Alberta
Summer Vacation Idea – Central Alberta’s collection of Train stations preserved along the Highway 56 Corridor

Article submitted by Paul O’Neil
For decades, the railroad station or “depot” was the transportation hub of many communities across North America. As the “storefront” for the railway company, the depot was the town’s gateway, handling express freight, serving travelers, and providing vital communication in an erathat is now almost forgotten. In Canada’s West, the remaining small-town depots that continue to exist are now museums, private businesses or residences, or in the worst cases have been left to deteriorate as hulks on private property.
There is however a special historical railway on the Prairies that has developed into a true “historic railway district”. A visit to the depots preserved by the Canadian Northern Society in Central Alberta provides a glimpse into the past – an entire collection of classic railroad station designs, carefully and lovingly maintained by a dedicated group of volunteers.

History Background:
Members of the Canadian Northern Society include historians, community volunteers, gardeners, and other local supporters who have since 1987 been active in the preservation of its namesake railway’s history, and in particular its depots. The Canadian Northern Railway (CNoR) traces its origins to Manitoba in 1896. Visionary founders Sir William Mackenzie and Sir Donald Mann – both instrumental as contractors in the completion of the Canadian Pacific Railway – grew the company from a modest short line between Gladstone and the Dauphin district of Manitoba into to a 9500 mile transcontinental system.
Despite the relative business success of the CNoR’s branchline network, negative financial impacts created by the First World War, together with mounting debt from the over-expansion led to the company being nationalized in late 1918. By 1924, operations in Central Alberta were amalgamated with the rival Grand Trunk Pacific Railway under the newly formed Canadian National Railways (CN) banner.
DEPOTS
Similar to other western railroads, the CNoR designed standard plans to be used at individual locations based on the size and importance of the locality to be served. In Alberta, the most common CNoR design was the combination freight and passenger “Third Class” station. Several “Second Class” depots intended primarily for divisional points were constructed, and a single-story “Fourth Class” depot design were also found. The designs were flexible enough that additions could be constructed as traffic or operations warranted. The distinctive pyramid or “semi-pyramid” roofline of a CNoR depot, a feature designed by company architect Ralph Benjamin Pratt, created a unique and pleasing image.
By the late 1960’s the depot-era on the former CNoR Battle River Subdivision (a large portion had by then been renamed the “Stettler Subdivision”) was drawing to a close. However, the presence of a branch line passenger service in the form of a Budd RDC service between Edmonton and Drumheller ensured the continued existence of several depots as passenger shelters that otherwise would most certainly face demolition. The Edmonton to Drumheller service lasted into VIA Rail Canada times until the Trudeau Government service cuts of November 1981 gutted passenger service across Canada.
ENTER THE CANADIAN NORTHERN SOCIETY
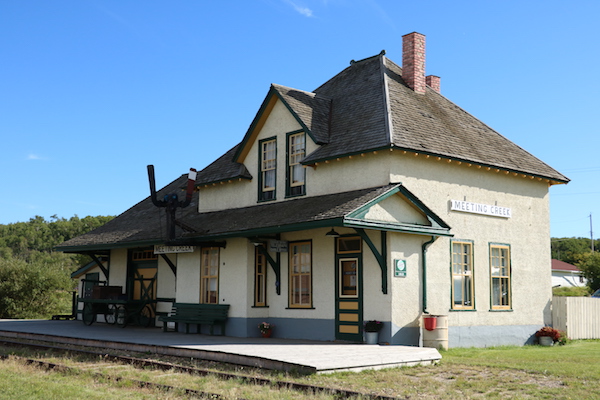
Meeting Creek, MP 21.2

My beautiful picture

By 1986, the CNoR Third Class depot at Meeting Creek was surviving on borrowed time, vandalized and yet escaping the fate of several identical structures in neighboring towns. As a result of an interest by a small group of younger railroaders and rail historians, powered perhaps by a few pints enjoyed in a Stettler pub, the Canadian Northern Society (CNoS) was soon established with the intent to save this classic structure from imminent destruction.
Armed with enthusiasm, some grant money, and the support of short-line Central Western Railway; the CNoS got to work repairing the roof, floors, rebuilding the wooden platform, painting, and replacing missing windows, doors and chimneys. By 1989 the Meeting Creek depot was resurrected from a sad state to her today’s 1940’s-era appearance.
Complimenting the station today is another vanishing prairie icon. A 1917 Alberta Pacific Grain elevator located across from the depot was purchased by CNoS from the Alberta Wheat Pool in 1992. Over the years, it too has been conserved by the Society and work continues into its second century. A second grain elevator, while privately owned, ensures that Meeting Creek continues to feature two classic prairie elevators that dominate the skyline in this picturesque location.
Donalda, MP 30.9:

