Brownstone Institute
The Vaccine Was “95% Effective” How?

From the Brownstone Institute
BY
The 1840 Treaty of Waitangi between the British Crown and Maori chiefs was a landmark event in the history of New Zealand. Drafted in English, a Maori translation was prepared, ostensibly to ensure that Maori could have an accurate understanding of the terms. In retrospect, it is less clear that a meeting of the minds was intended:
The English and Māori texts differ. As some words in the English treaty did not translate directly into the written Māori language of the time, the Māori text is not a literal translation of the English text. It has been claimed that Henry Williams, the missionary entrusted with translating the treaty from English, was fluent in Māori and that far from being a poor translator he had in fact carefully crafted both versions to make each palatable to both parties without either noticing inherent contradictions.
“The covid vaccine is 95% effective” is a contemporary Treaty of Waitangi. The original is in the language of clinical trials. It was never translated. The public interpreted this phrase in their native language, normal English. What Pfizer said and what the public heard were quite different. The public would have been far more skeptical of these products had the clinical trial results been translated into normal English.
What we need is a proper translation and an explanation of how miscommunication happened.
The Injections Did Not Stop Infection
By now, everyone knows that the Pfizer and Moderna products did not stop people from getting Covid. Covid disease has mowed a wide strip through the double and triple-masked talking heads who told everyone that the shots would make them immune.
What is less well known is that:
- The products were never expected to stop infection or transmission.
- The clinical trials did not test for their ability to do so.
A clinical trial is designed to test a drug for effectiveness, which is strictly defined by one or more endpoints. An endpoint is a measurable outcome that can be assessed for each participant. With that in mind, prevention of infection was not an endpoint of the BioNTech/Pfizer injection clinical trials. And, this was known in 2020 before the products were approved for emergency use and distributed to the public starting in 2021.
In this New England Journal of Medicine research summary, Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine, under Limitations and Remaining Questions, we find that “whether the vaccine protects against asymptomatic infection and transmission to unvaccinated persons” remains unanswered by the clinical trial.
What did the clinical trial test for, if not the ability of the mRNA vaccine to stop transmission and/or infection? The trial was designed to test the ability of the injections to prevent “symptomatic Covid 19 cases” defined as one or more of a number symptoms and a positive test (see page 7 of the supplementary appendix for details).
@pfizer tweeted in Jan 2021 that stopping transmission was their “highest priority”. Their product does not do that, nor did the tweet make a claim that it did so. But it was their highest priority nonetheless. That, and getting as many people injected as possible.

Failure to Prevent Infection Was Known Before the Rollout
In October 2022, a Pfizer executive testified to an EU body that Pfizer had not tested the ability of the vaccine to stop transmission. This story was shocking to some and generated accusations that Pfizer had lied about the capabilities of the shots. But this information had been available since the trial results were released early in 2021. Pfizer had already been criticized for this.
Dr William A Haseltine PhD, wrote in Forbes in September 2020:
What would a normal vaccine trial look like?
One of the more immediate questions a trial needs to answer is whether a vaccine prevents infection. If someone takes this vaccine, are they far less likely to become infected with the virus? These trials all clearly focus on eliminating symptoms of Covid-19, and not infections themselves. Asymptomatic infection is listed as a secondary objective in these trials when they should be of critical importance.
On October 21, 2020 the editor of the BMJ (British Medical Journal) Peter Doshi asked:
Will covid-19 vaccines save lives? Current trials aren’t designed to tell us
Peter Hotez, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, said, “Ideally, you want an antiviral vaccine to do two things . . . first, reduce the likelihood you will get severely ill and go to the hospital, and two, prevent infection and therefore interrupt disease transmission.”
Yet the current phase III trials are not actually set up to prove either. None of the trials currently underway are designed to detect a reduction in any serious outcome such as hospital admissions, use of intensive care, or deaths. Nor are the vaccines being studied to determine whether they can interrupt transmission of the virus….
