States will no longer tolerate an imbalanced relationship which encourages dependency.”
Hegseth went on to say that any security guarantees negotiated for Ukraine after almost three long years of war between that country and invading Russian forces “must be backed by capable European and non-European troops,” but only “as part of a non-NATO mission….To be clear, as part of any security guarantee, there will not be U.S. troops deployed to Ukraine.”
But what really brought the message home for attendees was when the U.S. defense secretary emphasized that America has security obligations throughout the world, particularly regarding China. That means, with NATO, the U.S. would focus on “empowering Europe to own responsibility for its own security.” To that end, Hegseth urged U.S. allies to exceed the 2-percent-of-GDP target for defense spending set by the alliance—which most fail to meet—and to aim for 5 percent.
Hegseth’s speech threw “the world’s biggest military alliance into disarray,” according to the A.P. But the message wasn’t unanticipated, nor was the reality of competing demands on American resources entirely unappreciated. France’s President Emmanuel Macron quickly called a meeting of European leaders “to discuss European security.” NATO Secretary General Mark Rutte agreed Europe and Canada “have not paid enough over the last 40 years…. The U.S. is rightly asking for a rebalancing of that.”
Poland, which has historical reasons to fears Moscow’s intentions, is already near the 5 percent target for defense. Last March, Poland’s President Andrzej Duda praised the U.S. role in defending Europe and supporting Ukraine, but asked other NATO countries to join his country in building military capability.
Unequal Commitments to Defense
At least since the end of the Cold War, most European countries have skated by on minimal military expenditures, counting on the United States to handle any threats that might emerge. That situation continued even after Russian troops poured into Ukraine.
“The British military—the leading U.S. military ally and Europe’s biggest defense spender—has only around 150 deployable tanks and perhaps a dozen serviceable long-range artillery pieces,” The Wall Street Journal reported in December 2023. “France, the next biggest spender, has fewer than 90 heavy artillery pieces, equivalent to what Russia loses roughly every month on the Ukraine battlefield. Denmark has no heavy artillery, submarines or air-defense systems. Germany’s army has enough ammunition for two days of battle.”
NATO’s last annual report revealed the U.S. represents 53 percent of the GDP of all countries in the alliance. But the U.S. makes 67 percent of alliance defense expenditures. NATO sets a goal for members to spend 2 percent of their GDP on defense. Even with rising tensions, only 11 of the alliance’s 32 members hit that benchmark in that report (the next report should show more meeting the goal).
Among the countries not hitting the 2 percent mark are Canada, France, and Germany—all wealthy countries that could significantly contribute to the alliance’s defense. Germany claims to have hit the 2 percent target in its latest budget. But Canada’s government reportedly told NATO that it “will never” hit the target. Writing about that admission, The Washington Post‘s Amanda Coletta noted that “nearly all of Canada’s 78 Leopard II tanks ‘require extensive maintenance and lack spare parts.'”
In supporting Ukraine, European countries gave somewhat more than the U.S. But Europe emphasized financial and humanitarian aid, so the U.S. has offered slightly more military assistance at €64 billion ($62.1 billion U.S.) compared to Europe’s €62 billion ($65 billion U.S.), according to the Kiel Institute for the World Economy.
The U.S. Can’t Afford To Continue as Europe’s Protector
As Hegseth emphasized in Brussels, the U.S. has security concerns around the world, especially in the Pacific with China, while European worries are more regional. But the U.S. has another big concern: The federal government spends far too much. After entitlements, defense spending is a major recipient of tax dollars—or, more accurately, of money borrowed from the future given the massive deficit. According to the Congressional Budget Office, “the federal budget deficit in fiscal year 2025 is $1.9 trillion. Adjusted to exclude the effects of shifts in the timing of certain payments, the deficit grows to $2.7 trillion by 2035.” Debt will also soar if the gap between spending and receipts continues.
Last year, the Cato Institute broke down federal spending, showing that Medicare, Medicaid, and other health entitlements make up 28 percent of the federal budget, Social Security is 22 percent, defense and income security account for 13 percent each, and net interest on the debt is 11 percent. Everything else makes up the remaining 13 percent. It’s going to be very difficult to balance the federal government’s books without addressing entitlements and defense spending.
Undoubtedly, with the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) turning its attention to the Pentagon, loads of waste, fraud, and abuse will be uncovered. But it’s impossible that so much financial mismanagement will be uncovered as to make up for trillions in deficits all by itself. Some priorities will have to be rejiggered to get spending controlled.
So, Hegseth’s blunt reminder to Europeans that their continent is their responsibility to defend is justified. Countries that together almost equal U.S. GDP and are mostly clustered together should be making more serious arrangements for their own defense.
Not all Trump administration pronouncements were so well-considered. The U.S. reportedly plans to meet with Russian envoys to discuss Ukraine’s future—without inviting Ukraine or European allies. That’s presumptuous and runs the risk that Ukraine just won’t stop fighting if it doesn’t like the terms.
In response, Ukraine’s President Volodymyr Zelenskyy called for the creation of an “armed forces of Europe” to defend the continent. French President Macron’s security meeting suggests Europeans are thinking along similar lines.
That could work out for everybody except the Russians. If Europeans assume greater responsibility for defending their continent and for supporting Ukraine, Washington, D.C. would likely be very happy.
|
|
|
Artificial Intelligence
AI Drone ‘Swarms’ Unleashed On Ukraine Battlefields, Marking New Era Of Warfare