9.7 miles south of Meeting Creek lies the Village of Donalda. Always an agrarian-based community, Donalda was never larger than 500 souls, and as such rated a Canadian Northern Railway “Third Class Depot”. Unfortunately, the original depot at Donalda was demolished in 1984.
Thanks to the efforts of the CNoS, the group was able to relocate an original CNoR “Fourth-Class” type depot, donated by a Saskatchewan farmer many miles to the east. All the Societyhad to do was physically move this building 700 miles from her location at Vandura, Saskatchewan to Donalda! Through fundraising and community support, the building was moved to Donalda in 1991. The depot was restored to her CN oxide red paint scheme, with cream trim on the windows and facia boards. The interior of the depot was refurbished to her heyday as a depot and is now included in the present-day collection of the Donalda & District Museum. Like Meeting Creek, a short section of original CNoR 60-pound steel main track remains preserved in front of the depot.
Warden MP 55.8:

Five miles south of Stettler is the one-time important junction of the CNoR Brazeau Subdivision, its westward extension into the coal fields at the foot of the Rockies. Originally, a “Fourth Class” station was located here, being destroyed by fire and replaced with a standard later version of the company’s “Third Class” design in 1919. This structure was sold and demolished in the 1980’s, and was recently replaced by a “representative” train order office/depot built entirely by CNoS volunteers, that features design features, artifacts, and “parts” of the original depot. It is used for educational purposes in a peaceful park-like setting along what is now short-line Alberta Prairie Railway.
Big Valley, MP 72.1:


Established in 1911, Big Valley was once hub of the division for the CNoR. By 1921 this one-time bustling terminal boasted well over 300 employees on payroll and featured a 10 stallroundhouse, coaling plant, water tank, and other terminal facilities. Big Valley’s 1912-built depot was a large “Second Class” design commonly constructed by the CNoR at divisionalpoints across the system. The main floor handled passenger and LCL business, while the second-floor housed accommodations for the agent – and later crews and offices.
The Big Valley depot was the second major conservation project for the Canadian Northern Society in 1989. Encouraged by the Village of Big Valley, CNoS began refurbishment of the station, and was able to raise funding from Alberta Historical Resources Foundation and various temporary job creation programs to restore the depot to today’s attractive 1940’s-era exterior appearance.
At the same time, short–line operator Central Western Railway was launching Alberta’s first tourist railroad service. Big Valley, like in her previous railroad life, again had the infrastructure to accommodate steam powered trains into the community. In addition, the 10-stall roundhouse,by then in ruins with only the concrete walls showing her prominence to the community was preserved as an interpretive park through the efforts of CNoS, Central Western, and the Village of Big Valley. Volunteers cleared and excavated the site, allowing the view of the ash and turntable pits, boiler room and machine shop. You can imagine the one-time bustling activity of Ten-Wheelers and Consolidations locomotives receiving service at the Roundhouse.
Big Valley today is the centerpiece of this rich CNoR heritage, plus a restored grain elevator to complete the scene of a bustling prairie railroad terminal. The Big Valley Historical Society also operates an excellent local museum in a classic garage on Railway Avenue, together with maintaining St. Edmund’s Church – a spiritual home of many of the community’s early railroaders. Serving as primary destination for Stettler based Alberta Prairie Railway, seasonal excursion trains arrive at Big Valley on a scheduled basis, where passengers spend a few hours in the community, experiencing the magic of its railway, ranching, and mining historical attractions.
Further along the line in the ghost town of Rowley is another preserved CNoR Third Class depot, built to a similar floor plan as Meeting Creek’s railway station. While not part of the Canadian Northern Society’s collection, it is certainly worth a visit while in historic “Rowleywood”.
Other Projects
In addition to its Stettler Subdivision projects, the Canadian Northern Society has and continues to support other railway preservation efforts.
Over the years the preservation of depots at Rowley, Smoky Lake, Viking, Canora in Saskatchewan, and Dauphin in Manitoba have all been supported by CNoS. A roundhouse project at the former CNoR divisional point of Hanna has also been aided by the CNoS. While the 1909 Viking depot is in fact a rival GTP station, the CNoS was instrumental in its 1991 preservation – and remarkably you can still catch a train here – with VIA Rail Canada’s flagship train “The Canadian” stopping upon request.
The CNoS collection of depots and the corresponding regional history that they represent has become part of the historical fabric of Western Canada. It is proud to have left this legacy – and its true hope is that future generations will continue to be educated by its efforts, and will perhaps contribute to the further preservation of each of these wonderful historic structures.
This summer the Canadian Northern Railway Historical Society invites you to visit these historic buildings along Alberta’s Highway 56 corridor.
Alberta
Upgrades at Port of Churchill spark ambitions for nation-building Arctic exports