Is It Even a Vaccine?
A vaccine that prevents infection is known as “neutralizing” or “sterilizing”. I am a software engineer with no training in medicine, pharmacology or clinical trials. I consider myself a good barometer of what the average untrained person would think about such things. Prior to 2021 I had thought that immunity was a necessary condition for a drug to earn the title of “vaccine”. If anyone had asked me, I would have told them that the Covid injections were a treatment, not a vaccine.
The Wikipedia article about vaccines (Mar 5 2023) aligns with my untrained understanding:
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. … A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body’s immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and to further recognize and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future.
Cornell Law provides the following legal definition of vaccine, sourcing 26 USC § 4132(a)(2), which is consistent with the above:
The term “vaccine” means any substance designed to be administered to a human being for the prevention of 1 or more diseases.
The definition published by the CDC prior to 2021 said much the same. But the CDC website changed the definition on or after August 2021. The older version found on the internet archive is here (emphasis added):
Immunity: Protection from an infectious disease. If you are immune to a disease, you can be exposed to it without becoming infected.
Vaccine: A product that stimulates a person’s immune system to produce immunity to a specific disease, protecting the person from that disease.
Here is the new version (emphasis added):
Vaccine: A preparation that is used to stimulate the body’s immune response against diseases.
The earlier pair of definitions is quite easy to understand. The latter, much more difficult. What exactly is a “preparation”? Does a vaccine stimulate the body or only prepare the body? What is or is not a vaccine according to the new definition?
While the CDC may think that they can change the meanings of words whenever they like, public memory retains the original meaning. The assumption of immunity permeates almost all non-expert level discussion of vaccines. A web search for “why are vaccines good” shows results that assume or imply immunity.
Even the CDC did not finish the job of memory-holing the old language. On the very same CDC website, under 5 Reasons It Is Important for Adults to Get Vaccinated, we read “By getting vaccinated, you can protect yourself and also avoid spreading preventable diseases to other people in your community.” And then, “Vaccines Can Prevent Serious Illness”.
The timing of the CDC’s edit suggests to me that prior to 2021, the CDC had the same understanding of vaccines as I do. I believe that they wanted a new definition because they knew that the products being developed at warp speed were not vaccines in the original sense of the word. And it was important that those products be called “vaccines” for reasons that I will explain later. This incident brings to mind a meme that I no longer have a link to. captioned: “We changed what ‘definition’ means so you can’t say that we redefined anything.”
What Does “95% Effective” Mean?
The “95% effective” message was repeated in nearly all reporting on the clinical trials. But the question, “effective at doing what?” was rarely asked. To answer this requires walking down the links of a chain of terminology from the world of clinical trials.
The first link in the chain is “risk”. Risk is the probability of a bad outcome. These are assumed to happen randomly within a group. A clinical trial must define in advance the bad outcomes that the drug intends to avoid. The next link is “endpoint”. Each distinct bad outcome is an “endpoint”. The trial compares the endpoints between a control group who did not take the drug and a test group, who did.
The purpose of a clinical trial is to determine the ability of a drug to reduce risk. A drug that reduces risk is “effective”. There are two ways of quantifying risk reduction. From the NIH glossary:
Absolute risk reduction (ARR) or risk difference
the difference in the incidence of poor outcomes between the intervention group of a study and the control group. For example, if 20 per cent of people die in the intervention group and 30 per cent in the control group, the ARR is 10 per cent (30–20 per cent).
Relative risk (RR)
the rate (risk) of poor outcomes in the intervention group divided by the rate of poor outcomes in the control group. For example, if the rate of poor outcomes is 20 per cent in the intervention group and 30 per cent in the control group, the relative risk is 0.67 (20 per cent divided by 30 per cent).
The difference between the ARR and RR (also known as “RRR”, to align with ARR) is in the denominator. The ARR divides by the number of participants in one of the groups. The RRR divides by the number of people with bad outcomes in the control group – a necessarily much smaller number.