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
Artificial intelligence-powered drones are making their first appearances on the battlefield in the Russia-Ukraine war as warfare creeps closer to full automation.
In bombardments on Russian targets in the past year, Ukrainian drones acting in concert were able to independently determine where to strike without human input.
It’s the first battlefield use of AI “swarm” technology in a real-world environment, a senior Ukrainian official and Swarmer, the company who makes the software, told the Wall Street Journal in a Tuesday report. While drones have increasingly defined modern battlefields, swarms until now had been confined to testing rather than combat.
“You set the target and the drones do the rest,” Swarmer Chief Executive Serhii Kupriienko told the WSJ. “They work together, they adapt.”
So far, the Swarmer technology has been used hundreds of times to target Russia assets, but was first used a year ago to lay mines on the front, the Ukrainian official told the WSJ. The software has been tested with up to 25 drones at once, but is usually utilized with only three.
Kupriienko told the WSJ that he was preparing to test up to 100 drones at once with the linking software.
A common arrangement used on the battlefield includes one reconnaissance drone to scout out the target and two explosive drones delivering the payload on target, the official told the WSJ.
While Western nations such as the U.S., France and the United Kingdom are also pursuing drone swarm technology, they have not deployed swarm technology on the battlefield the way Ukraine has, according to the WSJ. Currently, autonomous weapons are not regulated by any international authority or binding agreement, but ethical concerns around the technology has led many to call for increased regulation of weapons like the Swarmer system.
The Ukrainian Ministry of Foreign Affairs did not immediately respond to the Daily Caller News Foundation’s request for comment.
conflict
Trump Pentagon Reportedly Blocking Ukraine From Firing Western Missiles Deep Into Russia


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
The Department of Defense has spent months blocking the Ukrainian military from using American and British-made missiles to hit targets deep inside Russia, The Wall Street Journal reported Sunday, citing unnamed U.S. officials.
Undersecretary of Defense for Policy Eldridge Colby reportedly designed the procedure to review requests to carry out the long-range strikes with weapons that are either of U.S. origin or that require American intelligence or use components provided by the U.S., according to the WSJ. Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth reportedly has the final say on whether Ukrainian forces can use the MGM-140 ATACMS (Army Tactical Missile System) to hit targets in Russia.
The reported blocks on missile strikes coincides with a Trump administration effort to broker a peace deal between Russia and Ukraine. A Pentagon spokesperson declined to comment further on the matter.
BREAKING: President Vladimir Putin reacts to B-2 Flyover pic.twitter.com/1mzVn7DxlW
— Jack Poso 🇺🇸 (@JackPosobiec) August 15, 2025
The Biden administration allowed Ukraine to carry out strikes with ATACMS in November, weeks after President Donald Trump won the 2024 election, the New York Times reported. Trump criticized the move during a December interview with Time magazine.
“It’s crazy what’s taking place. It’s crazy,” Trump said. “I disagree very vehemently with sending missiles hundreds of miles into Russia. Why are we doing that? We’re just escalating this war and making it worse. That should not have been allowed to be done.”
Trump and Russian President Vladimir Putin met in Alaska on Aug. 15 for a summit meeting during which Trump sought to secure a cease-fire in Russia’s war with Ukraine. As Trump greeted Putin, a B-2A Spirit stealth bomber and several fighters carried out a flyover of Elmendorf Air Force Base.
Trump met with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky and major European leaders on Aug. 18 to update them on the summit.
In July, Trump reached an agreement with NATO where members of the alliance would purchase weapons, including MIM-104 Patriot surface-to-air missiles, and donate them to Ukraine.
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoQuebecers want feds to focus on illegal gun smuggling not gun confiscation
-

 Courageous Discourse1 day ago
Courageous Discourse1 day agoNo Exit Wound – EITHER there was a very public “miracle” OR Charlie Kirk’s murder is not as it appears
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoMinus Forty and the Myth of Easy Energy
-

 Uncategorized2 days ago
Uncategorized2 days agoNew report warns WHO health rules erode Canada’s democracy and Charter rights
-
 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days agoFrance stunned after thieves loot Louvre of Napoleon’s crown jewels
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoEmission regulations harm Canadians in exchange for no environmental benefit
-

 National1 day ago
National1 day agoPolitically Connected Canadian Weed Sellers Push Back in B.C. Court, Seek Distance from Convicted Heroin Trafficker
-
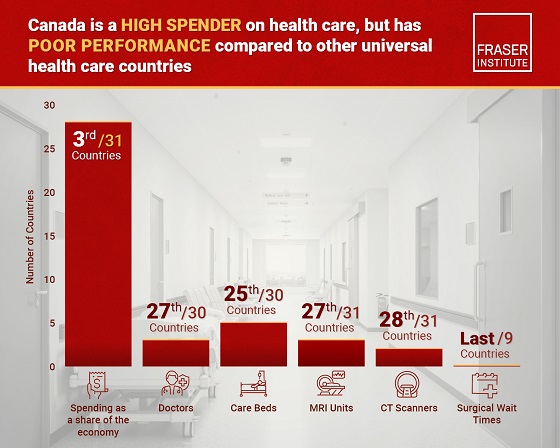
 Business24 hours ago
Business24 hours agoCanada has fewer doctors, hospital beds, MRI machines—and longer wait times—than most other countries with universal health care







