Alberta
Activity-Based Hospital Funding in Alberta: Insights from Quebec and Australia

From the Montreal Economic Institute
Quebec has experienced increased productivity and efficiency, as well as reduced costs, in those sectors to which ABF has been applied
Alberta’s healthcare system costs more than those of many of its peers across Canada and internationally, yet underperforms by many metrics—wait times perhaps being the most visible.(1) For instance, while Alberta consistently spends a fair deal more per capita on health care than Canada’s other large provinces do, the median wait time from referral by a GP to treatment by a specialist was 33.3 weeks in 2022, versus 29.4 weeks in Quebec, 25.8 weeks in British Columbia, and 20.3 weeks in Ontario. Albertans waited a median 232 days for a hip replacement that year, longer than those in Quebec, British Columbia, and Ontario.(2) In Australia, meanwhile, the median wait time for a total hip replacement in 2022 was 175 days in public hospitals.(3)
One of the things keeping Alberta’s healthcare system from better performance is that it relies on global budgets for its hospital financing. Such a system allocates a pre-set amount of funding to pay for an expected number of services, based largely on historical volume. The problem with global budgets is that they disregard the actual costs incurred to deliver care, while undermining incentives to improve outcomes. This ultimately leads to rationing of care, with patients viewed as a cost that must be managed.
Activity-based funding systems are associated with reduced hospital costs, increased efficiency, and shorter wait times, among other things.
An alternative is activity-based funding (ABF), which has largely replaced global budgeting in many OECD countries, and is starting to do so in some Canadian provinces.(4) With ABF, hospitals receive a fixed payment for each specific service delivered, adjusted for certain parameters.(5) If a hospital treats more patients and delivers more services, it receives more funding; if it does less, it receives less. In essence, the money follows the patient, which has a dramatic effect: patients are now viewed as a source of revenue, not merely as a cost. Studies have shown that ABF systems that include appropriate safeguards for quality and waste are associated with reduced hospital costs, increased efficiency, and shorter wait times, among other things.(6)
To increase its capacity and performance, Alberta should consider moving to such a system for hospital financing. As over 25% of total health spending in the province goes to hospitals,(7) driving down costs and finding efficiencies is of paramount importance.
ABF models vary by jurisdiction and context to account for distinct situations and the particular policy objectives being pursued.(8) Two jurisdictions provide interesting insights: Quebec, with ABF hospital funding being gradually implemented in recent years, and Australia, where after more than three decades, ABF is the rule, global budgets the exception.
ABF in Quebec: Increased Performance and Decreased Costs
Quebec’s hospital payment reforms over the past two decades have been aimed at better linking funding with health care delivery to improve care quality and access.(9) These patient-based funding reforms (a type of ABF) have resulted in increased volumes and efficiency, and reduced costs and wait times for a number of surgical and other procedures in Quebec.(10)
These reforms started in 2004, when Quebec applied ABF in the context of additional funding to select surgeries in order to reduce wait times through the Access to Surgery Program.(11) The surgeries initially targeted were hip replacement, knee replacement, and cataract surgeries, but other procedures were eventually integrated into the program as well. Its funding covered the volume of surgeries that exceeded those performed in 2002-2003, and it used the average cost for each specific surgery. Procedures were classified by cost category, which also took into account the intensity of resource use and unit cost based on direct and indirect costs.
The expansion of ABF in Quebec aims to relieve hospital congestion by driving down wait times and shrinking wait lists.
By 2012-2013, this targeted program had helped to significantly increase the volume of surgeries performed, as well as decrease wait times and length of stay.(12) However, as ABF was applied only to surplus volumes of additional surgeries, efficiency gains were limited. For this reason, among others, the Expert Panel for Patient-Based Funding recommended expanding the program,(13) and in 2012, the Government of Quebec began considering further pilot projects for gradual ABF implementation.(14)
- In 2015, ABF was implemented in the radiation oncology sector, which resulted in better access to services at a lower cost, with productivity having increased more than 26% by 2023-2024, and average procedure costs having fallen 7%.(15)
- In 2017-2018, ABF was implemented in imaging, which resulted in the number of magnetic resonance imaging tests increasing more than 22% while driving the unit cost of procedures down 4%.(16)
- Following the above successes, in 2018-2019, the colonoscopy and digestive endoscopy sector also moved to ABF, which led to a productivity increase of 14% and a 31% decrease in the case backlog.(17)
Overall, then, Quebec has experienced increased productivity and efficiency, as well as reduced costs, in those sectors to which ABF has been applied (see Figure 1).