The ARR is the number most relevant for a drug – such as the Pfizer injections – that was to be given to everyone. But the RRR is the preferred method of presentation for pharma when they want to exaggerate the effectiveness of a drug because it will always be a much larger number. Would you take a drug that could reduce the incidence of a rare disease by 50%? From 10 per 1 million to 5 per 1 million is an 50% RRR and an 0.0005% ARR.
The 95% figure cited for the covid injections is the relative risk. The absolute risk reduction was 0.84%. In a slide deck from the Canadian Covid Care Alliance(CCCA), slide 11 shows how the 91% was achieved (it is 91%, not 95%, because the it refers to an earlier version of the study):

The research paper COVID-19 vaccine efficacy and effectiveness—the elephant (not) in the room puts the ARR in the 1% range. The CCCA slide deck gives an ARR of 0.84%, though it is not clear how they reached this number, based on the other numbers in their slides.
A clinical trial finding of a 1% ARR means that 99% of the people who take the drug either did not experience the condition that the drug treats, or they did experience it, but were not helped by the drug. The 1% both had the condition and were helped by the drug. Another way of saying this is the Number Needed to Treat (NNT). NNT is the reciprocal of the ARR and is the number of people who must take the drug to help one person reach the endpoint. An ARR of 1% corresponds to an NNT of 100 people.
We can now answer the question of the meaning of vaccine effectiveness. The endpoint of the trial was a severe confirmed case of covid at least 7 days after the second dose. This endpoint requires the participant in the trial to have covid symptoms and a positive covid test. “95% effective” means that 95% of the patients who had Covid symptoms and a positive test were in the control group. Five percent were in the test group.
Here’s what “95% effective” did not mean: if you take the shots, then you will have a 95% lower chance of getting covid. But that is how most people understood it because that is what the words mean in normal English.
Then the Lying Started
Once the public had their hopes raised by the false translation of the “95% effective” message, the pandemic-industrial-complex went into high gear to amplify it. They stated the incorrect message loudly, frequently, and as if it were fact. The injections would – with 100% certainty (perhaps 200%) – protect you from infection. Many of the people who said this were doctors or scientific researchers who must have understood how to interpret clinical trials.
Here are some choice quotes that did not age well:
- “You’re not going to get Covid if you have these vaccinations.” Joe Biden, CNN Town Hall July 2021
- “Now we know that the vaccines work well enough that the virus stops with every vaccinated person. A vaccinated person gets exposed to the virus, the virus does not infect them, the virus cannot then use that person to go anywhere else,” she added with a shrug. “It cannot use a vaccinated person as a host to go get more people. [Vaccines] will get us to the end of this.” – Rachel Maddow, March 2021
- “When people are vaccinated they can feel safe that they won’t get infected, whether they’re outdoors or indoors.” – Dr. Anthony Fauci, May 2021(outdoors: seriously?)
- “Vaccination against COVID-19 prevents breakthrough infections, Stanford researchers find.” – Stanford Medicine, July 2021
- Vaccinated people become “dead ends” for the virus – Anthony Fauci, May 2021
Demonizing the Unvaxxed
The public has consistently over-estimated the infection fatality rate of Covid. Some even believed the fatality rate to be above 10%. They believed that we were in great danger. They also believed that the “95% effective” vaccine would bring the pandemic to a quick end, once everyone had taken it. Anyone who refused to do so was therefore risking not only their own life, but everybody else’s as well.
Dr Anthony Fauci estimated herd immunity would emerge when around 60% of the population had taken the vaccine … or perhaps 70, 80, no wait … 85%. Or maybe 100% (which would include large numbers who already had natural immunity). Bill Gates extended that to everyone on earth.
The narrative then turned to demonization of those who refused to submit to vaccine coercion. The selfish anti-social behavior of the anti-vaxxers with their stubborn attachment to “free dumb” that was keeping everyone locked indoors and forcing us all to wear diapers on our faces. Yale University behavioral researchers tested messaging strategies to determine whether shame, embarrassment or fear was most effective.