In August 2024, a shipment of zinc concentrate departed from the Port of Churchill — marking the port’s first export of critical minerals in over two decades. Photo courtesy Arctic Gateway Group
From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
‘Churchill presents huge opportunities when it comes to mining, agriculture and energy’
When flooding in northern Manitoba washed out the rail line connecting the Town of Churchill to the rest of the country in May 2017, it cast serious questions about the future of the community of 900 people on the shores of Hudson Bay.
Eight years later, the provincial and federal governments have invested in Churchill as a crucial nation-building corridor opportunity to get resources from the Prairies to markets in Europe, Africa and South America.
Direct links to ocean and rail

Aerial view of the Hudson Bay Railway that connects to the Port of Churchill. Photo courtesy Arctic Gateway Group
The Port of Churchill is unique in North America.
Built in the 1920s for summer shipments of grain, it’s the continent’s only deepwater seaport with direct access to the Arctic Ocean and a direct link to the continental rail network, through the Hudson Bay Railway.
The port has four berths and is capable of handling large vessels. Having spent the past seven years upgrading both the rail line and the port, its owners are ready to expand shipping.
“After investing a lot to improve infrastructure that was neglected for decades, we see the possibilities and opportunities for commodities to come through Churchill whether that is critical minerals, grain, potash or energy,” said Chris Avery, CEO of the Arctic Gateway Group (AGG), a partnership of 29 First Nations and 12 remote northern Manitoba communities that owns the port and rail line.
“We are pleased to be in the conversation for these nation-building projects.”
In May, Canada’s Western premiers called for the Prime Minister’s full support for the development of an economic corridor connecting ports on the northwest coast and Hudson’s Bay, ultimately reaching Grays Bay, Nunavut.
Investments in Port of Churchill upgrades
AGG, which purchased the rail line and port from an American company in 2017, is not alone in the bullish view of Churchill’s future.
In February, Manitoba Premier Wab Kinew announced an investment of $36.4 million over two years in infrastructure projects at the port aimed at growing international trade.
“Churchill presents huge opportunities when it comes to mining, agriculture and energy,” Kinew said in a release.
“These new investments will build up Manitoba’s economic strength and open our province to new trading opportunities.”
In March, the federal government committed $175 million over five years to the project including $125 million to support the rail line and $50 million to develop the port.
“It’s important to point out that investing in Churchill was something that both the Liberal and Conservative parties agreed on during the federal election campaign,” said Avery, a British Columbian who worked in the airline industry for more than two decades before joining AGG.
Reduced travel time
The federal financial support helped AGG upgrade the rail line, repairing the 20 different locations where it was washed out by flooding in 2017.
Improvements included laying more than 1,600 rail cars worth of ballast rock for stabilization and drainage, installing almost 120,000 new railway ties and undertaking major bridge crossing rehabilitations and switch upgrades.
The result has seen travel time by rail reduced by three hours — or about 10 per cent — between The Pas and Churchill.
AGG also built a dedicated storage facility for critical minerals and other commodities at the port, the first new building in several decades.
Those improvements led to a milestone in August 2024, when a shipment of zinc concentrate was shipped from the port to Belgium. It was the first critical minerals shipment from Churchill in more than two decades.
The zinc concentrate was mined at Snow Lake, Manitoba, loaded on rail cars at The Pas and moved to Churchill. It’s a scenario Avery hopes to see repeated with other commodities from the Prairies.
Addressing Arctic challenges
The emergence of new technologies has helped AGG work around the challenges of melting permafrost under the rail line and ice in Hudson Bay, he said.
Real-time ground-penetrating radar and LiDAR data from sensors attached to locomotives can identify potential problems, while regular drone flights scan the track, artificial intelligence mines the data for issues, and GPS provides exact locations for maintenance.
The group has worked with permafrost researchers from the University of Calgary, Université Laval and Royal Military College to better manage the challenge. “Some of these technologies, such as artificial intelligence and LiDAR, weren’t readily available five years ago, let alone two decades,” Avery said.
On the open water, AGG is working with researchers from the University of Manitoba to study sea ice and the change in sea lanes.
“Icebreakers would be a game-changer for our shipping operations and would allow year-round shipping in the short-term,” he said.
“Without icebreakers, the shipping season is currently about four and a half months of the year, from April to early November, but that is going to continue to increase in the coming decades.”
Interest from potential shippers, including energy producers, has grown since last year’s election in the United States, Avery said.
“We’re going to continue to work closely with all levels of government to get Canada’s products to markets around the world. That’s building our nation. That’s why we are excited for the future.”
Alberta
OPEC+ is playing a dangerous game with oil