The Department of Health and Social Services continued to expand ABF to more surgeries in 2023, following which it was expected that about 25% of the care and services offered in physical health in Quebec hospitals would be funded in this manner, with the goal of reaching 100% by 2027-2028.(18) Further, the 2024-2025 budget expanded ABF again to include the medicine, emergency, neonatal, and dialysis sectors.
This expansion of ABF aims to relieve hospital congestion by driving down wait times and shrinking wait lists.(19) It will also align Quebec’s health care funding with what has become standard in most OECD countries. In Australia, for instance, ABF is the rule, not the exception, covering a large proportion of hospital services.
Australia’s Extensive Use of ABF
Australia also implemented ABF in stages, as Quebec is now doing. It was first introduced in the 1990s in one state and adopted nationally in 2012 for all admitted programs to increase efficiency, while also integrating quality and safety considerations.(20) These considerations act as safeguards to ensure efficiency incentives don’t negatively impact services. For instance, there are adjustments to the ABF payment framework in the presence of hospital acquired complications and avoidable hospital readmissions, two measures of hospital safety and service quality.(21) If service quality were to decrease, funding would be adjusted, and payments would be withheld. Not only has ABF been successful in increasing hospital efficiency in Australia, but it has also enabled proactive service improvement, which has in turn had a positive impact on safety and quality.(22)
ABF now makes up 87.0% of total hospital spending in Australia, ranging from 83.6% in Tasmania to 93.0% in the Australian Capital Territory.
Currently, ER services, acute services, admitted mental health services, sub-acute and non-acute services, and non-admitted services are funded with ABF in Australia. This includes rehabilitation, palliative, geriatric and/or maintenance care.(23) Global budgets are still used for some block funding, but this is the exception, restricted to certain hospitals, programs, or specific episodes of care.(24) Small rural hospitals, non-admitted mental health programs, and a few other highly specialized therapies or clinics or some community health services tend to be block funded due to higher than average costs stemming from a lack of economies of scale and inadequate volumes, among other things.
When first introduced, ABF made up about 25% of hospital revenue (approximately where Quebec currently stands).(25) ABF now makes up 87.0% of total hospital spending in Australia, ranging from 83.6% in Tasmania to 93.0% in the Australian Capital Territory (see Figure 2).