President Biden said that we the nation was experiencing a “pandemic of the unvaccinated”. Later, Biden ominoulsy warned the unvaccinated that he had been waiting a long time for them to get injected, but “our patience is wearing thin”. In December of 2021 the White House issued a cheery year end greeting to the vaccinated. The unvaccinated, on the other hand, were “looking at a winter of severe illness and death.” Merry Christmas.
Even South Park, which I consider a reliable source of contrarian political opinion, ran a storyline set in the year 2050 in which every single character had to be vaccinated for the 30-year pandemic to end. This episode featured one lone holdout who would not get vaccinated due to a crustacean allergy i.e. for “shellfish reasons”. This gag took aim at people who considered the vaccine to be a violation of body autonomy, and those who objected to components used in its development for religious reasons, thereby scoring a “two for one”.
Volumes can, and will, be written about the intense onslaught of propaganda aimed at getting two needles in every deltoid. I will provide one more example that represents no more than the median level of insanity; plenty of people called for the same or worse. @ClayTravis, in February 2023, tweeted the results of a Rasmussen poll from 2022:
Last January 60% of Democrats wanted to lock everyone who didn’t get the covid shot in their houses. Over 40% of Democrats wanted those who rejected the covid shot sent to quarantine camps. Over 40% also wanted anyone who criticized the covid shot fined & imprisoned. Over a quarter wanted those who didn’t get the covid shot to have their kids seized.
While there were many agendas driving the madness, the Treaty of Waitangi effect was a critical part in carrying it out. If the message had been that “everyone is going to get exposed to covid – injected or not”, then it could not have happened. The misunderstanding convinced the public that mass vaccination would stop the pandemic; and that the holdouts were prolonging it. Without this belief, none of the coercion made any sense: employment mandates, school mandates, quarantine camps, or vaccine passports. As the hysteria fades, the last remaining mandates are being dropped as the reality sinks in that the shots do not stop the spread.
Welcome to Waitangi World. I hope that you have a pleasant stay.
Brownstone Institute
FDA Exposed: Hundreds of Drugs Approved without Proof They Work

From the Brownstone Institute
By
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved hundreds of drugs without proof that they work—and in some cases, despite evidence that they cause harm.
That’s the finding of a blistering two-year investigation by medical journalists Jeanne Lenzer and Shannon Brownlee, published by The Lever.
Reviewing more than 400 drug approvals between 2013 and 2022, the authors found the agency repeatedly ignored its own scientific standards.
One expert put it bluntly—the FDA’s threshold for evidence “can’t go any lower because it’s already in the dirt.”
A System Built on Weak Evidence
The findings were damning—73% of drugs approved by the FDA during the study period failed to meet all four basic criteria for demonstrating “substantial evidence” of effectiveness.
Those four criteria—presence of a control group, replication in two well-conducted trials, blinding of participants and investigators, and the use of clinical endpoints like symptom relief or extended survival—are supposed to be the bedrock of drug evaluation.
Yet only 28% of drugs met all four criteria—40 drugs met none.
These aren’t obscure technicalities—they are the most basic safeguards to protect patients from ineffective or dangerous treatments.
But under political and industry pressure, the FDA has increasingly abandoned them in favour of speed and so-called “regulatory flexibility.”
Since the early 1990s, the agency has relied heavily on expedited pathways that fast-track drugs to market.
In theory, this balances urgency with scientific rigour. In practice, it has flipped the process. Companies can now get drugs approved before proving that they work, with the promise of follow-up trials later.
But, as Lenzer and Brownlee revealed, “Nearly half of the required follow-up studies are never completed—and those that are often fail to show the drugs work, even while they remain on the market.”
“This represents a seismic shift in FDA regulation that has been quietly accomplished with virtually no awareness by doctors or the public,” they added.
More than half the approvals examined relied on preliminary data—not solid evidence that patients lived longer, felt better, or functioned more effectively.