This article supplied by Troy Media.
OPEC+ is cranking up oil supply into a weak market. It’s tried this strategy before, and it backfired
OPEC+ is once again charging headfirst into a market share war—a strategy that has repeatedly ended in disaster. Despite weak global demand, falling prices and rising output from non-OPEC countries, the cartel has chosen to flood the market. History shows this tactic rarely ends well for
OPEC+ or oil producers worldwide, including Canada.
OPEC+, a group of major oil-exporting countries led by Saudi Arabia and Russia, works together to manage global oil supply and influence prices. Its decisions have far-reaching consequences for the global energy market—including for Canadian oil producers.
Last Saturday, eight leading members of OPEC+ announced, after a virtual meeting, that they would increase production by 548,000 barrels per day starting in August. That is significantly more than the group’s recent additions of 411,000 bpd, and it puts them on track to fully unwind their
previous 2.2 million bpd in cuts a full year ahead of schedule.
It is a bold move, but it comes at a questionable time.
There is little geopolitical premium built into current oil prices, and the global market is already oversupplied. Brent crude futures are down more than six per cent so far this year. Analysts estimate inventories have been climbing by a million barrels per day in 2025 due in part to cooling demand in China and rising output from countries outside OPEC.
S&P Global Commodity Insights forecasts a supply surplus of 1.25 million barrels per day in the second half of the year. Brent crude stood at about US$68 per barrel on Friday, but S&P says it could fall to between US$50 and $60 later this year and into 2026. West Texas Intermediate, the U.S. benchmark, is also at risk of dropping below US$50 per barrel.
Canada is the world’s fourth-largest oil producer, with most of its output coming from Alberta’s oil sands. Though Canadian producers have higher costs than some OPEC+ members, their innovation and access to U.S. markets have made them increasingly competitive.
While the seasonal demand boost might justify a modest increase, OPEC+, especially Saudi Arabia, appears primarily motivated by market share concerns. With U.S. shale and countries like Canada, Kazakhstan and Guyana gaining ground, the cartel is falling back on its old tactic of flooding the market to squeeze out competitors.
Some observers, including Stanley Reed in The New York Times, have suggested that the move may be designed to please U.S. President Donald Trump, who “has made courting Saudi Arabia and regional allies like the United Arab Emirates a priority of his foreign policy.” But even geopolitical gamesmanship has not shielded OPEC+ from the consequences before—and likely will not this time either.
Back in 2014, fed up with the U.S. shale boom, OPEC opened the taps. The goal was to drive prices low enough to force out higher-cost producers. Instead, oil plunged into the US$30 range. According to the World Bank, the 70 per cent drop during that period was one of the three biggest oil crashes since the Second World War and the most prolonged since the supply-driven collapse of 1986. Saudi Arabia’s respected oil minister, Ali Al-Naimi, lost his job in the aftermath.
Then, in April 2020, as the COVID-19 pandemic loomed, OPEC and Russia launched a production war that sent oil prices into freefall, briefly into negative territory. Trump had to broker a ceasefire to rescue the U.S. shale industry, forcing Riyadh and Moscow to pull back. Both sides suffered significant economic damage.
For Canada, especially Alberta, the current fallout could be severe. The province is home to most of the country’s oil sands production. Cheaper global crude undercuts Canadian prices, squeezes royalty revenues, chills investment and puts jobs at risk across Canada. And this comes as governments are already grappling with fiscal pressures.
The oil market does not reward short-term thinking. If OPEC+ continues down this road, history suggests the outcome will be painful for them and the rest of us.
Toronto-based Rashid Husain Syed is a highly regarded analyst specializing in energy and politics, particularly in the Middle East. In addition to his contributions to local and international newspapers, Rashid frequently lends his expertise as a speaker at global conferences. Organizations such as the Department of Energy in Washington and the International Energy Agency in Paris have sought his insights on global energy matters.
Troy Media empowers Canadian community news outlets by providing independent, insightful analysis and commentary. Our mission is to support local media in helping Canadians stay informed and engaged by delivering reliable content that strengthens community connections and deepens understanding across the country
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoMatt Walsh slams Trump administration’s move to bury Epstein sex trafficking scandal
-