There is more variability, however, at the local hospital network level within territories or states. For instance, between 2019 and 2024, an average of 92.3% of total funding for the hospitals in the South Eastern Sydney Local Health District was ABF, and just 7.7% was block funding.(26) For the hospitals in the Far West Local Health District, in comparison, ABF represented an average of 72.0% of total funding, and block payments 28.0%, over the same period.(27)
The proportion of ABF funding per hospital is dictated, for the most part, by the types and volumes of patient services provided, but also by hospital characteristics and regional patient demographics.(28) For example, there could be a need to compensate for differences in hospital size and location, or to reimburse for some alternative element of the fixed cost of providing services. In the Far West Local Health District, on average 65.1% of block funding between 2019-2020 and 2023-2024 was provided for small rural hospitals, while only 1.4% of the block funding in the South Eastern Sydney Local Health District was for these types of hospitals.(29) Ultimately, these two districts serve very different populations, with the Far West Local Health District being the most thinly populated district in Australia.(30)
Overall, ABF implementation in Australia has significantly improved hospital performance. Early after ABF implementation, the volume of care in Australia increased, and waiting lists decreased by 16% in the first year.(31) Between 2005 and 2017 the hospitals that were funded by ABF in Queensland became more efficient than those receiving block funding.(32) In addition, ABF can contribute to reductions in extended lengths of stay and hospital readmission,(33) both of which are expensive propositions for health care systems and also tie up hospital beds and resources.
Conclusion
ABF has been associated with reduced hospital costs, increased efficiency, and shorter wait times, areas where Alberta is lacking and reform is needed. To increase its health system performance, Alberta should consider emulating Quebec and moving to an activity-based funding system. Indeed, based on the experience of countries like Australia, widespread application should be the goal, as it is in Quebec. Alberta patients have already waited far too long for timely access to the quality care they deserve. The time to act is now.
The MEI study is available here.
* * *
This Economic Note was prepared by Krystle Wittevrongel, Senior Policy Analyst and Alberta Project Lead at the MEI. The MEI’s Health Policy Series aims to examine the extent to which freedom of choice and entrepreneurship lead to improvements in the quality and efficiency of health care services for all patients.
The MEI is an independent public policy think tank with offices in Montreal and Calgary. Through its publications, media appearances, and advisory services to policy-makers, the MEI stimulates public policy debate and reforms based on sound economics and entrepreneurship.
Alberta
‘Weird and wonderful’ wells are boosting oil production in Alberta and Saskatchewan
From the Canadian Energy Centre
Multilateral designs lift more energy with a smaller environmental footprint
A “weird and wonderful” drilling innovation in Alberta is helping producers tap more oil and gas at lower cost and with less environmental impact.
With names like fishbone, fan, comb-over and stingray, “multilateral” wells turn a single wellbore from the surface into multiple horizontal legs underground.
“They do look spectacular, and they are making quite a bit of money for small companies, so there’s a lot of interest from investors,” said Calin Dragoie, vice-president of geoscience with Calgary-based Chinook Consulting Services.
Dragoie, who has extensively studied the use of multilateral wells, said the technology takes horizontal drilling — which itself revolutionized oil and gas production — to the next level.
“It’s something that was not invented in Canada, but was perfected here. And it’s something that I think in the next few years will be exported as a technology to other parts of the world,” he said.
Dragoie’s research found that in 2015 less than 10 per cent of metres drilled in Western Canada came from multilateral wells. By last year, that share had climbed to nearly 60 per cent.
Royalty incentives in Alberta have accelerated the trend, and Saskatchewan has introduced similar policy.
Multilaterals first emerged alongside horizontal drilling in the late 1990s and early 2000s, Dragoie said. But today’s multilaterals are longer, more complex and more productive.
The main play is in Alberta’s Marten Hills region, where producers are using multilaterals to produce shallow heavy oil.
Today’s average multilateral has about 7.5 horizontal legs from a single surface location, up from four or six just a few years ago, Dragoie said.
One record-setting well in Alberta drilled by Tamarack Valley Energy in 2023 features 11 legs stretching two miles each, for a total subsurface reach of 33 kilometres — the longest well in Canada.
By accessing large volumes of oil and gas from a single surface pad, multilaterals reduce land impact by a factor of five to ten compared to conventional wells, he said.
The designs save money by skipping casing strings and cement in each leg, and production is amplified as a result of increased reservoir contact.
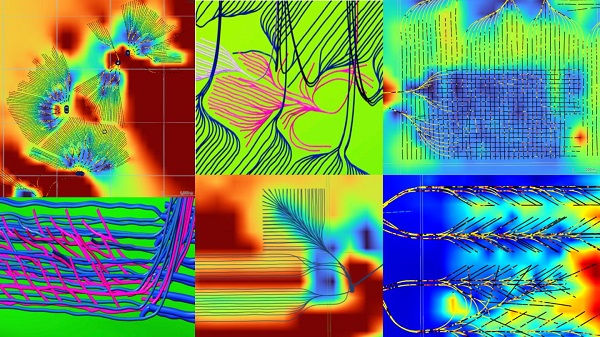
Here are examples of multilateral well design. Images courtesy Chinook Consulting Services.
Parallel
Fishbone
Fan
Waffle
Stingray
Frankenwells
Alberta
Alberta to protect three pro-family laws by invoking notwithstanding clause

