Great Reset
Canadian author with cerebral palsy says nurse called her ‘selfish’ for refusing euthanasia
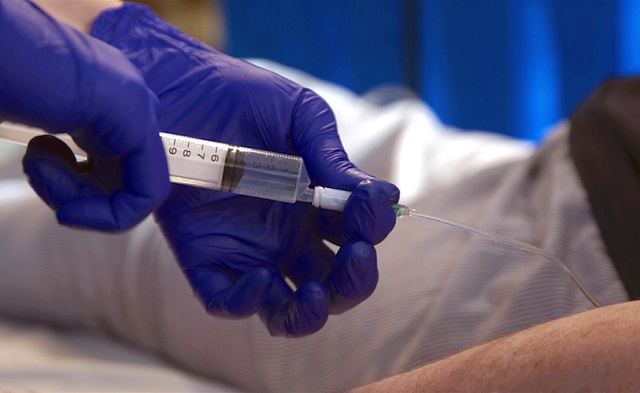
From LifeSiteNews
She was shamed by a nurse in 2019 for refusing MAiD at Medicine Hat Regional Hospital
In 2019, an Alberta nurse reportedly told Christian author Heather Hancock that she was “selfish” for not ending her life through the Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD) euthanasia program.
In a July 12 interview with the Daily Mail, Heather Hancock, a 56-year-old Christian author who suffers from cerebral palsy, said that she was shamed by a nurse in 2019 for refusing MAiD at Medicine Hat Regional Hospital in Alberta.
According to Hancock, during a lengthy hospital stay in 2019 for a bout of muscle spams, a nurse told her while helping her to the bathroom that Hancock “should do the right thing and consider MAiD,” and that her refusing MAiD was her “being selfish” and she is “not living” but “merely existing.”
Hancock recalled feeling “gobsmacked” and told the nurse that her life had value even if she spent most of it in a wheelchair.
“You have no right to push me to accept MAiD,” she says she told the nurse.
“They just view me as a drain on the medical system and that my healthcare dollars could be spent on an able-bodied person,” Hancock told the Daily Mail.
In addition to the alleged 2019 incidents, Hancock says she has been routinely encouraged to end her life via euthanasia.
Hancock, who has cerebral palsy, says she has been encouraged to take MAiD on three separate occasions since Canada launched its euthanasia program in 2016.
Hancock currently lives in an assisted-living center in Moose Jaw, Saskatchewan. Despite her disability, she remains an active writer and activist against Canada’s growing euthanasia program.
Unfortunately, Hancock’s experience is not unique as many Canadians have been reportedly offered MAiD.
In May, LifeSiteNews reported on a Canadian man who felt “completely traumatized” and violated that he was offered MAiD “multiple times” instead of getting the proper care he needed while in the hospital.
First introduced in 2016, MAiD was initially only available to those who were terminally ill. However, in 2021, the Trudeau government expanded the deadly practice to be available to those who were not a risk of death, but who suffered from chronic illness.
While MAiD does not yet apply to the mentally ill, this is not due to a lack of trying on behalf of the Trudeau government, who decided to delay the expansion of euthanasia to those suffering solely from such illnesses until 2027 following backlash from Canadians and prominent doctors.
The most recent reports show that MAiD is the sixth highest cause of death in Canada. However, it was not listed as such in Statistics Canada’s top 10 leading causes of death from 2019 to 2022. When asked why MAiD was left off the list, the agency explained that it records the illnesses that led Canadians to choose to end their lives via euthanasia, not the actual cause of death, as the primary cause of death.
According to Health Canada, in 2022, 13,241 Canadians died by MAiD lethal injections. This accounts for 4.1 percent of all deaths in the country for that year, a 31.2 percent increase from 2021.
While the numbers for 2023 have yet to be released, all indications point to a situation even more grim than 2022.
Censorship Industrial Complex
US Under Secretary of State Slams UK and EU Over Online Speech Regulation, Announces Release of Files on Past Censorship Efforts

Sarah Rogers’ comments draw a new line in the sand between America’s First Amendment and Europe’s tightening grip on online speech.
|
|
Digital ID
Canadian government launches trial version of digital ID for certain licenses, permits

From LifeSiteNews
The Employment and Social Development Canada (ESDC) department has officially confirmed it is developing a digital ID for certain licenses and permits.
The Employment and Social Development Canada (ESDC) department has officially confirmed it is developing a digital ID for certain licenses and permits, called “GC Issue and Verify,” which has already been listed on the Google Play store, as a trial-only app for certain users.
The digital ID claims the government can replace and be full “digital versions” of the “physical credentials they already provide today, like work permits and boating licenses.”
“Instead of only having physical credentials in their wallets, people will also be able to securely store their digital credentials on their mobile devices,” says the government.
According to ESDC officials, the digital IDs can be shared online or in-person “when needed, making it easy for departments, organizations, and businesses to validate their information.”
The government argued that since many Canadians already use “digital credentials without realizing it,” such as a digital ticket “stored on our mobile device instead of using a printed ticket,” this would be the same for IDs such as licenses.
ESDC said that “digital options” will be voluntary and that people can still use “traditional physical methods of verification,” instead.
READ: Canada releases new digital ID app for personal documents despite privacy concerns
The reality is that digital IDs and similar systems have long been pushed by globalist groups like the World Economic Forum, an organization with which Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney has extensive ties, under the guise of ease of access and security.
Also, Canadians do not want digital IDs, as noted by Canada’s Privy Council research from 2023, which said there is strong public resistance to the use of digital IDs to access government services.
GC Issue and Verify is one of two digital ID projects on the go. As reported by LifeSiteNews, the Liberal government under Carney recently quietly released a new type of digital ID app on Google’s Play Store called GC Wallet.
Both GC Wallet and GC Issue and Verify are now being tested with federal partners, those being Transport Canada and Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada.
During COVID, the Canadian federal government released a digital-type app called ArriveCAN app for travel that was a form of digital ID. The app was riddled with technical glitches along with privacy concerns from users.
As reported by LifeSiteNews, the Canadian government hired outside consultants tasked with looking into whether or not officials should proceed with creating a digital ID system for all citizens and residents.
Opp0sition MP Leslyn Lewis, recently warned Canadians to be “on guard” against a push by the ruling Liberal Party to bring forth digital IDs, saying they should be voluntary.
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day ago“Magnitude cannot be overstated”: Minnesota aid scam may reach $9 billion
-

 Haultain Research7 hours ago
Haultain Research7 hours agoSweden Fixed What Canada Won’t Even Name
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoLargest fraud in US history? Independent Journalist visits numerous daycare centres with no children, revealing massive scam
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex1 day ago
Censorship Industrial Complex1 day agoUS Under Secretary of State Slams UK and EU Over Online Speech Regulation, Announces Release of Files on Past Censorship Efforts
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoIs Ukraine Peace Deal Doomed Before Zelenskyy And Trump Even Meet At Mar-A-Lago?
-

 Business7 hours ago
Business7 hours agoWhat Do Loyalty Rewards Programs Cost Us?