And even when follow-up studies are conducted, many rely on the same flawed surrogate measures rather than hard clinical outcomes.
The result: a regulatory system where the FDA no longer acts as a gatekeeper—but as a passive observer.
Cancer Drugs: High Stakes, Low Standards
Nowhere is this failure more visible than in oncology.
Only 3 out of 123 cancer drugs approved between 2013 and 2022 met all four of the FDA’s basic scientific standards.
Most—81%—were approved based on surrogate endpoints like tumour shrinkage, without any evidence that they improved survival or quality of life.
Take Copiktra, for example—a drug approved in 2018 for blood cancers. The FDA gave it the green light based on improved “progression-free survival,” a measure of how long a tumour stays stable.
But a review of post-marketing data showed that patients taking Copiktra died 11 months earlier than those on a comparator drug.
It took six years after those studies showed the drug reduced patients’ survival for the FDA to warn the public that Copiktra should not be used as a first- or second-line treatment for certain types of leukaemia and lymphoma, citing “an increased risk of treatment-related mortality.”
Elmiron: Ineffective, Dangerous—And Still on the Market
Another striking case is Elmiron, approved in 1996 for interstitial cystitis—a painful bladder condition.
The FDA authorized it based on “close to zero data,” on the condition that the company conduct a follow-up study to determine whether it actually worked.
That study wasn’t completed for 18 years—and when it was, it showed Elmiron was no better than placebo.
In the meantime, hundreds of patients suffered vision loss or blindness. Others were hospitalized with colitis. Some died.
Yet Elmiron is still on the market today. Doctors continue to prescribe it.
“Hundreds of thousands of patients have been exposed to the drug, and the American Urological Association lists it as the only FDA-approved medication for interstitial cystitis,” Lenzer and Brownlee reported.
“Dangling Approvals” and Regulatory Paralysis
The FDA even has a term—”dangling approvals”—for drugs that remain on the market despite failed or missing follow-up trials.
One notorious case is Avastin, approved in 2008 for metastatic breast cancer.
It was fast-tracked, again, based on ‘progression-free survival.’ But after five clinical trials showed no improvement in overall survival—and raised serious safety concerns—the FDA moved to revoke its approval for metastatic breast cancer.
The backlash was intense.
Drug companies and patient advocacy groups launched a campaign to keep Avastin on the market. FDA staff received violent threats. Police were posted outside the agency’s building.
The fallout was so severe that for more than two decades afterwards, the FDA did not initiate another involuntary drug withdrawal in the face of industry opposition.
Billions Wasted, Thousands Harmed
Between 2018 and 2021, US taxpayers—through Medicare and Medicaid—paid $18 billion for drugs approved under the condition that follow-up studies would be conducted. Many never were.
The cost in lives is even higher.
A 2015 study found that 86% of cancer drugs approved between 2008 and 2012 based on surrogate outcomes showed no evidence that they helped patients live longer.
An estimated 128,000 Americans die each year from the effects of properly prescribed medications—excluding opioid overdoses. That’s more than all deaths from illegal drugs combined.
A 2024 analysis by Danish physician Peter Gøtzsche found that adverse effects from prescription medicines now rank among the top three causes of death globally.
Doctors Misled by the Drug Labels
Despite the scale of the problem, most patients—and most doctors—have no idea.
A 2016 survey published in JAMA asked practising physicians a simple question—what does FDA approval actually mean?
Only 6% got it right.
The rest assumed that it meant the drug had shown clear, clinically meaningful benefits—such as helping patients live longer or feel better—and that the data was statistically sound.
But the FDA requires none of that.
Drugs can be approved based on a single small study, a surrogate endpoint, or marginal statistical findings. Labels are often based on limited data, yet many doctors take them at face value.
Harvard researcher Aaron Kesselheim, who led the survey, said the results were “disappointing, but not entirely surprising,” noting that few doctors are taught about how the FDA’s regulatory process actually works.