From LifeSiteNews
Premier Danielle Smith said her government will use a constitutional tool to defend a ban on transgender surgery for minors and stopping men from competing in women’s sports.
Alberta Premier Danielle Smith said her government will use a rare constitutional tool, the notwithstanding clause, to ensure three bills passed this year — a ban on transgender surgery for minors, stopping men from competing in women’s sports, and protecting kids from extreme aspects of the LGBT agenda — stand and remain law after legal attacks from extremist activists.
Smith’s United Conservative Party (UCP) government stated that it will utilize a new law, Bill 9, to ensure that laws passed last year remain in effect.
“Children deserve the opportunity to grow into adulthood before making life-altering decisions about their gender and fertility,” Smith said in a press release sent to LifeSiteNews and other media outlets yesterday.
“By invoking the notwithstanding clause, we’re ensuring that laws safeguarding children’s health, education and safety cannot be undone – and that parents are fully involved in the major decisions affecting their children’s lives. That is what Albertans expect, and that is what this government will unapologetically defend.”
Alberta Justice Minister and Attorney General Mickey Amery said that the laws passed last year are what Albertans voted for in the last election.
“These laws reflect an overwhelming majority of Albertans, and it is our responsibility to ensure that they will not be overturned or further delayed by activists in the courts,” he noted.
“The notwithstanding clause reinforces democratic accountability by keeping decisions in the hands of those elected by Albertans. By invoking it, we are providing certainty that these protections will remain in place and that families can move forward with clarity and confidence.”
The Smith government said the notwithstanding clause will apply to the following pieces of legislation:
-
Bill 26, the Health Statutes Amendment Act, 2024, prohibits both gender reassignment surgery for children under 18 and the provision of puberty blockers and hormone treatments for the purpose of gender reassignment to children under 16.
-
Bill 27, the Education Amendment Act, 2024, requires schools to obtain parental consent when a student under 16 years of age wishes to change his or her name or pronouns for reasons related to the student’s gender identity, and requires parental opt-in consent to teaching on gender identity, sexual orientation or human sexuality.
-
Bill 29, the Fairness and Safety in Sport Act, requires the governing bodies of amateur competitive sports in Alberta to implement policies that limit participation in women’s and girls’ sports to those who were born female.”
Bill 26 was passed in December of 2024, and it amends the Health Act to “prohibit regulated health professionals from performing sex reassignment surgeries on minors.”
As reported by LifeSiteNews, pro-LGBT activist groups, with the support of Alberta’s opposition New Democratic Party (NDP), have tried to stop the bill via lawsuits. It prompted the Smith government to appeal a court injunction earlier this year blocking the province’s ban on transgender surgeries and drugs for gender-confused minors.
Last year, Smith’s government also passed Bill 27, a law banning schools from hiding a child’s pronoun changes at school that will help protect kids from the extreme aspects of the LGBT agenda.
Bill 27 will also empower the education minister to, in effect, stop the spread of extreme forms of pro-LGBT ideology or anything else to be allowed to be taught in schools via third parties.
Bill 29, which became law last December, bans gender-confused men from competing in women’s sports, the first legislation of its kind in Canada. The law applies to all school boards, universities, and provincial sports organizations.
Alberta’s notwithstanding clause is like all other provinces’ clauses and was a condition Alberta agreed to before it signed onto the nation’s 1982 constitution.
It is meant as a check to balance power between the court system and the government elected by the people. Once it is used, as passed in the legislature, a court cannot rule that the “legislation which the notwithstanding clause applies to be struck down based on the Charter of Rights and Freedoms, the Alberta Bill of Rights, or the Alberta Human Rights Act,” the Alberta government noted.
While Smith has done well on some points, she has still been relatively soft on social issues of importance to conservatives , such as abortion, and has publicly expressed pro-LGBT views, telling Jordan Peterson earlier this year that conservatives must embrace homosexual “couples” as “nuclear families.”
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta on right path to better health care
-

 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days ago‘Modern-Day Escobar’: U.S. Says Former Canadian Olympian Ran Cocaine Pipeline with Cartel Protection and a Corrupt Toronto Lawyer
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCanada is failing dismally at our climate goals. We’re also ruining our economy.
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta Emergency Alert test – Wednesday at 1:55 PM
-

 Health16 hours ago
Health16 hours agoCDC’s Autism Reversal: Inside the Collapse of a 25‑Year Public Health Narrative
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoCarney government’s anti-oil sentiment no longer in doubt
-

 Artificial Intelligence1 day ago
Artificial Intelligence1 day agoLawsuit Claims Google Secretly Used Gemini AI to Scan Private Gmail and Chat Data
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlberta to protect three pro-family laws by invoking notwithstanding clause