 National2 days ago
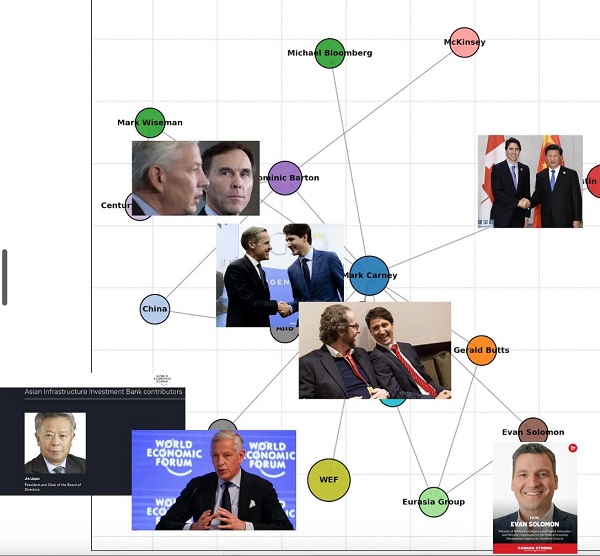
National2 days agoDemocracy Watch Blows the Whistle on Carney’s Ethics Sham
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoIs The Carney Government Making Canadian Energy More “Investible”?
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCompetition Bureau is right—Canada should open up competition in the air
-
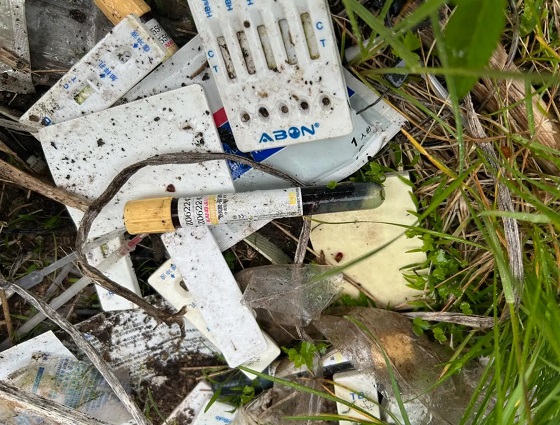

 Immigration1 day ago
Immigration1 day agoUnregulated medical procedures? Price Edward Islanders Want Answers After Finding Biomedical Waste From PRC-Linked Monasteries
-
 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoDemocracy Watchdog Says PM Carney’s “Ethics Screen” Actually “Hides His Participation” In Conflicted Investments
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoIt’s Time To End Canada’s Protectionist Supply Management Regime
-

 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoFreedom Convoy leaders’ sentencing hearing to begin July 23 with verdict due in August