Instead, physicians often rely on labels, marketing, or assumptions—believing that if the FDA has authorized a drug, it must be both safe and effective.
But as The Lever investigation shows, that is not a safe assumption.
And without that knowledge, even well-meaning physicians may prescribe drugs that do little good—and cause real harm.
Who Is the FDA Working for?
In interviews with more than 100 experts, patients, and former regulators, Lenzer and Brownlee found widespread concern that the FDA has lost its way.
Many pointed to the agency’s dependence on industry money. A BMJ investigation in 2022 found that user fees now fund two-thirds of the FDA’s drug review budget—raising serious questions about independence.

Yale physician and regulatory expert Reshma Ramachandran said the system is in urgent need of reform.
“We need an agency that’s independent from the industry it regulates and that uses high-quality science to assess the safety and efficacy of new drugs,” she told The Lever. “Without that, we might as well go back to the days of snake oil and patent medicines.”
For now, patients remain unwitting participants in a vast, unspoken experiment—taking drugs that may never have been properly tested, trusting a regulator that too often fails to protect them.
And as Lenzer and Brownlee conclude, that trust is increasingly misplaced.
- Investigative report by Jeanne Lenzer and Shannon Brownlee at The Lever [link]
- Searchable public drug approval database [link]
- See my talk: Failure of Drug Regulation: Declining standards and institutional corruption
Republished from the author’s Substack
Brownstone Institute
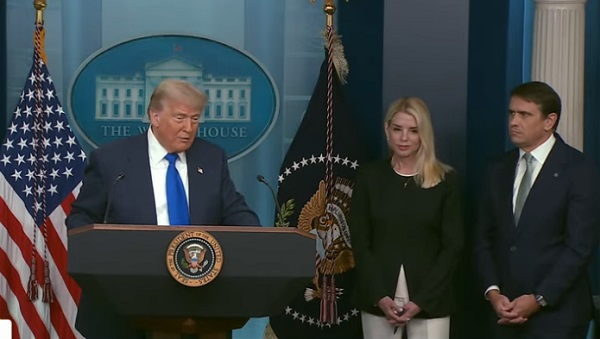
Anthony Fauci Gets Demolished by White House in New Covid Update

From the Brownstone Institute
By
Anthony Fauci must be furious.
He spent years proudly being the public face of the country’s response to the Covid-19 pandemic. He did, however, flip-flop on almost every major issue, seamlessly managing to shift his guidance based on current political whims and an enormous desire to coerce behavior.
Nowhere was this more obvious than his dictates on masks. If you recall, in February 2020, Fauci infamously stated on 60 Minutes that masks didn’t work. That they didn’t provide the protection people thought they did, there were gaps in the fit, and wearing masks could actually make things worse by encouraging wearers to touch their face.
Just a few months later, he did a 180, then backtracked by making up a post-hoc justification for his initial remarks. Laughably, Fauci said that he recommended against masks to protect supply for healthcare workers, as if hospitals would ever buy cloth masks on Amazon like the general public.
Later in interviews, he guaranteed that cities or states that listened to his advice would fare better than those that didn’t. Masks would limit Covid transmission so effectively, he believed, that it would be immediately obvious which states had mandates and which didn’t. It was obvious, but not in the way he expected.

And now, finally, after years of being proven wrong, the White House has officially and thoroughly rebuked Fauci in every conceivable way.
White House Covid Page Points Out Fauci’s Duplicitous Guidance
A new White House official page points out, in detail, exactly where Fauci and the public health expert class went wrong on Covid.
It starts by laying out the case for the lab-leak origin of the coronavirus, with explanations of how Fauci and his partners misled the public by obscuring information and evidence. How they used the “FOIA lady” to hide emails, used private communications to avoid scrutiny, and downplayed the conduct of EcoHealth Alliance because they helped fund it.
They roast the World Health Organization for caving to China and attempting to broaden its powers in the aftermath of “abject failure.”
“The WHO’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic was an abject failure because it caved to pressure from the Chinese Communist Party and placed China’s political interests ahead of its international duties. Further, the WHO’s newest effort to solve the problems exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic — via a “Pandemic Treaty” — may harm the United States,” the site reads.
Social distancing is criticized, correctly pointing out that Fauci testified that there was no scientific data or evidence to support their specific recommendations.
“The ‘6 feet apart’ social distancing recommendation — which shut down schools and small business across the country — was arbitrary and not based on science. During closed door testimony, Dr. Fauci testified that the guidance ‘sort of just appeared.’”
There’s another section demolishing the extended lockdowns that came into effect in blue states like California, Illinois, and New York. Even the initial lockdown, the “15 Days to Slow the Spread,” was a poorly reasoned policy that had no chance of working; extended closures were immensely harmful with no demonstrable benefit.
“Prolonged lockdowns caused immeasurable harm to not only the American economy, but also to the mental and physical health of Americans, with a particularly negative effect on younger citizens. Rather than prioritizing the protection of the most vulnerable populations, federal and state government policies forced millions of Americans to forgo crucial elements of a healthy and financially sound life,” it says.
Then there’s the good stuff: mask mandates. While there’s plenty more detail that could be added, it’s immensely rewarding to see, finally, the truth on an official White House website. Masks don’t work. There’s no evidence supporting mandates, and public health, especially Fauci, flip-flopped without supporting data.
“There was no conclusive evidence that masks effectively protected Americans from COVID-19. Public health officials flipped-flopped on the efficacy of masks without providing Americans scientific data — causing a massive uptick in public distrust.”
This is inarguably true. There were no new studies or data justifying the flip-flop, just wishful thinking and guessing based on results in Asia. It was an inexcusable, world-changing policy that had no basis in evidence, but was treated as equivalent to gospel truth by a willing media and left-wing politicians.
Over time, the CDC and Fauci relied on ridiculous “studies” that were quickly debunked, anecdotes, and ever-shifting goal posts. Wear one cloth mask turned to wear a surgical mask. That turned into “wear two masks,” then wear an N95, then wear two N95s.
All the while ignoring that jurisdictions that tried “high-quality” mask mandates also failed in spectacular fashion.

And that the only high-quality evidence review on masking confirmed no masks worked, even N95s, to prevent Covid transmission, as well as hearing that the CDC knew masks didn’t work anyway.
The website ends with a complete and thorough rebuke of the public health establishment and the Biden administration’s disastrous efforts to censor those who disagreed.
“Public health officials often mislead the American people through conflicting messaging, knee-jerk reactions, and a lack of transparency. Most egregiously, the federal government demonized alternative treatments and disfavored narratives, such as the lab-leak theory, in a shameful effort to coerce and control the American people’s health decisions.
When those efforts failed, the Biden Administration resorted to ‘outright censorship—coercing and colluding with the world’s largest social media companies to censor all COVID-19-related dissent.’”
About time these truths are acknowledged in a public, authoritative manner. Masks don’t work. Lockdowns don’t work. Fauci lied and helped cover up damning evidence.
If only this website had been available years ago.
Though, of course, knowing the media’s political beliefs, they’d have ignored it then, too.
Republished from the author’s Substack
-

 armed forces1 day ago
armed forces1 day agoCanada’s Military Can’t Be Fixed With Cash Alone
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoCOVID mandates protester in Canada released on bail after over 2 years in jail
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoTrump transportation secretary tells governors to remove ‘rainbow crosswalks’
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCanada’s loyalty to globalism is bleeding our economy dry
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCarney’s spending makes Trudeau look like a cheapskate
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlberta Next: Alberta Pension Plan
-

 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days agoProject Sleeping Giant: Inside the Chinese Mercantile Machine Linking Beijing’s Underground Banks and the Sinaloa Cartel
-

 C2C Journal23 hours ago
C2C Journal23 hours agoCanada Desperately Needs a Baby Bump